Valance Oral Solution, Divalproex
- Introduction
- Overview of Valance Oral Solution (Divalproex)
- Composition
- Divalproex mechanism of action
- Divalproex Uses
- Treatment of epilepsy and seizure disorders
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
- Divalproex for seizures
- Divalproex for Absence Seizures
- Divalproex for Complex Partial Seizures
- Divalproex for Acute Manic Episodes
- Divalproex for Migraines
- Divalproex for Anxiety
- Divalproex for Depression
- Divalproex for Dementia
- Divalproex Mood Stabilizer
- Divalproex for Sleep
- Divalproex Antipsychotic
- Divalproex for Schizophrenia
- Divalproex for PTSD
- Divalproex for Headaches
- Divalproex for Bipolar Disorder
- Divalproex for Mood Disorder
- Divalproex for Mental Health
- Divalproex for Pain
- Off-Label Uses
- Dosage and Administration
- Standard dosing regimens for epilepsy
- Bipolar disorder dosage guidelines
- Migraine prophylaxis dosing recommendations
- Pediatric dosing considerations
- Elderly patient dose adjustments
- Titration and monitoring requirements
- Oral solution administration instructions
- Divalproex overdose
- Divalproex sodium extended release tablets
- Divalproex Side Effects
- Common Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Drowsiness and fatigue
- Weight gain and increased appetite
- Tremors and dizziness
- Hair loss or thinning
- Serious Side Effects
- Hepatotoxicity and Liver Failure
- Pancreatitis
- Thrombocytopenia and Bleeding Risks
- Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy
- Suicidal ideation and Behavioral Changes
- Weight Gain
- Drug Interactions
- Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications
- Careful Administration
- Special Populations
- Administration to Elderly
- Adjustments due to altered metabolism
- Monitoring for sedation and falls
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Teratogenic risks and neural tube defects
- Risk-benefit assessment in seizure control
- Transfer into breast milk
- Divalproex sodium nursing considerations
- Administration to Children
- Safety considerations in children under 2 years
- Weight-based dosing
- Long-term monitoring for growth and development
- Overdosage
- Handling Precautions
- Storage and Stability
Introduction
Valance Oral Solution, which contains the active ingredient divalproex sodium, is a key medication used to treat a range of neurological and psychiatric conditions. It is effective for seizure disorders, stabilizing mood, and preventing migraines. The liquid form is a great option for patients who have trouble swallowing pills or need to adjust their dosage precisely.
Known for its versatility and a proven track record, this medication works by balancing the signals in the brain. This makes it a crucial tool for managing conditions caused by abnormal brain excitability.
Overview of Valance Oral Solution (Divalproex)
Therapeutic class and pharmacological profile
Divalproex is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood. It works by increasing the brain's calming signals and making nerve cells more stable. When the dosage is adjusted correctly, it is well-absorbed by the body and maintains predictable levels in the bloodstream.
Approved medical indications and clinical importance
This oral solution is a versatile medication approved to manage several conditions. It is used to control various types of epilepsy, treat the manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder, and prevent migraines. Its primary benefit is its ability to reduce the frequency of seizures and headaches while stabilizing mood, which gives patients greater control over their lives.
Divalproex benefits
The therapeutic benefits of this treatment are significant and include the effective control of both generalized and focal seizures. It also helps to stabilize mood by decreasing mood swings and irritability, and it offers long-term protection against debilitating migraine attacks. The medication's potential extends beyond these uses, as new research is exploring its possible neuroprotective effects in neurodegenerative diseases.

Composition
Active ingredient: Divalproex sodium
Divalproex sodium, the active ingredient, is a combination of sodium valproate and valproic acid. This unique structure is designed to be gentler on the stomach and to help the body absorb the medication more effectively.
Formulation specifics of oral solution
The liquid form of this medication allows for more precise dose adjustments, which is especially helpful for children and adults who require a flexible dosing schedule.
Excipients and stability factors
The solution contains ingredients like stabilizers, solvents, and flavorings to make it taste good, last longer, and ensure the medication remains consistent. It's important to store it properly to maintain its effectiveness.
Divalproex drug class
Divalproex is a medication that functions as both an antiepileptic drug (AED) and a mood stabilizer. It works by adjusting the brain's chemical signaling and controlling the channels that nerve impulses travel through.
Divalproex classification
This medication is known as a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant because it's effective against many different kinds of seizures. Its ability to treat both psychiatric and neurological disorders also classifies it as a psychotropic agent.
Divalproex vs Depakote
Divalproex and Depakote are the same medication, sharing the identical active ingredients. While their branding may lead to small differences in inactive ingredients or how they're formulated, they have the same clinical effect and safety profile when taken at the correct dose.
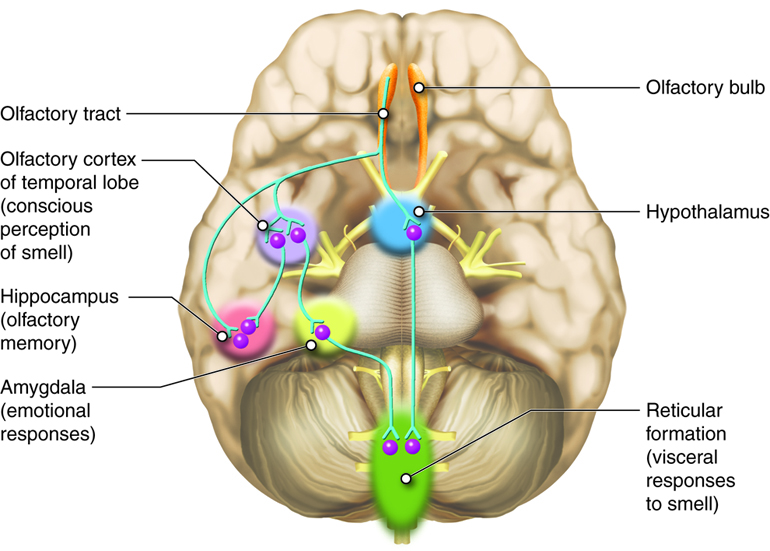
Divalproex mechanism of action
Effect on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels
Divalproex increases the amount of gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA in the brain. GABA is a neurotransmitter that helps calm the nervous system. By raising its levels, the medication reduces over-excitement and restores the brain's chemical balance.
