Introduction to Prednefrin Forte Eye Drop
Overview of Prednefrin Forte and its Therapeutic Class
Prednefrin Forte Eye Drop is a specialized ophthalmic formulation designed to treat inflammatory and allergic conditions of the eye. It belongs to a dual-action therapeutic class, combining the anti-inflammatory properties of corticosteroids with the vasoconstrictive effects of sympathomimetics. This potent blend targets both the source of inflammation and the symptomatic redness often associated with ocular surface disorders.
Manufacturer and Regulatory Status
Prednefrin Forte is manufactured by a reputable pharmaceutical company and is approved for ophthalmic use in multiple regulatory jurisdictions. It is dispensed under prescription-only guidelines in most regions, ensuring professional supervision during its use.
Indications as a Combination Anti-inflammatory and Vasoconstrictor Agent
This product is primarily indicated for the short-term treatment of steroid-responsive eye conditions that involve inflammation and vascular congestion. It effectively alleviates symptoms such as swelling, redness, and irritation by targeting the underlying immunologic and vascular responses.
Composition and Active Ingredients
Detailed Breakdown of Active Ingredients: Prednisolone Acetate and Phenylephrine Hydrochloride
Each milliliter of Prednefrin Forte contains:
- Prednisolone acetate 10 mg – a synthetic corticosteroid
- Phenylephrine hydrochloride 1.2 mg – an alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist
Role of Each Component in Ocular Therapy
Prednisolone acetate acts by inhibiting multiple inflammatory pathways, decreasing leukocyte migration, and suppressing capillary dilation. Phenylephrine, on the other hand, reduces hyperemia by constricting dilated conjunctival blood vessels, thereby minimizing redness and discomfort.
Inactive Ingredients and Formulation Type (Ophthalmic Suspension)
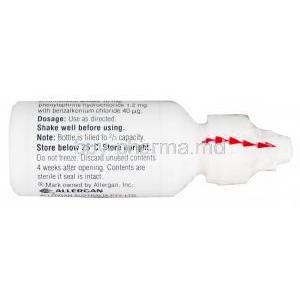
The formulation includes stabilizers, isotonic agents, and suspending agents such as benzalkonium chloride (preservative), sodium chloride, and polysorbates. It is provided as an ophthalmic suspension, requiring thorough shaking before each application to ensure even distribution of the active substances.
How Prednefrin Forte Eye Drop Works
Mechanism of Action of Prednisolone as a Corticosteroid
Prednisolone exerts its effect by modulating gene expression and inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. This leads to a marked reduction in conjunctival swelling and pain.
Mechanism of Action of Phenylephrine as a Sympathomimetic Agent
Phenylephrine stimulates alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the vascular smooth muscle, inducing vasoconstriction. This results in rapid decongestion of blood vessels, visibly reducing redness and promoting ocular comfort.
Combined Therapeutic Effect on Ocular Inflammation and Redness
Together, the agents work synergistically: one controlling the immune-mediated inflammation and the other providing immediate symptomatic relief by constricting dilated vessels. This dual action makes Prednefrin Forte particularly effective in acute and subacute ocular conditions.
Approved Medical Uses of Prednefrin Forte Eye Drop
Treatment of Steroid-responsive Inflammatory Conditions of the Eye
Indicated for use in conditions such as conjunctivitis, episcleritis, and keratitis where corticosteroid response is favorable. These conditions typically involve immune cell infiltration and tissue inflammation.
Management of Ocular Allergy with Vascular Congestion
Prednefrin Forte is used to manage seasonal or perennial allergic conjunctivitis where inflammation is accompanied by visible vascular dilation and eye redness.
Use in Post-operative Ocular Inflammation
Following ocular surgery, such as cataract removal, Prednefrin Forte may be prescribed to reduce post-operative inflammation and prevent complications like posterior capsule opacification.
Use in Anterior Uveitis and Iritis
These conditions involve inflammation of the anterior chamber of the eye and are commonly treated with topical corticosteroids. Prednefrin Forte provides targeted relief while improving vascular tone within the affected eye tissues.
Off-label and Investigational Uses
Use in Photophobia-related Ocular Discomfort
Though not officially approved, some practitioners use Prednefrin Forte for managing photophobia when it is secondary to ocular inflammation.
