Neostigmine
- I. Introduction
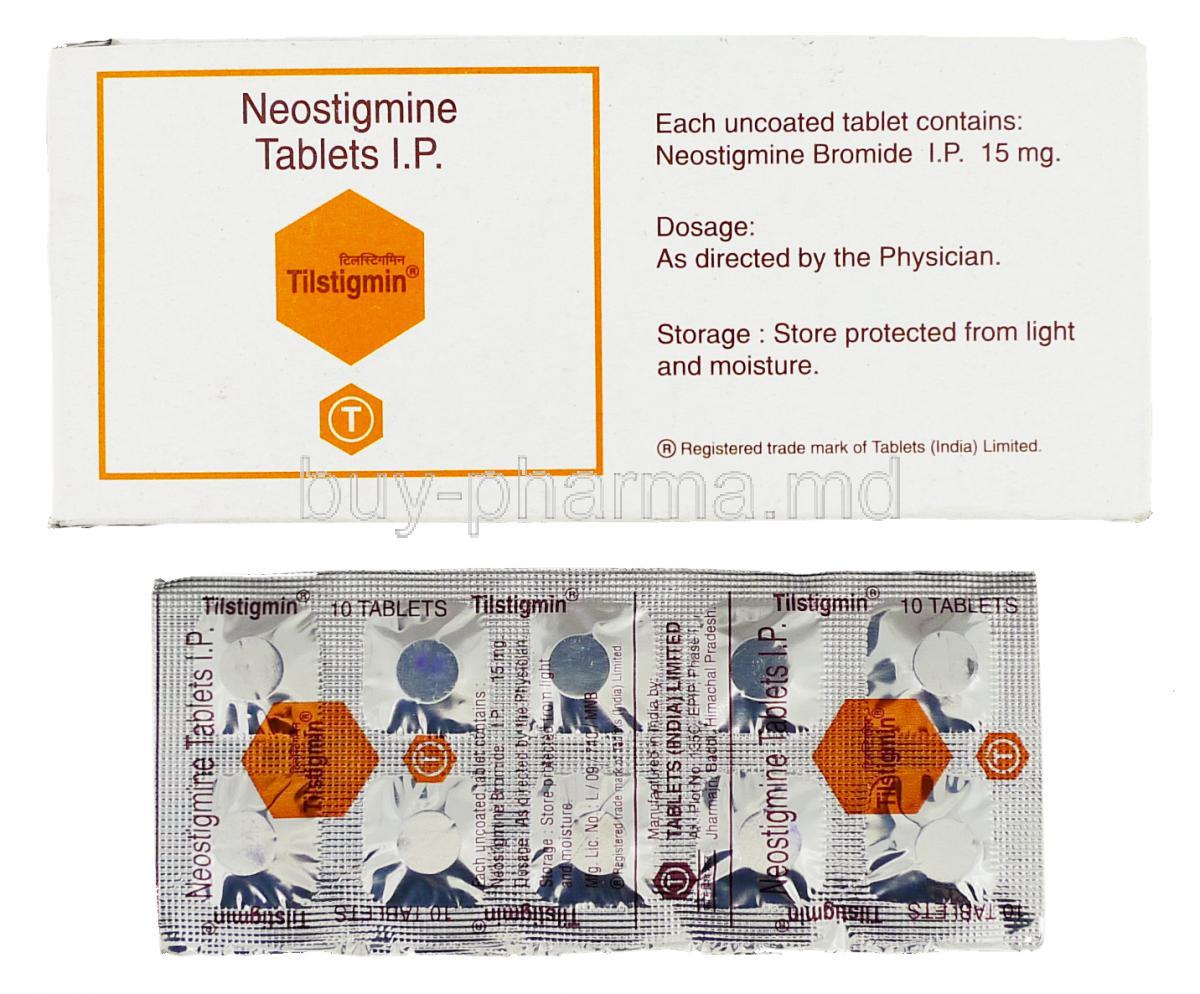
- II. Composition of Neostigmine
- III. How Neostigmine Works
- IV. Uses of Neostigmine
- V. Off-label Use of Neostigmine
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Interactions of Neostigmine
- VIII. Side Effects of Neostigmine
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XI. Overdose Information
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Neostigmine
Neostigmine is a compound that mimics the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system. It acts as an agonist for cholinergic receptors. Its primary role is to inhibit the action of acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine. This inhibition increases acetylcholine levels at nerve synapses, resulting in its therapeutic effects.
