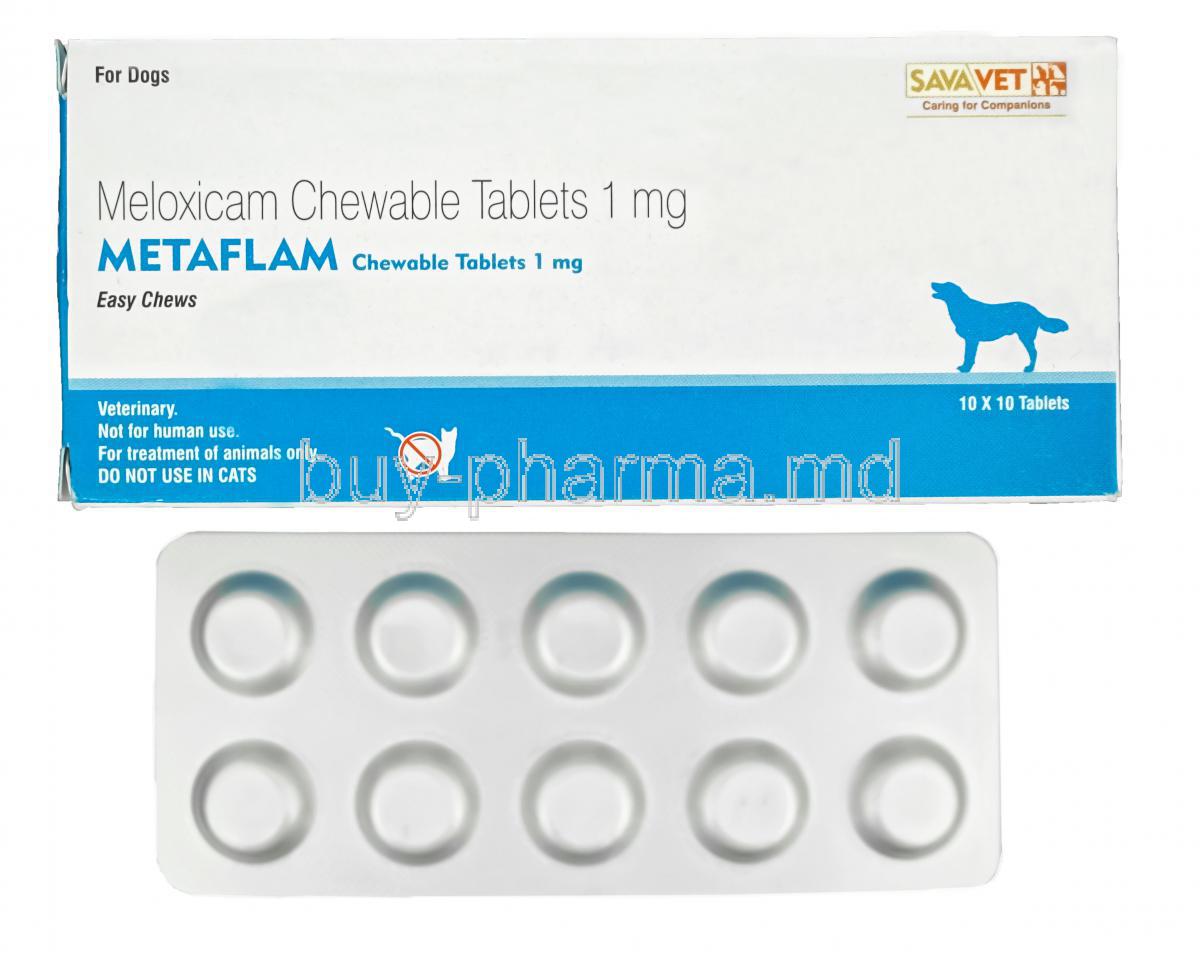
Introduction to Metaflam Chewable Tablets
Overview of Metaflam and its Classification as an NSAID
Metaflam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) formulated specifically for canine use. Its primary role lies in managing pain and inflammation associated with a wide range of musculoskeletal and postoperative conditions in dogs. As a veterinary analog of meloxicam, Metaflam delivers targeted therapeutic effects with a favorable safety profile.
Purpose of Meloxicam in Veterinary Medicine
Meloxicam, the active compound in Metaflam, is widely utilized for its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. In veterinary settings, it is commonly prescribed for the relief of chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis as well as for acute inflammation resulting from surgery or injury.
Benefits of Chewable Administration for Canine Compliance
- Palatable flavoring enhances voluntary ingestion - Eliminates the stress of forceful administration - Enables accurate dosing with scored tablets - Improves adherence to long-term treatment plans
Composition and Active Ingredients of Metaflam
Active Ingredient: Meloxicam (Concentration per Tablet)
Each Metaflam chewable tablet contains a precise amount of meloxicam, typically available in strengths such as 1.0 mg, 2.5 mg, or 5.0 mg, allowing for tailored dosing based on body weight.
