Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose/ N-Acetyl-Carnosine/ Glycerin Eye Drops
- 1. Introduction to Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose / N-Acetyl-Carnosine / Glycerin Eye Drops
- 2. Active Ingredients and Comprehensive Composition
- 3. Mechanism of Action: How the Eye Drops Work at a Cellular Level
- 4. Approved Medical Uses of the Eye Drops
- 5. Off-Label and Investigational Uses
- 6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Optimal Efficacy
- 7. Common and Uncommon Side Effects
- 8. Drug and Supplement Interactions
- 9. Contraindications and When Not to Use the Drops
- 10. Warnings and Important Safety Precautions Before Use
- 11. Guidelines for Careful Administration in Specific Populations
- 12. Signs and Management of Overdose or Accidental Ingestion
- 13. Storage and Handling Instructions
- 14. Handling Precautions and Disposal Best Practices
1. Introduction to Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose / N-Acetyl-Carnosine / Glycerin Eye Drops
This advanced ophthalmic solution integrates three synergistic components Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose, N-Acetyl-Carnosine, and Glycerin designed to support ocular surface integrity and comfort. By combining lubrication, antioxidant protection, and cellular hydration, this formulation offers multi-tiered therapeutic benefits for individuals suffering from various forms of ocular surface disorder.
Originally developed as part of emerging strategies to address chronic dry eye and oxidative stress-related ocular degeneration, this formulation represents a significant evolution in tear replacement therapies. Its origins stem from both biopharmaceutical innovation and ophthalmologic research into non-invasive treatments for age-related ocular deterioration.
- Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC): a bioadhesive polymer with superior mucoadhesive properties
- N-Acetyl-Carnosine: a dipeptide antioxidant known for its lens-penetrating potential
- Glycerin: a widely used humectant offering osmoprotective and lubricating benefits
When combined, these agents restore tear film stability, protect against oxidative insults, and promote cellular recovery of the ocular surface.
2. Active Ingredients and Comprehensive Composition
The effectiveness of these eye drops lies in the strategic combination of pharmacologically active and supportive ingredients.
- Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC): Functions as an artificial tear substitute, forming a protective layer over the cornea and enhancing tear film retention time.
- N-Acetyl-Carnosine: Acts as a potent antioxidant, penetrating the corneal barrier and delivering free radical scavenging effects that may help delay lens protein cross-linking seen in cataracts.
- Glycerin: Serves as an osmoprotectant and emollient, providing immediate hydration and improving ocular comfort by stabilizing hyperosmolar tear conditions.
The formulation may also include isotonic agents, buffering systems, and mild preservatives or preservative-free delivery systems to maintain sterility and pH balance optimal for ocular use.
3. Mechanism of Action: How the Eye Drops Work at a Cellular Level
This triple-action formula addresses multiple pathological processes underlying ocular surface disorders:
- Tear Film Stabilization: CMC enhances mucin layer stability, prolonging retention of tears on the corneal surface.
- Oxidative Stress Reduction: N-Acetyl-Carnosine neutralizes reactive oxygen species, reducing cellular damage in the cornea and lens.
- Corneal Protection: Glycerin supports hydration and shields epithelial cells from hyperosmolarity-related injury.
- Epithelial Healing: The combination supports faster recovery of micro-injuries and alleviates inflammation-induced discomfort.
At the molecular level, this formulation reduces protein carbonylation and lipid peroxidation, essential contributors to lens opacification and corneal degradation.
