Ethambutol
- I. Introduction to Ethambutol
- II. The Composition of Ethambutol
- III. Understanding How Ethambutol Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Ethambutol
- V. Off-Label Uses of Ethambutol
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Ethambutol
- VII. Ethambutol Side Effects
- VIII. Ethambutol Interactions
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Ethambutol Use
- X. Careful Administration of Ethambutol
- XI. Important Precautions When Using Ethambutol
- XII. Ethambutol Administration to Special Populations
- XIII. Overdosage of Ethambutol
- XIV. Storage of Ethambutol
- XV. Ethambutol Handling Precautions
I. Introduction to Ethambutol
A. Overview of Ethambutol
Ethambutol is a medication in the treatment of tuberculosis. It belongs to a group of drugs called antimycobacterial. Known for its effectiveness against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it plays a role in combination drug therapies reducing the chances of drug resistance.
B. Historical development and discovery
Ethambutol was first introduced in the 1960s when there was an advancement in combating tuberculosis. It came about as part of the effort to create medications that could effectively target drug strains of tuberculosis which were becoming more prevalent worldwide. Since then, Ethambutol has played a role in the efforts to control tuberculosis.
C. Importance in the field of medicine
Ethambutol's significance becomes evident when considering the threat to public health posed by tuberculosis. This antimicrobial drug plays a role in the medical community's efforts to combat and control tuberculosis, particularly strains resistant to multiple drugs. Its distinctive ability to target cells highlights its importance in multi-drug treatment protocols.
II. The Composition of Ethambutol
A. Molecular structure and characteristics
Ethambutol exhibits chirality with two centers that give rise to three stereoisomers. The molecular formula of this drug, C10H24N2O2 reflects its composition. Notably, its solubility in water, and stable crystal structure contribute to its bioavailability and effectiveness.
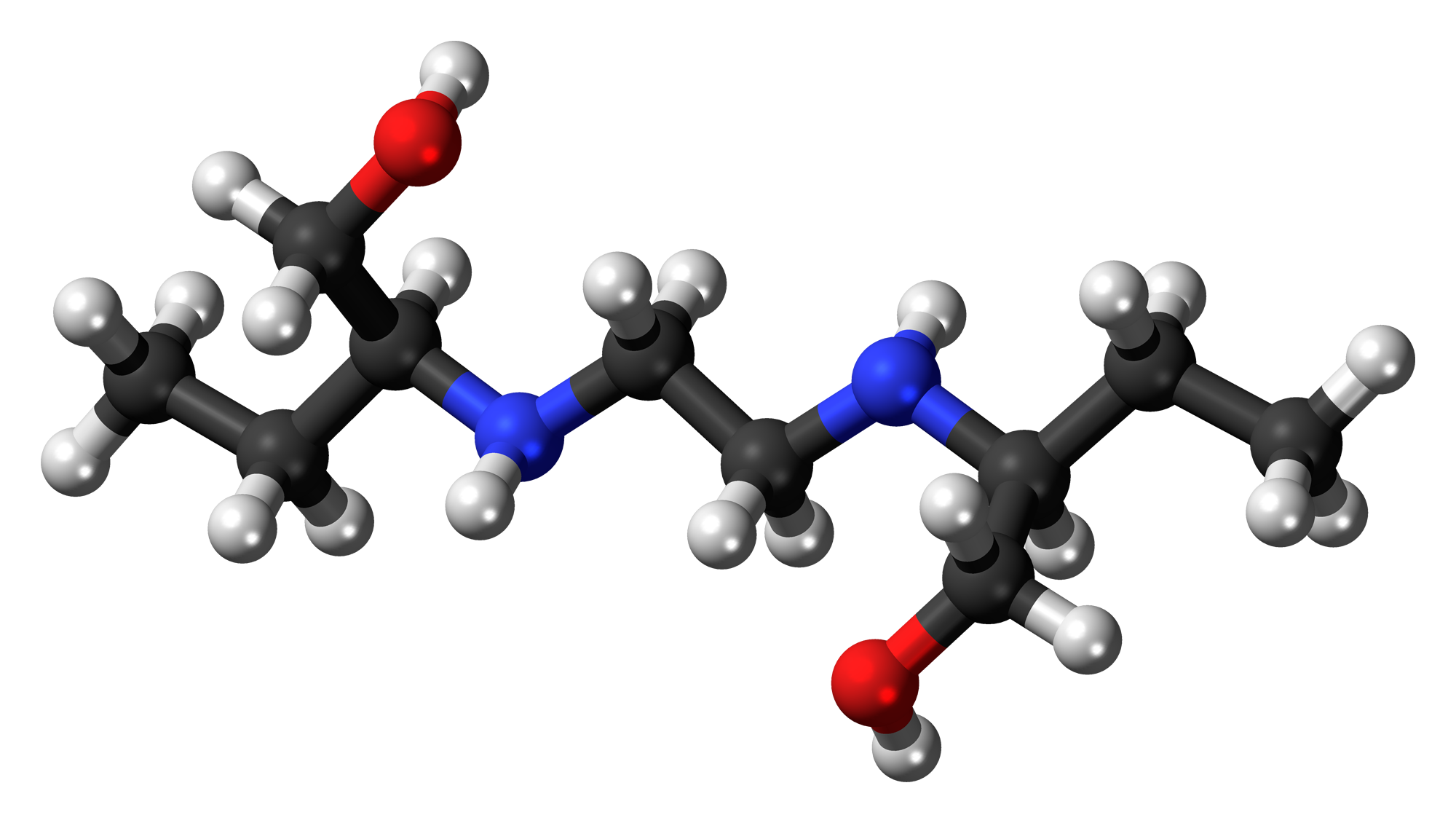
B. Formulations available
Ethambutol comes in forms to meet different requirements and make it easier for patients to follow their treatment. The commonly used format is oral tablets, available in different strengths like 100mg, 400mg, and 800mg. Less common conditions, like intravenous and intramuscular preparations, may also be used in severe cases.
C. Active and inactive ingredients
Ethambutol contains Ethambutol Hydrochloride as its component. The formulation also includes inactive ingredients such as magnesium stearate, sodium starch glycolate, colloidal silicon dioxide, and lactose monohydrate. These additional ingredients enhance the medication's stability, facilitate absorption in the body, and ensure patient tolerance.