Application in Contact Lens-related Inflammatory Episodes (Under Supervision)
In certain contact lens users who develop sterile infiltrates or inflammatory episodes, this eye drop may be cautiously used to control symptoms.
Experimental Use in Certain Cases of Episcleritis
Prednefrin Forte has shown anecdotal benefits in episcleritis, particularly when standard vasoconstrictors fail to provide adequate symptom control.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Adult Dosing Regimen and Frequency
Typically, one to two drops are instilled into the affected eye(s) up to four times daily. In more severe cases, dosing may be increased initially under medical supervision and then tapered based on response.
Technique for Proper Instillation of Eye Drops
- Wash hands thoroughly before use
- Shake the bottle well
- Tilt the head back and pull down the lower eyelid
- Instill one drop into the conjunctival sac without touching the dropper tip to any surface
- Close the eye gently and press on the inner corner to reduce systemic absorption
Duration of Therapy and Tapering Considerations
The treatment duration depends on the underlying condition but typically ranges from several days to two weeks. Gradual tapering is essential to prevent rebound inflammation.
Missed Dose Management
If a dose is missed, it should be applied as soon as remembered. If it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed one—do not double the dose to compensate.
Avoiding Contamination of the Dropper Tip
To prevent microbial contamination, patients should avoid touching the dropper tip to the eye, eyelid, or any other surface. The bottle should be tightly closed immediately after each use.
Side Effects of Prednefrin Forte Eye Drop
Overview of Adverse Reactions
While Prednefrin Forte Eye Drop is generally well-tolerated when used under medical guidance, it may cause side effects ranging from mild ocular discomfort to more serious complications with prolonged use. These effects can be localized to the eye or systemic due to corticosteroid absorption.
Ocular Side Effects: Stinging, Burning, Blurred Vision
Some patients may experience:
- A transient stinging or burning sensation immediately after instillation
- Temporary blurred vision due to the suspension formulation
- Watery or irritated eyes during the initial phase of treatment
These effects are usually short-lived and diminish with continued use.
Systemic Side Effects Due to Corticosteroid Absorption
Though rare, systemic absorption of corticosteroids through ocular tissues may lead to:
- Elevated blood pressure
- Suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
- Headaches, dizziness, or mood changes
This is more likely with prolonged use, higher doses, or use in children.
Long-term Use Complications
Extended application may result in:
- Increased intraocular pressure (IOP)
- Development of posterior subcapsular cataracts
- Delayed corneal healing
Regular monitoring is essential to prevent these outcomes.
Common and Mild Side Effects
Mild Discomfort Upon Instillation
Mild discomfort, such as a cooling or tingling sensation, may be felt for a few seconds post-application. This typically does not require cessation of therapy.
Temporary Redness or Dryness of the Eye
Patients may report slight conjunctival redness or a sensation of dryness, especially with multiple daily applications.
Increased Sensitivity to Light
Photophobia or light sensitivity can occur due to temporary pupil dilation from phenylephrine.
Temporary Increase in Intraocular Pressure
Short-term spikes in intraocular pressure are possible, especially in susceptible individuals such as glaucoma patients or steroid responders.
Drug Interactions and Incompatibilities
Interaction with Intraocular Pressure-lowering Agents
Concurrent use with glaucoma medications may reduce their efficacy or require dose adjustment. Monitoring IOP is advisable.
Caution with Other Topical Corticosteroids or Vasoconstrictors
Combining Prednefrin Forte with similar agents can amplify side effects like hypertension or ocular surface toxicity.
Risk with Systemic Medications That Affect Blood Pressure or Heart Rate
Phenylephrine may potentiate the hypertensive effects of MAO inhibitors or beta-blockers. Use with caution in patients on cardiovascular medications.
Concurrent Use with Contact Lenses
Soft contact lenses should not be worn during treatment. The preservative benzalkonium chloride can bind to lenses and irritate the eye.
Warnings and Black Box Considerations
Risk of Masking Ocular Infections
Prednisolone may suppress immune responses, delaying the diagnosis and treatment of bacterial, viral, or fungal eye infections.
Prolonged Use and Potential for Glaucoma or Cataract Formation
Extended corticosteroid use is linked to serious ocular side effects, necessitating frequent intraocular pressure checks and slit-lamp evaluations.
Avoidance in Viral Infections of the Cornea and Conjunctiva
Use is contraindicated in herpes simplex keratitis or varicella due to risk of exacerbation and corneal thinning.
