Dicyclomine Injection
- Introduction
- Uses of Dicyclomine Injection
- Off-label Uses
- How Dicyclomine Injection Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Administration to Specific Populations
- Side Effects
- Common Side Effects
- Interaction with Other Medications
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Important Precautions
- Careful Administration
- Storage and Handling
- Handling Precautions
- Overdose Management
- Conclusion
Introduction
Dicyclomine injection1 is considered a medication in the field of antispasmodics. It relieves specific medical conditions and is widely used by healthcare professionals. This article highlights the applications of this remarkable pharmaceutical, specifically its use in treating gastrointestinal disorders and its significance in postoperative recovery.
Uses of Dicyclomine Injection
Approved Use: Treating Muscle Spasms in the Gastrointestinal Tract
Dicyclomine injection is commonly used for its ability to relieve spasms in the GI) tract. It works by blocking the effects of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in muscle contractions. This leads to noticeable benefits, including:
- Reducing abdominal cramps
- Lessening the frequency and severity of spasmodic episodes
- Easing discomfort is often associated with digestive problems.
Dicyclomine can be used for flare-ups and long-term management, making it a versatile treatment option in gastroenterology.
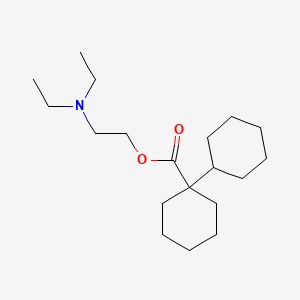
Effectiveness in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Besides its usefulness in reducing spasms in the gastrointestinal tract, dicyclomine has shown significant effectiveness in managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)8. IBS, a disorder affecting the digestive system, is characterized by symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. While it's not a cure-all solution, dicyclomine injection significantly helps alleviate these symptoms. Numerous clinical trials and empirical studies support the efficacy of this medication by demonstrating.
- A decrease in the severity of abdominal pain
- Improved quality of life for individuals suffering from IBS Increased compliance
- Satisfaction with strategies for managing IBS
Due to its targeted effects and strong efficacy, dicyclomine is increasingly recognized as an essential component of comprehensive treatment plans for IBS.
Postoperative Spasmodic Conditions
The potential benefits of using dicyclomine injection go beyond treating gastrointestinal issues. It can also be helpful in care, especially after abdominal surgeries, where patients often experience spasms. Administering dicyclomine can relieve situations by reducing discomfort, helping patients switch to oral feeding faster, and decreasing the need for additional pain relief treatments. These various uses of dicyclomine highlight its importance in medicine and its growing relevance in postoperative care.
Off-label Uses
The range of applications for dicyclomine injection goes beyond its approved uses, with studies exploring its effects in clinical situations. Although these off-label uses may not have undergone rigorous scientific validation, they still show promising therapeutic potential as approved ones.
Potential for Use in Functional Bowel Disorders
Functional bowel disorders refer to a group of conditions where there are issues with bowel function even though no structural abnormalities are found. Researchers6. have been studying the use of dicyclomine injection for these disorders, although it is not approved for them. Far, there have been positive outcomes when using it for conditions like functional dyspepsia and chronic idiopathic constipation.
These outcomes include:
- Reducing discomfort
- Improving gut movement
- Enhancing quality of life
These initial findings indicate that further research in this area holds promise.
Management of Biliary Colic
Severe abdominal pain caused by gallbladder issues, known as biliary colic, offers an opportunity for using dicyclomine injection. This medication's antispasmodic effects are believed to help alleviate the intensity of episodes in the biliary system.
This includes:
- Reducing spasms in the sphincter of Oddi
- Promoting bile flow
- Ultimately enhancing patient comfort.
Although not officially approved for this purpose, anecdotes and initial studies suggest that further research is warranted to confirm these findings.
How Dicyclomine Injection Works
Mechanism of Action
To comprehend how dicyclomine injection works in terms of its effects on the body, we need to explore its mechanism of action. Essentially, it acts as an agent, which means it hinders the functioning of acetylcholine—an important neurotransmitter.
Interaction with Muscarinic Receptors
Dicyclomine specifically has a preference for receptors, which are commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. By blocking these receptors, it reduces the nervous system's activation, leading to a decrease in involuntary muscle contractions.
The effects include:
- Slowed movement of food through the tract
- Relieved muscular tightness, within the digestive system
- Improved flexibility of the stomach
Duration and Onset of Effect
The way dicyclomine works in the body is that it starts to take effect quickly after it is taken, usually within 30 to 60 minutes. The results of the medication can last for around 4 to 6 hours. This can vary depending on each person's unique body chemistry.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines
Determining the amount of medication in therapeutic doses involves considering various factors, including the specific ailment, individual patient characteristics, and other medications being taken. Typically, standard recommendations suggest a dosage range of 10 to 20 mg to be taken four times a day.
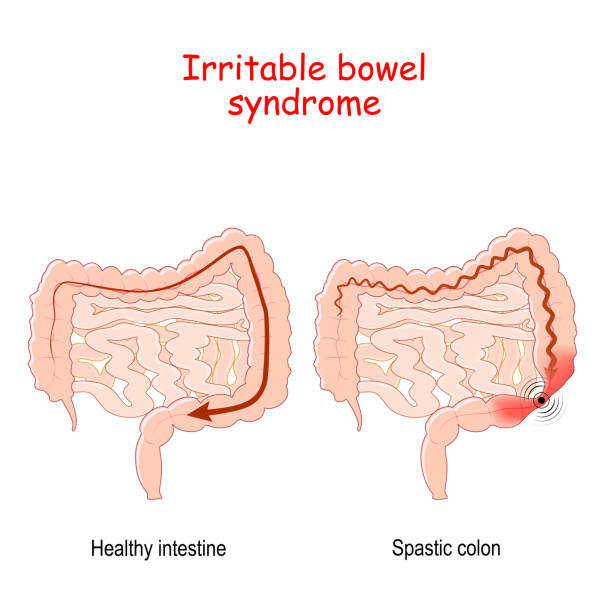
Administration Routes: Intravenous vs. Intramuscular
The choice between giving medication through a vein or injecting it into a muscle depends on how the symptoms must be relieved. When medication is given intravenously, it gets absorbed into the body quickly, while intramuscular administration is usually used for less urgent situations.
Frequency and Timing
Dosing schedules are typically determined based on the intensity and duration of symptoms. In some situations, it is recommended to administer the injection at equal time intervals to ensure a steady and adequate level of the medication.
Administration to Specific Populations
Administering dicyclomine injection requires careful consideration, especially for specific population groups. Different demographic categories have physiological differences, so a cautious and calibrated approach is necessary.
Administration to Elderly Patients
Treating patients who often have multiple health conditions and take multiple medications can be challenging when administering dicyclomine. The aging process affects how the body processes drugs. There is also a higher risk of experiencing harmful effects from anticholinergic substances.
Here are some essential things to consider:
- Adjusting the dosage to minimize side effects
- Closely monitoring for signs of anticholinergic delirium
- Reviewing all other medications being taken to prevent possible interactions
Being highly vigilant in pharmacovigilance when treating this specific age group.

Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
When giving dicyclomine injections to women and nursing mothers, we face the dilemma of weighing the risks against the benefits. This drug can pass through the barrier and enter breast milk, so we must be cautious.
Some factors to consider are;
- We have limited data on how this drug affects the fetus.
- There is a possibility of anticholinergic syndromes.
- There are valid medical reasons that may justify its use.
Overall, it is generally recommended to use this medication in a closely monitored manner under strict medical supervision.

Administration to Children
The medical needs of children, who are still growing and developing, require attention. It is generally advised to avoid using dicyclomine injections in infants due to an increased risk of respiratory complications.
When it comes to children, the following guidelines should be followed:
- Adjusting the dosage according to their age
- Closely monitoring for any adverse reactions
- Preferably administering oral forms of medication whenever possible.

Side Effects
Overview of Common Side Effects
The everyday practical use of dicyclomine injection is somewhat limited by the range of side effects4 it may cause. These unwanted effects can vary from bothersome to requiring immediate medical attention.

Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Although dicyclomine injection is primarily used to treat disorders, it can unexpectedly cause specific side effects related to the digestive system. These side effects may include:
- Experiencing nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Abdominal bloating
Neurological Side Effects
The neurological aspect is also affected by the side effects caused by dicyclomine. Patients might encounter issues such as:
- Headaches
- Confusion or delirium (especially in older patients)
- Difficulty sleeping
Common Side Effects
Some adverse reactions have become well known in the setting due to their higher occurrence rate and impact on patient comfort.
Dry Mouth
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a side effect of the anticholinergic effects of dicyclomine, leading to a decrease in saliva production.

Blurred Vision
The injection of Dicyclomine may impact the eye accommodation reflex, causing vision to become blurry. This is particularly important for individuals who need vision for tasks like driving or operating machines.

