Azithromycin
- Understanding Azithromycin: A Comprehensive Introduction
- The Journey of Azithromycin: From Discovery to Present Day
- Azithromycin: The Science Behind the Medication
- The Clinical Applications of Azithromycin
- Correct Dosage and Administration of Azithromycin
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Azithromycin
- Safety Measures When Using Azithromycin
- Procuring Azithromycin: Price and Accessibility
- Azithromycin in COVID Scientific Applications and Research
- Azithromycin and Alcohol Interactions
- FAQs in Relation to Buy Azithromycin
- Understanding Azithromycin before purchasing it from us at Buy Pharma!
Rationale for azithromycin in COVID-19
Understanding Azithromycin: A Comprehensive Introduction
Azithromycin, a type of antibiotic classified as a macrolide, has gained popularity since its discovery in 1980. It is widely prescribed for treating a range of bacterial infections, such as respiratory issues, skin problems, and gastrointestinal illnesses. In this section, we will delve into the background scientific aspects and medical uses of azithromycin.
The Journey of Azithromycin: From Discovery to Present Day
Azithromycin, which was first introduced by Pliva, a company in Croatia in 1980, was initially sold under the brand name Zithromax. Due to its ranging antibacterial effects and convenient pharmacokinetic properties. Including a long half-life that allows for once-a-day dosing. It quickly gained popularity. Eventually, it also became available as a medication, making it even more accessible to patients worldwide.
Azithromycin: The Science Behind the Medication
Azithromycin primarily works by blocking the ribosomes, which are cellular structures responsible for producing proteins necessary for bacterial growth and replication. This inhibition of protein synthesis effectively stops the bacteria from growing, enabling our system to eliminate them more effectively from our bodies.
The Antibacterial Spectrum: Understanding the Range of Azithromycin
- Gram-positive bacteria: It is effective in fighting against Streptococcus pneumoniae, which commonly causes pneumonia, and Staphylococcus aureus, which is often responsible for skin infections.
- Gram-negative bacteria; It works well to combat Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis, both of which are known to cause respiratory infections.
- Atypical pathogens: Azithromycin is also effective in treating bacterial infections, like Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia trachomatis.
The Clinical Applications of Azithromycin
Azithromycin is a prescribed antibiotic that is highly effective in treating a wide range of bacterial infections. It is frequently used to address issues like bronchitis and pneumonia as well as skin conditions such as cellulitis or impetigo. Additionally, it has been found to be helpful in managing illnesses caused by bacteria like Campylobacter jejuni or Helicobacter pylori.
Azithromycin has also shown promise in treating transmitted diseases like chlamydia infection and has even been explored in some cases involving COVID-19 patients, although further research is required to confirm its effectiveness against this particular virus. With its versatility and proven track record, azithromycin continues to be a medication in modern healthcare.
Azithromycin, an antibiotic medication widely used today, effectively combats bacterial infections by obstructing protein synthesis within the bacteria itself. This mechanism empowers our immune system to eliminate these organisms more efficiently. Azithromycin exhibits spectrum activity, against various types of bacterial infections and can be relied upon for addressing respiratory, skin, and gastrointestinal ailments. Given its range of applications and well-documented efficacy, azithromycin remains a cornerstone of modern medical treatment.
Correct Dosage and Administration of Azithromycin
Azithromycin is an adaptable antibiotic that is commonly prescribed for a range of bacterial infections. It is essential to adhere to the recommended dosage and administration instructions in order to maximize its efficacy. In this section, we will delve into the guidelines for using azithromycin and provide helpful tips on how to administer it correctly.
Dosage Guidelines: Ensuring Proper Use of Azithromycin
The appropriate amount of azithromycin you should take depends on factors like the type and severity of your infection, your age, weight, and kidney function. In general;
- For respiratory infections in adults, it is usually recommended to take a single 500 mg dose on the first day, followed by 250 mg daily for four days.
- Children with ear or throat infections (acute otitis media or streptococcal pharyngitis) may be prescribed a single dose based on their body weight (10 20 mg/kg).
- In cases of transmitted diseases like chlamydia or gonorrhea in adults, your healthcare provider might prescribe a one-time dose of 1 2 grams based on your specific needs.
