Rifabutin
I. Introduction
A. Overview of Rifabutin
Rifabutin is an antibiotic that falls under the ansamycin class. It is well known for its effectiveness in treating infections caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC).
This pharmaceutical compound has been specifically designed to combat these types of infections and plays a role in modern medicine.
What sets Rifabutin apart from compounds, like rifampicin is its distinct molecular structure, which includes a unique spiropiperidyl component.
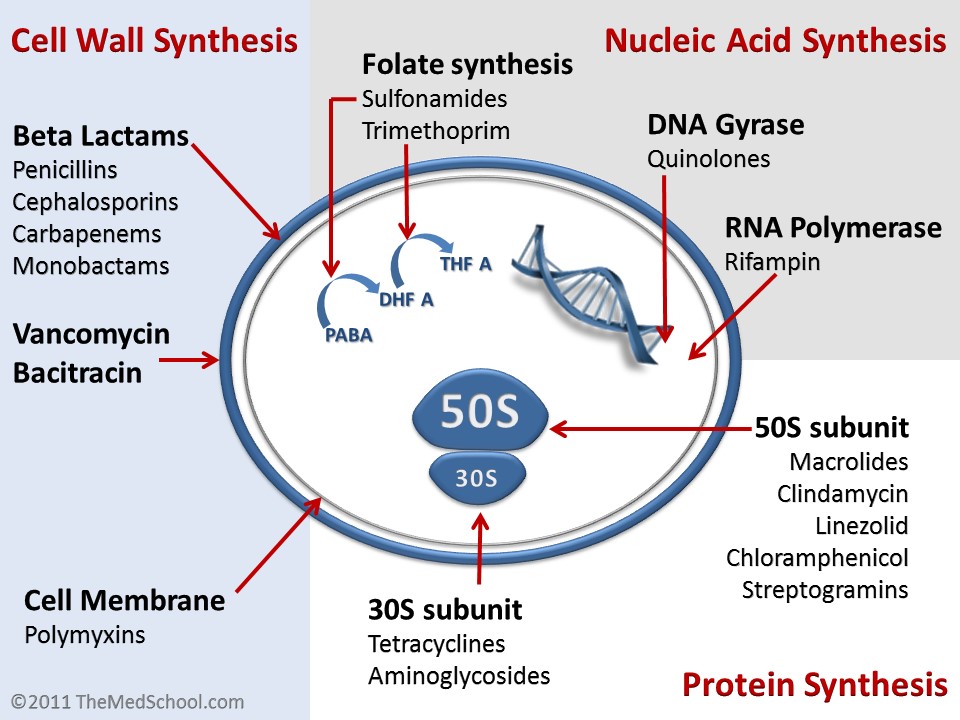
Antibiotic Mechanisms of Action
B. Importance in the Medical Field
Rifabutin has gained recognition in the field of medicine due to its diverse role in treating challenging infections. It has made a contribution to healthcare for various reasons;
1. Effective Treatment; Rifabutin's strong activity against infections has brought about a revolutionary change in managing diseases like tuberculosis.
2. Versatile Pharmacology; Apart from tuberculosis, this medication is also used for non-tuberculous mycobacterial conditions making it a versatile option for therapy.
3. Combination Therapy; The compatibility of Rifabutin with antimicrobial agents ensures a synergistic effect leading to better outcomes for patients.
These characteristics highlight the role of this compound in clinical practice and global health initiatives.
C. Historical Development
The story behind the discovery of Rifabutin is truly fascinating, showcasing the blend of advancement and medical necessity.
Developed by Adria Laboratories in the 1980s, this compound underwent meticulous refinement over the years. In 1992 it received FDA approval for treating tuberculosis and later for MAC infections.
The timeline of Rifabutin development highlights aspects such as pharmaceutical ingenuity in creating a unique compound through cutting-edge chemistry, a clinical focus on addressing persistent and emerging mycobacterial challenges, and collaborative efforts among researchers, regulators, and clinicians to ensure safety and efficacy standards are met.
Rifabutin's legacy as a pharmacological innovation continues to inspire as a model for drug development from conception to clinical implementation.