Risk of Secondary Infection Due to Immunosuppression
Prolonged suppression of local immune defense can increase the risk of opportunistic infections.
Contraindications for Prednefrin Forte Eye Drop
Known Hypersensitivity to Corticosteroids or Phenylephrine
Patients with a history of allergic reactions to any component of the formulation must avoid use.
Presence of Untreated Purulent Ocular Infections
Prednefrin Forte should not be used in bacterial conjunctivitis or keratitis unless combined with an appropriate antimicrobial.
Herpes Simplex Keratitis (Dendritic Keratitis)
This viral eye disease can worsen with corticosteroid use, leading to serious corneal damage.
Narrow-angle Glaucoma
Phenylephrine may precipitate angle closure and should be avoided in patients with anatomically narrow anterior chamber angles.
Careful Administration and Monitoring Requirements
Monitoring Intraocular Pressure During Extended Use
Regular tonometry is essential to detect pressure elevations early, especially in long-term therapy.
Use Under Ophthalmologist Supervision Only
Due to its potent pharmacological profile, Prednefrin Forte should be used only with specialized medical oversight.
Baseline and Follow-up Visual Acuity Assessments
Vision testing should be performed before, during, and after treatment to detect complications like cataract formation or visual field changes.
Important Precautions During Use
Avoiding Abrupt Discontinuation After Prolonged Use
Gradual tapering of the dose is recommended to avoid rebound inflammation or adrenal suppression.
Preventing Contamination of Eye Drops
Patients should avoid touching the dropper tip to any surface, including the eye, to prevent microbial contamination.
Not Sharing the Eye Drop with Others
Prednefrin Forte is prescribed for individual use only. Sharing may result in cross-contamination or incorrect usage.
Awareness of Visual Changes or Worsening Symptoms
Any new or worsening symptoms such as eye pain, vision changes, or persistent redness should be reported immediately to a healthcare provider.
Administration in Special Populations
Use in Elderly Patients
- Greater susceptibility to corticosteroid-induced ocular hypertension
- Age-related thinning of the cornea and sclera increases complication risk
- Regular monitoring for systemic absorption effects is advised
Use in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
- Animal studies indicate potential teratogenic effects; human data is limited
- Should only be used if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk
- Trace amounts may be excreted in breast milk; caution is advised during lactation
Use in Pediatric Patients
- Limited safety data available for children under 12 years
- Risk of systemic corticosteroid absorption is higher in young children
- Dosage should be adjusted based on age, and therapy closely monitored
Overdose and Emergency Management
Signs and Symptoms of Ocular or Systemic Overdose
Overuse may lead to:
- Severe ocular irritation
- Marked increase in intraocular pressure
- Systemic hypertension or tremors (from phenylephrine)
Immediate First-aid Response Steps
- Irrigate the eye with sterile saline or water
- Discontinue the medication immediately
- Seek medical evaluation promptly
When to Seek Emergency Ophthalmic Care
Urgent care is required if the patient experiences:
- Severe eye pain
- Sudden loss of vision
- Signs of allergic reaction such as swelling or difficulty breathing
Storage and Handling Instructions
Recommended Temperature and Light Protection
Store at temperatures below 25°C and protect from direct sunlight and heat sources.
Shake Well Before Use Instruction for Suspension
As an ophthalmic suspension, the bottle must be shaken vigorously before each use to ensure uniform dispersion of the active ingredients.
Shelf Life and Expiration Monitoring
Check the expiration date before use. Discard the bottle 28 days after opening, even if product remains.
Safe Disposal of Unused or Expired Product
Dispose of according to local regulations. Do not flush or pour down drains. Use take-back programs if available.
Handling Precautions and Patient Counseling Points
Instructions on Hand Hygiene Before Application
Patients should wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before applying the drops to minimize the risk of infection.
Avoidance of Eye Drop Contamination
Educate patients on not allowing the dropper tip to touch the eye or any surface during administration.
Advising Patients on Not Using Beyond Prescribed Duration
Prolonged use beyond medical instruction increases the risk of adverse effects and must be strictly avoided.
Counseling on Blurred Vision Post-instillation and Driving Precautions
Warn patients that temporary blurred vision may occur and they should refrain from driving or operating machinery until vision clears.