Temozolomide
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Temozolomide
- III. Off-label Use of Temozolomide
- IV. How Temozolomide Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition of Temozolomide
- VII. Side Effects of Temozolomide
- VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Careful Administration
- X. Important Precautions
- XI. Drug Interactions
- XII. Overdosage
- XIII. Storage of Temozolomide
- XIV. Summary and Conclusion
I. Introduction
Historical Background of Temozolomide
Temozolomide, a type of imidazotetrazine medication, was first created in the early 1980s. It was developed as a convenient and stable option compared to its predecessor, dacarbazine. One of its advantages is its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, making it a practical treatment choice for brain tumors.
Current Status and Relevance in Oncology
Today temozolomide plays a role in treating specific aggressive brain tumors, such as glioblastoma multiforme and anaplastic astrocytoma. Its targeted capability to cause DNA damage in cancer cells makes it an essential tool in neuro-oncology. Ongoing research is expanding its use to tackle challenging forms of cancer.
II. Uses of Temozolomide
Primary Indications
- Glioblastoma Multiforme
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme
Temozolomide is a chemotherapy drug used to treat glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most aggressive type of brain cancer. It is usually given with radiation therapy and then as a maintenance treatment after surgery. This combination of treatments can improve the survival of patients with GBM, who otherwise have a poor prognosis12. However, the survival benefit is still limited and depends on several factors, such as the genetic profile of the tumor and the type of anti-epileptic drugs used345.
References:
Protracted Adjuvant Temozolomide in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 2015.
Treatment of Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Temozolomide is a medication used to treat brain tumors such as anaplastic astrocytoma, a type of aggressive and cancerous brain tumor. It is one of the first-line treatment options because it can pass through the blood-brain barrier and destroy tumor cells, often combined with radiation therapy.
Here are some references:
Temozolomide - Wikipedia Anaplastic astrocytoma - Wikipedia Temozolomide (Oral Route) Side Effects - Mayo Clinic Treatment and prognosis of IDH-mutant astrocytomas in adults
III. Off-label Use of Temozolomide
Metastatic Melanoma
Temozolomide is an oral alkylating agent that can cross the blood-brain barrier and disrupt the DNA replication of melanoma cells. It has shown some activity in treating metastatic melanoma, especially in the brain, but with limited survival benefit and significant toxicity.
Here are some references:
A Phase I/II study of lomustine and temozolomide in patients with cerebral metastases from malignant melanoma Temozolomide for the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma: A Systematic Review
Neuroendocrine Tumors
Temozolomide is a cancer medicine that belongs to the class of alkylating agents. It is used to treat some types of brain tumors, such as glioblastoma multiforme and anaplastic astrocytoma, by slowing or stopping the growth of cancer cells.
Here are some references:
Temozolomide - NCI - National Cancer Institute Temozolomide - Wikipedia
Other Off-label Applications
Temozolomide is a brain-penetrant alkylator used in clinical trials to treat primary and secondary central nervous system (CNS) lymphomas, combined with rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. It has shown some activity and tolerability in this setting, but the optimal dose and schedule are still unclear.
Here are some references:
How I treat CNS lymphomas - American Society of Hematology Immunochemotherapy with Rituximab and Temozolomide for Central Nervous System Lymphomas - Cancer
IV. How Temozolomide Works
Mechanism of Action
Temozolomide is a type of medication that transforms into its form through chemical changes in the body. This active form modifies and alters the DNA structure through alkylation/methylation processes. Such modifications occur at locations within the DNA molecule, ultimately resulting in cell death. It's worth mentioning that temozolomide mainly focuses on targeting the O6 position of guanine, one of the building blocks of DNA consisting of four nucleotide bases.
Impact on Cancer Cells
Temozolomide can modify DNA, which hampers the growth of tumor cells and leads to programmed cell death, known as apoptosis. This interference with the functioning of cells is particularly harmful to cancer cells compared to cells making it a valuable tool in cancer treatment.