II. Uses of Rifabutin
A. Treatment of Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) a disease, continues to pose a significant global health challenge(1). However, the introduction of Rifabutin has brought about an era in managing this condition. Rifabutin is primarily used as part of a combination treatment. Offers several benefits;
1. Antimycobacterial Potency; It effectively targets the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium by inhibiting its RNA synthesis process.(2)
2. Resistance Management; By virtue of its mechanism of action Rifabutin helps minimize the development of drug-resistant strains.(3)
3. Compatibility with Antiretroviral Therapy; This is particularly important for patients who're co-infected with HIV and TB, as Rifabutin has minimal interactions with many antiretroviral drugs.(4)
The versatility of Rifabutin, along with its pharmacodynamic profile, makes it an essential component in the therapeutic landscape of TB management.
1. PubMed Central - Experience with Rifabutin Replacing Rifampin in the Treatment of Tuberculosis
2. PubMed - Rifabutin. A review of its antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy
3. Science Direct - The efficacy of rifabutin for rifabutin-susceptible, multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
4. Research Gate - Protease inhibitor-containing antiretroviral treatment and tuberculosis: can rifabutin fill the breach?
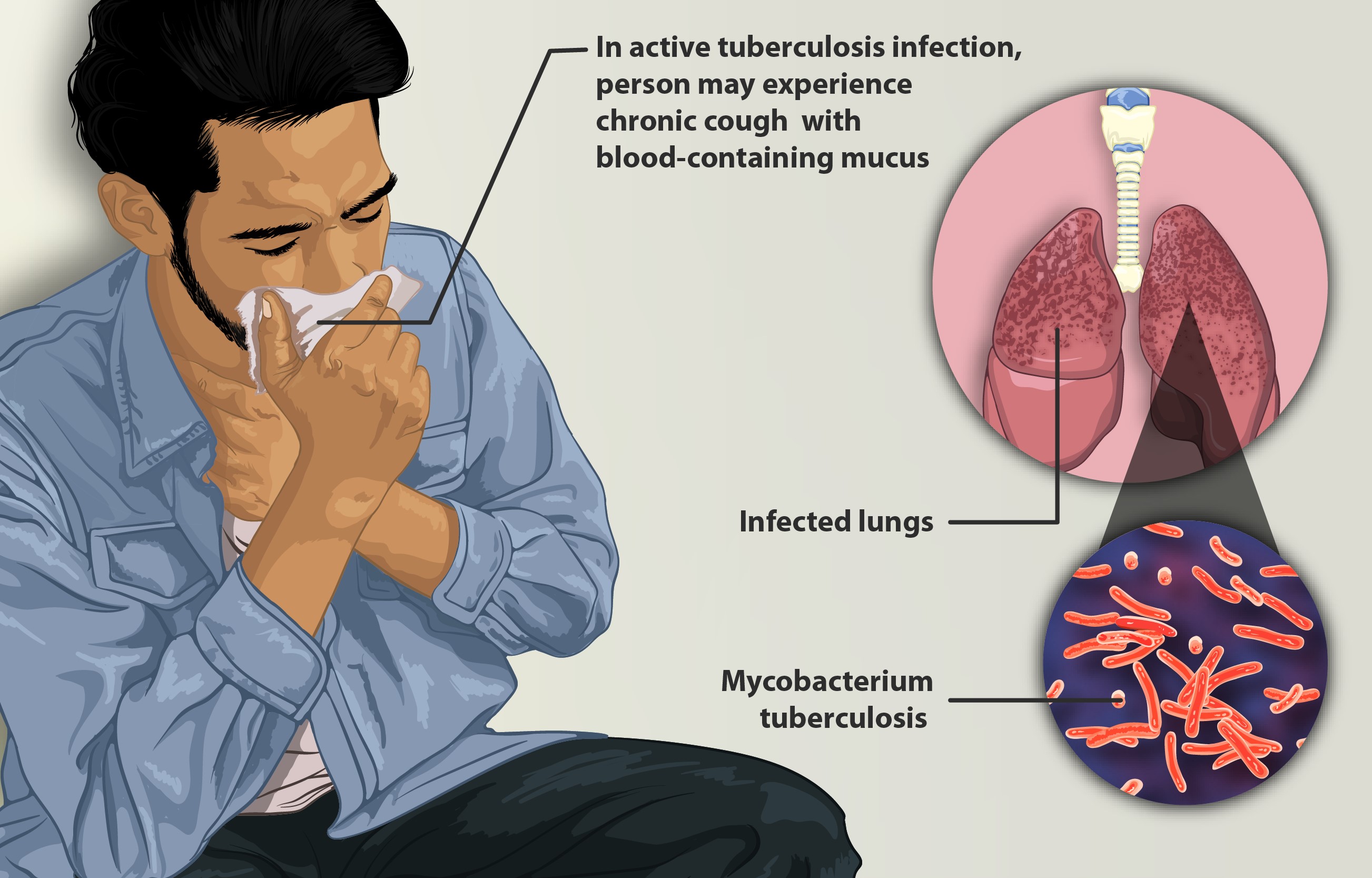
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
B. Prophylaxis Against Mycobacterium Avium Complex
Rifabutin has proven to be crucial in preventing Mycobacterium Avium Complex (MAC) infections, which pose a threat to individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Its broad spectrum activity helps suppress mycobacterial species, including MAC making it an effective choice for prophylaxis.
