Fratin
- I. Introduction to Fratin
- II. Composition of Fratin
- III. How Fratin Works
- IV. Uses of Fratin
- V. Off-Label Uses of Fratin
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Administration to Special Populations
- VIII. Side Effects of Fratin
- IX. Important Precautions and Warnings
- X. Interaction with Other Medications
- XI. Overdosage of Fratin
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
I. Introduction to Fratin
A. Overview of Fratin
Fratin is a pharmaceutical product carefully developed to tackle various health issues. Its formulation is based on the research findings and provides hope for patients with specific medical conditions.
B. Historical Background and Development
Fratins origin can be traced back to an advancement in medical science. The development of this medication involved a process that included thorough research, extensive testing, and a solid dedication to pushing the boundaries of healthcare innovation.
II. Composition of Fratin
A. Active Ingredients
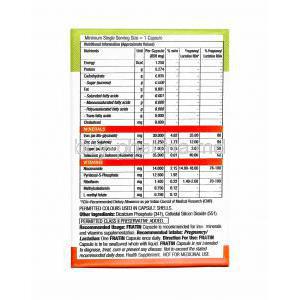
The effectiveness of Fratin primarily depends on its components. Fratin is a medicine that contains iron and folic acid as its active ingredients 12
III. How Fratin Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Fratin functions by employing a mechanism that acts directly on cells to alter biological reactions. The focused nature of its approach demonstrates the accuracy and refinement of pharmacology.
B. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetic profile describes how Fratin interacts with the body, including how it's absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated. On the other hand, pharmacodynamics focuses on understanding the physiological and biochemical effects of the drug.
IV. Uses of Fratin
A. Primary Indications and Therapeutic Benefits
It is used to treat iron and folic acid deficiency, which can lead to anemia characterized by weakness, fatigue, difficulty in breathing, headache, irritability, and difficulty in concentration 12.
V. Off-Label Uses of Fratin
A. Exploring Non-Approved Applications
The use of Fratin for purposes not officially approved has garnered attention due to reports and preliminary studies.
VI. Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
Fratin's recommended dosage follows guidelines that are carefully designed to maximize the effectiveness of the treatment while minimizing any potential risks.
B. Dosage Adjustments for Specific Populations
Dosage adjustments are necessary for groups of people considering factors such as age, existing health conditions, and the use of other medications at the same time.
VII. Administration to Special Populations
A. Elderly Patients: Special Considerations
Fratin should be administered carefully for patients, keeping a close watch for any possible changes in how the medication affects their body and how their body processes the drug.

B. Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risks and Recommendations
When administering Fratin to women and nursing mothers, it is essential to evaluate the potential risks and benefits thoroughly, always prioritizing safety as the primary concern.
C. Pediatric Use: Safety and Efficacy
In the field of medicine, it is crucial to carefully calibrate Fratins dosage and administration for the safety and effectiveness of younger patients.
VIII. Side Effects of Fratin
A. Common Side Effects: Identification and Management
Typical adverse effects of Fratin, although controllable, require quick identification and suitable interventions. These consist of;
- Constipation,
- flushing,
- diarrhea, or
- upset stomach
IX. Important Precautions and Warnings
A. Contraindications: When to Avoid Fratin
Fratins' contraindications are crucial to consider preventing its utilization in situations where the potential benefit is overshadowed by the risk.
B. Careful Administration: Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies
To make sure that Fratin is administered safely it is essential to monitor and put in place strategies to minimize any potential risks.
X. Interaction with Other Medications
A. Known Drug Interactions
Fratins interaction with medications may cause changes in the desired treatment outcomes, so it is essential to carefully assess the patient's current medication regimen.

B. Impact on Diagnostic Tests
Fratin can affect the outcomes of diagnostic tests, which means that healthcare providers need to consider this impact when interpreting the results.
XI. Overdosage of Fratin
A. Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
The signs of a Fratin overdose consist of symptoms that can appear in different degrees of severity. It is essential to recognize and intervene when these symptoms arise.
Some essential indications include issues like:
- feeling dizzy or disoriented,
- gastrointestinal discomforts such as experiencing nausea or vomiting, and
- Cardiac irregularities that could lead to palpitations or arrhythmias.
While this list is not exhaustive, it serves as a guideline for identifying Fratin overdosing early.
B. Emergency Management and Antidotes
When someone experiences an overdose, it is vital to seek medical help. The primary focus in managing a Fraction overdose is to stabilize the patient's signs, ensuring their heart and breathing are functioning correctly. Depending on the severity of the overdose and the symptoms shown, specific antidotes may be administered. Supportive care also plays a role in the emergency response, including managing fluids and treating symptoms. Healthcare providers must be adaptable in their management strategies as the clinical situation evolves.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Proper Storage Conditions
The effectiveness and safety of Fratin are closely connected to how it's stored. To ensure its therapeutic value remains intact, it is essential to store Fratin in the way:
- Keep it at a controlled room temperature away from direct sunlight and moisture.
- Store it in its original packaging to prevent any contamination or degradation.
- Make sure it is out of reach of children to avoid any ingestion. Following these storage guidelines is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of Fratin.
B. Safe Handling and Disposal Practices
Properly managing and getting rid of Fratin requires adherence to safety protocols. It's essential to consider key factors, such as:
- using protective gear like gloves when handling the medication especially if its damaged or broken.
- Additionally, it's crucial to follow regulations for disposing of Fratin correctly to minimize any negative environmental impact and prevent misuse.
- Education is also essential in informing patients and caregivers, about disposal practices emphasizing the importance of taking care of the environment and ensuring everyones safety.
By implementing these measures we can significantly reduce the risks associated with mishandling and disposal of Fratin.