It is important to note that your healthcare provider will determine the suitable dosage for you. Make sure to follow their instructions and complete the entire course of medication, even if you start feeling better before finishing all the doses.
Key Tips for Azithromycin Administration: Enhancing Effectiveness
To make sure that azithromycin works effectively without causing many side effects, it's recommended to take it with food. Having azithromycin alongside a meal can help minimize issues like nausea or stomach pain. However, remember not to take antacids containing aluminum or magnesium within two hours or after your dose as they can affect its absorption.
It's important to stick to a schedule when taking azithromycin. This means taking it to maintain steady levels in your body, which enhances its effectiveness. If needed set reminders or alarms to ensure you take it at the time every day. Avoid missing doses of azithromycin, as this can reduce its efficacy and increase the risk of resistance.
If you happen to forget a dose, try to take it as soon as possible unless your next dose is due shortly. In that case, skip the missed dose. Continue with your regular dosing schedule. For advice related to your specific situation, consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. They will be able to provide tailored instructions based on your needs and circumstances. For information on using antibiotics correctly, you can also visit the Antibiotic Use page on the CDC's website.
In summary, azithromycin is an antibiotic used to treat infections. To ensure its effectiveness, follow the dosage and administration guidelines mentioned above – taking it with food, sticking to a consistent schedule, and avoiding missed doses. Remember that consulting with professionals is always advisable for individualized instructions.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Azithromycin
Like any other medication, Azithromycin may have some side effects, for certain patients. Although most individuals handle the drug well it's important to understand the risks that come with using it. In this section, we will talk about both uncommon side effects of azithromycin and consider how the benefits compare to any possible negative reactions.
Most people who take azithromycin usually don't have any side effects. However, a small number of users may experience some adverse reactions such as
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
These symptoms are usually temporary. Tend to resolve on their own without needing medical attention. If you happen to have severe headaches while using azithromycin, it would be wise to consult with a healthcare professional, for guidance.
A Closer Look at Rare but Serious Side Effects of Azithromycin
In uncommon instances, azithromycin may result in more severe adverse effects that require immediate medical attention. These include signs of a reaction such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips or throat hives, rash, and itching. Additionally, there is a possibility of experiencing a heart rhythm condition called a prolonged QT interval that could potentially lead to life-threatening arrhythmias (source). If you suspect a reaction or have concerns about your heart rhythm while taking azithromycin, it is crucial to seek emergency medical assistance without delay.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits: A Balanced View of Azithromycin Use
Like any medication, it's important to consider both the advantages and potential risks of using azithromycin. This antibiotic is effective in treating infections for many patients with minimal side effects. However, individuals who are at risk for antimicrobial resistance or have experienced drug interactions should discuss alternative treatment options with their healthcare provider.
To make a decision about azithromycin usage it's crucial to understand the possible side effects and risks by consulting with your doctor. By being aware of adverse reactions and recognizing rare but severe symptoms that require immediate attention, you can safely utilize this potent antibiotic to combat various bacterial infections.
Azithromycin is a medication prescribed for infections; however, it may lead to side effects like diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and headaches. In instances, it can also cause serious allergic reactions or abnormal heart rhythm conditions that necessitate immediate medical attention. It's important to weigh the benefits against potential risks and consult your healthcare provider before deciding on azithromycin usage.
Safety Measures When Using Azithromycin
To maximize the effectiveness of azithromycin and reduce any risks, it is essential to take necessary safety measures. In this section, we will provide guidelines on how to avoid any drug interactions with azithromycin and address considerations for individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Avoiding Potential Drug Interactions with Azithromycin
Like any medication, it's important to be aware of drug interactions that can happen when you're taking azithromycin. Some medicines may not mix well with azithromycin, which can reduce its effectiveness or increase side effects. To avoid these problems;
- Make sure to let your healthcare provider know about all the medications you're currently using, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter products, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
- Always consult with your doctor before starting any medications.
- If you have to take a medication that is known to interact with azithromycin (such as antacids containing aluminum or magnesium), follow your doctor's guidance on how to time the doses.
