1. Introduction to Femoston
What is Femoston?
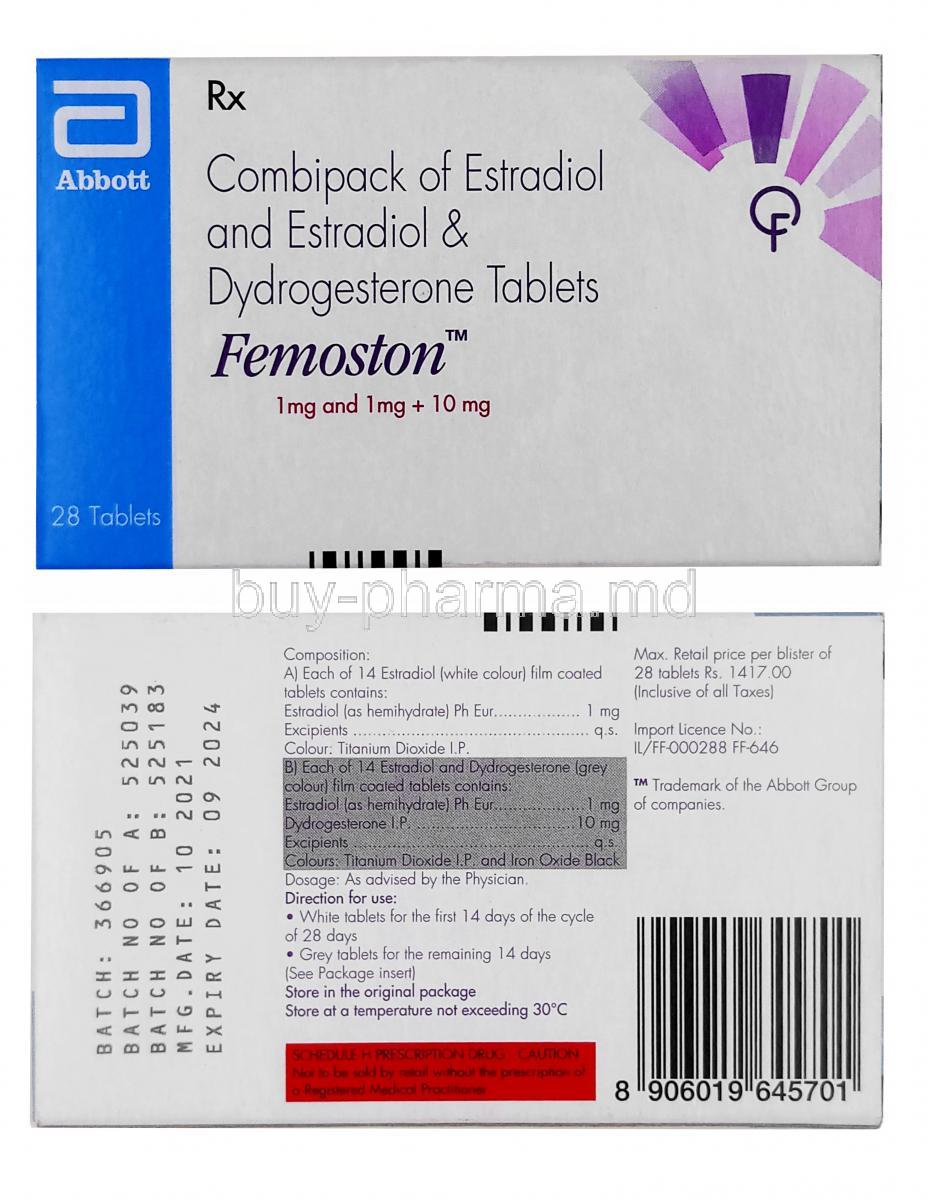
Femoston is a well-established oral hormone replacement therapy (HRT) that combines two key hormones—estradiol and dydrogesterone—to address estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal and perimenopausal women. It is designed to restore hormonal equilibrium, alleviating a range of menopause-related symptoms.
Overview of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT aims to compensate for declining endogenous hormone levels during menopause. It reduces vasomotor symptoms such as hot flashes, improves bone density, and supports urogenital health.
Purpose of Combining Estradiol and Dydrogesterone
- **Estradiol**: Replaces natural estrogen lost during menopause. - **Dydrogesterone**: A synthetic progestogen that counteracts estrogen’s effect on the endometrium, reducing the risk of hyperplasia and carcinoma.
Forms and Strengths Available
- Femoston 1/10: 1 mg estradiol + 10 mg dydrogesterone - Femoston 2/10: 2 mg estradiol + 10 mg dydrogesterone - Available in 28-day packs with 14 estrogen-only tablets followed by 14 combination tablets.
