Azax, Azithromycin
- Introduction to Azax (Azithromycin)
- Composition of Azax (Azithromycin)
- How Azax (Azithromycin) Works
- Uses of Azax (Azithromycin)
- Off-Label Uses of Azax (Azithromycin)
- Dosage and Administration of Azax (Azithromycin)
- Common Side Effects of Azax (Azithromycin)
- Serious Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Interactions of Azax (Azithromycin) with Other Medications
- Contraindications of Azax (Azithromycin)
- Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- Administration to Specific Populations
- Handling Overdosage of Azax (Azithromycin)
- Storage and Handling Precautions for Azax (Azithromycin)
- Conclusion: The Role of Azax (Azithromycin) in Modern Medicine
Introduction to Azax (Azithromycin)
Azithromycin, which is commercially marketed as Azax represents an example in the realm of antibiotics providing a distinctive therapeutic profile.
This article explores the nuances of Azithromycin tracing its historical background, developmental trajectory, and its broad applications in contemporary medical practices.
The evolution of Azax from a concept to an essential component, in the field of pharmaceuticals showcases the progress made in medical science and its unwavering dedication to improving healthcare solutions.
Overview of Azithromycin
Azithromycin, a type of antibiotic belonging to the macrolide family is well known for its ranging effectiveness. This medication is highly regarded for its ability to treat bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections and even more complex sexually transmitted diseases. The versatility and effectiveness of Azithromycin have solidified its status as a favored option, in treatment.
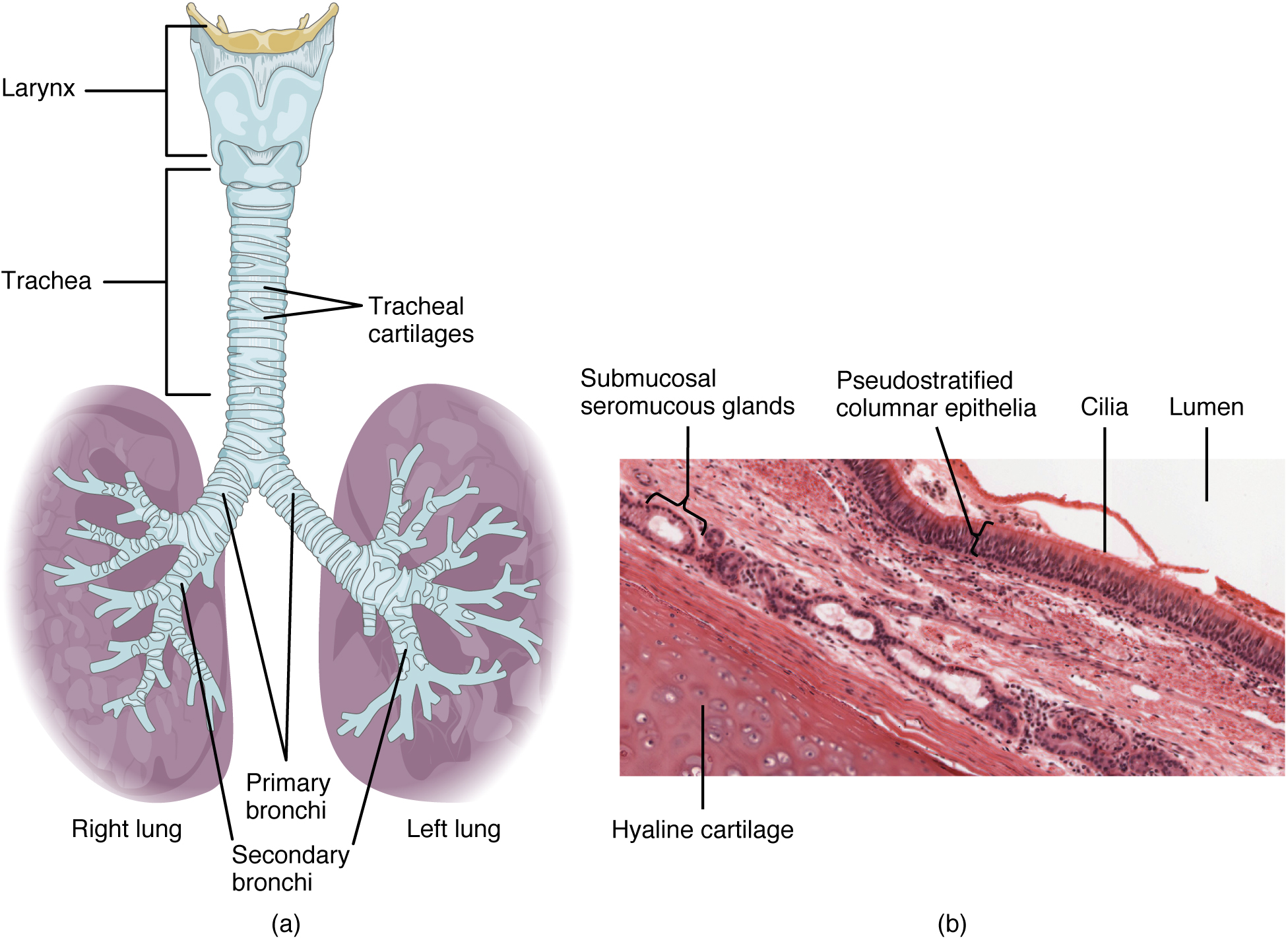
Respiratory system
Historical Context and Development
In the 1980s a Croatian pharmaceutical company called Pliva developed Azithromycin. This antibiotic was patented in 1981, and it was later introduced to the market in the early 1990s. Its creation represented a breakthrough in antibiotic research as it provided a different option, with reduced dosage requirements and a lower likelihood of resistance development.
Scope of the Article
The goal of this in-depth analysis is to shed light on what Azax is made of, including its active and inactive components. Additionally, we will delve into how Azax works and understand its interactions, with pathogens and the human body.
Composition of Azax (Azithromycin)
Active Ingredient Profile
Azax relies on Azithromycin as its component, which is a type of antibiotic created through a combination of natural and synthetic elements. The molecular structure of Azithromycin is carefully crafted to target bacterial cells. By inhibiting protein synthesis, in these cells, Azax effectively hampers their growth, which then prevents them from multiplying.