B. Overview of its Importance in the Medical Field
The realm of medicine places great importance on neostigmine. Primarily its utilization revolves around countering the effects resulting from non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents effectively reversing muscle relaxation experienced during surgical procedures. Additionally, it is an effective remedy for myasthenia gravis - a neuromuscular disease causing varying degrees of muscle weakness and fatigue.
C. Brief History and Development
Neostigmine origins can be traced back to 1931 when it was initially synthesized as a better alternative to physostigmine. An alkaloid with similar applications is a quaternary ammonium compound. Neostigmine is not easily absorbed into the central nervous system. This characteristic minimizes the potential for side effects and expands its therapeutic index when compared to its predecessor.
II. Composition of Neostigmine
A. Chemical Structure
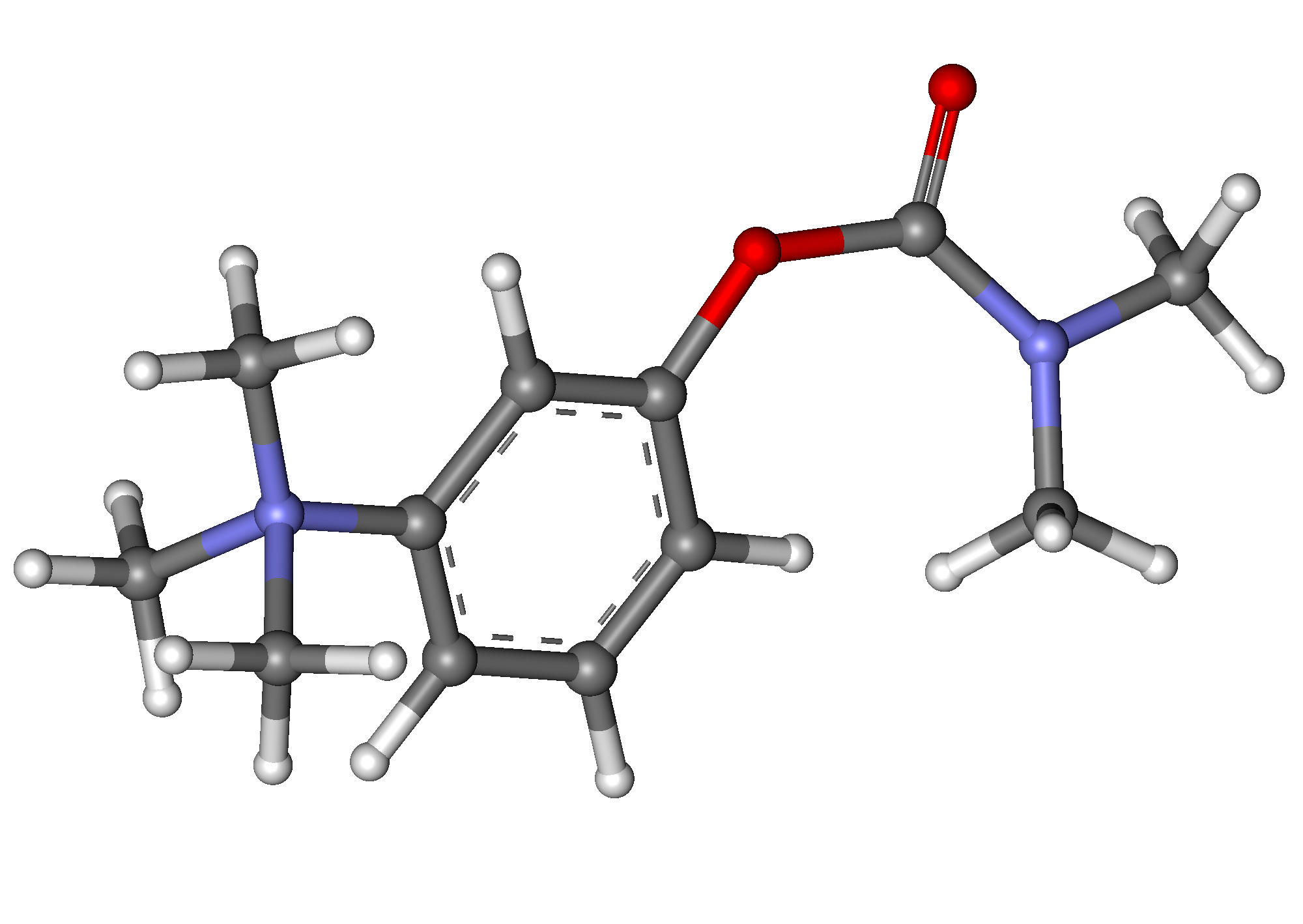
Neostigmine exhibits a structural characteristic with its permanently charged molecule due to quaternary nitrogen. Additionally, it contains a carbamate group attached to this quaternary nitrogen, which plays a pivotal role in its inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase.