Role in neuronal firing and mood stabilization
This medication works by controlling the flow of sodium and calcium into nerve cells, which reduces repetitive nerve firing. This action helps to not only control seizures but also stabilize mood and ease manic symptoms in people with bipolar disorder.
Neuroprotective properties and anticonvulsant activity
Evidence suggests that this medication has neuroprotective qualities, likely because of its ability to reduce cell death and inflammation. It is also effective as a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant, meaning it can suppress both generalized and partial seizures. The combination of protecting nerve cells and controlling seizures makes divalproex a vital tool in the long-term treatment of neurological conditions.
Divalproex Uses
Treatment of epilepsy and seizure disorders
Divalproex is a well-known first-line treatment for a variety of seizures and epilepsy. It works by regulating brain activity to reduce the hyperexcitability and sudden bursts of electrical signals that cause epileptic episodes.
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
For those suffering from generalized tonic-clonic seizures, divalproex is an indispensable medication. It significantly lessens the intensity and frequency of seizures and lowers the risk of their progression. Its broad effectiveness makes it a go-to choice for managing epilepsy, whether it's of unknown origin or a result of another condition.
Divalproex for seizures
This medication is used to treat a wide variety of seizure disorders. It effectively controls generalized epilepsy, manages focal seizures that spread, and helps prevent seizures from coming back. Its flexible dosing makes it a valuable tool for long-term treatment plans.
Divalproex for Absence Seizures
Divalproex is very effective at controlling absence seizures. Boosting the brain's calming signals, it reduces the sudden and brief episodes of unresponsiveness that characterize this type of seizure.
Divalproex for Complex Partial Seizures
For complex partial seizures, this medication helps stabilize abnormal brain activity. This reduces the auras, repetitive behaviors, and loss of awareness that can occur during these episodes.
Divalproex for Acute Manic Episodes
Divalproex is a common prescription for treating acute manic episodes. It works quickly to calm brain activity, which helps to reduce symptoms like hyperactivity, impulsivity, and irritability within just a few days of use.

Divalproex for Migraines
Divalproex is prescribed to prevent migraines. It helps to lower the frequency and intensity of headaches, allowing patients to function better day-to-day and rely less on other medications to treat an attack.
Divalproex for Anxiety
While divalproex isn't primarily prescribed for anxiety, some doctors have observed that it can have a calming effect. Patients who have both anxiety and bipolar disorder may find that it helps with feelings of tension and restlessness.
Divalproex for Depression
While not an antidepressant, divalproex has been studied as an additional treatment for depressive episodes, especially in mood disorders that show both manic and depressive symptoms. Its ability to stabilize mood can help lessen the emotional shifts that often worsen depression.
Divalproex for Dementia
Researchers have studied divalproex for its potential to help with behavioral issues in people with dementia. The results have been mixed, but for some patients, the medication's calming effects might be useful when other treatments haven't worked.

Divalproex Mood Stabilizer
As a mood stabilizer, divalproex is a top choice. It works by regulating the brain's neurotransmitters, which helps prevent emotional instability and is a key part of long-term psychiatric treatment.
Divalproex for Sleep
Some patients on divalproex have reported better sleep. By calming restlessness and distracting thoughts at night, the medication may indirectly lead to more restful sleep.
Divalproex Antipsychotic
While not classified as an antipsychotic, divalproex is sometimes used alongside other medications to treat psychotic conditions. Its calming properties can make primary antipsychotic treatments more effective and easier to tolerate.
Divalproex for Schizophrenia
When used with standard antipsychotic medications, divalproex can help manage mood swings and aggression in people with schizophrenia. It's not a primary treatment on its own, but it can be a key part of a full treatment plan.

Divalproex for PTSD
Early research suggests that divalproex might help lessen hyperarousal and intrusive thoughts in people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Although more study is needed, it shows potential as a treatment for some patients.
Divalproex for Headaches
In addition to preventing migraines, divalproex may also help with chronic daily headaches. By stabilizing overactive nerve cells, it can reduce the burden of frequent headaches.
Divalproex for Bipolar Disorder
For a long time, doctors have considered divalproex to be one of the most reliable treatments for bipolar disorder. Its ability to maintain stability makes it a fundamental part of psychiatric care.

Divalproex for Mood Disorder
Divalproex is frequently used to help patients who struggle with recurring mood disorders because it effectively dampens severe emotional shifts. Its stabilizing effects aren't limited to bipolar disorder; they also benefit people with other conditions marked by mood instability.
Divalproex for Mental Health
This medication is vital for managing mental health. It helps to control manic episodes, depressive moods, and cognitive problems related to seizures, which in turn helps patients build resilience and integrate more easily into social situations.
Divalproex for Pain
There is growing interest in using divalproex for pain relief. By calming overactive nerves in the brain, it could be beneficial for treating neuropathic pain and certain headache disorders, expanding its range of therapeutic uses.
Off-Label Uses
Neuropathic pain management
Divalproex has been studied for its potential to relieve nerve pain. By calming overactive nerve cells and boosting the brain's calming signals, it may reduce the severity of chronic pain conditions. In some studies, patients with peripheral neuropathies, diabetic nerve pain, and post-herpetic neuralgia showed significant improvement. Because it works in several ways, divalproex can be a good option when common pain relievers aren't effective.
Specifically, it works by:
- Reducing abnormal nerve firing
- Regulating the activity of sodium and calcium channels
- Calming overactive pain signals in the central nervous system
Anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder
Even though it isn't officially approved for anxiety disorders, divalproex has been used to manage conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By increasing the amount of calming GABA in the brain, it can help reduce the overactive neural responses associated with fear, hypervigilance, and intrusive memories. For people with anxiety that is difficult to treat, using divalproex as an additional medication can provide a stabilizing effect, improving both daily function and sleep.