Inactive Excipients and Formulation Details
The formulation includes excipients designed for chewability and flavor, such as: - Lactose monohydrate - Microcrystalline cellulose - Beef flavoring agents (non-allergenic) - Sodium starch glycolate
Available Tablet Strengths and Flavoring Agents
Metaflam is produced in several dosages for veterinary flexibility. The tablets are often beef-flavored to increase palatability, making daily administration easier for both pets and owners.
Mechanism of Action: How Meloxicam Works in Dogs
Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase (COX-2) Enzyme Activity
Meloxicam selectively inhibits the COX-2 isoenzyme responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins that mediate inflammation and pain, sparing COX-1 to preserve gastric and renal function.
Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic, and Antipyretic Effects
- Suppresses production of inflammatory mediators - Alleviates soft tissue and joint pain - Reduces fever by modulating hypothalamic responses
Comparison to Other Veterinary NSAIDs
Compared to older NSAIDs like phenylbutazone or aspirin, meloxicam offers: - Greater COX-2 selectivity - Lower gastrointestinal risk - Better tolerability in long-term use
Approved Veterinary Uses of Metaflam Chewable Tablets
Relief of Inflammation and Pain Associated with Osteoarthritis
Metaflam is indicated for chronic conditions such as canine osteoarthritis, significantly reducing lameness, stiffness, and mobility limitations.
Post-Operative Pain Management (Orthopedic and Soft Tissue Surgery)
Used both preemptively and postoperatively, meloxicam minimizes surgical inflammation and discomfort, promoting faster recovery.
Management of Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Muscle strain - Tendonitis - Traumatic injuries
Acute and Chronic Conditions Involving Lameness and Stiffness
Suitable for both sudden-onset lameness and long-term degenerative joint disease, providing continuous relief with proper dosing.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses of Meloxicam in Dogs
Use in Dogs with Cancer-Related Pain
Meloxicam may be used off-label to manage bone or soft tissue cancer pain, especially in palliative care.
Use in Dental Pain Management
Following dental extractions or oral surgeries, meloxicam provides effective analgesia for acute pain.
Potential Application in Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD)
Although not formally approved, meloxicam is often employed to reduce inflammation and spinal pain in cases of IVDD.
Considerations for Extra-Label Use Under Veterinary Supervision
- Requires careful risk-benefit analysis - Adjusted dosing based on underlying conditions - Must follow regulatory guidelines on extra-label veterinary drug use (ELDU)
Recommended Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Initial Dosing (Loading Dose) and Maintenance Dosing Strategy
Typically initiated with a loading dose of 0.2 mg/kg, followed by a maintenance dose of 0.1 mg/kg once daily.
Weight-Based Dosage Recommendations (mg/kg)
- Dogs under 10 kg: individualized dosing via scored tablets - Larger dogs: full tablet strengths as per weight tiers
Frequency and Duration of Therapy
- Once daily oral administration - Duration depends on condition (e.g., post-op vs chronic arthritis)
Administration Tips: With or Without Food, Palatability
- Can be given with or without food - Chewable flavor eases direct administration - Encourage ingestion with treats or after meals
Important Precautions for Safe and Effective Use
Importance of Veterinary Assessment Prior to Initiation
Pre-treatment evaluation of liver and kidney function is essential to prevent adverse events.
Monitoring During Long-Term Therapy
- Periodic blood work (BUN, creatinine, ALT/AST) - Assessment of appetite, energy, and urination patterns
Use in Dogs with Hepatic or Renal Impairment
- Dosage adjustments may be required - Contraindicated in severe hepatic or renal insufficiency
Importance of Hydration and Regular Follow-Ups
Adequate hydration minimizes renal strain. Scheduled follow-ups help adjust dosing and monitor safety.
Common and Serious Side Effects of Metaflam in Dogs
Frequently Observed Side Effects
- Vomiting - Soft stool or diarrhea - Reduced appetite - Lethargy
Rare but Serious Adverse Reactions
- GI ulceration and bleeding - Acute kidney injury - Anaphylactoid reactions
Signs Requiring Immediate Veterinary Attention
- Blood in vomit or feces - Persistent vomiting - Jaundice or excessive thirst - Collapse or seizures
Reporting Adverse Events to Veterinary Authorities
Pet owners and veterinarians are encouraged to report reactions to pharmacovigilance databases for NSAIDs.
Drug Interactions and Concomitant Use Considerations
Interaction with Corticosteroids and Other NSAIDs
Co-administration increases the risk of gastrointestinal complications and should be strictly avoided.
Caution with Nephrotoxic Drugs or ACE Inhibitors
Concomitant use may exacerbate renal toxicity, particularly in volume-depleted dogs.
Synergistic or Antagonistic Effects with Other Medications
- Diuretics may reduce meloxicam clearance - Potential masking of pain symptoms when used with sedatives
Time Interval Required Between Different NSAID Therapies
A washout period of 5–7 days is typically advised before transitioning to or from another NSAID.