B. Formulations Available
Neostigmine is widely available in various pharmaceutical formulations. These include intravenous injections, typically administered in hospitals for medical purposes. Additionally, oral tablets containing neostigmine are used by individuals at home to treat conditions such as myasthenia gravis.
C. Differences and Similarities Between Forms
Even though intravenous and oral neostigmine has the same mode of action. Their utilization depends on the urgency and circumstances of the treatment. The intravenous form is preferable for immediate action, such as reversing muscle relaxants in the operating room. On the other hand, the oral form is prescribed for long-term management of conditions like myasthenia gravis because it provides a prolonged and sustained effect.
III. How Neostigmine Works
A. Mechanism of Action
The functional mechanism behind neostigmine centers around its ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity – an essential enzyme regulating neurotransmitters. By restraining this enzyme's function, it successfully halts the degradation process that typically affects acetylcholine – a critical neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals between nerve synapses. Consequently, there is a notable rise in the concentration level of acetylcholine within the synaptic cleft. Thereby enhancing and improving overall nerve signal transmission.
B. Pharmacokinetics
The quaternary structure of neostigmine hinders its absorption through the gastrointestinal tract, leading to poor oral uptake. To overcome this limitation and ensure efficient drug delivery, Intravenous administration proves effective as it allows for swift and maximal bioavailability. Typically patients experience the onset of neostigmine effects within 20 to 30 minutes following administration. The hepatic metabolism contributes to its elimination pathway as neostigmine is excreted via renal routes.
C. Pharmacodynamics
Neostigmine exerts its effects by temporarily blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase, a crucial enzyme. This leads to an increase in the levels of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction facilitating a prolonged interaction between acetylcholine and its receptors. As a result, nerve signals are transmitted for an extended period leading to sustained muscular contraction.
IV. Uses of Neostigmine
A. Approved Therapeutic Uses
B. Specific Diseases or Conditions Treated
V. Off-label Use of Neostigmine
A. Common Off-label Uses
B. Research Supporting Off-label Uses
C. Patient Testimonials and Case Studies
VI. Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosage for Different Conditions
The dosage of Neostigmine may differ significantly based on the specific condition being treated. To provide a general overview. In the case of Myasthenia Gravis, the standard oral dosage falls within the range of 15 to 375 mg per day, divided into 3 to 6 doses. Alternatively, for the reversal of Neuromuscular Blockade through intravenous administration, the typical dose ranges from 0.5 to 2.5 mg.
B. Dosage Adjustments for Special Populations
The need for dosage modifications should not be overlooked for specific patient groups. Elderly individuals, for instance, may require a reduction in dose due to physiological changes impacting drug metabolism and excretion. Additionally, individuals with renal or liver disease should have their dosages adjusted accordingly, as compromised hepatic or renal function can necessitate alterations.
C. Administration Techniques
Neostigmine can be administered via various routes depending on the clinical situation. For oral administration. It is recommended to swallow tablets whole with a glass of water, either with or without food. On the other hand, intravenous administration is generally performed by healthcare professionals within a hospital setting.
VII. Interactions of Neostigmine
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
Neostigmine has the potential to interact with other drugs, which could potentially impact its effectiveness or lead to an increase in side effects. It is worth noting that interactions with certain drugs are particularly noteworthy. For example, Anticholinergic drugs can negate the effects of neostigmine. Furthermore, aminoglycoside antibiotics have been shown to enhance the neuromuscular blocking effect of neostigmine potentially.