Impulse control disorders
Divalproex can be helpful for patients with impulse control issues, such as aggression, intermittent explosive disorder, or compulsive behaviors. By calming rapid mood changes and reducing overactive brain activity, it helps patients better regulate their behavior. In controlled settings, it has been shown to reduce the number of aggressive outbursts, which leads to more stable relationships.
Adjunct in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder
Divalproex is sometimes used with antipsychotic medications to treat people with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. While it doesn't directly treat psychotic symptoms, it helps stabilize mood, reduce agitation, and manage emotional instability. Doctors have noticed that when used with atypical antipsychotics, it can improve a patient's adherence to treatment and overall tolerability.
In short, it:
- Supports mood stability in schizoaffective conditions.
- Helps control irritability and aggression.
- Works well with traditional antipsychotic medications.
Autism spectrum disorder and behavioral regulation
Studies have explored using divalproex to help reduce irritability, aggression, and repetitive behaviors in both children and adults with autism spectrum disorder. By helping to balance brain chemistry, it can improve adaptability and social function. Although this research is still in its early stages, it presents a potential medical option when other, non-medication interventions are not enough.
Huntington's disease (HD) and movement disorders
The neuroprotective and membrane-stabilizing properties of divalproex have led to its use in experimental treatments for Huntington's disease and other movement disorders. The medication may help reduce involuntary movements and behavioral issues by calming abnormal nerve activity. Although it doesn't cure these conditions, adding it to a treatment plan can make patients more comfortable and help them maintain their daily functions. Early studies also suggest it could be helpful for conditions like dystonia and myoclonus, where other treatments may not work well. This versatility demonstrates the wider neurological value of divalproex beyond its typical uses.
Dosage and Administration
Standard dosing regimens for epilepsy
For treating epilepsy, the dosage of divalproex is tailored to the individual patient and their specific seizure type. Treatment begins with a low dose that is gradually increased to achieve a therapeutic level in the blood. The typical maintenance dose is 10–60 mg/kg per day, usually taken in two or three separate doses. This method is designed to provide consistent seizure control while keeping side effects to a minimum.
Bipolar disorder dosage guidelines
For bipolar disorder, the dosage of divalproex usually begins at around 750 mg per day. The dose is then adjusted based on how well symptoms are controlled and the level of the medication in the blood. An effective maintenance dose is typically between 750–1500 mg daily. In cases of severe mania, higher doses might be needed, but close monitoring is essential to ensure the medication is both effective and safe.
Migraine prophylaxis dosing recommendations
To prevent migraines, divalproex treatment usually begins with a lower dose, typically 250–500 mg per day. If the migraines persist, the dose may be gradually increased to 1000 mg. The purpose of this treatment is to reduce the frequency and severity of headaches over time, not to provide immediate relief during an attack.
Pediatric dosing considerations
Dosing for children is based on their weight, usually beginning at 10–15 mg/kg per day. The dose is then increased every few days until the desired effect is achieved. It's crucial to monitor children closely, as they are more susceptible to liver damage.

Elderly patient dose adjustments
Because older adults metabolize the drug more slowly, a cautious approach is necessary. Treatment begins with a lower dose that is increased gradually, with adjustments based on the patient's tolerance and lab tests. Doctors pay close attention to potential side effects like sedation, tremors, and confusion in this patient population.
Titration and monitoring requirements
Effective treatment requires regular monitoring of the medication's levels in the blood, as well as checking liver function and blood counts. The dose is adjusted gradually to find a balance between controlling symptoms and preventing side effects. The therapeutic range is typically 50–125 mcg/mL, which may vary depending on the condition being treated.
Oral solution administration instructions
The liquid form of this medication allows for exact dosing, and it should be measured with a special tool, not a regular spoon. To prevent an upset stomach, it is best to take it with food or a drink. Taking the medication at the same time each day helps keep its levels stable in your body.
Divalproex overdose
An overdose of this medication can cause serious problems, including central nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, and liver damage. Signs of an overdose include confusion, severe drowsiness, breathing difficulties, and in the most serious cases, a coma. Treatment focuses on supportive care, decontaminating the stomach, and, for severe cases, using hemodialysis.
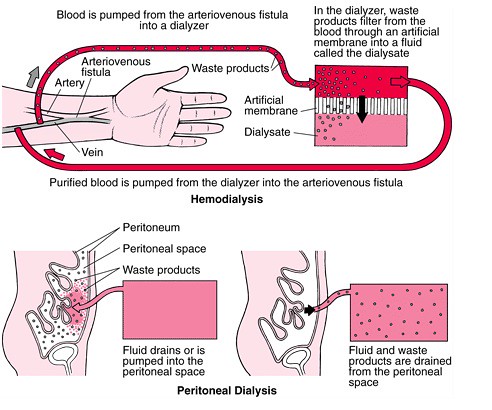
Divalproex sodium extended release tablets
Extended-release versions of this medication can be taken just once a day, which helps keep the amount of the drug in your system steady and makes it easier to remember to take. These tablets also reduce the highs and lows in drug levels, which can lead to fewer side effects like an upset stomach or feeling drowsy compared to immediate-release options.
Divalproex Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal disturbances
Common side effects of this medication include nausea, vomiting, and stomach discomfort, which are usually temporary and can be managed by taking the medication with food. Some people might also experience diarrhea or indigestion, which may require a change in the medication's form or dosing schedule.
Drowsiness and fatigue
Drowsiness, or somnolence, is a common side effect, especially when you first start the medication or increase your dose. Feeling tired or fatigued can interfere with daily life, but it usually improves as your body gets used to the medication.
Weight gain and increased appetite
Some patients may notice an increase in appetite and gradual weight gain. Those on the medication long-term should receive guidance on lifestyle changes to help reduce the risk of heart and metabolic issues.

Tremors and dizziness
Fine tremors are a common, dose-related side effect. Dizziness may also occur when you first start the medication, but it typically gets better as your body adjusts or if the dose is lowered.
Hair loss or thinning
Hair loss can occur as a side effect, but it is often reversible with continued use of the medication or by taking supplements like zinc and selenium.