- Studies have shown that Rifabutin successfully reduces the occurrence of MAC in high-risk populations, such as AIDS patients.
- Additionally, it offers a safety profile providing a manageable option for prevention.
This highlights the nature of Rifabutin in both treating and preventing different types of mycobacterial diseases.
C. Other Approved Indications
Rifabutin goes beyond its uses and has a wide range of other approved applications showcasing its versatility as a medication. Some common but still important uses include;
1. Helicobacter Pylori Eradication; It is used in combination with drugs to effectively eliminate this bacterium.
2. Alternative Treatment for Resistant Strains; When traditional antimycobacterial drugs don't work, Rifabutin can be used as a second-line treatment option.
These additional indications highlight the ways in which Rifabutin can be utilized, solidifying its position as an invaluable agent in modern pharmacology. Its broad therapeutic potential emphasizes the need for research and adaptation in the field of pharmaceutical sciences.
III. Off-label Use
A. Usage in Non-tuberculous Mycobacterial Infections
Rifabutin has shown potential in treating nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) infections, even though it is not officially approved for this use. Clinical experience has shed light on rifabutin effectiveness in this area;
1. Tailored Therapy; Doctors have been able to adapt treatment plans for NTM infections, and initial results show promise in combating strains.
2. Combination Approach; When used alongside antimycobacterial agents, Rifabutin has demonstrated synergistic effects, particularly in cases that are resistant to conventional treatment methods.
3. Clinical Support; Several case studies and small clinical trials provide evidence supporting the use of Rifabutin.
These insights highlight the versatility of Rifabutin as a solution for the complex challenges presented by NTM infections.
B. Experimental Uses in Various Conditions
Rifabutin has also been studied in other conditions showing promising potential for future therapeutic applications. One exciting aspect of this research is the exploration of combinations, where Rifabutin collaborates with new agents to target specific resistant strains.
Additionally, there is an investigation into the antimicrobial role of Rifabutin against viruses, fungi, and parasites. This includes research and development efforts in early-phase clinical trials. The experimental versatility of Rifabutin demonstrates the pursuit of medical progress and hints at its future therapeutic possibilities.
C. Legal and Ethical Considerations
The use of Rifabutin for purposes not approved by authorities requires strict adherence to both legal and ethical guidelines. It involves ensuring that patients are well informed and consent to off-label use after receiving education about it.
Additionally, compliance with international medical and legal standards when using Rifabutin off-label is crucial. A thorough assessment of the risks and benefits based on the best available evidence is also necessary. By following these ethical and legal requirements, we can ensure that the off-label applications of Rifabutin align with responsible medical practices.
IV. How Rifabutin Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Rifabutin works in a powerful way. It mainly focuses on two things;
1. Slowing down the synthesis of RNA; By attaching to the RNA polymerase enzyme in bacteria, it hinders the process of transcription.
2. Stopping the growth of mycobacteria; It prevents the spread of types of mycobacterial species, including those responsible for tuberculosis (TB) and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC).
This specific mechanism is what makes Rifabutins therapeutic benefits stand out.
B. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
To truly grasp how Rifabutin behaves within the body, we must delve into its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Let's explore its journey step by step;
1. Absorption; When taken orally, Rifabutin is well absorbed into the bloodstream, demonstrating bioavailability.
2. Distribution; It spreads widely throughout tissues achieving therapeutic concentrations in specific organs targeted for treatment.
3. Metabolism and Excretion; The liver extensively metabolizes Rifabutin before it is eliminated from the body through both kidneys and fecal (intestinal) excretion.
By understanding this interplay of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, we can gain insights into the effectiveness and safety profile of Rifabutin as a therapeutic agent.
V. Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
When it comes to giving Rifabutin, it's important to follow the dosage guidelines that are specific to the type of infection and the patient's condition.
The dosage may need to be adjusted based on the medications being taken, as well as any issues with kidney or liver function.
These guidelines are designed to ensure the possible treatment results while keeping side effects to a minimum.
B. Special Populations
1. Administration to Elderly
Elderly patients need attention when taking Rifabutin. It's important to monitor any changes in how the body processes the medication, the likelihood of experiencing side effects, and potential interactions with other drugs. In some cases, personalized dosage plans might be needed to adapt to the changes that come with aging.
2. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
When prescribing Rifabutin to women or nursing mothers, it is important to strike a careful balance between the need for treatment and the potential risks involved.
It is advisable to consult with specialized healthcare professionals to closely monitor the situation and explore alternative treatment options to provide personalized care.
3. Administration to Children
When it comes to giving Rifabutin to children, there are some things to keep in mind. It's crucial to use the dose for their age, regularly monitor them, and take into account their unique physical characteristics.
The key is to tailor the treatment for each child based on established guidelines and clinical expertise.
VI. Composition
A. Active Ingredients
The main essence of Rifabutin's effect lies in its active component. The key compound, Rifabutin itself, plays a role in producing its therapeutic benefits. It works by inhibiting DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which leads to its effectiveness against different types of mycobacterial species. This unique molecular structure is what gives Rifabutin its strength and targeted action.
B. Inactive Ingredients
Rifabutin formulation includes chosen inactive ingredients that play a crucial role in its pharmacological delivery.
These ingredients include excipients like lactose or magnesium stearate, ensuring the dosage form. Stabilizers are also included to maintain stability, and coloring agents and coatings are added to enhance the visual appeal and encourage patient compliance.
These inactive ingredients are essential for maintaining Rifabutin's presentation quality, stability, and patient acceptability.
C. Available Formulations
Rifabutin is usually found in forms that are designed to be convenient and effective for patients.
These include capsules, which are a common oral form that contain varying amounts of the active ingredient.
There are also special formulations available that cater to specific patient groups or unique treatment needs.
The range of options for Rifabutin therapy shows how it can be tailored to meet the requirements of patients and healthcare professionals.
VII. Side Effects
A. Common Side Effects
As with any medication, Rifabutin can cause side effects that require close monitoring. Some of these include problems like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
There may also be changes in the skin, such as rashes or discoloration. It's important to check liver enzymes through laboratory tests as they can be affected by the medication.
While these side effects are typically temporary and can be managed, patients should be informed about them, and healthcare providers should remain vigilant in their observations.

B. Serious Side Effects
Rifabutin treatment options come with some risks that need to be taken seriously. These risks include abnormalities like neutropenia or anemia, ocular disorders such as uveitis, and the possibility of severe liver problems, in individuals who are predisposed. Monitoring these side effects and taking immediate action when necessary is crucial.
C. Managing Side Effects
It is important to manage side effects when undergoing Rifabutin therapy. This involves monitoring to identify and address any potential side effects early on.
Patients should be educated about these side effects so they can recognize and report them promptly.
Therapeutic adjustments, such, as modifying the dosage or providing care may also be necessary.
By adopting this approach we can achieve a therapeutic balance that maximizes the benefits of treatment while minimizing associated risks.
VIII. Interactions
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
The way Rifabutin interacts with medications is a crucial consideration in its clinical use. When taken alongside antiretrovirals, there is a possibility of changes in blood levels that may require dosage adjustments.
Additionally, Rifabutin can impact the metabolism of administered drugs, such as oral contraceptives. It is important to have an understanding of these interactions and manage them carefully to maintain the effectiveness of Rifabutin in treatment.
B. Food Interactions
The way you eat and drink can also affect how Rifabutin works in your body. It's important to keep an eye on what you eat and drink while taking Rifabutin to ensure it is properly absorbed and processed.
C. Impact on Laboratory Tests
Rifabutin can have an impact on laboratory tests, which might result in changes. These changes could involve the liver enzymes indicating how well the liver is functioning. There may also be some alterations in the counts of white blood cells. It's important to interpret these laboratory findings when someone is undergoing Rifabutin therapy. This emphasizes the need for an approach to managing Rifabutin treatment taking into account various factors and potential interactions.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
A. Specific Warnings
It is important to approach the administration of Rifabutin with caution and pay attention to warnings. These warnings include,. Are not limited to;
1. Hepatic Impairment; Individuals with liver dysfunction need monitoring, during Rifabutin therapy.
2. Ocular Effects; Regular eye examinations are necessary to detect uveitis at a stage.
3. Reactions; There is a possibility of experiencing hypersensitivity or autoimmune manifestations.
These warnings highlight the importance of evaluation and vigilance when undergoing Rifabutin therapy.