These precautions will help ensure the effective use of azithromycin without any unwanted interactions.
Azithromycin During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: What You Need to Know
Pregnant women should exercise caution when considering the use of antibiotics like azithromycin. Although studies indicate that it is generally safe, during pregnancy it is always advisable to consult your healthcare provider before commencing any treatment if you're pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
Similarly, breastfeeding mothers should also take care when using azithromycin. While the medication can pass into breast milk it usually does so in amounts that are unlikely to harm a nursing baby . Nonetheless discussing your options with your healthcare provider before starting any treatment remains important.
Monitoring Your Health During Azithromycin Treatment
To make sure you use azithromycin safely and effectively, it's important to follow these guidelines; Take the medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Don't skip doses. Stop taking it early without consulting your healthcare provider. Keep an eye out for any side effects and promptly inform your doctor if you notice any unusual symptoms or if your condition worsens.
If you have a reaction, such as difficulty breathing, hives, or swelling, seek emergency medical attention right away. By following these safety measures, you can maximize the benefits of azithromycin while minimizing risks. Remember to consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about drug interactions or other aspects of using this antibiotic safely.
To ensure the effective use of azithromycin, it is crucial to take safety precautions such as informing your healthcare provider about all medications you are currently taking to avoid potential drug interactions. Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should also exercise caution when using this antibiotic while being vigilant for side effects and promptly reporting any symptoms or worsening conditions to their doctor.
Procuring Azithromycin: Price and Accessibility
For patients, it can be quite a task to find the appropriate medication without breaking the bank. In this section, we will delve into the expenses associated with azithromycin. Discuss the pros and cons of both generic and brand name alternatives. Additionally, we will offer guidance on locating sources for purchasing this antibiotic, whether from brick-and-mortar pharmacies or online platforms.
Estimating the Cost of Azithromycin: A Comprehensive Guide
The price of azithromycin can vary depending on factors such, as the strength of the dosage, the quantity needed, whether it is a brand name or generic version, your location, and where you choose to make the purchase.
Generic vs. Brand-Name Azithromycin: Is There a Real Difference?
In some cases, there is usually no discernible difference in how effective or safe generic and brand name azithromycin are. The FDA has requirements that all approved generics must meet to ensure they are essentially the same as their branded counterparts in various aspects such as dosage form (like tablets), strength (such as 250 mg), route of administration (for example, oral) and quality performance characteristics like dissolution rate.
Regarding efficacy, both forms contain the active ingredient(s), so they should work equally well following prescription guidelines. When it comes to safety, generic drugs go through the same rigorous testing procedures as brand-name drugs to guarantee their suitability for consumption. Additionally, generic medications often come with a price tag compared to their branded counterparts, making them a more financially feasible option for many patients.
Finding Reliable Sources to Buy Azithromycin: Physical and Online Options
To ensure that you get a product, it is important to purchase azithromycin from a trusted source. If you prefer buying medication from pharmacies, it is advisable to visit reputable establishments that strictly adhere to the requirement of valid prescriptions before dispensing antibiotics like azithromycin.
In summary, this section examines the affordability and availability of azithromycin, including a comparison between brand name options. It also offers tips on finding reliable sources for purchasing this antibiotic both in physical pharmacies and online. The emphasis is placed on the significance of visiting establishments that insist on valid prescriptions or checking if websites are accredited by organizations like VIPPS.
Azithromycin in COVID Scientific Applications and Research
In the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists have been investigating treatments to combat the virus. One particular medication that has caught their attention is Azithromycin, an antibiotic commonly prescribed for infections. This section will delve into its role in managing COVID-19 cases and examine recent scientific discoveries on the topic.
