Acetylsalicylic Acid
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Composition and Properties
- 3. Uses of Acetylsalicylic Acid
- 4. Mechanism of Action
- 5. Dosage and Administration
- 8. Interaction with Other Medications
- 9. Contraindications and Precautions
- 10. Special Considerations in Administration
- 11. Overdose and Management
- 12. Storage and Handling Precautions
1. Introduction
Overview of Acetylsalicylic Acid
Aspirin, also called acid, is a widely used medicine recognized for its pain-relieving, anti-swelling, and fever-reducing effects. It is used globally and is important in treating a range of issues, from simple pains to serious heart conditions.
Historical Development and Discovery
The discovery of Acetylsalicylic Acid represents an achievement in the realm of medical advancements. Initially created in 1897 by Felix Hoffmann, a chemist working at Bayer AG, this medication evolved from a willow bark derivative into an essential component of contemporary healthcare, bringing about a significant change in the way pain and inflammation are treated.
Common Names and Brand Associations
Acetylsalicylic Acid, commonly known as Aspirin, is an acknowledged medication found under various brand names worldwide. It is familiar to people in both prescribed and nonprescribed forms.
2. Composition and Properties
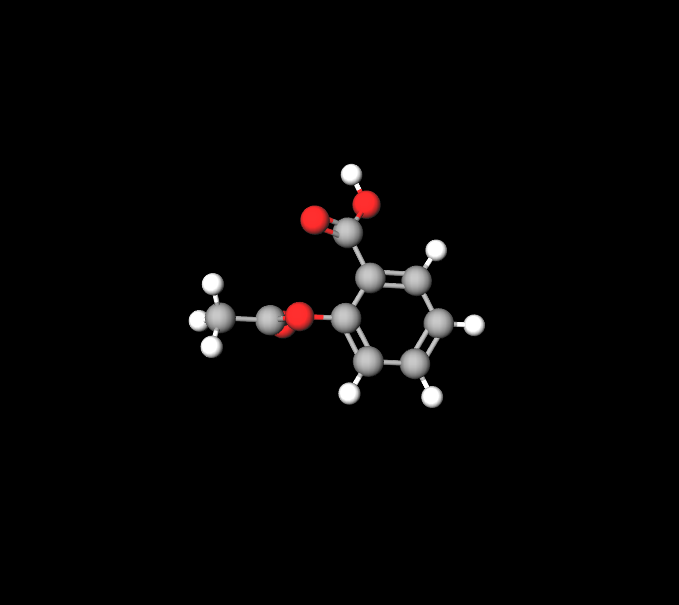
Chemical Structure and Formula
Acetylsalicylic Acid (C9H8O4) contains an ester bond connecting the acetyl and salicylate groups. This specific arrangement plays a role in its therapeutic effects, affecting its durability and absorption in the body.
Physical and Chemical Properties
This substance stands out for its crystal like look and has a slight ability to dissolve in water but shows better solubility in alcohol. Its physical properties play a role in its effectiveness and longevity.
3. Uses of Acetylsalicylic Acid
Primary Indications: Pain Relief, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antiplatelet Effects
-
Pain Relief and Swelling Reduction:
- Aspirin is widely used to relieve mild to moderate pain and reduce swelling associated with various health conditions.
- It can be effective for headaches, colds, flu, sprains, strains, menstrual cramps, arthritis, and migraines 12.
- For severe pain, doctors may recommend combining aspirin with other pain relievers or NSAIDs 1.
-
Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases:
- Aspirin is beneficial for individuals at high risk of cardiovascular events (such as heart attack, clot-related strokes, and blood flow problems).
- Daily low-dose aspirin can help prevent blood clots by making the blood less “sticky.”
- It is recommended for people with heart or blood vessel disease, poor blood flow to the brain, high blood cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, or those who smoke 134.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
- As an NSAID, aspirin suppresses inflammation by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2).
- By reducing prostaglandin production, it alleviates inflammation and pain in affected tissues 56.
4. Mechanism of Action
How Acetylsalicylic Acid Works in the Body
The reason why Acetylsalicylic Acid works well is because it can block cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. By doing this, it changes how prostaglandins, which are important in causing inflammation, pain, and fever, are made.
Inhibition of COX Enzymes and Effects on Prostaglandin Synthesis
Acetylsalicylic Acid works by focusing on COX 1 and COX 2 enzymes, which help decrease the creation of prostaglandins. This action helps in relieving pain and inflammation, as well as lowering fever levels.
