Xith, Azithromycin
- Introduction to Azithromycin
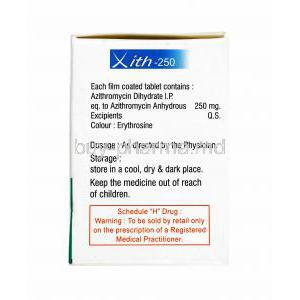
- Composition of Azithromycin
- How Azithromycin Works
- Uses of Azithromycin
- Azithromycin for Strep Throat
- Off-Label Uses of Azithromycin
- Azithromycin dosage
- Azithromycin side effects
- Azithromycin interactions
- Azithromycin and Alcohol
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Special Considerations in Azithromycin Administration
- Overdose and Emergency Handling
- Storage and Handling Precautions for Azithromycin
- Important Precautions When Using Azithromycin
Introduction to Azithromycin
Azithromycin, an antimicrobial medication plays a crucial role in today's medical treatments, especially in fighting different bacterial infections. It falls under the category of antibiotics known for its effectiveness and wide range of uses.
Azithromycin was developed as a variation of erythromycin in the 20th century and has since gained recognition for its improved performance in how it works within the body and its better tolerability compared to older alternatives.
Its significance in healthcare is highlighted by its inclusion in the World Health Organization's Essential Medicines List indicating its importance, for a fundamental healthcare system.
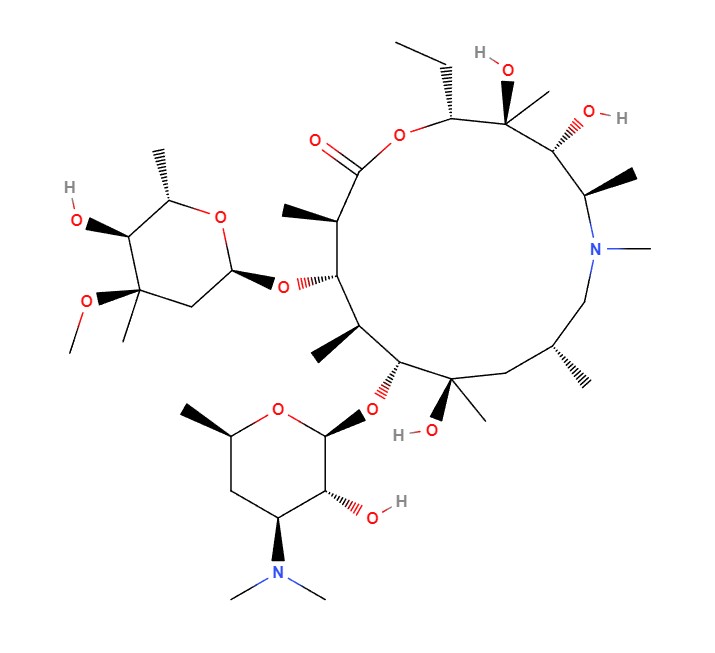
Azithromycin
Composition of Azithromycin
Azithromycin has a molecular composition with a nitrogen atom added to the lactone ring of the erythromycin molecule. This alteration gives it pharmacological effects and a longer half life allowing for easier and less frequent dosing schedules.
- The chemical structure is C38H72N2O12.
- It contains Azithromycin dihydrate as the active ingredient.
Azithromycin comes in forms, like oral tablets, capsules, suspension, and intravenous formulations to meet different medical needs and patient preferences.
How Azithromycin Works
The way Azithromycin works is quite fascinating and complex. It attaches to the 50S part of the ribosome, which then stops RNA-dependent protein synthesis. This process prevents bacteria from growing and reproducing effectively controlling the infection.
When it comes to infections Azithromycin is known for its effectiveness against a variety of organisms including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as certain atypical pathogens.
Its ability to target a range of bacteria makes it a versatile treatment option for conditions such as respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and more serious illnesses, as sexually transmitted diseases.
Uses of Azithromycin
Azithromycin is an antimicrobial medication widely used for its broad-spectrum antibacterial properties. It is commonly prescribed for treating bacterial infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, and skin infections. Additionally, it plays a role in combating sexually transmitted diseases like chlamydia and gonorrhea.