Rationale for azithromycin
Azithromycin as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19
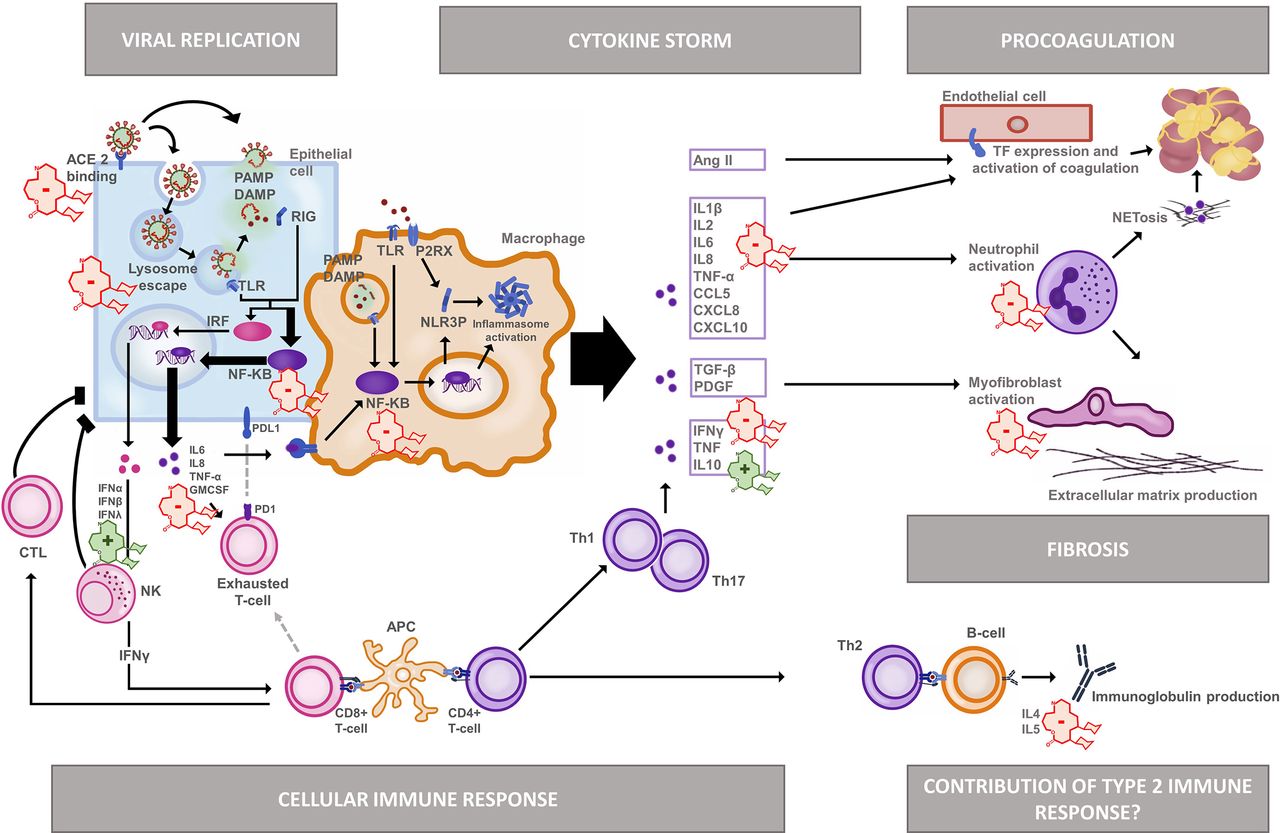
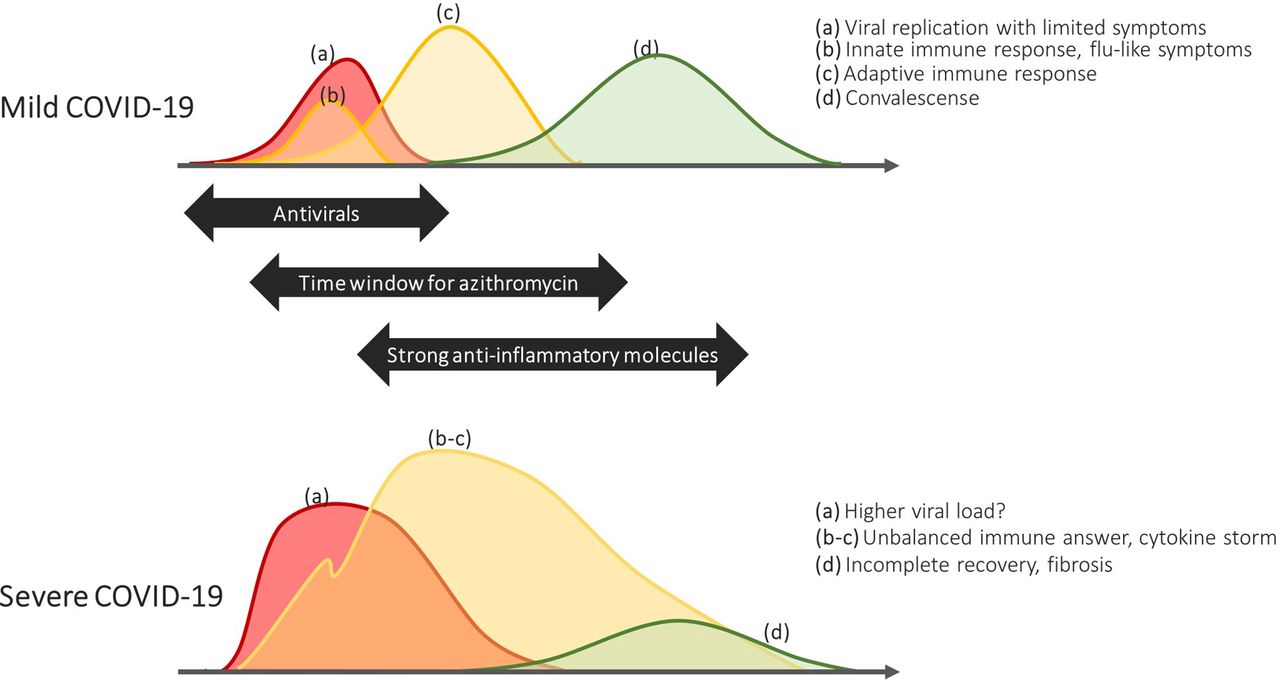
Although Azithromycin is mainly recognized as an antibiotic, it also has inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties that could potentially be helpful in managing viral infections like SARS-CoV-2 (the virus responsible for causing COVID-19). In the stages of the pandemic, there was a suggestion that combining azithromycin with other medications like hydroxychloroquine might have positive effects on patients, by reducing inflammation and inhibiting the replication of the virus.
Evidence from Clinical Trials and Studies
The RECOVERY Trial, a scale-based study called Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 therapy, examined various treatments for COVID-19. Among these treatments was azithromycin. The trial did not find any significant improvement in mortality or length of hospitalization for patients who received this drug compared to those who did not.
A number of observational studies have provided mixed results regarding the effectiveness of azithromycin when used in combination with hydroxychloroquine. Some studies showed a decrease in mortality rates, while others observed no differences among the groups that were treated.
Several randomized controlled trials have also been conducted to assess the benefits of using azithromycin for COVID-19 patients. However, due to limitations such as sample sizes and varying methodologies, the results remain inconclusive .

Azithromycin's Role in Current Treatment Guidelines