Resistance Factors
Resistance to temozolomide can occur due to mechanisms, with the most notable one being the increase in a DNA repair protein known as O6 methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT). This protein has the ability to eliminate alkyl groups caused by temozolomide essentially fixing the DNA damage and enabling cancer cells to survive.
V. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines
The amount of temozolomide given depends on the specific condition being treated. It is usually given in cycles. When treating glioblastoma multiforme, it is common to administer daily during radiotherapy and then have cycles of higher doses.
Administration Route and Timing
Temozolomide comes in the form of capsules that are taken orally. Typically it is recommended to bring them a day and the timing is carefully synchronized with radiation treatments if they are being used together.
Dose Adjustments and Modifications
Sometimes it might be required to change the dosage depending on how a person can tolerate the medication, their liver and kidney function, and if they experience any specific side effects. Doctors keep an eye on blood counts and can adjust the dosage as necessary to minimize any potential harmful effects.
VI. Composition of Temozolomide
Active Ingredients
Temozolomide is the component, which is a derivative of imidazotetrazine.
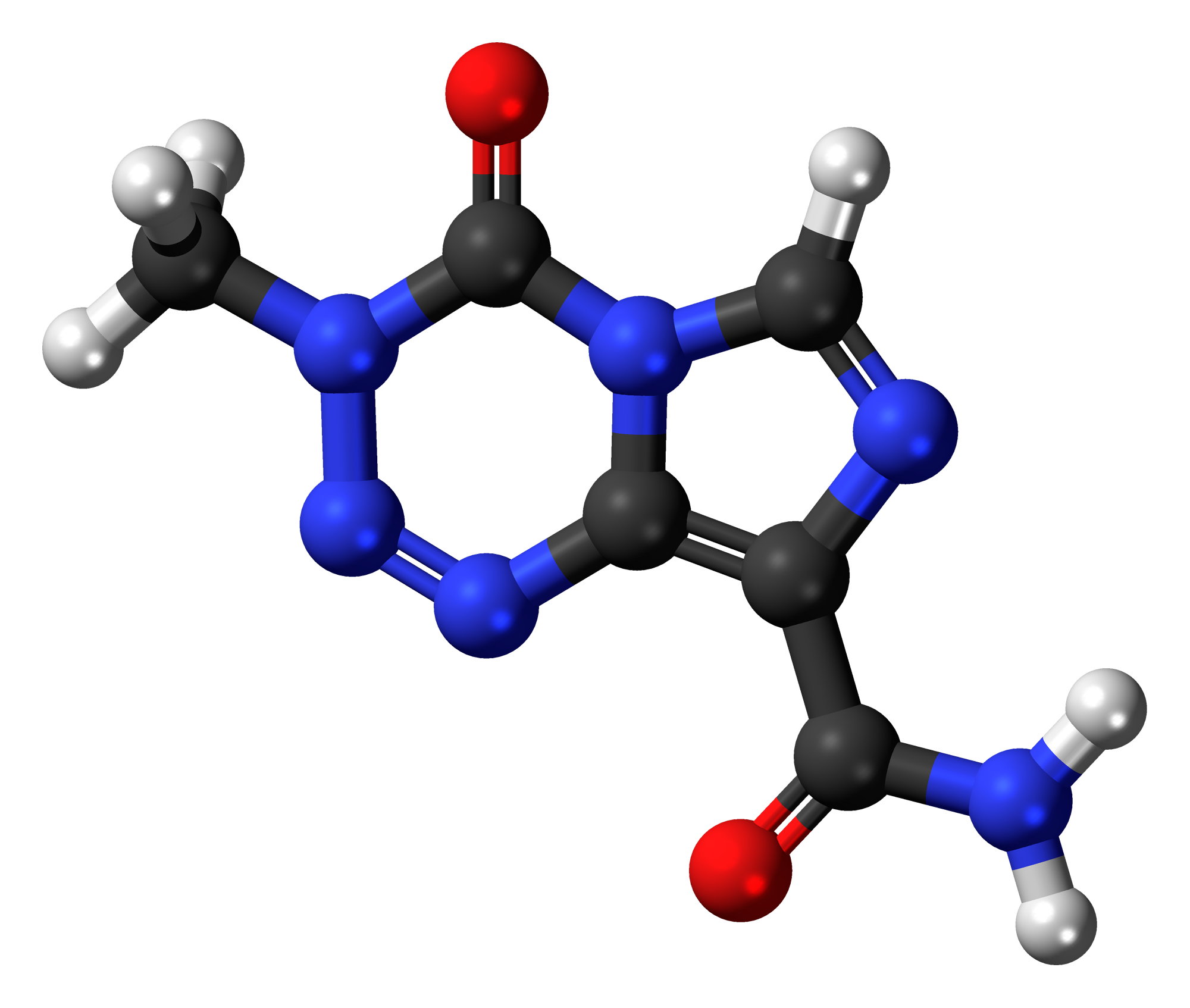
Excipients and Formulations
The capsules of Temozolomide have inactive components depending on the manufacturer. These typically consist of lactose monohydrate, colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate, tartaric acid, and stearic acid.