B. Drug-Food Interactions
Although neostigmine can be taken with or without food, its absorption may be affected by certain dietary components. It has been observed that the consumption of high-fat meals can potentially delay the absorption of oral neostigmine.
C. Drug-Disease Interactions
Individuals with certain medical conditions need to exercise caution when using Neostigmine. One such condition is Cardiac Disease, as this medication can potentially cause bradycardia. Therefore it should be used with caution in patients who have cardiac disease. Individuals with Asthma should also be careful when using Neostigmine as it can increase bronchial secretions. It is recommended that asthmatic patients are closely monitored while taking this medication.
VIII. Side Effects of Neostigmine
A. Common Side Effects
Neostigmine can cause some common side effects, which are generally mild and temporary. These may include feelings of nausea, episodes of vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
B. Less Common, Serious Side Effects
While not as frequently observed, specific individuals may undergo more significant side effects, including severe allergic reactions, respiratory distress, and cardiac arrhythmias.
C. Managing Side Effects
By adjusting the dosage or providing supportive care. One can often effectively manage the occurrence of side effects. Nevertheless, seeking prompt medical attention becomes essential if severe or unexpected side effects manifest. Before commencing neostigmine, please consult your healthcare provider about potential side effects and their necessary remedies.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
A. Known Warnings
Neostigmine should be used with a clear understanding of its possible risks. It can potentially cause bradycardia and other arrhythmias leading to a slow heart rate. Therefore, patients who already have cardiac conditions should approach its use with caution. Additionally, its worth noting that neostigmine can stimulate gut motility, which might exacerbate obstructive disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
B. Absolute Contraindications
It is advisable to refrain from using neostigmine in certain circumstances. One such situation is a mechanical bowel or urinary tract obstruction, as neostigmine affects smooth muscles and can cause further complications. Additionally, neostigmine should not be used in cases of peritonitis, an inflammatory condition of the abdominal lining.
C. Relative Contraindications
When considering the usage of neostigmine. It is important to evaluate its advantages and drawbacks in specific circumstances carefully. For individuals with epilepsy, caution should be exercised due to neostigmines' potential to decrease the seizure threshold. Similarly, asthmatic patients must exercise care when using neostigmine as it can heighten bronchial secretions.
X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
A. Administration to Elderly
In the elderly population, it is worth noting that physiological changes can impact how drugs are metabolized and eliminated from the body. It is, therefore, necessary to consider dose adjustment and closely monitor for any potential adverse effects as part of the treatment plan.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Neostigmine should only be administered during pregnancy or while breastfeeding if necessary. It is crucial to carefully evaluate the advantages compared to the risks associated with this medication. Moreover, it must be utilized solely under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
C. Administration to Children
It is important to note that children may need a lower dosage of neostigmine. Additionally, it is necessary to closely monitor their response to treatment in order to make any necessary adjustments to the dosage.
XI. Overdose Information
A. Symptoms of Overdose
An excessive intake of neostigmine may result in the manifestation of symptoms such as severe nausea and vomiting and significantly heightened salivation as well as muscle weakness that could potentially lead to paralysis.
B. First Aid and Immediate Response to Overdose
If you suspect an overdose, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. It is crucial to provide supportive care, which involves maintaining an open airway and closely monitoring vital signs.
C. Medical Interventions for Overdose
In the event of an overdose, the most common approach is to cease administration of the medication and provide the necessary support. In such cases, Atropine may be utilized as a means to mitigate the adverse consequences brought on by an overdose.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Proper Storage Conditions
For optimal preservation, Neostigmine necessitates room temperature storage while preventing exposure to light or moisture. Moreover, ensuring its unavailability for children and pets is paramount.
B. Safety Measures in Handling Neostigmine
When using neostigmine, it is essential to refrain from touching the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. If contact does happen, washing the affected area with water is recommended to ensure cleanliness and safety.
C. Disposal of Unused or Expired Neostigmine
Please do not dispose of unused or expired medication in household trash or pour it into drains. It is important to return them to a pharmacy or a local waste disposal company to guarantee safe and proper disposal.