Torsemide
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Torsemide
- III. Composition
- IV. How Torsemide Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Administration to Special Populations
- VII. Side Effects
- VIII. Interaction with Other Drugs and Substances
- IX. Warnings, Contraindications, and Precautions
- X. Storage, Overdosage, and Handling Precautions
- XI. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Pharmacology is a field with countless types of drugs, each with its own distinct features and uses. Among these, Torsemide is particularly noteworthy.
It plays a role in cardiovascular medicine and has made significant contributions to treating different conditions, especially heart failure and high blood pressure.
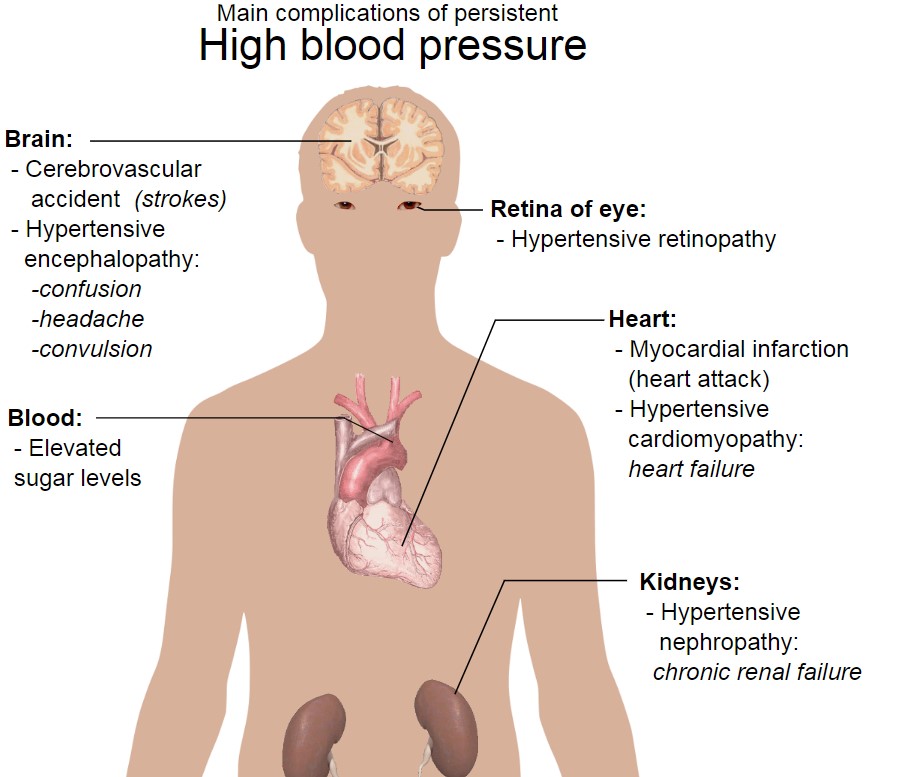
Hypertension effects
A. Definition of Torsemide
Torsemide is an effective medication that falls under the category of loop diuretics. These medications are named after their ability to impact the loop of Henle, a section of the kidney's nephron. Loop diuretics play a role in managing conditions characterized by excessive fluid buildup.
Torsemide, in particular, is well known for its diuretic properties helping to eliminate water and sodium from the body to alleviate fluid retention. This is especially beneficial in conditions such as heart failure and hypertension, where fluid retention can be problematic.
B. Overview of Therapeutic Class
Loop diuretics, like Torsemide play a role in the treatment guidelines for various cardiovascular conditions. These medications work by promoting the elimination of sodium and water from the body, thereby reducing extracellular fluid volume.
This not helps to decrease swelling but also improves high blood pressure, which is a common complication in patients with heart failure or kidney diseases. 2
- High Ceiling Diuretics; As diuretics they have the ability to induce significant diuresis even in cases of severe fluid overload.
- Relieving Symptoms; By removing fluids from the body, these medications alleviate discomfort and symptoms associated with fluid retention, such as difficulty breathing, swollen legs and ankles, and fatigue.
- Impact on Kidney Function; While they increase urine production, it's important to administer these diuretics and monitor renal function closely due to their potential impact on kidney function.
C. Historical Background and Development
Torsemide was developed in the 20th century to address the need for a stronger and more dependable diuretic for treating edematous conditions.
Since its introduction in practice, it has become a crucial component of cardiovascular medicine due to its superior pharmacokinetic characteristics and longer-lasting effects compared to other options.