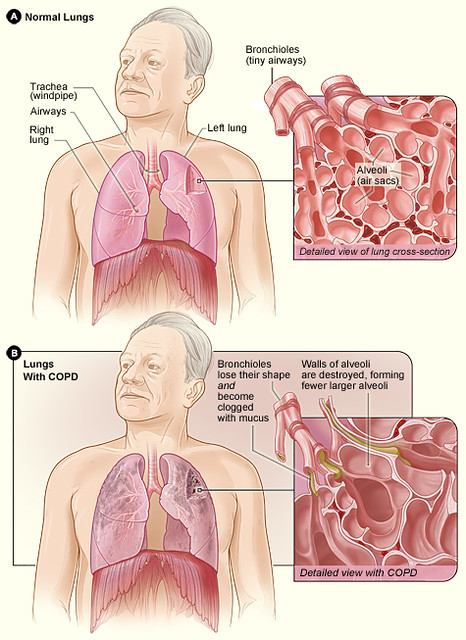
Bronchitis
- For Bronchitis and Pneumonia infections Azithromycin is effective due to its ability to penetrate tissues extensively and remain in lung tissue for an extended period.
- In cases of bacterial sinusitis, it proves to be efficient by reducing bacterial presence and improving symptoms rapidly.
- When it comes to skin and soft tissue infections such as impetigo and cellulitis Azithromycin demonstrates effectiveness.
- In the realm of sexually transmitted diseases, Azithromycin stands out as a primary treatment choice for chlamydia and is often combined with other antibiotics for gonorrhea management.
Compared to some beta-lactam antibiotics Azithromycin shows tendencies towards resistance development, among common pathogens. Its daily dosing regimen enhances patient compliance compared to medications that require multiple daily doses.
Furthermore, Azithromycin's unique ability to concentrate in tissues allows for therapeutic levels. This feature enables treatment durations which can result in decreased overall side effects and improved treatment outcomes.
These characteristics make it a popular choice in medical situations surpassing outdated macrolides like erythromycin and versatile alternatives such, as amoxicillin and doxycycline.
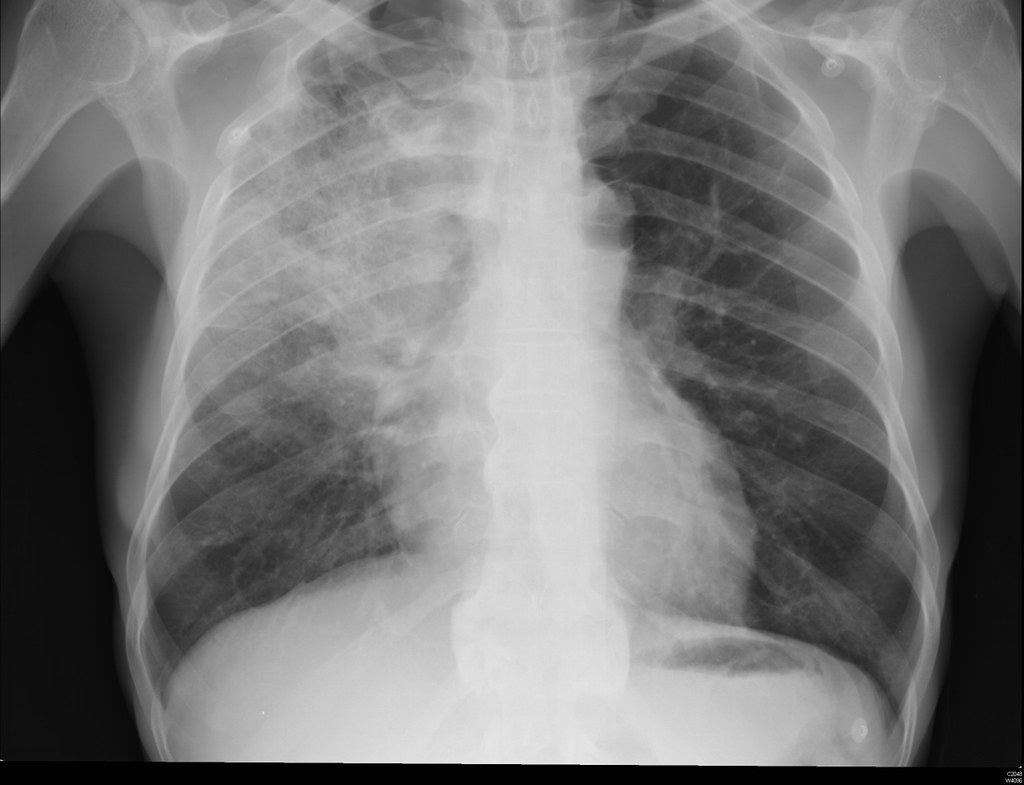
Pneumonia
Azithromycin for Strep Throat
Azithromycin, a type of antibiotic known as a macrolide offers an option instead of penicillin and its derivatives for treating strep throat, especially in cases where patients have allergies to penicillin. Strep throat, caused by Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria typically requires treatment with antibiotics to prevent complications and relieve symptoms.