Regulatory Status and Approval History
Femoston is approved in numerous countries for HRT use, including within the EU and Asia-Pacific regions. It adheres to stringent pharmaceutical regulations and has been in clinical use for over two decades.
2. Composition and Pharmacological Classification
Active Ingredients: Estradiol Hemihydrate and Dydrogesterone
- Estradiol hemihydrate is a bioidentical estrogen. - Dydrogesterone is a selective progestogen with high oral bioavailability.
Pharmacologic Class
Femoston belongs to the **Estrogen/Progestogen combination** class used in sequential HRT regimens.
Tablet Composition and Color-Coding
- Estrogen-only tablets: typically light-colored (white or pink) - Combination tablets: slightly darker shades (orange or yellow) Each tablet contains precise hormone doses to ensure cyclic endometrial protection.
Inactive Ingredients and Formulation Specifics
Includes excipients such as lactose monohydrate, maize starch, hypromellose, and magnesium stearate, contributing to stability and absorption.
3. How Femoston Works in the Body
Mechanism of Action of Estradiol
Estradiol binds to intracellular estrogen receptors, initiating gene transcription. This leads to restored thermoregulatory balance, urogenital integrity, and bone mineralization.
Mechanism of Action of Dydrogesterone
Dydrogesterone exerts a progestogenic effect by binding to progesterone receptors, transforming the endometrium from proliferative to secretory, which is essential to prevent hyperplasia.
Role of Cyclic Hormone Replacement
Cyclic HRT mimics the natural menstrual hormone cycle, offering endometrial safety and regular withdrawal bleeding.
Hormonal Balance Restoration
Femoston is tailored for women experiencing estrogen deficiency, promoting physiological stability and symptom control.
4. Approved Uses of Femoston
- Alleviation of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (e.g., hot flushes, night sweats)
- Prevention of osteoporosis in high-risk postmenopausal women intolerant to non-estrogen therapies
- Improvement of urogenital symptoms such as vaginal dryness, dyspareunia, and urgency
- Management of irregular menstrual cycles during the menopausal transition
5. Off-Label Uses of Femoston
- Hormonal support in women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI)
- Treatment of secondary amenorrhea unrelated to anatomical abnormalities
- Adjunctive hormonal therapy in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Perimenopausal mood stabilization where psychiatric comorbidities are hormone-sensitive
- Part of hormone replacement protocols in assisted reproductive technologies
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Starting Dose and Titration
- Typically initiated at Femoston 1/10. - May be adjusted to Femoston 2/10 based on symptom control and endometrial response.
Cyclic vs. Continuous Regimens
- Cyclic: Recommended for women with intact uteri to mimic menstrual patterns. - Continuous: Reserved for long-term therapy when bleeding is no longer desired.
Guidelines for Switching from Other HRTs
- Direct switch allowed without washout in most cases. - Clinical evaluation necessary before transition.
Missed Dose Instructions
- Missed dose within 12 hours: take immediately. - If >12 hours: skip missed tablet and continue with the next dose.
Administration with or Without Food
- Oral administration once daily, preferably at the same time each day. - Food does not significantly impact absorption.
7. Common and Serious Side Effects of Femoston
7.1 Common Side Effects
- Breast tenderness or enlargement
- Breakthrough bleeding or spotting
- Headache, dizziness, or nausea
- Mild mood fluctuations and water retention
7.2 Serious Adverse Reactions
- Increased risk of venous thromboembolism (e.g., DVT, pulmonary embolism)
- Potential for endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma without adequate progestogenic support
- Long-term use may be associated with an increased risk of breast malignancy
- Liver function abnormalities and risk of gallstone formation
- Migraine exacerbation and visual disturbances
8. Important Precautions Before and During Use
- HRT should only be prescribed at the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary
- Annual reassessment of cardiovascular and oncologic risk
- Routine gynecologic exams and mammography are mandatory
- Patients should be informed of early symptoms of thromboembolic events
- Use with caution in women who smoke or consume alcohol regularly
9. Contraindications to Femoston Therapy
- Known or suspected breast cancer or other estrogen-dependent malignancies
- History or current evidence of venous thromboembolism or arterial thrombotic events
- Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Active or severe liver disease, including hepatic tumors
- Pregnancy and known allergy to estradiol, dydrogesterone, or any excipients
10. Warnings and Risk Factors
Long-Term Use and Breast Cancer Surveillance
Prolonged administration of estrogen-progestogen combinations, such as Femoston, has been associated with a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer. The risk escalates with treatment duration and diminishes gradually after cessation. Therefore, routine breast screening—including mammography—is essential, particularly in patients undergoing long-term therapy.
Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Risk
Hormone replacement therapy may marginally elevate the risk of thromboembolic and ischemic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke. The risk is further amplified in smokers and women with underlying hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or diabetes mellitus. Vigilant cardiovascular assessment is imperative before initiating therapy.
Increased Risk of Gallbladder Disease
Estrogen influences bile composition and flow, heightening the incidence of gallstones and cholecystitis in susceptible individuals. Femoston should be used cautiously in patients with a history of biliary disorders.
Worsening of Pre-Existing Conditions
Femoston can exacerbate certain chronic conditions, including:
- Epilepsy – possible increased seizure frequency
- Asthma – estrogen may affect airway reactivity
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Hepatic dysfunction
Monitoring Thyroid Function in Those on Thyroid Hormone Therapy
Estrogens increase serum thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG), which may alter total thyroid hormone levels. In patients on levothyroxine, careful monitoring and dosage adjustments may be required to maintain euthyroidism.
11. Drug Interactions with Femoston
Effects of CYP3A4 Inducers and Inhibitors
Estradiol metabolism is mediated by the CYP3A4 enzyme system. Concomitant use of:
- Inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenobarbital): may reduce efficacy
- Inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole): may increase systemic exposure
Monitoring is advised when Femoston is used alongside these agents.
Impact of Antiepileptic Drugs
Medications such as carbamazepine and phenytoin accelerate hepatic metabolism of estrogens and progestogens, reducing the therapeutic effect of Femoston. Alternative HRT strategies may be required for epileptic patients.
Interaction with St. John’s Wort
St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum), a popular herbal remedy, can significantly induce estrogen metabolism. Its concurrent use may result in breakthrough bleeding and decreased symptom control.
Effect on Binding Globulins and Other Hormone Therapies
Femoston may alter serum concentrations of hormone-binding globulins, including corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG) and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). This can affect the pharmacodynamics of co-administered hormonal agents.
Altered Efficacy with Anticoagulants and Corticosteroids
Estrogens may interfere with the action of warfarin and other oral anticoagulants. Additionally, they can alter corticosteroid metabolism, requiring dose modifications in concurrent steroid therapy.
12. Administration in Special Populations
12.1 Use in Elderly Women
In women over 65, the benefits of HRT must be weighed against potential risks such as cognitive decline and vascular complications. Lower starting doses are advisable, with ongoing clinical evaluation. Research has shown that prolonged HRT may increase the likelihood of dementia in older age groups.
12.2 Use in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
- **Pregnancy**: Femoston is classified as Category X and is contraindicated. Exposure during pregnancy may lead to fetal harm, including genital abnormalities. - **Lactation**: There is no established benefit for using HRT during breastfeeding. Hormonal components may be excreted in breast milk and affect infant development.
12.3 Pediatric and Adolescent Use
Femoston is not indicated for children or adolescents. Off-label use in hormonal disorders such as delayed puberty or amenorrhea is not recommended due to the lack of safety data and potential for growth disturbances.
13. Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose
Excessive ingestion may result in:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Breast tenderness
- Abdominal pain or withdrawal bleeding
Immediate Steps in Case of Accidental Ingestion
If overdose is suspected, symptomatic treatment should be initiated. No specific antidote exists for estrogen or progestogen overdose.
Poison Control Consultation and Supportive Care
Consultation with a poison control center is advised for risk assessment. Supportive care including fluid management and antiemetics may be warranted.
14. Storage and Stability Information
Recommended Storage Temperature Range
Store Femoston tablets at room temperature, ideally between 15°C and 30°C (59°F–86°F), to maintain potency and shelf life.
Protect from Moisture, Heat, and Light
Do not store the medication in humid areas such as bathrooms. Keep away from direct sunlight and extreme heat to prevent degradation.
Shelf Life and Expiration Guidance
Refer to the manufacturer’s packaging for expiration dates. Do not use tablets past the expiration date, as hormonal efficacy and safety may be compromised.
Handling of Blister Packs and Opened Tablets
Tablets should remain in the original blister pack until the time of use. Avoid unnecessary handling and ensure dry hands during removal.
15. Handling and Dispensing Precautions
Pharmacist Guidelines for Proper Dispensing
- Verify indication and patient eligibility before dispensing - Ensure correct strength and cyclic regimen are provided - Counsel on missed dose protocol and side effect reporting
Patient Counseling Points
- Explain the importance of adherence and regular follow-up - Advise on potential drug interactions and symptom monitoring - Reinforce the need for routine breast and pelvic exams
Disposal of Expired or Unused Medication
Do not flush down the toilet or pour into drains. Return expired medication to a pharmacy take-back program or dispose of following local regulations.
Avoiding Accidental Ingestion by Children
Store the medication in a secure location, out of reach of children. Blister packs should be kept intact and returned to their outer carton after each use.