Inactive Ingredients and Their Roles
In addition to the ingredient that has an active role in Azax, there are various other substances included. These additional components have functions, in maintaining the medication's stability how easily it can be absorbed by the body, and how well patients tolerate it.
Some examples of these substances are dibasic calcium phosphate pregelatinized starch, sodium croscarmellose, and magnesium stearate. Each of these elements plays a part in ensuring that the active ingredient works optimally and is delivered effectively.
How Azax (Azithromycin) Works
Mechanism of Action in Bacterial Infections
Azax works by using an effective method of action. Its active ingredient, azithromycin attaches to the 50S subunit found in bacterial cells. This attachment stops the production of proteins, which is crucial, for bacterial growth and reproduction. As a result Azax effectively stops the spread of infections and enables the body's immune system to eliminate any remaining harmful bacteria.
Immune-system
Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
Azax has the ability to prevent the growth and multiplication of bacteria making it a powerful bacteriostatic agent. When taken orally Azithromycin is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream reaching its concentration, in a short period of time. Its ability to distribute widely throughout the body and stay active for a time allows for shorter treatment periods and helps patients follow their prescribed regimens more easily.
Uses of Azax (Azithromycin)
Treating Bacterial Infections
Azax scientifically referred to as Azithromycin is a tool in the fight against numerous bacterial infections(1). Its ranging ability to combat different types of harmful bacteria makes it highly effective.
Azithromycin works by hindering the synthesis of proteins, which is crucial, for their survival and reproduction(2). This mechanism enables it to effectively treat a range of bacterial infections, including both common and uncommon ones.
1. PubMed - Azithromycin
2. National Library of Medicine - Mechanism of action, resistance, synergism, and clinical implications of azithromycin
Use in Respiratory Tract Infections
Azax excels in treating respiratory tract infections, which encompass a range of conditions such as ;
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
The combination of azithromycin's capacity to concentrate in lung tissue and its extended half-life makes it a favored option for tract infections due, to its convenience and effectiveness.