Based on the evidence, most health organizations do not recommend using azithromycin to treat COVID-19 unless it is prescribed for a bacterial co-infection. For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) explicitly advises against its use in clinical trial settings. Similarly, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) does not endorse the administration of azithromycin for COVID-19 patients without an established bacterial infection.
While there was hope that azithromycin could be a potential treatment option for COVID-19, current scientific evidence does not support its widespread use in managing this viral infection. Nevertheless, ongoing research may uncover insights into how this medication could contribute to combating the pandemic.
Researchers have been studying the potential of azithromycin, an antibiotic used to treat infections in managing COVID-19 cases, due to its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. However, based on scientific evidence and recommendations from health organizations, its widespread use in treating COVID-19 outside clinical trial settings is not supported unless it is prescribed for a bacterial co-infection.
Azithromycin and Alcohol Interactions
When you are prescribed any medication, it is crucial to understand the interactions it may have with other substances, such as alcohol. In this section, we will discuss the risks of combining azithromycin and alcohol and provide guidelines on how to safely consume these substances together.
Azithromycin: A Brief Overview
Azithromycin is a prescribed antibiotic used to treat different types of bacterial infections, including respiratory infections, skin infections, and gastrointestinal illnesses. It is important to understand how azithromycin interacts with alcohol in order to achieve the possible outcomes when taking the medication.