III. Understanding How Ethambutol Works
A. Mechanism of action
Ethambutol works by interfering with the creation of the cell wall in mycobacteria. Its main action is to block transferases, which are enzymes responsible for producing arabinogalactan, an essential component of the mycobacterial cell wall. As a result, it hampers the synthesis of the cell wall leading to reduced growth and survival of bacteria.
B. Effect on bacterial cells
Due to Ethambutol's actions, the bacteria's cell wall is weakened, making them more susceptible and less capable. This outcome is seen as hindered growth and reproduction of bacteria, ultimately resulting in the demise of the microorganism. Essentially Ethambutol disrupts the solidity and defensive role of the cell wall leading to its ultimate downfall.
C. Importance of Ethambutol's mode of action
Ethambutol's way of working is quite remarkable because it specifically targets species. This targeted approach helps reduce any harm to cells making the drug safer. Moreover, Ethambutol's mode of action sets it apart from medications used for tuberculosis, making it an essential part of multi-drug treatment plans to fight against drug resistance.
IV. Approved Uses of Ethambutol
A. Therapeutic uses in tuberculosis treatment
Ethambutol is an antibiotic that doctors prescribe in combination with medications to treat tuberculosis (TB) effectively. It plays a role in fighting against this infectious disease12.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Ethambutol:
B. Other bacterial infections
Ethambutol is used to treat tuberculosis (TB) and is usually given with at least one other tuberculosis medicine, such as isoniazid, rifampicin, and pyrazinamide. It may also be used to treat Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium kansasii1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Ethambutol:
C. Combinational therapy implications
V. Off-Label Uses of Ethambutol
A. Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacterial infections
Ethambutol is often included in a treatment plan when dealing with infections caused by mycobacteria.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Ethambutol:
B. Research and experimental uses
C. Precautions and considerations
Ethambutol is used with other medications to treat tuberculosis (TB) and is usually given together with at least one other tuberculosis medicine such as isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Ethambutol:
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Ethambutol
A. Standard dosage and frequency
The amount of Ethambutol needed differs based on the patient's weight and the type of infection. Usually, the initial phase of treatment involves taking 15 mg per kg every day for two months. Afterward, maintenance therapy usually consists of a dosage of 15 mg per kg three times a week. Following this treatment plan is crucial to achieve the best possible therapeutic outcome.