1. NIH - Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD
2. National Library of Medicine - Appropriate prescribing of azithromycin for community‐acquired pneumonia
Application in Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Azax has also shown effectiveness in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections(1). Its strong ability to fight against a variety of skin pathogens makes it a great choice for addressing conditions, like Impetigo, Cellulitis, and Folliculitis. The way the drug moves through the body reaching the site of infection effectively guarantees the possible treatment results.
1. National Library of Medicine - Directly observed therapy with azithromycin for skin and soft tissue infections in injection drug users
Efficacy in Sexually Transmitted Infections
Azithromycin plays a role in treating sexually transmitted infections (STIs) with proven effectiveness. It is commonly used to treat infections like Chlamydia trachomatis in a single dose.
Additionally, it is often used in combination with antibiotics to combat Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The convenient dosing regimen of Azax, which usually involves a short course of therapy greatly improves patient compliance. This is vital, for managing STIs.
Off-Label Uses of Azax (Azithromycin)
Potential in Viral Infections
While Azax (Azithromycin) is commonly used as an agent recent research has shed light on its potential effectiveness in managing specific viral infections.
The reason behind this application lies in azithromycin's anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to regulate the immune response of the body.
In cases of viral respiratory infections, Azax has shown promise in alleviating symptoms and possibly shortening the duration of illness.
However, it is important to emphasize that the use of Azax for infections should be approached cautiously and only, under the guidance of a medical professional as inappropriate usage can contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Use in Inflammatory Diseases
The use of Azax for treating diseases has brought about new possibilities. It is not limited to its effects but also seems to have an impact on regulating the body's inflammatory processes.
Some examples of, off-label applications include managing respiratory diseases with an inflammatory aspect and certain dermatological conditions.
Azax is believed to work by reducing the production of cytokines which helps alleviate the symptoms associated with these diseases.
Emerging Research and New Applications
The range of uses for Azax continues to expand as ongoing research and clinical trials take place. Researchers are exploring therapeutic applications, including the treatment of gastroparesis by harnessing Azax's prokinetic effects.
Additionally, there is potential for Azax to be useful in autoimmune disorders. These emerging uses, although in the research phase highlight the versatility of Azax and its ability to go beyond traditional antibiotic usage.
However, it is important to emphasize that any, off-label use should always be supported by scientific evidence and conducted under the guidance of medical experts.
Dosage and Administration of Azax (Azithromycin)
Standard Dosage Guidelines
The recommended amount of Azax (Azithromycin) to take may vary depending on the infection and its severity.
- Generally for adults the initial dose is a strength taken on the first day followed by a lower maintenance dose, for the following four days.
- For children, the dosage is usually determined based on their body weight and the type of infection they have.
It is crucial to follow the instructions provided by a healthcare professional when using Azax and complete the entire treatment regimen to avoid developing antibiotic resistance.
Dosage Adjustments for Specific Populations
It is important to make changes to the dosage for groups of people to ensure their safety and effectiveness. These groups include;
- Patients, with kidney or liver problems may need to have their dosage adjusted.
- Older patients may require dosages depending on their overall health and the medications they are taking at the same time.
- If a woman is pregnant or breastfeeding Azax should only be used if absolutely necessary and after a healthcare provider has carefully considered the risks and benefits.
Administration Techniques and Recommendations
Azax can be taken by mouth either in tablet or liquid form. It is usually recommended to have it with a meal to minimize any stomach discomfort.
When using the form make sure to shake the bottle thoroughly before measuring the dose accurately with a proper measuring device.
Patients are advised to stick to a schedule when taking the medication in order to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Common Side Effects of Azax (Azithromycin)
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Some of the frequently mentioned effects of Azax are related to the digestive system. These may include feeling nauseous and vomiting experiencing diarrhea or loose stools well as abdominal pain and discomfort. Usually, these symptoms are mild and temporary tending to subside as the body gets accustomed, to the medication.
Dermatological Reactions
Sometimes people may experience reactions to Azax although it is not very common. These reactions can appear as a rash and itching or hives. In some cases more serious skin reactions, like Stevens-Johnson syndrome can occur. If you have any long-lasting skin reaction it's important to seek medical attention promptly from a healthcare professional.