Contraindications: When Metaflam Should Not Be Used
Known Hypersensitivity to Meloxicam or Other NSAIDs
Dogs with a history of allergic reactions to NSAIDs must not receive Metaflam.
Pre-Existing GI Ulcers or Active Bleeding Disorders
Meloxicam can exacerbate gastrointestinal and coagulation issues, increasing the risk of severe outcomes.
Severe Renal, Hepatic, or Cardiac Dysfunction
Organ-compromised animals are more susceptible to NSAID-related toxicity and should be managed with alternative treatments.
Use in Dehydrated or Hypotensive Animals
Administration in dehydrated dogs can precipitate acute renal failure; rehydration is essential before starting therapy.
Warnings and Black Box Alerts for Veterinary Use
Risk of Gastrointestinal Perforation and Bleeding
Meloxicam, like all NSAIDs, carries the potential to cause serious gastrointestinal complications. These include mucosal erosion, ulceration, and in severe cases, gastrointestinal perforation with internal bleeding. The risk increases with long-term use, pre-existing GI conditions, or concurrent administration of corticosteroids.
Use Only Under Direct Veterinary Supervision
Veterinary oversight is critical during meloxicam therapy to ensure appropriate dosing, identify contraindications, and monitor for adverse effects. Regular clinical evaluations and laboratory tests are recommended for dogs receiving prolonged treatment.
Warning Against Use in Cats Unless Specifically Prescribed
Meloxicam has a narrow safety margin in felines. Its use in cats should be limited to specific veterinary indications and formulations approved for that species. Even a single overdose can be fatal in cats due to their limited ability to metabolize NSAIDs.
Careful Administration in Special Canine Populations
Use in Geriatric Dogs
Elderly dogs often exhibit reduced hepatic and renal clearance, increasing their susceptibility to NSAID toxicity. Age-related changes in body composition may also influence drug distribution and plasma concentrations.
- Lower initial dosages are recommended
- Close monitoring of kidney and liver function is essential
- Frequent re-evaluation of therapy necessity is advised
Use in Pregnant, Breeding, and Lactating Dogs
The safety of meloxicam in pregnant and nursing dogs has not been fully established. Prostaglandin inhibition may interfere with labor and embryonic development.
- Use only if the potential benefit outweighs the risk
- Avoid during late gestation unless medically indicated
- Monitor nursing puppies for signs of NSAID exposure
Use in Puppies and Juvenile Dogs
Data regarding meloxicam use in puppies under 6 months is limited. Their immature organ systems may impair drug metabolism and excretion.
- Avoid use in very young dogs unless clearly warranted
- Alternative analgesics may be more suitable
- Monitor growth and behavior closely during treatment
Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose (GI Bleeding, Seizures, Renal Failure)
An overdose of meloxicam can result in significant toxicity, presenting as:
- Profuse vomiting, sometimes with blood
- Black or tarry stools (melena)
- Seizures or tremors
- Oliguria or anuria indicating acute kidney injury
Immediate Steps in Suspected Overdose Situations
- Contact a veterinarian or emergency animal poison control immediately - Discontinue the medication - Provide details on the dose ingested and time of ingestion
Decontamination and Supportive Care Protocols
Veterinary interventions may include:
- Induction of emesis if recent ingestion
- Activated charcoal to limit systemic absorption
- Intravenous fluids to support renal function
- Gastroprotective agents and anti-seizure medications as needed
Proper Storage and Shelf-Life Guidelines
Ideal Storage Temperature and Humidity Conditions
Store Metaflam chewable tablets at controlled room temperature (20°C–25°C / 68°F–77°F). Avoid high humidity and fluctuations in temperature that may compromise tablet stability.
Protection from Light and Moisture
Keep the product in its original blister packaging until use to shield it from light and moisture. Exposure to these elements may degrade the active ingredient.
Shelf-Life After Opening or Partial Tablet Use
Unused portions of tablets should be stored securely and used within the timeframe specified in the prescribing information, typically within a few days. Discard if the tablet shows signs of discoloration or crumbling.
Safe Disposal of Expired or Unused Tablets
Do not flush or dispose of veterinary drugs in household trash. Follow local pharmaceutical disposal guidelines or return to a veterinary clinic with drug take-back services.
Handling Precautions and Owner Instructions
Safe Handling by Pet Owners, Especially Children
Keep all medication out of reach of children. Although flavored for canine use, ingestion by humans—especially children—may result in toxicity or allergic reaction.
Hand Washing After Administration
Always wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling the tablet, particularly if it has been broken or crushed. Avoid touching eyes, mouth, or face during administration.
Avoiding Accidental Ingestion by Humans or Other Pets
- Do not leave tablets unattended or accessible to other animals - Store in a child-proof container - In case of accidental ingestion, contact poison control or seek immediate medical attention