Impact on Platelet Aggregation and Blood Flow
The reason why Acetylsalicylic Acid is effective in protecting the heart against issues is because it can stop platelets from clumping together, ultimately preventing blood clot formation.
5. Dosage and Administration
General Dosage Guidelines
The amount of Acetylsalicylic Acid taken can differ significantly, usually falling within the range of 75 mg to 325 daily for heart health purposes, with higher amounts used for pain management and reducing inflammation.
Modifications in Dosage Based on Age, Weight, and Health Condition
Different populations require tailored dosage adjustments, such as doses for the elderly to minimize side effects and modified doses for children and teenagers to prevent Reyes syndrome.
Route of Administration: Oral, Rectal, and Others
The usual way to take Acetylsalicylic Acid is by mouth. There are also versions that can be used rectally for people who can't swallow pills.
8. Interaction with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions and Potential Risks
When you take acetylsalicylic acid along with medications, such as warfarin or corticosteroids, it can increase the risk of bleeding or cause stomach issues. It's important to monitor and adjust the dosage when using these drugs together.
Acetylsalicylic Acid and Alcohol: Risks and Recommendations
It's essential to be cautious when combining aspirin with alcohol as it can worsen stomach problems, heightening the chances of ulcers and bleeding. It is recommended for patients to limit or refrain from consuming alcohol while using this medication.
Effects of Dietary Supplements and Herbal Preparations
- Taking supplements like omega-3 fatty acids could potentially boost the blood-thinning properties of acid.
- Additionally, herbal remedies such as Ginkgo biloba and St. John’s Wort may heighten the chances of bleeding.
9. Contraindications and Precautions
Absolute Contraindications: Who Should Not Use Acetylsalicylic Acid
People who have allergies to NSAIDs, a history of ulcers, or bleeding disorders like hemophilia should steer clear of acetylsalicylic acid as it could lead to serious side effects.
Precautions for People with Pre-existing Conditions
Patients suffering from ailments like asthma-controlled high blood pressure or kidney problems require thorough evaluation and treatment to minimize the possible dangers linked to the use of acetylsalicylic acid.
Guidelines for Safe Use and Risk Avoidance
Consistent checks, modifying doses as needed, and taking gastro medications can help reduce the potential dangers of prolonged treatment. It's important for patients to communicate any signs, like ringing in the ears, as it might signal harmful effects.
10. Special Considerations in Administration
Administration to Elderly Patients: Risks and Dosage Adjustments
Elderly individuals are more prone to experiencing impacts from acetylsalicylic acid, so it is important to use lower doses and closely watch for any signs of stomach bleeding or kidney function issues.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Profile and Recommendations
During the stages of pregnancy, it is usually best to steer clear of using acetylsalicylic acid due to its possible impact on the baby's blood flow and delivery process. However, in these phases, doctors may recommend low doses of acetylsalicylic acid with close medical monitoring.
Administration to Children: Age-specific Guidelines and Safety
When giving children medication, it's important to be very careful to prevent the possibility of Reyes syndrome, especially when dealing with infections. It's crucial to follow guidelines closely when prescribing medication to ensure the safety of the child.
11. Overdose and Management
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Signs of taking too much acetylsalicylic acid can show as rapid breathing, ringing in the ears, dizziness, and feeling disoriented. In situations, it could lead to serious issues such as bleeding and unconsciousness.
Immediate Steps and Antidote Information
In the event of an overdose, the first steps involve washing out the stomach and using activated charcoal. To address acidosis, doctors may give sodium bicarbonate and provide additional care to keep the body's fluid and electrolyte levels in check.
Long-term Management and Follow-up
Regular checkups are essential to monitor the health of your kidneys and liver, ensuring they are functioning well and recovering properly over time to avoid any long-term harm.
12. Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper Storage Conditions for Acetylsalicylic Acid
It's important to store acetylsalicylic acid in a dry location, away from sunlight and moisture, to preserve its effectiveness and prolong its shelf life.

Handling Precautions to Ensure Safety
Remember to handle the medication to prevent it from being exposed to too much heat or moisture, as this could cause it to deteriorate.
Disposal Recommendations and Environmental Concerns
Properly dispose of unused aspirin by following pharmacy instructions or utilizing return programs to avoid environmental pollution and accidental ingestion.