Serious Side Effects
Hepatotoxicity and Liver Failure
Divalproex can cause serious liver damage, particularly in children under two and those with metabolic disorders. It is essential to have regular liver function tests. Watch for key warning signs such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin), abdominal swelling, and a general feeling of being unwell.
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, a serious condition, can happen at any time while you're on this medication. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience these, you must stop taking the medication immediately and seek urgent medical help.

Thrombocytopenia and Bleeding Risks
Blood abnormalities, such as a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia), can increase the risk of bleeding. Patients might notice symptoms like easy bruising, nosebleeds, or that they bleed for longer than usual. If this happens, a doctor may need to lower the dose or stop the medication.
Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy
High levels of ammonia in the blood can cause encephalopathy, a condition that affects brain function. This can lead to symptoms like lethargy, vomiting, confusion, and a decline in mental abilities. It's crucial to recognize and treat this quickly to prevent the condition from getting worse.
Suicidal ideation and Behavioral Changes
Like many other anti-seizure medications, divalproex can be associated with suicidal thoughts and behavioral changes. It's important for patients to be monitored for any signs of worsening mood, aggression, or unusual behavior.
Weight Gain
Weight gain is one of the most difficult long-term side effects. It's often caused by a combination of increased appetite, changes in metabolism, and lifestyle challenges, which can lead to significant changes in body weight. To help manage this, it's recommended that patients take a proactive approach with their diet and exercise.
Drug Interactions
Interaction with other antiepileptics
Divalproex can interact with other anti-seizure medications, which can affect how well they work and how they are tolerated. For example, it can increase the level of lamotrigine in the blood, which raises the risk of severe skin rashes. When taken with phenytoin or carbamazepine, it can cause unpredictable changes in drug levels, potentially making the treatment less effective or leading to toxicity. Because of this, when using multiple medications, it's essential to closely monitor drug levels and a patient's clinical condition.
Effects with anticoagulants and aspirin
Using divalproex with anticoagulants (blood thinners) or aspirin increases the risk of bleeding. This happens because aspirin and divalproex compete for the same proteins in the blood, which raises the amount of active drug in the system and boosts the effects of the blood thinners. When these medications are used together, doctors should watch for signs of bruising, blood in the urine, or bleeding in the stomach or intestines.
Central nervous system depressants
Using divalproex with other central nervous system depressants, such as benzodiazepines, opioids, or sedatives, can increase drowsiness, confusion, and poor motor coordination. This combination can be especially risky for older adults or anyone who operates machinery.
Interactions with antidepressants and antipsychotics
Using divalproex with antidepressants or antipsychotics requires careful clinical judgment. Some antidepressants can affect how the liver processes divalproex, changing its levels in the body. Pairing divalproex with antipsychotics can also increase side effects like sedation, tremors, and metabolic stress. Even with these risks, this combination is sometimes necessary for complex psychiatric conditions, so doctors must adjust the doses very carefully.
Drinking alcohol while on divalproex makes its sedative and liver-damaging effects much worse. Lifestyle habits like heavy drinking, poor diet, or drug use can also worsen the medication's negative effects. Patients undergoing this treatment are strongly advised to completely stop drinking or to drink only in strict moderation.
Divalproex and alcohol
Drinking alcohol while on divalproex can make you feel more drowsy and uncoordinated. It also puts extra stress on your liver, increasing the risk of liver damage. For these reasons, it's highly recommended that you avoid alcohol completely while taking this medication.

Warnings and Precautions
Risk of liver toxicity in young children
Children under two are at a higher risk of liver damage from divalproex, particularly if they are also taking other anti-seizure medications. Because they can experience rapid liver failure, it's essential to be extremely careful and to regularly monitor their liver function.
Risk of birth defects and teratogenicity
Divalproex poses a serious risk of birth defects, including neural tube defects and developmental disorders. Women of childbearing age should be counseled on contraception and other treatment options. The medication should only be used during pregnancy when no safer alternatives exist.
Risk of pancreatitis
Taking divalproex can cause a life-threatening condition called pancreatitis, which may begin soon after you start the medication or after you've been on it for a while. Symptoms include severe stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. If you suspect this, you need to stop taking the medication immediately.
Monitoring requirements (liver function, CBC, ammonia levels)
To ensure safe treatment, routine monitoring is essential. This includes:
- Checking liver function before starting the medication and at regular intervals afterward.
- Performing a complete blood count to detect low platelet levels (thrombocytopenia).
- Measuring serum ammonia levels in patients who show changes in their mental state.
This careful monitoring helps to identify potential toxicity early, which prevents serious complications.
Mental health monitoring for mood and behavior changes
Patients on this medication must be watched closely for any new psychiatric symptoms, as divalproex has been linked to suicidal thoughts, agitation, and sudden mood swings. Catching these behavioral changes early is crucial for providing a quick intervention and lowering the risk of psychiatric complications.
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to divalproex or valproate
Individuals who have had an allergic reaction to divalproex or similar medications should not take it. Allergic reactions can include a rash, anaphylaxis, or swelling of the face and throat.
Pre-existing liver disease
Due to the high risk of serious liver damage, individuals with chronic or acute liver problems should not take this medication. The body relies heavily on the liver to process divalproex, making it unsafe for these individuals.
Mitochondrial disorders (POLG gene mutations)
People with mitochondrial disorders caused by POLG gene mutations (like Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome) face a much higher risk of acute liver failure if they take divalproex. Because of this, doctors may consider genetic testing before starting treatment for anyone who might have these conditions.
Urea cycle disorders
Divalproex can cause a dangerous buildup of ammonia in people with urea cycle disorders, leading to brain damage and a metabolic crisis. Therefore, this medication should not be used in these individuals.
Pregnancy for migraine prophylaxis indication
When prescribed only for migraine prevention, divalproex is not recommended for pregnant women. The risk of birth defects is far greater than any potential benefit, so other treatment options should be explored.
Careful Administration
Patients with renal impairment
You should use caution when giving divalproex to people with kidney problems. While the liver does most of the work to process the drug, poor kidney function can cause some of its byproducts to build up. To prevent the drug from accumulating, causing metabolic issues, or leading to unexpected neurotoxicity, doctors should regularly monitor patients with reduced kidney function.