Available Strengths and Forms
Temozolomide is often found in capsules, which come in strengths (ranging from 5 mg to 250 mg). This allows for dosing plans that can be tailored to meet the unique requirements of each patient.
VII. Side Effects of Temozolomide
Overview of Common Side Effects
Temozolomide, similar to chemotherapy medications, can cause various side effects. Some experienced adverse reactions may include; Feeling nauseous and vomiting, Experiencing fatigue, Dealing with constipation Having headaches Experiencing hair loss Experiencing low blood cell counts (referred to as myelosuppression). It is important to note that everyone's experience with these side effects may vary.
Managing Side Effects: Tips for Patients
Managing the side effects is crucial for patients receiving temozolomide treatment. It is essential to consider some strategies such as using anti-emetics to control feelings of nausea and vomiting, engaging in light physical activities to reduce fatigue, following a high-fiber diet and staying hydrated to manage constipation, and ensuring regular blood monitoring to assess myelosuppression and taking necessary actions promptly.
Serious and Rare Side Effects
Although temozolomide is usually well tolerated, there have been instances where it can cause more severe side effects. These may include pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis jiroveci, a serious lung infection. Additionally, liver toxicity and severe skin reactions, like Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, can sometimes occur.
VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
Known Contraindications
Temozolomide should not be used in patients with a known allergy to the drug or its ingredients. Moreover, individuals with compromised bone marrow function are generally unsuitable for temozolomide treatment.
Black Box Warnings
Temozolomide comes with a black box warning due, to the risk of myelosuppression, a condition that can cause infections, bleeding, or anemia that may be life-threatening.
Pre-existing Condition Considerations
Patients with existing liver conditions, significant kidney problems, or a history of infections might need to be more closely observed and have their dosage adapted accordingly while undergoing temozolomide treatment.
IX. Careful Administration
Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals with age-related decline in organ function may exhibit heightened vulnerability to the effects of chemotherapy drugs, such as temozolomide. It is advisable to exercise caution when determining dosage, regularly monitor their response, and consider starting with an initial dose for this patient population.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Temozolomide falls under Category D in terms of its classification for pregnancy, indicating risks to the fetus. Women and nursing mothers should avoid its use as it may harm the development of the fetus or the well-being of the infant.
Administration to Children
Temozolomide has been proven to be safe and effective for conditions, in children. However, when administering this medication to patients, it is essential to carefully consider the dosage and closely monitor any potential side effects.
Monitoring During Treatment
Patients receiving treatment should undergo regular blood tests to assess their hematologic status. Additionally, it is essential to monitor liver and kidney function during treatment.
X. Important Precautions
Pre-treatment Assessments
To ensure the initiation of temozolomide treatment, it is crucial to conduct a thorough assessment. This assessment should encompass the following elements; A blood count to evaluate overall blood health, Liver function tests to assess liver performance, Renal function assessment to determine kidney functionality, An evaluation of any existing infections that may impact treatment effectiveness.