Azithromycin is preferred for treating strep throat due to its ability to penetrate tissues well and its lasting effects, allowing for shorter treatment durations typically lasting just five days. This antibiotic works by stopping the production of proteins, which effectively stops the bacteria from growing and spreading.
- Dosage Instructions; Azithromycin is usually prescribed as a 500 mg dose on the first day followed by 250 mg daily for the next four days. This dosing schedule promotes patient adherence compared to treatments that require multiple doses throughout the day.
- Effectiveness; Studies have shown that azithromycin is just as effective as penicillin in treating infections with similar success rates seen in clinical outcomes compared to traditional treatments.
- Suitability for Allergic Patients; It serves as an alternative for patients who cannot take beta-lactam antibiotics due to allergies offering them an effective and safe treatment choice.
While azithromycin is generally well tolerated potential side effects may include issues and temporary hearing problems. Important factors, for healthcare providers to consider when prescribing this medication.
Making sure that patients grasp the significance of finishing the treatment regimen is crucial, in order to avoid the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains.
Off-Label Uses of Azithromycin
Azithromycin, known for its approved uses is often utilized in settings for purposes not officially endorsed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This exploration of applications showcases the drug's versatility and ongoing research aimed at broadening its therapeutic scope.
The off-label uses of Azithromycin encompass a range of conditions that intrigue both clinicians and researchers.
These include treating asthma, cystic fibrosis, and certain inflammatory diseases where its anti-inflammatory properties are as valuable as its antibacterial effects.
These applications capitalize on the drug's ability to regulate responses and reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines. In asthma treatment, Azithromycin serves as a therapy for patients with severe or neutrophilic asthma to help minimize exacerbations.
For fibrosis patients, it is used to enhance lung function by reducing bacterial presence and inflammation in the airways. In cases of diseases like bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome post lung transplantation its potential benefits are being investigated.
Extensive research supports the off-label advantages of Azithromycin. Clinical trials have shown results in reducing asthma exacerbations suggesting a possible shift in asthma management approaches.
Likewise using Azithromycin in cystic fibrosis patients has been linked to quality of life and reduced hospitalization rates indicating a broader role, beyond infection control.
Ongoing research and real-world use of Azithromycin beyond its approved indications show that there is still much to uncover about its potential, for treatment indicating that we have yet to fully understand its complete range of therapeutic benefits.
Azithromycin dosage
Azithromycin works best when taken correctly and in the right amounts. Following the recommended dosage instructions helps achieve the desired treatment results and lowers the risk of side effects.
- For adults, it is common to start with a 500 mg dose on the day followed by 250 mg each day for four days.
- Children's doses are adjusted based on their weight. It's important to adjust dosages for groups of people to minimize risks and improve the effectiveness of the drug.
Patients with liver or kidney issues may need dosing schedules to avoid harmful effects from too much medication buildup. The way Azithromycin is given can vary, including through tablets, liquid suspensions, or intravenous injections depending on the medical condition being addressed.
To get the most out of Azithromycin, it is recommended to take it with food to reduce stomach discomfort and avoid taking antacids within two hours of a dose to prevent interference, with absorption.
Azithromycin side effects
Azithromycin is usually well tolerated. Like any medication, it can lead to side effects. Common reactions may involve issues related to the system like feeling nauseous, vomiting, or having diarrhea. Managing these symptoms effectively requires treating them and ensuring proper hydration.
In rare cases, serious adverse effects such as liver damage, QT interval prolongation, and severe allergic reactions can occur. Immediate medical attention is necessary in situations. It is crucial to discuss the long-term health consequences, especially for individuals, with existing health conditions or those undergoing extended Azithromycin treatment. This could potentially heighten the risk of resistance and cardiovascular complications.
Azithromycin interactions
Azithromycin may react with medications leading to changes in its effectiveness or an increased risk of side effects. Common interactions include stronger blood thinning effects when combined with warfarin and a higher chance of muscle issues when taken with statins.
- When it comes to food and drinks while Azithromycin can be consumed with or without food mixing it with alcohol could raise the risk of liver damage.