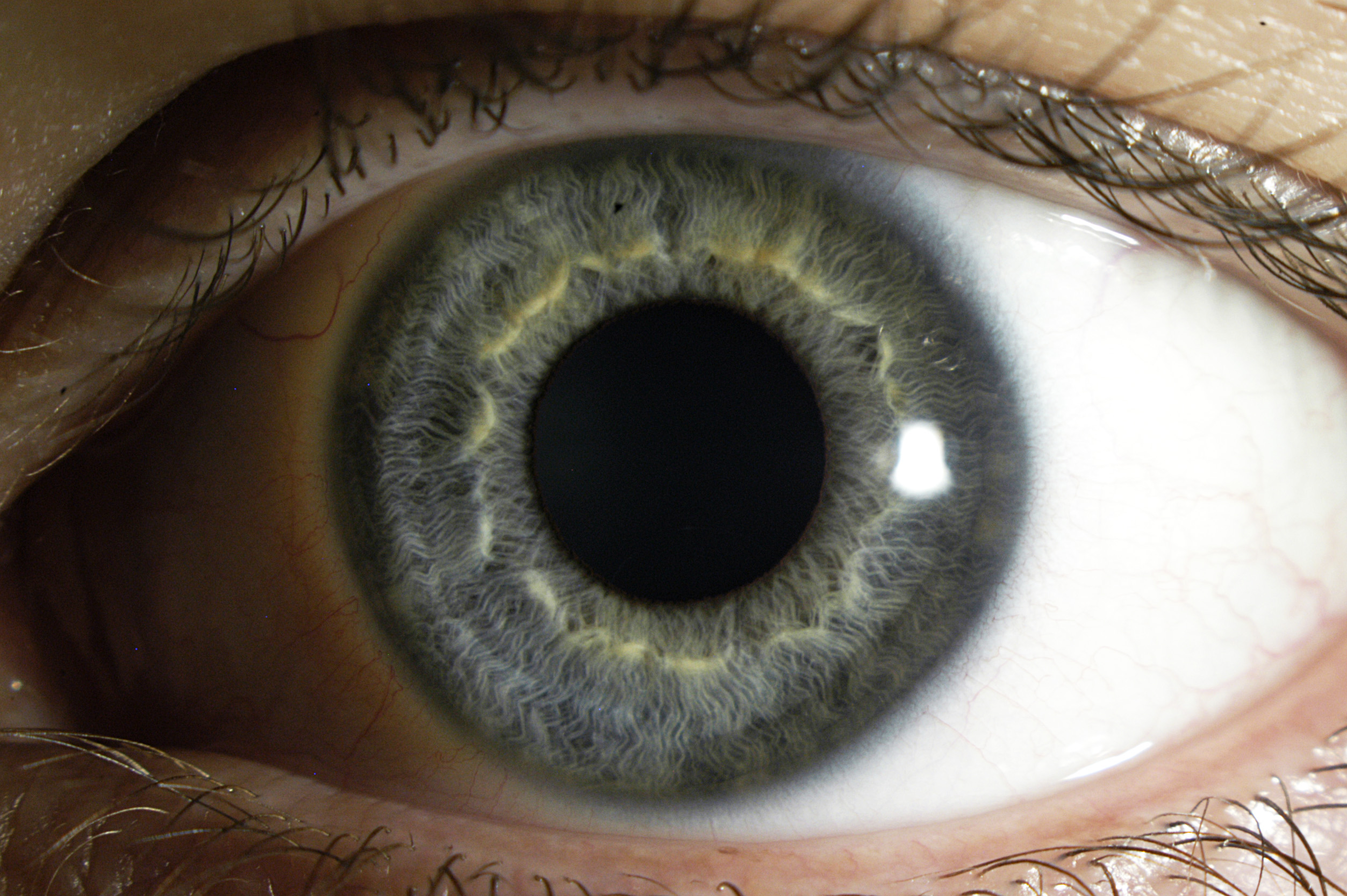
4. Approved Medical Uses of the Eye Drops
Clinically, this ophthalmic solution is indicated for:
- Dry Eye Syndrome (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca): Enhances ocular surface moisture and relieves burning, itching, and foreign body sensation.
- Ocular Irritation: Reduces discomfort from allergens, environmental exposure, or screen-induced eye strain.
- Contact Lens Wear: Used to relieve dryness and promote comfort during lens wear.
- Post-Operative Healing: Aids in the regeneration of epithelial tissues following cataract or refractive surgery.
5. Off-Label and Investigational Uses
Beyond its approved uses, the formulation has garnered interest in several off-label scenarios:
- Cataract Prevention: N-Acetyl-Carnosine is under investigation for its ability to delay senile cataract development through anti-glycation and anti-oxidation mechanisms.
- Pterygium and Pinguecula: Used adjunctively to reduce redness and irritation associated with these ocular surface growths.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: The antioxidant component may help mitigate oxidative stress contributing to microvascular retinal damage.
- Glaucoma Neuroprotection: Preliminary data suggest potential roles in protecting retinal ganglion cells through oxidative load reduction.
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Optimal Efficacy
Correct usage is essential to achieve the desired therapeutic effect:
- Recommended Dosage: 1-2 drops instilled into each affected eye, 2 to 4 times daily, or as directed by a healthcare provider.
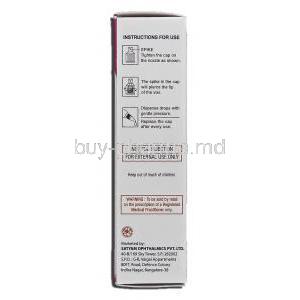
- Instillation Technique: Ensure hands are clean, tilt head back, and gently pull the lower eyelid to form a pouch. Avoid touching the dropper tip to the eye.