Patients with metabolic disorders
People with metabolic disorders, such as those affecting the urea cycle or mitochondria, face a greater risk when taking divalproex. In these individuals, the medication can cause a dangerous buildup of ammonia or lead to severe liver failure. Therefore, a thorough metabolic evaluation and continuous monitoring are crucial before and throughout treatment.
Patients with coagulopathies
Divalproex can affect how platelets work and reduce the blood's ability to clot. In people who already have a bleeding disorder, even minor injuries can lead to significant bleeding. To catch any problems early and reduce the risk of bleeding complications, it's important to regularly check platelet counts and blood clotting with lab tests.
Concurrent use with hepatotoxic drugs
Combining divalproex with other medications that can harm the liver, such as tuberculosis drugs, alcohol, and some chemotherapy agents, increases the risk of liver damage. Doctors must carefully weigh these risks and consider other treatment options. If the combination is necessary, they should closely monitor the patient's liver enzymes.
Special Populations
Administration to Elderly
Adjustments due to altered metabolism
As people get older, their liver function slows down and their body's ability to bind to proteins changes. These natural shifts mean that older adults are exposed to more divalproex than younger people, so careful dosing is crucial. Starting with the lowest effective dose and slowly increasing it helps reduce the risk of toxicity.
Monitoring for sedation and falls
In older adults, sedation, confusion, and poor motor coordination are particularly noticeable side effects. These can increase the risk of falls and related injuries. To ensure the medication is effective while keeping them physically safe, careful monitoring and dose adjustments are essential.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Teratogenic risks and neural tube defects
Divalproex carries a significant risk of causing birth defects. Exposure to the medication in the womb has been linked to neural tube defects, facial deformities, and developmental delays. This risk is highest during the first trimester of pregnancy, so it is crucial for women of childbearing age to receive counseling about this risk before starting the medication.
Risk-benefit assessment in seizure control
In some cases, divalproex may be a necessary treatment for severe epilepsy, as a mother's seizures can be life-threatening. The decision to continue the medication must be made on a case-by-case basis, carefully balancing the health risks to the mother against the potential risks to the fetus.
Transfer into breast milk
Small amounts of divalproex can pass into breast milk. While most infants don't have major problems, there is a slight risk of sedation, liver issues, or developmental delays. For this reason, it is recommended that breastfed infants are regularly monitored by a pediatrician.

Divalproex sodium nursing considerations
Nursing mothers on divalproex should be aware of signs of drowsiness, feeding problems, or jaundice in their infant. A care team that includes an obstetrician, a neurologist, and a pediatrician can help ensure the mother's treatment continues safely while she is breastfeeding.
Administration to Children
Safety considerations in children under 2 years
Children under the age of two are at a particularly high risk of liver damage from this medication, especially when it is taken with other anticonvulsants. For this reason, it should only be used in this age group when no safer options exist. If it is used, very close monitoring is required from the very beginning of treatment.
Weight-based dosing
Dosage for children is calculated by their weight, typically starting at 10–15 mg/kg per day. The dose is then carefully increased in small steps until it reaches a level that is effective without causing side effects.
Long-term monitoring for growth and development
When treating children with this medication long-term, care goes beyond just controlling seizures. Doctors need to regularly monitor their growth, cognitive development, and overall mental health. This comprehensive approach ensures that the benefits of the treatment do not negatively affect the child's long-term well-being.
Overdosage
Symptoms of overdose
An overdose of divalproex can cause a variety of serious symptoms. Common signs include severe drowsiness, confusion, and stomach problems. More severe cases can lead to low blood pressure, slowed breathing, metabolic acidosis, and even coma. Dangerous complications like high ammonia levels and brain swelling can also occur, often leading to a decline in neurological function.
Emergency management and supportive treatment
Immediate medical help is crucial for an overdose. Treatment is based on supportive care, which includes:
- Stabilizing the patient's breathing and circulation.
- Giving activated charcoal if the ingestion was recent.
- Administering intravenous fluids to maintain blood flow.
- Monitoring vital signs, electrolytes, and liver function.
Patients often need to be in the intensive care unit to manage multi-organ issues.
Role of hemodialysis and L-carnitine therapy
For severe overdoses, hemodialysis can effectively lower the amount of divalproex in the blood and help stabilize the body's metabolism. L-carnitine therapy has also been shown to help reverse the drug's damaging effects on the mitochondria, particularly in cases of liver damage or brain dysfunction. Using these treatments together can be vital when standard supportive care isn't enough.
Handling Precautions
Safe preparation and administration of oral solution
Be careful when preparing and giving the oral solution. Use a special measuring tool to ensure you give the exact dose and avoid giving too much or too little. Mix the solution gently to prevent foam and make sure the medication is evenly distributed.
Avoiding dosing errors with liquid formulations
Liquid medications can be difficult to measure precisely, which can lead to incorrect dosing. Clear labels, standardized measuring tools, and simple instructions help to minimize this risk. Patients and caregivers should always remember that using regular household spoons is not a safe or accurate way to measure the medication.
Caregiver guidance for home use
Caregivers are vital for making sure the medication is given safely. They need to be trained on how to measure it correctly, spot side effects, and understand how important it is to stick to the schedule. Providing written instructions and having healthcare professionals offer regular reminders helps ensure safety at home.
Storage and Stability
Recommended storage conditions
Divalproex oral solution must be stored at controlled room temperature, away from excessive heat, light, and moisture. Freezing should be avoided, as it may affect the formulation’s integrity.
Shelf life and stability of oral solution
The solution remains stable throughout its intended shelf life when kept under suitable conditions. After opening, bottles need to be securely sealed, and any noticeable changes in color, smell, or texture should lead to disposal.
Disposal recommendations for unused medication
Unused or expired divalproex solution should be disposed of in a safe and responsible way. Don't flush the medication down the toilet. Instead, use pharmacy take-back programs or community hazardous waste facilities. Proper disposal prevents accidental ingestion and protects the environment.

