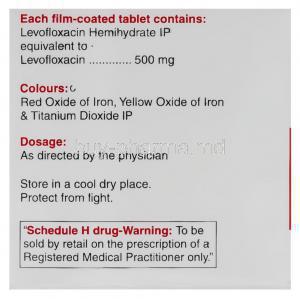
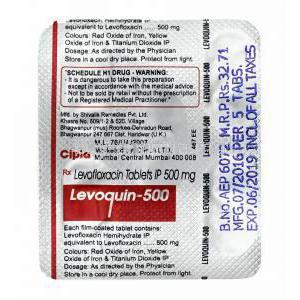
Levofloxacin
Uses
Levoquin is used in the treatment of different types of bacterial infections such as infections on the skin, sinuses, kidneys, bladder, prostate, eye Levoquin is also used in the treatment of tuberculosis (tb).
How it Works
Levoquin is known as a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Levoquin works by helping to kill the bacteria which are causing the infection. Levoquin kills bacteria by inhibiting the DNA replication.
Common Side effects
Some of the potential side effects of Levoquin can include the symptoms below;
Nausea,
Diarrhoea,
Allergic reaction