B. Dosage adjustment factors
Dosage modifications are required in situations. Some factors that may require adjustments are; Renal impairment; Since Ethambutol is mainly excreted through the kidneys, the functioning of the kidneys is crucial in determining the dosage. Age; It is advisable to start treatment with a dosage for elderly patients. Comorbidities; Certain conditions like liver disease might require adjustments to the dosage.
C. Procedures for correct administration
Ethambutol is usually taken by mouth without food to enhance absorption. Maintaining a schedule for taking the medication is crucial, ensuring that it is taken at the same time every day. If a dose is missed, it should be taken soon as possible unless it's close to the next scheduled dose. It is not recommended to take two doses.
VII. Ethambutol Side Effects
A. Overview of side effects
As with any medication Ethambutol has the potential to cause side effects. Although most individuals tolerate the drug well it is essential to be aware of any adverse reactions and seek advice from a healthcare professional if they occur.
B. Most common side effects
Ethambutol is often associated with side effects, including; Visual changes, such as alterations in vision, blurry vision, and difficulty distinguishing between red and green colors. Gastrointestinal issues, like feelings of nausea, vomiting, and discomfort in the area. Joint discomfort.
C. Less common and rare side effects
Frequently experienced adverse reactions may include mental confusion, headaches, dizziness, skin rash, or itching. In some cases, more severe side effects such as peripheral neuropathy, optic neuritis, and hallucinations may occur, requiring immediate medical attention.
VIII. Ethambutol Interactions
A. Interactions with other medications
Ethambutol may interact with other medications, potentially affecting its effectiveness and safety. For instance, antacids that contain aluminum can decrease the absorption of Ethambutol. Additionally, when combined with drugs like rifampin and isoniazid, Ethambutol can enhance the benefits.
B. Food and lifestyle interactions
Certain dietary and lifestyle factors can impact the effectiveness of Ethambutol. It is recommended to take the medication with food to ensure absorption. It is advisable to limit or avoid alcohol consumption as it can worsen Ethambutol's potential for liver toxicity.
C. Effect of interactions on efficacy and safety
Drug interactions can significantly influence the safety and effectiveness of Ethambutol. These interactions may. Enhance or reduce its intended therapeutic effects, which could result in treatment not working or causing harm. How you eat and live can also affect how Ethambutol is absorbed and processed in your body, potentially changing how well it works. It's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all your medications, supplements, and lifestyle choices so they can optimize your Ethambutol therapy.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Ethambutol Use
A. Overview of warnings
Ethambutol is an effective drug against mycobacterial infections, but it should be used with caution due to some associated risks. One significant concern is its ability to cause neuritis, which can result in vision changes or color blindness. Additionally, monitoring kidney function is important since the drug is primarily eliminated through the kidneys.
B. Specific contraindications
Ethambutol should not be used in the following situations; Individuals with hypersensitivity to Ethambutol or any of its ingredients. People who have experienced neuritis as a result of previous Ethambutol treatment. It can be challenging for children under the age of five to conduct accurate eye tests in this age group.
C. Relative contraindications
Although not considered contraindications, it is essential to carefully consider and potentially adjust the dosage or closely monitor the following conditions; 1. Insufficiency; When kidney function is reduced, there is a higher chance of increased drug concentration in the bloodstream, leading to potential toxicity risks. 2. Cataracts; Ethambutol can potentially worsen this condition or interfere with its diagnosis. 3. Peripheral neuropathy; Pre-existing conditions may be aggravated by using Ethambutol. It is crucial to consider these factors and proceed with caution when prescribing or using Ethambutol in cases.
X. Careful Administration of Ethambutol
A. Importance of careful administration
To ensure the possible outcome and minimize any potential side effects, following the guidelines precisely when administering Ethambutol is crucial. This includes administering the dosage at the right time and closely monitoring its results.