These qualities make it possible for patients to take it daily, which is highly advantageous in real-life situations as it improves patient adherence and maximizes the effectiveness of treatment.
D. Scope of Usage: On-label and Off-label
Torsemide is typically prescribed for the treatment of edema caused by heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and kidney disease; It can also be used to manage blood pressure.(1)
However, Torsemide has been found to have benefits beyond its approved uses. Some doctors prescribe it off-label to treat hypercalcemia and, to an extent, unexplained swelling.(2)
Furthermore, some healthcare providers utilize Torsemide properties to help with ascites in patients with liver cirrhosis.(3)
1. Mayo Clinic - Torsemide
2. Medline Plus - Torsemide
3. WebMD - Torsemide Uses Side Effects and more
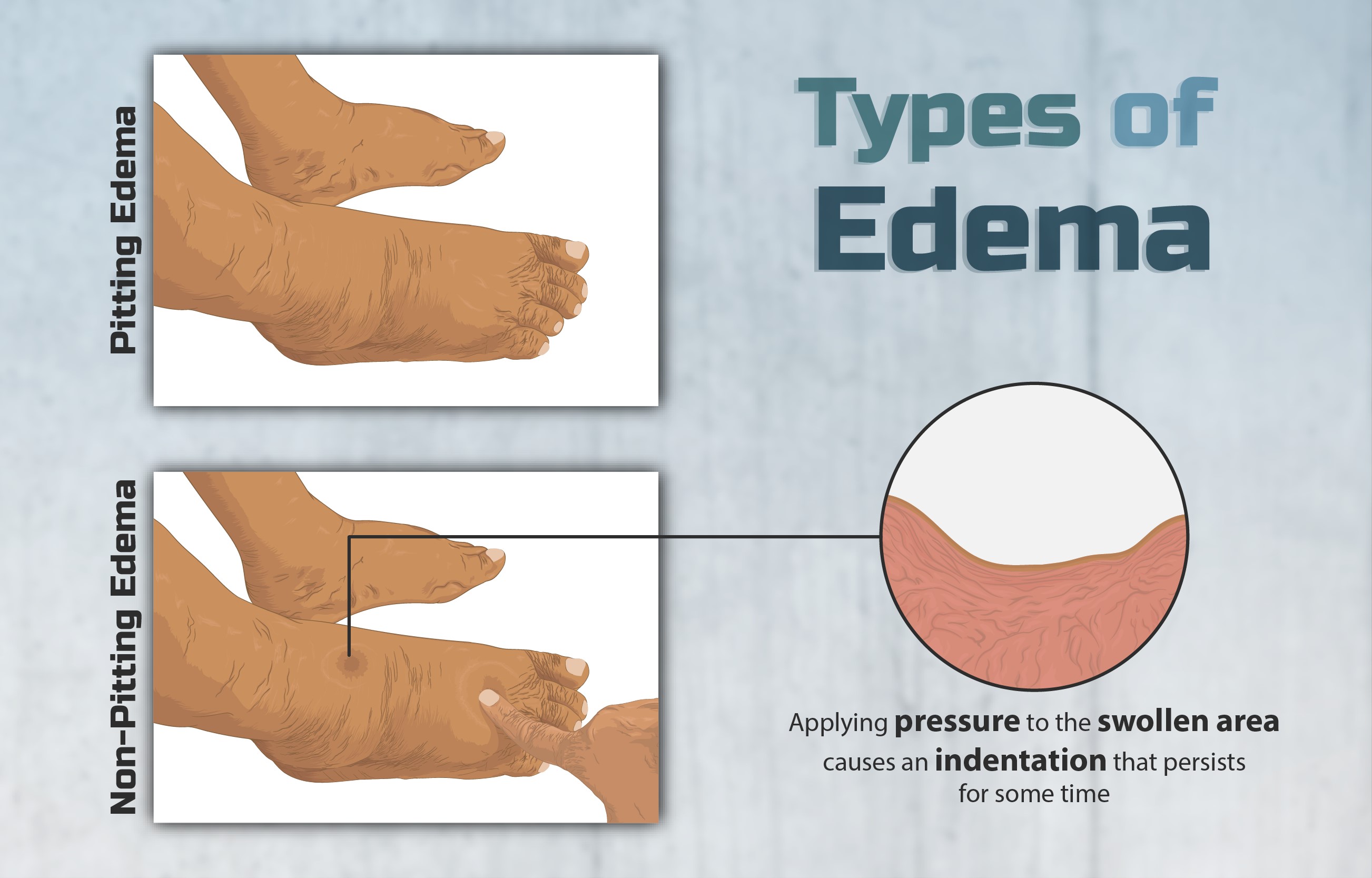
Type of Edema
E. Importance in Medical Practice
Torsemide plays a role in modern medicine. It offers a strong method to manage excessive fluid, ultimately improving the quality of life for patients with heart failure, high blood pressure, and related ailments.