Valance Oral Solution, Divalproex FAQ
- What is Divalproex used for?
- What is Divalproex?
- Is Divalproex a narcotic?
- Is Divalproex a controlled substance?
- What is Divalproex sodium used for?
- Is Divalproex the same as Depakote?
- Does Divalproex cause weight gain?
- What is Divalproex sodium?
- Does Divalproex make you sleepy?
- What does Divalproex treat?
- How does Divalproex work?
- Is Divalproex an antipsychotic?
- How long does Divalproex take to work?
- Is Depakote the same as Divalproex?
- How long does it take for Divalproex to work?
- Can Divalproex be crushed?
- How long does Divalproex stay in your system?
- Is Depakote and Divalproex the same?
- How much Divalproex is too much?
- Is Divalproex a psychotropic medication?
- Can you overdose on Divalproex?
- What are the side effects of Divalproex?
- What is the brand name of Divalproex sodium?
- Are Divalproex and valproic acid the same?
- Are Divalproex and valproic acid interchangeable?
- Are Divalproex and valproate the same?
- Are Divalproex and valproic acid the same thing?
- What are Divalproex pills used for?
- What is Divalproex used for?
- Are Depakote and Divalproex the same thing?
- Are Divalproex and Depakote the same?
- Are Divalproex and Depakote the same drug?
- Can Divalproex be crushed?
- Can Divalproex cause weight gain?
- Can Divalproex cause tremors?
- Can Divalproex make you sleepy?
- Can Divalproex cause hyponatremia?
- Can Divalproex sodium be crushed?
- Can Divalproex cause depression?
- Can Divalproex cause hair loss?
- Can Divalproex be used for depression?
- Can Divalproex be crushed?
- Can Divalproex cause constipation?
- Can Divalproex cause anxiety?
- Can Divalproex cause weight loss?
- Can Divalproex cause insomnia?
- Can Divalproex cause erectile dysfunction?
- How Divalproex sodium works?
- How Divalproex works?
- Divalproex how long to take effect?
- Divalproex how does it work?
- Divalproex how long does it take to work?
- Divalproex how to take?
- Divalproex how fast does it work?
- Divalproex how many times a day?
- Divalproex how often to take?
- Divalproex how long does it last?
- How does Divalproex sodium work?
- How does Divalproex work for bipolar?
- How does Divalproex work in the brain?
- What Divalproex is prescribed for?
- Divalproex what does it do?
- Divalproex what to avoid?
- Divalproex what does it look like?
- Divalproex what type of drug?
- What does Divalproex do to the brain?
- What is Divalproex used to treat?
- Divalproex when to take?
- When does Divalproex peak?
- When does Divalproex start working?
- When to take Divalproex sodium?
- When to check Divalproex levels?
- Divalproex which class of drug?
- Why Divalproex is used?
- Why is Divalproex a hazardous drug?
- Why does Divalproex smell sweet?
- Why does Divalproex cause weight gain?
- Why does Divalproex smell like vanilla?
- Why is Divalproex prescribed?
- Why take Divalproex?
- Why take Divalproex at night?
- Why does Divalproex smell good?
- Why is Divalproex given?
- Why does Divalproex cause hair loss?
- Why is Divalproex enteric coated?
- Why can Divalproex be crushed?
- Will Divalproex show on a drug test?
- Will Divalproex make you sleepy?
- Can Divalproex cause weight gain?
- Can Divalproex cause erectile dysfunction?
- Can Divalproex make you sleepy?
- Can Divalproex cause tremors?
- Can Divalproex cause liver problems?
- Can Divalproex capsules be opened?
- Can Divalproex cause seizures?
- Can Divalproex DR be crushed?
- Can Divalproex cause hair loss?
- Can Divalproex cause hyponatremia?
- Can Divalproex cause tardive dyskinesia?
- Can Divalproex cause depression?
What is Divalproex used for?
Divalproex is mainly utilized for treating seizure disorders like epilepsy, helping to manage bipolar disorder by stabilizing mood, and preventing migraine headaches.
What is Divalproex?
Divalproex is a medication composed of valproic acid derivatives, serving as both an anticonvulsant and a mood stabilizer.
Is Divalproex a narcotic?
No, Divalproex isn't a narcotic; it's categorized as an anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer.
Is Divalproex a controlled substance?
No, Divalproex is not classified as a controlled substance under U.S. federal law.
What is Divalproex sodium used for?
Divalproex sodium is utilized for managing epilepsy, treating manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder, and preventing migraine headaches.
Is Divalproex the same as Depakote?
Yes, Depakote is the trade name for Divalproex sodium.
Does Divalproex cause weight gain?
Yes, weight gain can be a potential side effect of Divalproex, particularly with prolonged use.
What is Divalproex sodium?
Divalproex sodium is the sodium salt of valproic acid formulated for improved gastrointestinal tolerance and effectiveness.
Does Divalproex make you sleepy?
Yes, Divalproex can lead to drowsiness or sleepiness as a potential side effect.
What does Divalproex treat?
Divalproex is used to treat epilepsy, manage bipolar disorder (mania), and assist in the prevention of migraines.
How does Divalproex work?
Divalproex raises gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels in the brain, which helps stabilize nerve activity and diminishes seizures or mood fluctuations.
Is Divalproex an antipsychotic?
No, Divalproex is not classified as an antipsychotic; it is an anticonvulsant and a mood stabilizer.
How long does Divalproex take to work?
Divalproex can begin to show effects for mood stabilization within just a few days, though it may take several weeks for seizure control or migraine prevention to take effect.
Is Depakote the same as Divalproex?
Yes, Depakote is the commercial name for Divalproex sodium.
How long does it take for Divalproex to work?
It may require a few days to notice mood improvements and several weeks for complete effectiveness in managing seizures or migraines.
Can Divalproex be crushed?
Extended-release or delayed-release Divalproex tablets must not be crushed, as doing so could impact drug absorption and efficacy.
How long does Divalproex stay in your system?