B. Risk factors to consider
When administering Ethambutol, considering risk factors, such as age, is important. Elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug toxicity because their organs may not function properly. Additionally, comorbidities, like liver or kidney disease, can affect how the drug is processed and eliminated from the body. It's also crucial to consider any medications as they can potentially interact with Ethambutol affecting its effectiveness and safety.
C. Monitoring during therapy
To identify and properly manage potential side effects, it is crucial to monitor patients undergoing Ethambutol therapy regularly. This involves eye exams, liver function tests, and assessments of renal function. Any indications of vision alterations, jaundice, or abnormal fatigue should be promptly reported to the healthcare professional in charge.
XI. Important Precautions When Using Ethambutol
A. Precautions for immunocompromised patients
Patients with weakened systems, like individuals living with HIV/AIDS, might need to modify their medication doses or be monitored more frequently. This is because they have a chance of experiencing side effects and developing severe forms of tuberculosis. The use of drugs can also impact how Ethambutol is processed in the body, so it's essential to adjust the dosage carefully.
B. Precautions for patients with kidney or liver disease
Patients with kidney or liver conditions need to be monitored while undergoing treatment with Ethambutol. This is because these organs are essential in processing and eliminating the drug from the body. Sometimes, dosage adjustments may be needed to avoid any potential harmful effects.
C. Drug resistance considerations
Using Ethambutol for tuberculosis treatment is not advisable because there is a significant risk of developing drug resistance. It is commonly used alongside antimycobacterial medications to enhance the effectiveness of therapy and reduce the chances of resistance. It is recommended to conduct drug susceptibility testing to monitor any indications of resistance.
XII. Ethambutol Administration to Special Populations
A. Administration to elderly patients
As people grow older, they tend to be more sensitive to the side effects of medications because their bodies change with age. When prescribing Ethambutol to patients, it's essential to take a cautious approach and consider starting treatment with a lower dosage. It is crucial to monitor these patients' kidney function, liver function, and eye health.
B. Administration to pregnant women and nursing mothers
Ethambutol falls under Pregnancy Category C, which means its safety during pregnancy is not definitively established. Therefore doctors should only prescribe it to women if the potential benefits outweigh the possible risks. As Ethambutol can pass into breast milk, caution should be exercised when used by nursing mothers. Monitoring the baby for any signs of side effects, like jaundice or rash, is essential.
C. Administration to children
Ethambutol is typically deemed safe for children aged five and above. However, for children under five, Ethambutol might be an option if they can actively participate in acuity testing since the medication could affect their vision. The dosage is usually determined based on their body weight. It's essential to monitor pediatric patients for any indications of toxicity or side effects during the entire treatment duration.
XIII. Overdosage of Ethambutol
A. Symptoms of Ethambutol overdose
An excessive amount of Ethambutol can lead to symptoms. These may include; Problems with vision; Taking much Ethambutol suddenly could cause optic neuritis leading to impaired or loss of sight. Upset stomach; Feeling nauseous, vomiting, and experiencing abdominal pain are commonly reported symptoms. Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet; One might feel a sensation of tingling or numbness in their extremities. Confusion or hallucinations, Mental disorientation, and experiencing things that aren't there are also possible effects.
B. Management and treatment of overdose
The usual approach to treating an overdose of Ethambutol involves providing support and addressing symptoms. In severe instances, hospitalization might be necessary. Depending on the patient's situation, treatment options may include; using lavage or activated charcoal to limit drug absorption, managing fluid and electrolyte levels to ensure proper hydration and balance, closely monitoring renal and liver function as well as taking care of ocular health.
C. Prevention of overdosage
To avoid an overdose of Ethambutol, it is essential to follow the treatment plan and avoid making any unauthorized changes to the dosage. It is crucial to store the medication out of reach of children. Regularly monitoring drug levels in patients with insufficiency can also help prevent overdosing.
XIV. Storage of Ethambutol
A. Ideal storage conditions
Store Ethambutol at room temperature around 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) away from extreme heat, moisture, and direct sunlight. It is advisable to keep the medicine in its container tightly sealed to safeguard against any possible contamination.