Its powerful diuretic effect, along with its pharmacokinetic characteristics highlights its importance in clinical settings. Torsemide becomes more valuable when treating cases that don't respond well to other diuretics.
Therefore it's crucial to acknowledge the contribution of Torsemide in healthcare as it remains an essential tool in combating conditions caused by fluid overload.
II. Uses of Torsemide
A. On-label Uses
The applications of Torsemide, in therapy are wide-ranging. Cover various conditions, including cardiovascular diseases and renal dysfunctions. The approved uses, as determined by regulatory authorities, include the following;
1. Treatment of Edema in Heart Failure
Heart failure is when the heart struggles to pump blood adequately, often resulting in fluid retention, known as edema. Torsemide, a diuretic, is crucial in helping the body eliminate this excess fluid.
Targeting the loop of Henle achieves benefits such as reducing pulmonary congestion, easing shortness of breath, relieving peripheral edema and swelling in limbs, and optimizing cardiac function by reducing strain caused by fluid overload.(1)
1. Mayo Clinic - Torsemide Oral Route
2. Management of Chronic Renal Disease
In kidney disease, Torsemide emerges as a ray of hope for treatment. When the kidneys struggle to eliminate sodium and water, Torsemide's mode of action works against this inefficiency. It does not help alleviate swelling but also balances electrolyte levels, a common problem in renal disease.(1)
1. PubMed - Torsemide in Advanced Renal Failure
3. Hypertension Control
Torsemide is commonly used to regulate hypertension, a condition characterized by high blood pressure. Managing hypertension requires an approach, and Torsemide plays a crucial role in this regard.
By facilitating the excretion of sodium and reducing blood volume, Torsemide effectively helps control blood pressure levels. Its effectiveness is particularly notable in cases of hypertension, where traditional antihypertensive medications may not be as effective.(1)
1. Healthline - Torsemide Oral Tablet
B. Off-label Uses
Aside from its approved uses, Torsemide has a pharmacological profile that allows it to be used for various off-label purposes. These unconventional but medically validated applications further support the versatility of Torsemide as a treatment option.
1. Liver Cirrhosis Management
When it comes to liver cirrhosis, a long-term condition marked by liver scarring and reduced function dealing with retention becomes quite a tough task.
Torsemide, thanks to its diuretic effect helps in managing ascites, which is a major issue, in cirrhosis. Removing excess fluid build-up not only improves patient comfort but also reduces complications associated with fluid overload.
2. Other Emerging Applications
Torsemide has a range of potential applications that continue to emerge.
- These include its use in managing hypercalcemia, where it helps the kidneys get rid of calcium.
- It is also being explored as a treatment for preeclampsia, a high blood pressure disorder during pregnancy.
- Additionally, researchers are investigating its role in reducing kidney damage caused by chemotherapy drugs.
The expanding scope of Torsemides uses, both approved and off-label, confirms its importance in medical practice. Its effectiveness in treating clinical conditions establishes it as a valuable tool in healthcare.
III. Composition
A. Active Ingredients
Torsemide contains an ingredient called pyridine sulfonylurea, which is chemically known as 1 isopropyl 3 [(4 m toluidino 3 pyridyl) sulfonyl]urea.
This particular molecule plays a role in its ability to act as a diuretic. Its unique structure enables it to selectively interact with the Na K 2Cl symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, thereby initiating its diuretic effect.
B. Inactive Components
In addition to the active ingredient Torsemide formulations also contain various inactive or excipient components. These ingredients play a role in ensuring optimal stability, bioavailability, and administration properties.
Some common inactive components include lactose, which acts as a filler magnesium stearate used as different polymers, for tablet binding purposes and coloring agents added for aesthetic appeal.
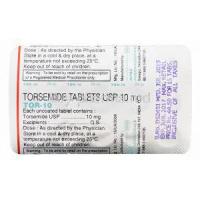
C. Available Formulations: Tablets and Injections
Torsemide can be found in two forms for purchase; tablets and injections.