- For individuals with conditions like myasthenia gravis or liver problems using Azithromycin requires caution as it could worsen symptoms or interact unfavorably with their treatments.
Having a grasp of these interactions is crucial, for avoiding undesired outcomes and ensuring the safe use of Azithromycin.
Azithromycin and Alcohol
When thinking about using azithromycin and alcohol it's important to understand how they might interact and what it means for a person's health. Azithromycin is a used antibiotic that treats various bacterial infections but its effects can be affected by alcohol.
Alcohol can change how medications are processed in the body by affecting liver enzymes, which can impact how well the drug works and its safety. One concern with combining azithromycin and alcohol is that it could worsen side effects like stomach issues and dizziness potentially making it harder for a person to stick to their treatment plan.
- Increased Side Effects; Mixing azithromycin with alcohol could raise the chances of experiencing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. This could lead to dehydration. Make the antibiotic less effective in treating the infection.
- Impaired judgment Dizziness; Both azithromycin and alcohol have the potential to cause dizziness and make someone feel light-headed. Using them together can magnify these effects affecting a person's ability to concentrate or coordinate activities.
- Liver Strain; Since both substances are broken down in the liver taking them at the same time can strain liver function further which is especially concerning for those with existing liver issues.
While having an amount of alcohol might not have a big impact on how well azithromycin works for everyone it's generally recommended to avoid or cut down on drinking when you're, on antibiotics. Teaching patients about the dangers and promoting careful conduct can ensure that the treatment works effectively and protects the health of patients.
Warnings and Contraindications
When prescribing Azithromycin it's important to be cautious especially if the patient has health conditions that could increase risks or change how the drug works. People with liver issues or who are allergic to macrolides should steer clear of this medication to avoid serious side effects.
- Genetic differences can impact how Azithromycin is processed in the body potentially making some individuals more prone to side effects or reducing its effectiveness.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to drugs or substances, and lifestyle choices, like smoking can also affect how well Azithromycin works and how safe it is.
Special Considerations in Azithromycin Administration
The dosage of Azithromycin needs to be adjusted based on demographic groups to ensure effectiveness and safety.
- For Elderly Patients; Special care is necessary due to the higher chances of existing health conditions and use of other medications, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrest and liver side effects.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding; Azithromycin should only be used during pregnancy if absolutely necessary considering its ability to pass through the placenta. It is also present in breast milk. Caution is advised when giving it to nursing mothers.
- Pediatric Use and Dosage Adjustments; The dosing, for children should be carefully calculated based on their weight and the severity of their condition to minimize the risk of overdose and improve treatment outcomes.
Overdose and Emergency Handling
Azithromycin overdose is a health issue that requires prompt attention. It is important to identify the symptoms to help minimize any negative effects.
- Signs of an overdose may involve nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and hearing difficulties. More severe indications could entail liver problems and significant QT prolongation.
- When dealing with an Azithromycin overdose there is no antidote available; hence treatment focuses on providing support and addressing symptoms. Immediate steps may include lavage and giving activated charcoal to lessen absorption.
- To prevent overdoses it is crucial to educate patients on the correct dosage and proper storage of Azithromycin. Regular monitoring and discussions, with healthcare providers, can also aid in ensuring that patients adhere to their prescribed dosages.
Storage and Handling Precautions for Azithromycin
Storing and handling Azithromycin correctly is vital to maintain its effectiveness and safety. Following the recommended storage conditions is crucial for preserving the stability and potency of the drug.
- It's important to store Azithromycin at room temperature shielded from light and moisture to prevent any deterioration of its components.
- Regarding shelf life and expiration details, Azithromycin typically remains usable for, up to two years from the manufacturing date.
- Patients are advised to check the expiration date before using the medication to ensure its efficacy and safety. When it comes to disposal and environmental concerns it's essential to dispose of expired or unused Azithromycin properly to avoid harm. Patients should be encouraged to return any leftover medication to pharmacies that offer disposal options.

Medicine in Cupboard
Important Precautions When Using Azithromycin
When Azithromycin is prescribed and used it's important to follow precautions to get the best results and reduce risks. Keeping an eye out for any signs of the medication becoming less effective is crucial in detecting drug resistance which can lead to necessary adjustments in treatment plans.
Patients need to be reminded to finish the prescribed course of Azithromycin even if they start feeling better to prevent resistance from developing and make sure the infection is completely treated. Providing patients and caregivers with education on how to use Azithromycin correctly potential side effects and the importance of sticking to dosing schedules is essential, for achieving the desired treatment outcomes.