Neurological Effects
Rarely individuals may experience neurological effects when using Azax. These effects might include;
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Change in taste perception
- In rare cases seizures or significant neurological disorders.
Serious Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Cardiac Risks and Concerns
Azithromycin may have the potential to pose risks, especially for individuals who already have heart conditions.
Some of the concerns include QT prolongation, which can result in an irregular heartbeat, as well as Torsades de pointes, a rare but serious issue with heart rhythm
. If patients have a history of problems it is important for them to have a conversation about these risks, with their healthcare provider.
Hepatotoxicity and Liver Function
In instances, Azax has been known to cause hepatotoxicity, which can affect the functioning of the liver. If you experience any of the following symptoms it could indicate liver impairment;
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
- Abdominal pain
- Unusual fatigue or weakness.
It is important to monitor liver function in patients who are taking Azax particularly if they have existing liver conditions.
Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis
If someone has a reaction, to Azax it's important to take it seriously and get medical help right away. Signs of an allergic reaction can include trouble breathing or swallowing swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, and a severe rash or itching. If you experience any of these symptoms it's crucial to seek emergency care immediately.
Interactions of Azax (Azithromycin) with Other Medications
Impact on Drug Efficacy
Azax (Azithromycin) has the potential to interact with medications, which may impact how effective they are. For example, it is recommended to take antacids containing magnesium or aluminum at least 2 hours before or after Azax to avoid any decrease, in the absorption of the antibiotic.
Additionally, Azithromycin can reduce the effectiveness of contraceptives so alternative or additional contraceptive methods may be necessary. Healthcare providers should thoroughly review a patient's list of medications to ensure the best possible treatment outcomes.
Avoiding Harmful Drug Combinations
There are combinations of drugs that should not be taken with Azax because they can cause serious side effects. Some examples include;
- Warfarin and other blood thinners as Azithromycin might increase their effects.
- Also, drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval (such as antiarrhythmics) should be avoided due to the risk of developing cardiac arrhythmias.
It is important for patients to always inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking, including, over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Adjusting Treatment Plans
When healthcare professionals come across situations where drug interactions cannot be avoided they have the option to make changes, to the treatment plan.
This could mean adjusting the dosage of Azax or the other drug involved or even prescribing a medication that carries a lower risk of interaction.
It is crucial to conduct monitoring and follow-up to ensure that the modified treatment regimen remains effective and safe.
Contraindications of Azax (Azithromycin)
Medical Conditions Precluding Use
Azax should not be prescribed to patients with medical conditions because it may worsen these conditions.
- These contraindications consist of liver disease as Azithromycin can potentially harm the liver further.
- Additionally, individuals with a known history of QT prolongation or torsades de pointes should avoid using Azax.
- Furthermore, those, with a renal impairment that affects drug excretion should also steer clear of this medication.
Healthcare providers must carefully review a patient's medical history before considering the prescription of Azax.
Drug Allergies and Sensitivities
Azax should not be used by patients who have a confirmed allergy to Azithromycin, or any ketolide antibiotics.
Signs of a reaction may include the presence of hives breathing difficulties and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
If it is determined that Azax is essential for patients with hypersensitivity, to similar medications they should be carefully observed and monitored.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring for Side Effects
It's important to monitor for any potential side effects when using Azax.
This involves keeping an eye out for signs of liver problems like jaundice and being aware of any symptoms such, as palpitations or chest pain.
If you notice any symptoms make sure to inform your healthcare provider right away.
Precautions in Specific Health Conditions
Patients who have health conditions like liver or kidney disease heart rhythm disorders or myasthenia gravis should exercise caution when using Azax. It is often necessary to make adjustments, to the dosage and closely monitor these cases to avoid worsening of the condition.
Guidelines for Safe Use
To ensure the usage of Azax it is important for patients to follow the recommended dosage and duration of treatment. It is advised to take the medication at a time every day in order to maintain steady blood levels. Patients should avoid skipping doses or discontinuing the medication prematurely even if their symptoms improve as this can contribute to the development of resistance.
Administration to Specific Populations
Azax (Azithromycin) in Elderly Patients
Administering Azax to patients requires careful consideration due to physiological changes associated with aging.