During Treatment Monitoring
It is crucial to remain vigilant throughout the treatment process. Making appointments for blood tests and evaluations to monitor any potential side effects is essential for ensuring safe administration.
Post-treatment Follow-up
After finishing the temozolomide treatment, it is essential to monitor the patient's disease progression, the recovery of their bone marrow function, and any potential long-term side effects that may appear later.
XI. Drug Interactions
Potential Interaction with Other Medications
Using temozolomide and drugs that suppress the bone marrow can worsen the suppression. For acid, an anticonvulsant, it is possible to interact with temozolomide and affect how it is cleared from the body.
Interaction with Food and Alcohol
For absorption, it is advised to take Temozolomide on an empty stomach. It's essential to be cautious while consuming alcohol as it can worsen the side effects of Temozolomide, especially those related to liver stress.
Managing and Avoiding Interactions
To avoid any complications, it is essential for patients to inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. It is also recommended to monitor blood and organ function to detect any potential drug interactions early. Additionally, patients should consult with their healthcare professional before making any changes to their diet or alcohol intake while using temozolomide.
XII. Overdosage
Recognizing Signs of Overdosage
It is crucial to be able to identify the indications of a dosage of temozolomide for prompt intervention. Patients might experience myelosuppression, which can lead to decreased levels of blood cells. Additionally, they may encounter intensified feelings of nausea and vomiting well as significant abnormalities in liver function. Recognizing these symptoms is vital to seek medical attention and prevent any potential complications from arising.

Immediate Steps and Management
If you suspect an overdose, it's essential to take action; Reach out to a healthcare professional or contact a poison control center immediately. Stop administering temozolomide. Start providing measures like hydration and antiemetics. Keep an eye on blood counts and organ functions.
Long-term Consequences
Long-term exposure to temozolomide can have effects on the body. It may cause issues with bone marrow function, persistent liver problems, and an increased likelihood of developing secondary tumors.
XIII. Storage of Temozolomide
Recommended Storage Conditions
It is crucial to store it properly to ensure its effectiveness. The recommended storage conditions include; 1. Keep it at room temperature between 20 and 25 degrees Celsius (68 and 77 degrees Fahrenheit). 2. Store the medication in its container, designed to be child resistant. 3. Avoid exposing it to moisture and direct sunlight. Following these guidelines will help maintain the efficacy of temozolomide.
Handling Precautions
Since temozolomide is a cytotoxic substance, it is crucial to exercise caution when dealing with it; Make sure to wear gloves when handling the capsules. Avoid any contact with tablets. After taking the medication, thoroughly wash your hands.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Disposing of temozolomide that is no longer needed or has expired is essential to protect the environment and prevent accidental exposure. It is recommended to seek guidance from a pharmacist or a local disposal program to ensure disposal. It is advised not to flush the capsules down toilets or drains.
XIV. Summary and Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
Temozolomide is a part of the treatment for certain types of brain tumors mainly because it can effectively pass through the protective barrier around the brain. Although it is typically well tolerated,, its use has risks, such as severe suppression of bone marrow activity. It's vital to monitor and follow prescribing guidelines to ensure that we can maximize the benefits while minimizing any potential risks.
Current Research and Future Prospects
Temozolomide continues to be a research focus in the ever-changing oncology field. Researchers are currently investigating its potential when used alongside targeted therapies and immunotherapies. The goal is to determine if these combinations can improve effectiveness and broaden the applications of temozolomide to treat cancers.
Patient Resources and Support
Patients who are prescribed temozolomide should be provided with resources and support. They need to consult with an oncology nurse or pharmacist to learn about the side effects and how to manage them. They should also be referred to support groups that can provide emotional and psychological support during their treatment journey. Additionally, access to financial assistance programs should be made available to help alleviate the cost burden associated with their treatment. Temozolomide is a component in the modern oncology arsenal, particularly in managing specific brain tumors. This underscores the need for research and a patient-centered approach to care.