- Treatment Duration: May vary from short-term symptomatic relief to long-term management depending on severity of dry eye or oxidative pathology.
- Combination Therapy: If used with other ophthalmic medications, maintain a 5-minute interval between applications.

7. Common and Uncommon Side Effects
Most individuals tolerate the eye drops well, but adverse effects can occur:
- Common Side Effects: Transient burning or stinging upon instillation, eye redness, and mild blurred vision.
- Less Frequent Reactions: Sensation of foreign body in the eye, mild allergic conjunctivitis.
- Rare Events: Corneal epithelial erosion, periocular dermatitis, and lid swelling, typically associated with hypersensitivity or misuse.
Persistent or worsening symptoms should prompt medical evaluation.
8. Drug and Supplement Interactions
While topical, the formulation can interact with other substances affecting the eye:
- Ophthalmic Agents: Concurrent use with corticosteroids or NSAID eye drops may necessitate staggered application times to avoid dilution.
- Systemic Medications: Drugs affecting tear production (e.g., antihistamines, beta-blockers) may influence efficacy.
- Contact Lens Products: Avoid mixing with incompatible cleaning solutions or inserting lenses immediately post-application unless specified as lens-compatible.
- Dietary Antioxidants: May offer additive benefit or affect endogenous redox balance when combined with the antioxidant properties of N-Acetyl-Carnosine.
Healthcare provider consultation is advised when combining ocular therapies or supplements.

9. Contraindications and When Not to Use the Drops
While Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose / N-Acetyl-Carnosine / Glycerin Eye Drops are generally well tolerated, certain conditions preclude their use. These contraindications are crucial to prevent adverse outcomes and ensure patient safety.
- Hypersensitivity: Individuals with a known allergy to any active or inactive component of the formulation should not use this product, as it may trigger severe ocular or systemic allergic reactions.
- Active Ocular Infections: Use during viral, bacterial, or fungal eye infections, such as conjunctivitis, may exacerbate symptoms or interfere with the healing process.
- Compromised Corneal Integrity: Patients with severe corneal thinning, ulceration, or recent ocular trauma should avoid use unless explicitly directed by an ophthalmologist.
10. Warnings and Important Safety Precautions Before Use
To maximize therapeutic benefit while minimizing risks, users must adhere to strict safety protocols.
- Avoid Dropper Tip Contamination: Ensure the dropper tip does not touch the eye, hands, or any surface, to maintain sterility and prevent infection.
- Practice Hygienic Application: Always wash hands before and after instillation. Use in a clean environment to avoid introducing debris into the eye.
- Monitor Visual Changes: If blurred vision, increased discomfort, or other visual abnormalities occur or worsen, discontinue use and seek prompt medical attention.
- Medical Oversight for Chronic Use: Long-term administration, particularly in degenerative or age-related conditions, should be supervised by an eye care professional to evaluate efficacy and safety.

11. Guidelines for Careful Administration in Specific Populations
11.1 Administration in Elderly Patients
Elderly patients often present with a multifactorial ocular surface disease profile, requiring careful evaluation before initiating therapy.
- Age-Related Changes: Aging leads to reduced tear production, altered eyelid anatomy, and meibomian gland dysfunction, all of which may influence drug efficacy.
- Comorbidity Consideration: Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and neurodegenerative diseases can complicate ocular therapy and necessitate dosage adjustments or enhanced monitoring.
11.2 Use in Pregnant and Nursing Women
The safety of this formulation in pregnant or lactating individuals has not been conclusively established, necessitating cautious use.
- Pregnancy: Limited data from human studies and animal models suggest minimal systemic absorption, but potential fetal risk cannot be ruled out. Use only if the therapeutic benefit justifies the potential risk.
- Lactation: Although topical administration poses minimal risk of excretion into breast milk, clinical judgment should guide usage during breastfeeding.

11.3 Pediatric and Adolescent Administration
Administration to children and adolescents should be approached with clinical discretion.
- Indicated Conditions: May be used in children with diagnosed dry eye syndrome or allergic conjunctivitis under specialist supervision.
- Specialist Oversight: A pediatric ophthalmologist should evaluate suitability, dosage, and safety profile for young patients.
- Neonatal Use: Not recommended for neonates unless specifically prescribed due to immature ocular surface defenses and higher systemic absorption risk.