Divalproex has a half-life of approximately 9 to 16 hours, and it typically takes about 2 to 4 days to be eliminated from the body after discontinuation.
Is Depakote and Divalproex the same?
Yes, Depakote is a brand name for Divalproex sodium, and they refer to the same medication.
How much Divalproex is too much?
The toxic dose of Divalproex differs from person to person, but any levels exceeding the recommended therapeutic range (50–125 mcg/mL in the bloodstream) can pose risks. Overconsumption may result in severe issues like liver failure, pancreatitis, or central nervous system depression.
Is Divalproex a psychotropic medication?
Yes, Divalproex is classified as a psychotropic medication since it influences mood, behavior, and brain function, especially in treating bipolar disorder and seizures.
Can you overdose on Divalproex?
Yes, an overdose of Divalproex is possible and can lead to drowsiness, confusion, tremors, low blood pressure, respiratory depression, or even coma. It is essential to seek medical attention in cases of suspected overdose.
What are the side effects of Divalproex?
Common side effects may include nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, tremors, weight gain, and hair loss. More serious effects can involve liver toxicity, pancreatitis, or blood disorders.
What is the brand name of Divalproex sodium?
The most recognized brand name of Divalproex sodium is Depakote.
Are Divalproex and valproic acid the same?
They are similar but not the same. Divalproex is a compound that metabolizes into valproic acid within the body, created for better gastrointestinal tolerance.
Are Divalproex and valproic acid interchangeable?
They may be interchangeable in certain situations, but variations in absorption and formulation indicate that substitution should occur only under medical supervision.
Are Divalproex and valproate the same?
Valproate is the active form produced when Divalproex or valproic acid is metabolized, making them closely related yet not chemically identical.
Are Divalproex and valproic acid the same thing?
No, Divalproex is a combination of sodium valproate and valproic acid, whereas valproic acid is the standalone active ingredient.
What are Divalproex pills used for?
Divalproex tablets are prescribed for managing epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and for the prevention of migraine headaches.
What is Divalproex used for?
Divalproex is utilized for managing seizures, stabilizing mood in bipolar disorder, and preventing migraines.
Are Depakote and Divalproex the same thing?
Yes, Depakote is the brand name for Divalproex sodium.
Are Divalproex and Depakote the same?
Yes, they are identical, with Depakote serving as the brand name for Divalproex sodium.
Are Divalproex and Depakote the same drug?
Yes, Divalproex and Depakote refer to the same medication, with the only difference being their generic versus brand names.
Can Divalproex be crushed?
Extended-release or delayed-release Divalproex tablets must not be crushed, as this can change the drug's release and absorption, potentially leading to side effects or diminished effectiveness.
Can Divalproex cause weight gain?
Yes, Divalproex can lead to weight gain, which is a fairly common side effect, particularly with prolonged use.
Can Divalproex cause tremors?
Can Divalproex make you sleepy?
Yes, Divalproex frequently leads to drowsiness or sleepiness, especially when beginning treatment or raising the dose.
Can Divalproex cause hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia is not typically a common side effect of Divalproex, although electrolyte imbalances can occur in rare instances and should be monitored closely.
Can Divalproex sodium be crushed?
No, extended-release or delayed-release formulations of Divalproex sodium must not be crushed, as this affects absorption and effectiveness.
Can Divalproex cause depression?
While Divalproex is primarily prescribed to stabilize mood, it may, in certain individuals, lead to depressive symptoms or fluctuations in mood.
Can Divalproex cause hair loss?
Yes, hair loss or thinning can happen with Divalproex, but it typically reverses once the medication is adjusted or stopped.
Can Divalproex be used for depression?
Divalproex is not mainly an antidepressant; however, it can be utilized for mood stabilization in patients with bipolar disorder who also suffer from depression.
Can Divalproex be crushed?
Standard immediate-release tablets can occasionally be crushed, but delayed-release or extended-release forms should never be crushed.
Can Divalproex cause constipation?
Yes, constipation is a potential side effect of Divalproex, though it is less frequently observed.
Can Divalproex cause anxiety?
Anxiety is not a common side effect, but some patients may experience unexpected changes in mood or behavior.
Can Divalproex cause weight loss?
Weight loss is rare with Divalproex; weight gain is much more commonly reported.
Can Divalproex cause insomnia?
Insomnia isn’t one of the most prevalent effects, but some individuals may experience sleep disturbances.
Can Divalproex cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, sexual side effects like erectile dysfunction can occur with Divalproex, although they are not very common.
How Divalproex sodium works?
Divalproex sodium raises levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, soothing overactive nerve signals, which helps in reducing seizures and stabilizing mood.
How Divalproex works?
Divalproex operates by enhancing GABA activity and modulating voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels, which helps manage seizures, stabilize mood, and prevent migraines.
Divalproex how long to take effect?
Divalproex may start to take effect within a few days for mood stabilization, but achieving control over seizures or preventing migraines can take several weeks.
Divalproex how does it work?
Divalproex how long does it take to work?
It might take several days to observe changes in mood, whereas the complete therapeutic effects for seizures or migraines typically emerge in one to two weeks or even longer.
Divalproex how to take?
Divalproex should be taken precisely as directed, typically with food to minimize stomach upset, and at the same time each day to maintain consistent levels.
Divalproex how fast does it work?
Some patients might observe enhancements in mood or a reduction in seizures in just a few days, though the complete benefits could require several weeks.
Divalproex how many times a day?
The dosing frequency varies based on the formulation; immediate-release is typically taken several times a day, whereas extended-release is usually taken once a day.
Divalproex how often to take?
It should be taken as directed, typically two to three times a day for standard tablets, or once a day for extended-release tablets.
Divalproex how long does it last?
The duration of effect varies based on the formulation, with extended-release versions lasting around 24 hours, while immediate-release forms necessitate multiple daily doses.
How does Divalproex sodium work?
Divalproex sodium boosts GABA activity and influences sodium and calcium channels, diminishing irregular brain signaling that leads to seizures or mood fluctuations.
How does Divalproex work for bipolar?
Divalproex stabilizes mood by soothing excessive neuronal activity, aiding in the management of manic episodes and diminishing mood swings in bipolar disorder.