B. Shelf life and expiration
The expiration date of Ethambutol is typically printed on the medication package. This date tells you how long the drug is effective and safe. It's not recommended to use Ethambutol after it has expired because its effectiveness may decrease, and it could potentially be harmful to your health.
C. Safe disposal methods
It is advisable to dispose of Ethambutol in accordance, with the guidelines provided by your waste disposal agency or a pharmacist. It is generally not recommended to flush medications down the toilet or pour them into the drain unless you have received instructions to do so. It is essential to dispose of any unused or expired medicine to avoid accidental ingestion or misuse.
XV. Ethambutol Handling Precautions
A. Safety measures in handling Ethambutol
When using Ethambutol it is crucial to refrain from touching your skin, eyes, or mucous membranes. Ensure that your hands are clean and dry, before handling the medication to prevent any chances of contamination. Additionally, it is advisable to store the medicine out of reach of children and pets to avoid ingestion.
B. Procedures in case of accidental exposure
If you accidentally come into contact, with it like if it spills on your skin or you swallow it take action. If it touches your skin rinse the area with water. If you eat it or if it gets in your eyes, get help right away.
C. Guidelines for healthcare professionals and patients
Healthcare providers need to give guidance on how to handle and store Ethambutol correctly to ensure safety. Patients should follow the dosage schedule strictly and promptly inform any abnormal symptoms or side effects. Regularly checking vision, kidney, and liver function should be included in the treatment plan to guarantee the drug's efficient use.
Ethambutol FAQ
- What are Ethambutol side effects?
- What are Ethambutol adverse effects?
- What are Ethambutol side effects on the eye?
- What is the Ethambutol dosage?
- What is Ethambutol MOA?
- What are the uses of Ethambutol?
- What is the drug class of Ethambutol?
- What is Ethambutol?
- What is the cost of Ethambutol?
- What is Ethambutol used for?
- What are the vision changes associated with Ethambutol?
- What is the class of Ethambutol?
- What is Ethambutol toxicity?
- What is Ethambutol optic neuropathy?
- What is Ethambutol Hydrochloride?
- What is the price of Ethambutol?
- What are Ethambutol contraindications?
- What is the structure of Ethambutol?
- What are Ethambutol interactions?
- What is Ethambutol HCl?
- What is the generic name for Ethambutol?
- Is Ethambutol an antibiotic?
- Is Ethambutol used for TB?
- What are Ethambutol warnings?
- What is the form of Ethambutol?
- Can Ethambutol cause color blindness?
- What are Ethambutol nursing considerations?
- Are Ethambutol, Rifampin and Isoniazid examples of what?
- How does weight impact Ethambutol dosing?
- What are the indications for Ethambutol?
- What is Ethambutol used to treat?
- What is Ethambutol for MAC?
- How do Ethambutol and Isoniazid interact?
- How to treat Ethambutol side effects?
- What is Ethambutol medication?
- What is the mechanism of Ethambutol?
- Can Ethambutol cause ototoxicity?
- What are the ophthalmology screening guidelines for Ethambutol?
- What does the Ethambutol eye test involve?
- What are the Ethambutol eye exam guidelines?
- Is Ethambutol an antibiotic?
- What is the action of Ethambutol?
- Does Ethambutol cause blindness?
- Can Ethambutol cause blindness?
- Does Ethambutol cause hair loss?
- How does Ethambutol work?
- Should Ethambutol be taken with or without food?
- How should you take Ethambutol?
- Is there an alternative to Ethambutol?
- What are the long-term side effects of Ethambutol?
- What is the interaction between Isoniazid and Ethambutol?
- What is the interaction between Rifampin and Ethambutol?
- What is the interaction between Ethambutol and Rifampin?
- Can Ethambutol be taken with alcohol?
- What is the interaction between Ethambutol and Pyrazinamide?
- Can Ethambutol cause optic neuritis?
- What are the Ethambutol vision screening guidelines?
- Can Ethambutol be taken with vitamin B6?
- What is the price of Ethambutol in India?
- What is the trade name of Ethambutol?
- What is the dosage for Ethambutol 400mg tablet?
- How is Ethambutol toxicity treated?
- Can Ethambutol cause thrombocytopenia?
- What class of antibiotic is Ethambutol?