Potential Risks of Mixing Azithromycin and Alcohol
- Gastrointestinal effects: Both azithromycin and alcohol can cause issues in the system, such as feelings of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or stomach pain. If these two substances are combined, there is a chance of experiencing these side effects.
- Liver function: Although it is rare (seen in more than 1% of patients treated with azithromycin), there have been reports suggesting a connection between using azithromycin and liver damage.
- If you consume amounts of alcohol while taking this antibiotic, it could potentially worsen any existing risk factors for liver problems.
- Feeling drowsy or dizzy: Some individuals may feel drowsy or dizzy as a side effect when taking azithromycin. Consuming alcohol can make these effects more pronounced, affecting coordination and increasing the chances of accidents or injuries.
Guidelines for Combining Azithromycin and Alcohol Safely
While there is no prohibition against consuming alcohol while taking azithromycin, it is generally recommended to exercise moderation. Here are some tips for combining the two;
1. Alcohol intake: It's advisable to limit your alcohol consumption to a moderate level. For women, this means having up to one drink per day, while men can have up to two drinks per day while undergoing azithromycin treatment.
2. Avoid binge drinking: It's best to refrain from drinking sessions that could lead to intoxication. Intoxication may worsen side effects or interact negatively with the medication.
3. Monitor your body's response; Pay attention to how your body reacts when you consume both substances simultaneously. If you notice any symptoms or worsening side effects, it might be wise to abstain from alcohol until you've completed your course of antibiotics.
In summary, although there isn't a contraindication between azithromycin and alcohol use it is crucial always to exercise caution when mixing medications with alcoholic beverages.
By following the guidelines mentioned above, patients can minimize risks associated with this combination and ensure optimal results from their antibiotic treatment plan.
When taking azithromycin, it's important to be mindful of interactions with alcohol. Combining the two can increase the chances of experiencing issues and exacerbate any pre existing risk factors, for liver problems. To ensure consumption of both substances simultaneously, it is advisable to moderate your alcohol intake and closely observe how your body reacts.
FAQs in Relation to Buy Azithromycin
Can I Just Buy Azithromycin?
No it is not possible to purchase azithromycin without a prescription. Azithromycin is an antibiotic that should only be used under the guidance and prescription of a healthcare professional to ensure usage and dosage for your specific medical condition. It is always important to consult with a healthcare expert before taking any medication.
Can You Buy Azithromycin Over the Counter?
Azithromycin cannot be purchased without a prescription as it is a medication that requires a prescription, from a doctor or healthcare provider. Obtaining the prescription is essential to legally and safely acquire this antibiotic.
Why Is Azithromycin No Longer Recommended?
In some cases Azithromycin might not be the best choice due to the growing resistance of bacteria, leading to a decrease in its effectiveness against certain infections. Nonetheless, it continues to be a treatment option for various conditions as long as medical professionals prescribe it appropriately based on the specific needs and circumstances of each patient.
Can I Take Azithromycin Without Doctor Advice?
It's crucial to consult your doctor before taking azithromycin to avoid health risks. These risks include dosages, adverse side effects, or worsening of existing conditions. Following guidance when using antibiotics like azithromycin is essential for ensuring safe and effective treatment outcomes. If you're experiencing symptoms of infections, it's important to seek timely medical attention.
Delaying treatment can lead to complications. Potentially contribute to antimicrobial resistance. Additionally, make sure to inform your doctor about any medications you're currently taking to prevent potential drug interactions. Your doctor will be able to determine if azithromycin is suitable for your condition and medical history.
Understanding Azithromycin before purchasing it from us at Buy Pharma!
Azithromycin is a prescribed antibiotic that is often used to effectively treat different bacterial infections. It has also been extensively studied for its role in COVID-19 treatment protocols. When using this medication, it's crucial to follow the dosage and usage instructions, take into account any possible adverse reactions or risks, practice safety measures, and consider factors like affordability and availability.
It's worth noting that Azithromycin should not be consumed with alcohol as it may lead to interactions. If you're looking to purchase Azithromycin, you can visit Buy Pharma.md, where they offer competitively priced quality medications with shipping options.