B. Contraindications
Rifabutin may not be suitable in situations due to various contraindications.
- One of these is if someone has a known allergy or hypersensitivity to Rifabutin or any of its components.
- Additionally, caution should be exercised when taking Rifabutin alongside medications that have strong interactions.
Being aware of these contraindications is important in order to prevent any effects.
C. Important Precautions
When administering Rifabutin it is important to follow precautions. These include monitoring hepatic function for any signs of impairment ensuring compatibility with other medications and carefully considering the risks and benefits, during pregnancy and lactation. These precautions help ensure that therapy is optimized while minimizing any negative effects.
X. Careful Administration
A. Monitoring Requirements
The monitoring protocol for Rifabutin involves conducting a series of assessments to ensure safety and optimize treatment outcomes. These assessments include;
1. Liver Function Tests; These tests are conducted to detect any liver damage or toxicity that may arise as a result of using Rifabutin.
2. Complete Blood Counts; This evaluation helps assess the health of the patient's blood, including red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin levels, and platelet counts.
3. Ophthalmological Assessments; Regular eye examinations are performed to monitor for any complications that may occur due to Rifabutin usage.
By implementing this monitoring approach, healthcare providers can promptly identify any issues or side effects and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan if needed.
B. Patient Education and Compliance
In order for patients to effectively follow their Rifabutin therapy it is important to provide them with an education that covers the areas;
1. Administration; Clear instructions on how to take the medication
2. Managing Side Effects; Teaching patients how to recognize and report any effects they may experience.
3. Regular Monitoring; Emphasizing the importance of adhering to scheduled laboratory tests and follow-up appointments
. By providing patients with support, we can greatly improve their compliance and increase the likelihood of successful therapy outcomes.
C. Special Handling Precautions
It is important to exercise caution when handling Rifabutin ensuring that it is dispensed properly stored correctly and protected from contamination. This involves following pharmacy practices and adhering to sterile procedures when necessary.
XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Recommended Storage Conditions
Rifabutin should be stored in conditions to maintain its effectiveness;
Temperature; It is best to keep it at room temperature from excessive heat and moisture.
Light Exposure; Store it in a dark place to prevent any degradation.
Container; Make sure to store it in its original container to preserve its integrity.
Following these storage guidelines will help ensure that Rifabutin remains therapeutically effective.
B. Handling Precautions
When it comes to dealing with Rifabutin it's important to follow the guidelines, for handling pharmaceuticals. This includes using containment measures and avoiding direct contact whenever necessary.
C. Disposal Guidelines
It is important to follow the guidelines and take environmental factors into account when disposing of Rifabutin. This ensures that proper methods are used to prevent any exposure or contamination.
XII. Overdosage
A. Symptoms of Overdose
If someone takes much Rifabutin they may experience problems with their stomach changes in vision or issues, with their blood. It is important to recognize these symptoms in order to properly handle the situation.
B. Management and Treatment Protocols
When someone overdoses on Rifabutin, the first step is to assess the severity of their symptoms. After that, it's important to provide measures like hydration or treatment for specific symptoms. The person should be closely monitored for any delayed effects well. This approach focuses on ensuring the safety and recovery of the patient.
C. Prevention Measures
To prevent overdose it is important to ensure that patients receive education, regular monitoring and adhere to the prescribed dosage regimens. Healthcare providers have a role to play in being proactive, in this regard.
XIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
This article explores the aspects of Rifabutin, including its composition and how to manage overdose situations highlighting the intricate nature of its clinical application.
B. Future Research and Development
Continuous dedication to research and development plays a vital role in discovering new applications for Rifabutin improving its formulations and enhancing its therapeutic effectiveness.
C. Clinical Significance and Contributions to Medicine
Rifabutin has had an impact on the treatment of mycobacterial infections, and its complex pharmacological profile confirms its crucial role in modern medicine. Its careful use, based on expertise and focusing on patient well-being, will continue to make a substantial contribution to global health.