Dizziness
This feeling, commonly referred to as headedness or dizziness, is another side effect of anticholinergic medication. It is recommended that patients avoid engaging in activities that demand thinking or physical coordination until they get used to the drug.
Interaction with Other Medications
The complex world of pharmacotherapy is filled with challenges, and one of the significant ones is the occurrence of drug-drug interactions. Despite its effectiveness as a treatment, Dicyclomine injection is not exempt from this phenomenon.
Potential for Drug-Drug Interactions
It is essential to examine the simultaneous use of dicyclomine with other medications to avoid any negative interactions. These interactions can lead to reduced effectiveness of the treatment or increased toxicity.
Some common examples of medications that can cause these interactions are:
- Drugs with anticholinergic properties
- Medicines that have a soothing effect on the central nervous system
- Drugs that affect the activity of liver enzymes
Dicyclomine and Antacids
The simultaneous use of antacids and dicyclomine deserves attention. Antacids can disrupt how dicyclomine is absorbed, reducing its effectiveness as a treatment. It is recommended to:
- Take antacids and dicyclomine at different times
- Regularly check if the treatment is working as expected
- Adjust dosages based on how you respond to the treatment.
Dicyclomine and Antidepressants
The interaction between dicyclomine and certain antidepressants, tricyclics, can lead to an increase in anticholinergic effects. Doctors need to be aware of symptoms such as:
- Difficulty urinating
- Blurry vision
- Faster heart rate
In some cases, adjustments to medications or even discontinuation may be required.
Warnings and Contraindications
Conditions where Dicyclomine Should be Avoided
Although dicyclomine has a therapeutic range, there are certain situations where it should not be used. These include:
- Ulcerative colitis
- Myasthenia gravis
- Glaucoma
In some instances, it is advisable to consider alternative treatment options.
Risk Factors for Severe Side Effects
Specific patient populations and medical situations have a likelihood of experiencing severe side effects. These include:
- Individuals People with kidney or liver problems
- Those who are taking multiple anticholinergic medications at the same time
In such cases, it is crucial to prioritize careful monitoring and attention above everything else.

Important Precautions
Monitoring Requirements
Monitoring patients is essential for reducing risks. Consistent clinical and laboratory assessments can provide information about the treatment's effectiveness and safety.
Pre-administration Screening
Gathering a patient history and conducting a detailed physical examination before starting dicyclomine treatment is crucial. Considering the patient's medications and existing health conditions can help prevent adverse effects.
Careful Administration
Recommended Monitoring During Use
After starting dicyclomine treatment, it is essential to evaluate its effectiveness. This involves monitoring factors such as:
- Blood pressure
- Heart rate
- Conducting tests to assess liver and kidney function
Signs that Indicate Dosage Adjustment
When the treatment outcomes are not as good as expected or severe side effects occur, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage. Some signs that might indicate:
- This need is relief from symptoms
- The emergence of side effects that are difficult to manage
- The development of new medical conditions.
Storage and Handling
Following guidelines for storing and handling dicyclomine injections is crucial to maintaining their effectiveness and safety. Failing to do so can significantly impact the medication's therapeutic benefits and overall safety.
Optimal Storage Conditions
It is crucial to store dicyclomine injection to maintain its pharmacological properties. Here are some guidelines for storage:
- Temperature: Keep the solution within the range of 20 25°C (68 77°F)
- Light: Avoid exposing the medication to direct sunlight or other sources of radiation
- Humidity: Store the medicine in an area with humidity to prevent degradation caused by moisture
Failure to adhere to these storage conditions may lead to changes in the molecular composition of the drug.
Shelf-life and Expiry
Similar to medications, dicyclomine injection has a limited period of effectiveness. After this period, the drug should not be utilized. The expiry date is usually indicated on the packaging. It is crucial to strictly adhere to this requirement to ensure the safety and well-being of patients.
Handling Precautions
Safe Disposal of Unused Medication
To ensure that unused or expired medication doesn't harm the environment or accidentally harm people, it's important to follow procedures for proper disposal. It is strongly advised to adhere to the guidelines provided by the FDA for medication disposal. These guidelines typically include sealing the medication in a container that can't be easily punctured and using authorized programs explicitly designed for drug takeback.
Contamination Prevention
It is crucial to follow strict aseptic techniques to prevent contamination during the administration process. Some important points to keep in mind are:
- Always use a needle and syringe for each administration
- Cleanse the rubber stopper using a swab soaked in 70% isopropyl alcohol.
Overdose Management
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
The threat of overdose is an avoidable risk that hangs over us. As a healthcare provider, it is crucial to stay alert for signs such as:
- Vision
- Extreme drowsiness or unconsciousness
- Difficulty breathing

Immediate Actions and Antidotes
When there is a risk of overdose, it is essential to act quickly and seek medical help, which may involve hospitalization. Immediate actions that can be taken include providing support using activated charcoal and administering physostigmine as an antidote for anticholinergic toxicity.
Conclusion
Ensuring storage, handling, and overdose management of dicyclomine injection is extremely important. Following the recommended storage guidelines is crucial to maintain the medication's effectiveness. It is also essential to handle the injection to minimize potential contamination or misuse risks.
To ensure effective use, closely monitoring signs of overdose and strictly following all handling precautions is essential. By taking this approach, we can ensure that the medication remains effective and prioritize patient safety.