- The tablets come in strengths, such as 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, and 100mg providing flexibility when determining the dosage.
- On the hand injections are commonly used in urgent situations as they offer immediate and controlled administration.
IV. How Torsemide Works
A. Mechanism of Action
The way Torsemide works can be described as its ability to block the Na-K-2Cl symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidneys.
This prevents the reabsorption of sodium, potassium, and chloride ions resulting in increased excretion of these electrolytes and water through urine.As a result, it acts as a diuretic. It is commonly used for conditions where fluid retention is an issue.
B. Pharmacokinetics
The way Torsemide is processed by the body, known as pharmacokinetics, involves how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. Here are the important points to consider;
- Absorption; Torsemide is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Distribution; It spreads widely throughout the body and has a tendency to bind with plasma proteins, especially albumin.
- Metabolism; The main site of metabolism is the liver, where cytochrome P450 2C9 plays a significant role.
- Excretion; The primary method of elimination is through the kidneys.
Both unchanged drugs and its metabolites are excreted this way.
C. Pharmacodynamics
The field of pharmacodynamics helps us understand how drugs affect the body. When you take Torsemide orally, its diuretic effects start within an hour. Reach their peak after about 2 to 3 hours.
The effects typically last for around 6 to 8 hours when taking tablets. It may be a bit longer with injections. It's important to note that individual responses can differ depending on factors like kidney function and other medications being taken concurrently.
D. Comparative Analysis with Other Diuretics
When comparing Torsemide with loop diuretics such as furosemide and bumetanide, there are a few notable advantages.
- Torsemide has better oral bioavailability, which means it consistently delivers the desired therapeutic effect.
- It has a duration of action allowing for once daily dosing in many situations.
- Torsemide provides a predictable diuretic response making it easier to manage clinically.
V. Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
The appropriate dose of Torsemide should be tailored to each individual based on their condition, how they respond to the medication, and any other treatments they may be undergoing.
Typically when addressing retention in heart failure, the initial recommended dosage typically falls within the range of 10 to 20 mg per day. It is usually advised to begin with a daily dose of 5 mg to manage blood pressure.
B. Dosage Adjustments
1. Renal Impairment
In individuals with impaired kidney function it is crucial to use dosage with care and closely monitor parameters. Adjusting the dose or extending the time, between doses might be required, depending on the level of impairment.
2. Hepatic Impairment
The dose of Torsemide may need to be adjusted if there is any liver damage. It is important to evaluate liver function and carefully adjust the medication in order to achieve the desired therapeutic effects while minimizing any potential risks.
C. Administration Routes and Techniques
Torsemide is available in tablet form for intake or can be administered through injection under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
When taking it orally, it is recommended to have it with food to minimize any discomfort in the stomach.
For administration, proper protocols for dilution and infusion rate should be followed by the healthcare provider to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment for the patient.
VI. Administration to Special Populations
A. Elderly Patients
When prescribing Torsemide to patients, it's important to be cautious due to the possible changes in how their bodies process and respond to medications.
Since older adults may have decreased kidney function and take medications, it's crucial to closely monitor them and possibly adjust the dosage accordingly. Here are some important things to keep in mind;
1. Begin with a dose within the recommended range.
2. Regularly check kidney function and electrolyte levels.
3. Pay attention to any negative side effects or interactions with other medications they might be taking.
Taking these precautions will help ensure the safety and effectiveness of administering Torsemide to patients.
B. Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Torsemide is classified as Pregnancy Category B, which means that animal studies have not shown any harm to the fetus. However, there is a lack of human studies.
Therefore it should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
- Regarding breastfeeding; Torsemide is present in breast milk, in amounts.
- Nursing mothers should consult healthcare professionals to assess the risks and benefits.
- It is advisable to monitor the infant for any negative effects.
C. Pediatric Use
The use of Torsemide in children has not been definitively proven to be safe and effective. Therefore it should be used with caution in this age group taking into account their physiological characteristics, such as kidney development and fluid levels. Collaborating with experts and carefully monitoring the patients is crucial to ensure the best possible treatment results.
VII. Side Effects
A. Common Side Effects
1. Electrolyte Imbalance
Torsemide can cause imbalances in levels leading to certain conditions. These may include;
- Levels of sodium (hyponatremia)
- Low levels of potassium (hypokalemia)
- Low levels of magnesium (hypomagnesemia).
