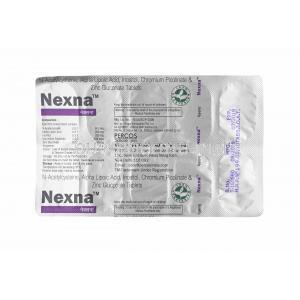
Nexna
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Nexna
- III. How Nexna Works
- IV. Uses of Nexna
- V. Off-Label Use of Nexna
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Side Effects of Nexna
- VIII. Interactions of Nexna
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Important Precautions
- XI. Administration to Special Populations
- XII. Overdose and Emergency Management
- XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
A. Overview of Nexna
Nexna, a pharmaceutical breakthrough, has emerged as a crucial player in medicine. Its exceptional composition and wide range of uses have made it a preferred medication for treating health conditions.
B. Historical Development and FDA Approval
The story of Nexna from its inception to receiving FDA approval showcases its dedication to research and groundbreaking innovation. After undergoing clinical trials, Nexna has established a new standard for its effectiveness as a therapeutic treatment.
C. Significance in Modern Medicine
Today Nexna has become a pillar in contemporary therapeutic approaches providing solutions when conventional treatments are not sufficient. Its importance in pushing forward healthcare is beyond question.
II. Composition of Nexna
A. Active Ingredients and Their Roles
The effectiveness of Nexna lies in its chosen active components. Each ingredient has been thoroughly selected based on its pharmacological properties, which play a crucial role in the overall therapeutic benefits of the medication. The composition of Nexna varies depending on the type of product. For example, Nexna TX Tablet contains Tranexamic acid 1, while Nexna Tablet contains Alpha Lipoic Acid, Chromium Picolinate, Inositol, N Acetylcysteine, and Zinc Gluconate 2.

B. Excipients and Their Functions
In addition to the ingredients, Nexna also includes certain essential substances for improving the stability of the medication, its ability to be absorbed by the body, and making it easier for patients to take.
III. How Nexna Works
A. Mechanism of Action in the Body
Nexna functions by employing a method of operation focusing on particular pathways within the body to produce its beneficial outcomes.
B. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
How Nexna is processed and interacts with the body is crucial in understanding its characteristics, such as the correct dosage, effectiveness, and safety factors.
IV. Uses of Nexna
A. Primary Indications and Therapeutic Benefits
Nexna TX Tablet is a medication used to treat bleeding. It helps to prevent or reduce bleeding in conditions like tooth removal, heavy periods, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, nosebleed, and in any oral, prostate, or bladder surgery 1. It is an anti-fibrinolytic that works by preventing the breakdown of clots which leads to the stoppage of bleeding 1.
B. Spectrum of Diseases and Conditions Treated
Nexan's therapeutic range covers a variety of diseases and conditions, highlighting its versatility as a pharmaceutical treatment.
V. Off-Label Use of Nexna
A. Exploring Non-FDA Approved Applications
Although Nexna is officially approved for purposes, there is growing evidence suggesting its potential in other fields, which has led to the exploration of off-label applications backed by emerging research.
B. Case Studies and Research Findings
There have been instances where case studies and research findings have shown that Nexna can be used for purposes other than what it was initially approved for. This indicates that Nexna has the potential to be beneficial beyond its approved uses.
VI. Dosage and Administration
A. Recommended Dosages for Various Conditions
The recommended dosage of Nexna depends on the condition and is customized to ensure its effectiveness while minimizing potential risks. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage based on how the patient responds to the treatment and their tolerance levels.

B. Administration Methods and Techniques
The successful management of Nexna necessitates the following approaches and methodologies to ensure that drug administration is effective and patient outcomes are optimized.
VII. Side Effects of Nexna
A. Common Side Effects and Management
The most common side effects of Nexna TX Tablet include tiredness, nasal congestion, and pain in muscle, bone, or joint 23. Other side effects may include pain in the chest, cough, shortness of breath, swelling of limbs, fatigue, etc123. If any of these side effects persist or worsen, it is recommended to consult a doctor 123.
B. Rare but Serious Adverse Reactions
Though they are not common, there have been instances where people have experienced serious adverse reactions. It's essential to monitor and seek medical attention promptly in such situations.
VIII. Interactions of Nexna
A. Drug-Drug Interactions and Risks
Using Nexna with medications requires careful evaluation of possible interactions and associated risks.
B. Food and Lifestyle Interactions
Certain foods and the way we live can have an impact on how Nexna works and how safe it is, which is why it's essential for patients to be educated and make adjustments, to their lifestyle.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
A. Identifying High-Risk Groups
It is crucial to prioritize the recognition and identification of high-risk groups to ensure the administration of this medication.
Specific populations, including individuals with existing conditions or those taking other medications at the same time, may encounter increased risks. Conducting assessments and remaining vigilant, in screening these groups are vital to prevent any potential adverse effects.
B. Conditions Warranting Caution
Some medical conditions require the use of this medication. Patients who have had irregularities in hepatic or renal impairments need to be monitored closely and may need adjusted dosing protocols to ensure their safety.
X. Important Precautions
A. Monitoring and Safety Measures
To ensure the effectiveness of the treatment, it is crucial to monitor and implement safety measures.
- This involves conducting blood tests to assess the functioning of organs and keeping a close eye on any signs of adverse reactions.
- These precautions are necessary for the detection and effective management of possible complications.

B. Managing Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
Establishing protocols for managing allergic reactions in patients with known allergies or sensitivities is extremely important. This involves stopping medication administration and providing suitable countermeasures, such as antihistamines or corticosteroids if severe reactions occur.
XI. Administration to Special Populations
A. Elderly Patients: Adjustments and Considerations
Elderly individuals often need consideration due to the natural physiological changes that come with aging.
- Some of these considerations may include adjusting medication dosages or scheduling increased monitoring for side effects or drug interactions. It is crucial to customize treatment plans according to the requirements of these patients.
B. Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety and Risks
The safety of this medication for women and nursing mothers is not fully established. It is essential to consider the potential risks to the fetus or infant compared to the therapeutic benefits for the mother. In situations, alternative treatment options should be taken into account.
C. Pediatric Use: Guidelines and Limitations
Strict guidelines and restrictions bind the usage of this medication in populations. It is important to note that the effectiveness and safety of the drug may vary considerably between children and adults. Therefore it is crucial to make dosage adjustments and closely monitor its effects in children.
XII. Overdose and Emergency Management
A. Recognizing Symptoms of Overdosage
It is crucial to identify the signs of taking too much medication to ensure timely intervention.
Some symptoms to watch out for may include experiencing dizziness or fainting, difficulty breathing, and shortness of breath. In situations where seeking immediate medical attention is vital.
B. Immediate Steps and Antidotes
If someone experiences an overdose, it is crucial to act to minimize the impact. This involves providing antidotes if they are accessible and offering symptomatic care to stabilize the individual.
XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Optimal Storage Conditions
It is essential to store the medication to ensure its effectiveness and safety. This involves keeping it at room temperature, away from light and moisture, and out of reach of children.
B. Safe Handling and Disposal Methods
It is crucial to handle and dispose of medication safely to avoid any exposure or harm to the environment. Following the regulations when disposing of unused or expired medication is recommended.