How does Divalproex work in the brain?
In the brain, Divalproex elevates GABA levels and diminishes overactive nerve signals, offering anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing effects.
What Divalproex is prescribed for?
Divalproex is used to treat epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and to prevent migraine headaches.
Divalproex what does it do?
Divalproex minimizes seizure activity, stabilizes mood in bipolar disorder, and helps prevent migraine attacks.
Divalproex what to avoid?
Patients should steer clear of alcohol, sudden discontinuation, and combining Divalproex with specific medications without medical advice, as this could lead to interactions.
Divalproex what does it look like?
Divalproex tablets and capsules differ among manufacturers, but they are typically white, yellow, or pink, and may come in round, oval, or capsule shapes.
Divalproex what type of drug?
Divalproex is a medication used for both seizure control and mood stabilization.
What does Divalproex do to the brain?
Divalproex reduces irregular electrical activity, boosts inhibitory neurotransmission via GABA, and stabilizes the firing of nerve cells in the brain.
What is Divalproex used to treat?
Divalproex is prescribed for managing seizures, treating bipolar disorder, and preventing migraine headaches.
Divalproex when to take?
Divalproex is usually taken at consistent times each day, with or following meals, as instructed by a healthcare professional.
When does Divalproex peak?
The highest blood concentration of Divalproex usually takes place within 3 to 4 hours for delayed-release tablets and approximately 4 to 17 hours for extended-release formulations.
When does Divalproex start working?
Divalproex can begin to decrease seizures or stabilize mood in just a few days, but achieving full therapeutic effects may require 1 to 2 weeks or even longer.
When to take Divalproex sodium?
Divalproex sodium is best taken at the same time every day, typically with food, to ensure consistent levels and minimize stomach irritation.
When to check Divalproex levels?
Blood levels are typically monitored after achieving a steady state, approximately 2 to 4 days following the initiation or adjustment of the dose, and then periodically thereafter to confirm safety and effectiveness.
Divalproex which class of drug?
Divalproex is classified as an anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer.
Why Divalproex is used?
Divalproex is utilized to manage epilepsy, regulate manic episodes in bipolar disorder, and prevent migraine headaches.
Why is Divalproex a hazardous drug?
Divalproex is regarded as hazardous because of the risks of liver toxicity, teratogenic effects during pregnancy, and possible harm from exposure during handling.
Why does Divalproex smell sweet?
Certain formulations of Divalproex possess a naturally sweet or vanilla-like scent, which arises from the chemical makeup of valproate salts.
Why does Divalproex cause weight gain?
Divalproex can lead to weight gain by changing metabolism, boosting appetite, and influencing energy balance.
Why does Divalproex smell like vanilla?
The sweet, vanilla-like aroma originates from the chemical composition of the valproic acid derivatives found in Divalproex.
Why is Divalproex prescribed?
Divalproex is used to manage seizures, bipolar disorder, and to assist in preventing migraines.
Why take Divalproex?
Taking Divalproex assists in stabilizing irregular brain activity, managing mood swings, and decreasing the occurrence of seizures or migraines.
Why take Divalproex at night?
Some patients take Divalproex at night to minimize daytime drowsiness and to synchronize dosing with the extended-release effect.
Why does Divalproex smell good?
The pleasant or sweet smell of certain Divalproex tablets is associated with the excipients and valproate component found in the formulation.
Why is Divalproex given?
Divalproex is prescribed for patients requiring seizure management, mood stabilization, or migraine prevention.
Why does Divalproex cause hair loss?
Hair loss associated with Divalproex may be connected to disruptions in nutrient metabolism, specifically biotin and zinc, although it is generally reversible.
Why is Divalproex enteric coated?
Divalproex features an enteric coating designed to shield the stomach from irritation and enable the medication to dissolve in the intestine, facilitating improved absorption.
Why can Divalproex be crushed?
Only immediate-release forms of Divalproex can be crushed; delayed-release and extended-release forms should not be crushed as it changes absorption and effectiveness.
Will Divalproex show on a drug test?
Standard drug tests do not include Divalproex, since it is neither a controlled substance nor considered a drug of abuse.
Will Divalproex make you sleepy?
Yes, drowsiness or sleepiness is a frequent side effect of Divalproex, especially during the initial treatment phase or when changing the dosage.
Can Divalproex cause weight gain?
Yes, weight gain is a fairly common side effect of Divalproex, often associated with shifts in appetite and metabolism during extended treatment.
Can Divalproex cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, while not frequently observed, Divalproex has been linked to sexual side effects, including erectile dysfunction in certain patients.
Can Divalproex make you sleepy?
Yes, drowsiness or sleepiness is a common side effect of Divalproex, particularly when beginning treatment or raising the dosage.
Can Divalproex cause tremors?
Yes, tremors are a recognized side effect of Divalproex and may appear as slight shaking, especially in the hands.
Can Divalproex cause liver problems?
Yes, Divalproex does pose a risk of significant liver toxicity, particularly in young children and during the initial six months of treatment, necessitating consistent monitoring of liver function.
Can Divalproex capsules be opened?
Some sprinkle capsule formulations of Divalproex can be opened and combined with soft food, but delayed-release and extended-release versions should remain unchanged.
Can Divalproex cause seizures?
While Divalproex is effective in managing seizures, suddenly stopping the medication or dosing it improperly can lead to breakthrough seizures.
Can Divalproex DR be crushed?
No, delayed-release (DR) tablets of Divalproex must not be crushed, as this damages the protective coating and changes how the drug is absorbed.
Can Divalproex cause hair loss?
Yes, experiencing hair loss or thinning can be a side effect of Divalproex, but it is typically reversible through dose adjustment or supplementation.
Can Divalproex cause hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia is not typically a common side effect of Divalproex; however, electrolyte imbalances can occasionally arise and should be monitored in patients who are at risk.
Can Divalproex cause tardive dyskinesia?
Tardive dyskinesia is generally not connected to Divalproex; rather, it is more commonly associated with prolonged use of antipsychotics.