2. Gastrointestinal Issues
Patients may experience issues such as feelings of queasiness and the urge to vomit. They may also face challenges with bowel movements, either in the form of constipation or diarrhea.
3. Skin Reactions
Sometimes you may experience skin reactions such as rashes or itching. If these reactions persist you might need to manage the symptoms.
B. Severe and Rare Side Effects
While rare, there are instances of more severe side effects that can happen, such as;
- Severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis.
- Acute pancreatitis.
- Possible damage, to the ears (cytotoxicity), especially when higher doses are given or when administered intravenously at a pace.
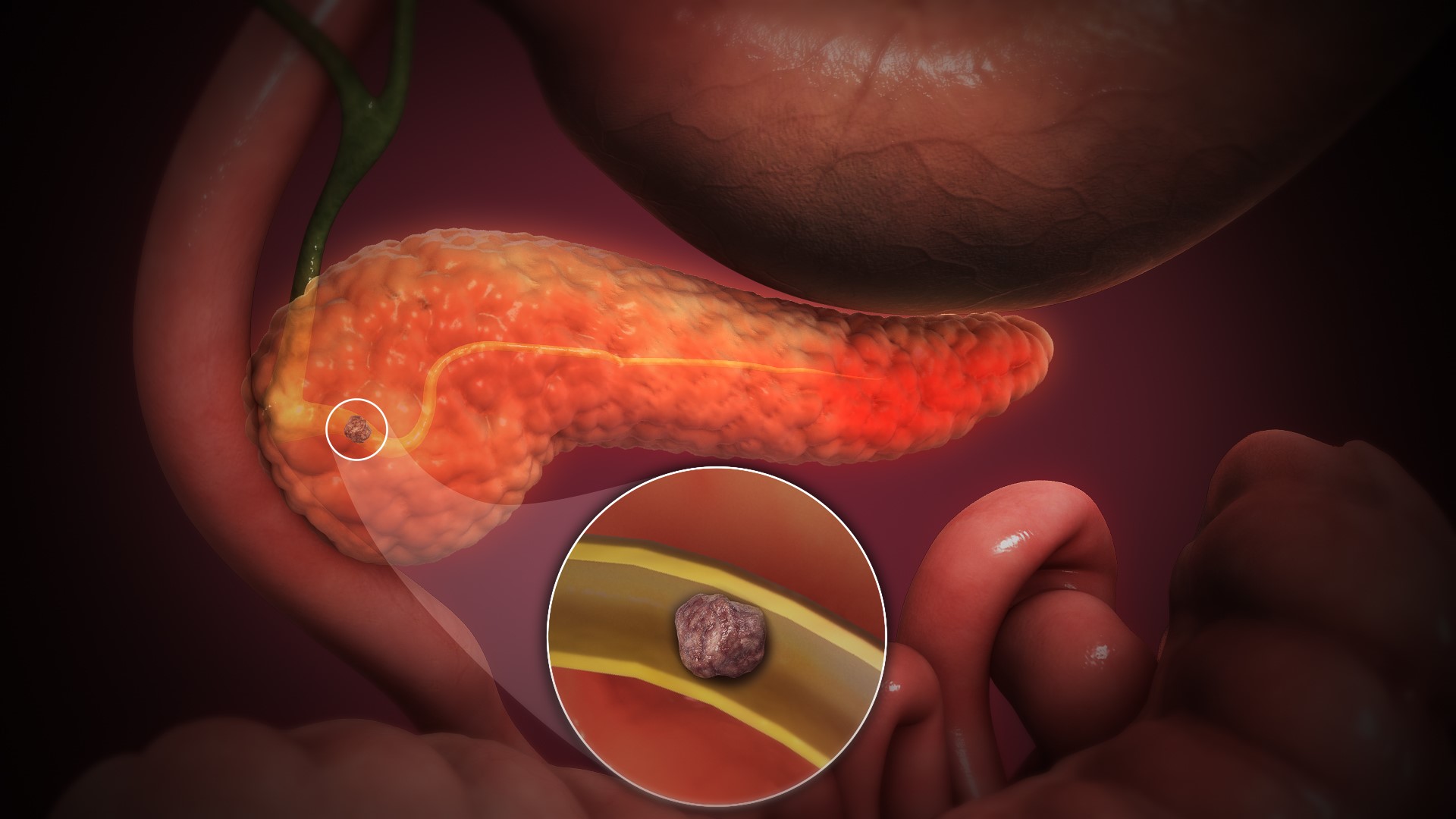
3D Medical Animation Acute Pancreatitis
C. Long-term Side Effects
Long-term medication use can have side effects, including chronic kidney injury or hearing problems. Monitoring and evaluating these risks is crucial to minimize any potential harm.