These changes, including reduced liver and kidney function, can affect how Azithromycin is processed in the body. As a result, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage to minimize any side effects
Moreover, elderly patients often have medical conditions and may be taking multiple medications, which increases the risk of interactions, between drugs.
It is crucial to monitor both the effectiveness and any potential side effects of Azax in this patient population.
Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
The use of Azax during pregnancy and breastfeeding is a matter of careful consideration. Although studies on animals have not shown any harm there is a lack of sufficient and well-conducted research, on pregnant women.
Hence it is recommended to use Azax during pregnancy only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks to the unborn baby. Likewise, caution should be exercised when giving Azax to mothers who are breastfeeding since it can be passed through breast milk and may impact the nursing baby.
Pediatric Administration Guidelines
Administering Azax to pediatric patients necessitates following guidelines that consider the child's age, weight, and the severity of the infection.
The dosage, for children, is usually determined based on their body weight. It is crucial to exercise caution to prevent administering too little or too much.
When it comes to children, especially infants it is essential to observe them closely for any indications of adverse reactions.
Handling Overdosage of Azax (Azithromycin)
Recognizing Symptoms of Overdosage
It is crucial to be able to identify the signs of taking much Azax. Symptoms of an overdose may consist of feelings of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and indications of liver problems, like jaundice.

Nausea
In severe instances an overdose can result in hearing loss, extreme dizziness or irregular heartbeats.
Immediate Actions and Treatment Protocols
If someone takes much Azax it's important to seek immediate medical help. The treatment mainly focuses on providing support and relief for the symptoms.
If the overdose happened recently the doctor may consider doing a lavage. It's crucial to monitor the liver and kidney functions and in severe cases of overdose keeping an eye, on the heart is also essential to handle any possible complications.
Long-term Management of Overdose Effects
The long term care after an overdose of Azax primarily involves addressing any lingering symptoms and taking measures to avoid potential complications.
It may be necessary to schedule check-up visits to monitor the patient's recovery progress and address any side effects that might have occurred due, to the overdose.
Storage and Handling Precautions for Azax (Azithromycin)
Optimal Storage Conditions
Azax should be stored at room temperature away, from light and moisture. It's important to keep the medication in its packaging until you're ready to use it. Try not to store it in bathrooms or areas that are humid or hot as these conditions can cause the medication to deteriorate.
Shelf Life and Expiry
The usual duration of effectiveness, for Azax is generally years starting from the manufacturing date provided that it is stored correctly.
However, it is essential to verify the expiration date mentioned on the packaging and refrain from using the medication after that date as its efficiency and safety might be compromised.
Safe Disposal Practices
It's important to dispose of any unused or expired Azax. Avoid flushing it down the toilet or pouring it into a drain unless specifically instructed.
Many localities offer drug take-back programs and pharmacies may also provide disposal services.
Proper disposal is crucial to prevent contamination and accidental ingestion by children or animals.
Conclusion: The Role of Azax (Azithromycin) in Modern Medicine
Summary of Key Points
Azax, which is a name for Azithromycin has become an essential antibiotic in modern medicine. Its ability to fight a range of bacteria along with its relatively safe nature has made it a go-to option for treating various bacterial infections.
This includes infections in the respiratory tract, skin, and soft tissues as well, as certain sexually transmitted infections. The flexibility of its dosing schedule often requiring shorter treatment courses compared to antibiotics has improved patient adherence and the effectiveness of treatment.
Future Directions and Research
The future of Azax in the field of medicine is closely tied to research and development. New studies are examining its uses beyond just bacterial infections, such as its effectiveness against certain viral infections and inflammatory diseases.
Additionally, there is a growing curiosity about how Azax can be incorporated into treatment plans especially considering the increasing problem of antibiotic resistance.
It is important to continue researching in order to make use of Azax to minimize any possible side effects and explore new avenues, for therapy.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
In summary, although Azax (Azithromycin) is a tool in medicine it should be used responsibly. This means using it to prevent resistance being aware of its possible side effects and following established guidelines for its use.
Healthcare professionals should stay updated on the research about Azax to maximize its benefits while preventing misuse. Patients are advised to adhere to their treatment plans and consult their healthcare providers if they have any concerns, about using Azax.