12. Signs and Management of Overdose or Accidental Ingestion
Though rare, excessive use or unintentional ingestion requires immediate response.
- Ocular Overuse: Symptoms may include eye redness, excessive tearing, or persistent discomfort. Temporarily discontinue use and consult a healthcare provider.
- Systemic Absorption: Repeated high-frequency dosing may lead to systemic exposure, particularly in children or those with compromised tear drainage systems.
- Ingestion: If swallowed, rinse mouth and seek medical advice. Monitor for gastrointestinal discomfort or other symptoms. In case of large quantity ingestion, contact poison control services.
13. Storage and Handling Instructions
Proper storage is essential to maintain product integrity and prevent microbial contamination.
- Temperature Control: Store between 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F), avoiding extreme heat or freezing.
- Light and Moisture Protection: Keep container tightly closed and away from direct light or humidity.
- Expiration Monitoring: Discard the bottle after 30 days from opening or by the expiry date, whichever comes first.
- Travel Tips: Store in a clean, cool travel case when on the move to prevent contamination and temperature fluctuations.
14. Handling Precautions and Disposal Best Practices
Environmental and personal safety should be considered during and after product use.
- Personal Use Only: The dropper bottle should not be shared to avoid cross-contamination and potential infection transmission.
- Disposal of Leftovers: Dispose of unused or expired drops as per local pharmaceutical waste regulations. Do not flush or pour into drains.
- Environmental Responsibility: Follow eco-conscious disposal protocols to reduce environmental contamination from pharmaceutical products and packaging.
Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose/ N-Acetyl-Carnosine/ Glycerin Eye Drops FAQ
- What is the use of Rewet eye drops?
- How many times should I use lubricating eye drops?
- Is sodium carboxymethyl cellulose safe?
- What is sodium carboxymethyl cellulose eye drops used for?
- What are the side effects of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose?
- Can I use carboxymethylcellulose eye drops daily?
- When not to use carboxymethylcellulose sodium?
- Is carboxymethyl cellulose FDA approved?
- What is N acetyl carnosine used for?
- What are the side effects of N-acetylcarnosine?
- What is N-acetyl carnosine eye drops used for?
- What are the hazards of N-acetyl L alanine?
- How to use glycerin for eyes?
- What is the drug glycerin used for?
- Is glycerin ok in eye drops?
- Is glycerin safe for eyes?
What is the use of Rewet eye drops?
Rewet Eye Drop is typically utilized to provide relief from the burning sensation and discomfort caused by dry eyes.
How many times should I use lubricating eye drops?
Up to four times a day
Is sodium carboxymethyl cellulose safe?
Yes
What is sodium carboxymethyl cellulose eye drops used for?
It is often applied as an agent to alleviate irritation and discomfort caused by dry eyes or exposure to wind or sunlight.
What are the side effects of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose?
The usual adverse reactions caused by Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose include irritation, itchiness, and blurry eyesight.
Can I use carboxymethylcellulose eye drops daily?
Yes
When not to use carboxymethylcellulose sodium?
- If you feel any discomfort in your eyes.
- Notice any changes in how you see things
- Persistent redness and irritation in your eyes.
Is carboxymethyl cellulose FDA approved?
Yes
What is N acetyl carnosine used for?
Some researchers believe that N-acetylcarnitine (also known as NAC) may help counteract the impact of stress due to its characteristics.
What are the side effects of N-acetylcarnosine?
Feeling generally tired, burning eyes, and experiencing blurry distance vision after looking at the computer screen
What is N-acetyl carnosine eye drops used for?
It helps stop and undo the process of the eye lens becoming hard and cloudy or changing color, aiding in the prevention and treatment of cataracts associated with aging.
What are the hazards of N-acetyl L alanine?
May lead to discomfort in breathing and skin, as well as significant irritation to the eyes.
How to use glycerin for eyes?
Lean your head slightly. Gaze upwards while gently pulling down your lower eyelid to create a small pocket in the corner of your eye for the drops or gel application purposes, as directed on the packaging instructions. Position the dropper above your eye and dispense 1 or 2 drops as required. Lower your gaze. Softly shut your eye for a minute or two to allow the solution to take effect. Using one finger positioned near the corner of your eye by the nose area gently apply pressure after administering the drops or gel.
What is the drug glycerin used for?
Address conditions associated with eye pressure, like glaucoma, and alleviate pressure in the eye prior to eye surgery.
Is glycerin ok in eye drops?
Yes
Is glycerin safe for eyes?
Yes