VIII. Interaction with Other Drugs and Substances
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
Torsemide has the potential to interact with medications leading to various outcomes such as decreased effectiveness or increased toxicity. Some examples include;
- It can enhance the effects when used alongside other blood pressure-lowering agents.
- There is a possibility of increased bleeding if taken with anticoagulants like warfarin.
- The effectiveness of agents may be altered when combined with torsemide.
B. Drug-Food Interactions
Certain food choices have the potential to affect how well Torsemide works. For instance, if you consume a diet high in sodium, it may diminish the effects of the medication. On the hand, including potassium-rich foods, in your diet can help balance out the risk of hypokalemia.
C. Impact on Laboratory Tests
Torsemide has the potential to affect laboratory tests, such as changes in levels of electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. It can also have an impact on function tests.
Healthcare professionals need to be aware of these interactions and side effects. They should provide patient education and regularly follow up to ensure Torsemide's safe and effective use.
IX. Warnings, Contraindications, and Precautions
A. Warning and Black Box Alert
Like medications, Torsemide has certain warnings that healthcare professionals need to follow. Although it doesn't have a box warning it's crucial, for patient safety to pay close attention to specific warnings and contraindications.
B. General Contraindications
Torsemide should not be given in the following situations;
- Anuria which's when the kidneys are unable to produce urine.
- Hypersensitivity to Torsemide or any sulfonylurea medications.
- Severe liver failure, especially when combined with kidney problems.
C. Important Precautions in Usage
To ensure the effective use of Torsemide for therapeutic purposes it is important to take certain precautions into consideration;
1. Regular monitoring of levels and renal function is necessary to prevent any potential imbalances that may have negative effects.
2. Patients with preexisting liver or kidney disease should exercise caution as adjustments, in dosage might be necessary to accommodate their conditions.
3. It is important to avoid administering Torsemide to patients who have known allergies to sulfonamide medications.
D. Careful Administration Guidelines
It is crucial to follow the recommended protocols to ensure the possible results in administering treatments. This involves making dosage adjustments for patients with kidney or liver issues, closely monitoring blood pressure levels for individuals with hypertension, and being mindful of any potential interactions with other medications.
X. Storage, Overdosage, and Handling Precautions
A. Proper Storage Conditions
It is extremely important to store Torsemide in order to ensure that it remains effective and safe. This involves the steps;
- Keep it at room temperature away, from any moisture or heat.
- Store it in its packaging until you are ready to use it in order to shield it from light.
- Make sure to keep the medication out of reach of children and pets.
B. Overdosage: Symptoms and Management
If someone takes much Torsemide, it is important to take immediate action. This can cause symptoms such as;
- Excessive urination leads to dehydration
- Potentially dangerous imbalances in electrolytes
- Cdiovascular issues like low blood pressure.
Managing an overdose involves providing care rehydrating the person replacing electrolytes and in severe cases considering hemodialysis, as a treatment option.
C. Handling Precautions and Disposal
Handling and disposing of Torsemide correctly is crucial to ensure safety and environmental compliance. This includes following regulations for the disposal of medical waste utilizing approved medication take-back programs whenever possible and seeking guidance from a pharmacist on proper disposal methods if take-back programs are not available.
XI. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
Torsemide, a medication with therapeutic benefits, is commonly used to treat conditions such as edema, hypertension, and renal disorders. To ensure results while minimizing any potential risks, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of how to properly administer the drug, be aware of its possible side effects and interactions and take into account any specific considerations for different patient populations.
B. Current Research and Future Prospects
Ongoing scientific studies are further investigating the impacts of Torsemide in different clinical scenarios. Researchers are exploring its applications in cardiovascular disease as well as comparing its effectiveness with other diuretics. There is also interest, in uncovering new uses for Torsemide improving formulations to enhance patient compliance and safety and developing strategies to minimize side effects and interactions.
C. Final Thoughts on Clinical Relevance and Usage
To conclude, Torsemide is a part of modern pharmacotherapy. Its distinct qualities and ranging uses highlight its importance in clinical practice. By following the recommendations outlined here, healthcare professionals can use Torsemide wisely, taking into account each patient's requirements and promoting improved health outcomes for various patient groups.