Tiromel
- Introduction to Tiromel (Liothyronine Sodium)
- Composition and Formulation of Tiromel
- Medical Uses of Tiromel (Approved Indications)
- Off-Label and Experimental Uses of Tiromel
- Mechanism of Action: How Tiromel Works in the Body
- Recommended Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Side Effects of Tiromel: What to Expect
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Special Warnings and Precautions with Tiromel Therapy
- Administration in Special Populations
- Overdose and Emergency Management
- Storage and Handling Instructions for Tiromel
- Handling and Dispensing Precautions
Introduction to Tiromel (Liothyronine Sodium)
Overview of Tiromel: What is it and its pharmaceutical classification
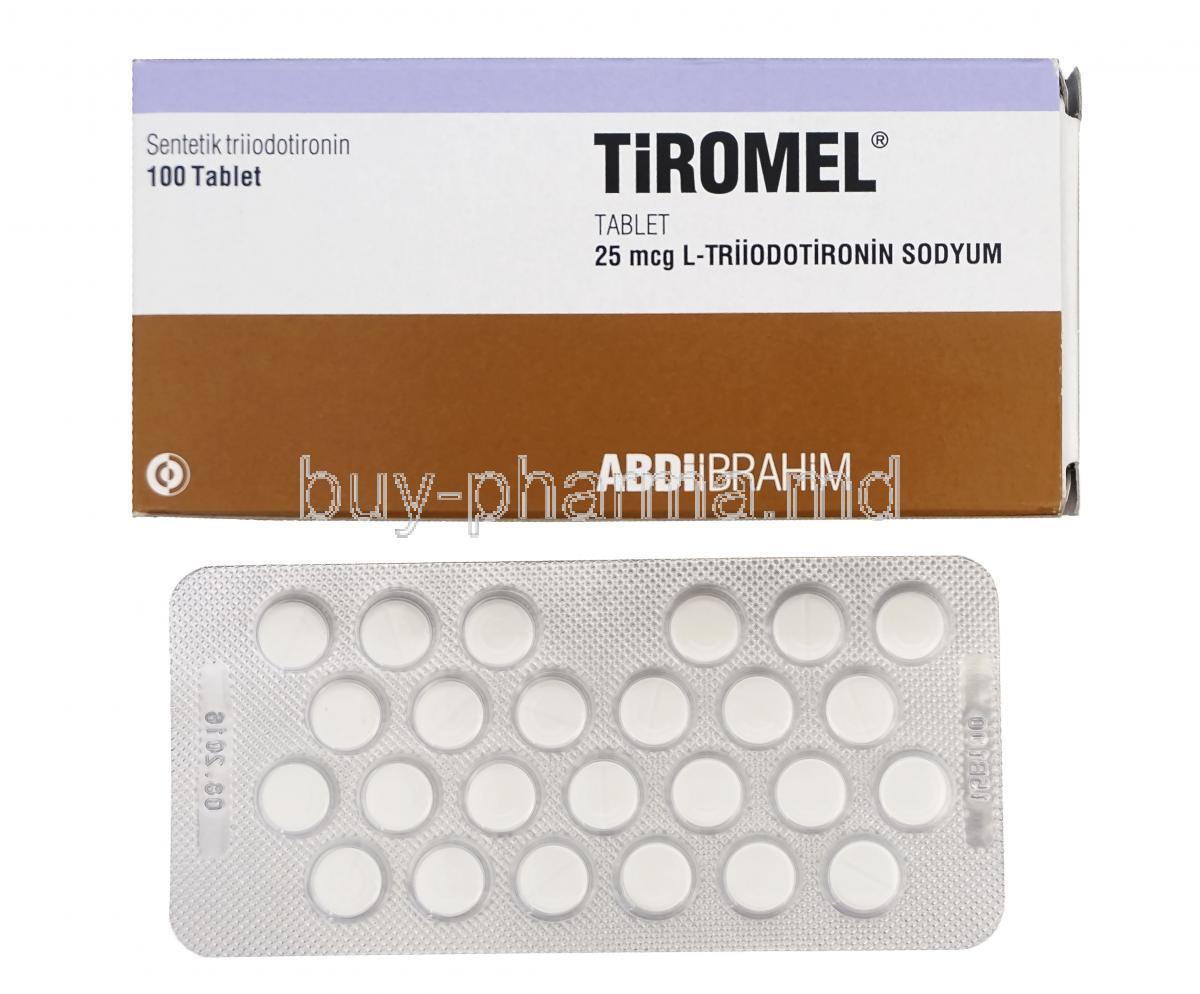
Tiromel is a man-made version of triiodothyronine (known as T3), which is a thyroid hormone that helps regulate metabolism in the body. It falls under the category of thyroid medications. It acts as a metabolic stimulant. In settings, Tiromel is primarily prescribed for cases where the body's natural production or balance of thyroid hormones is inadequate.
Differences between Tiromel and Levothyroxine
While both Tiromel and levothyroxine treat hypothyroidism, Tiromel (T3) acts faster and is more potent than levothyroxine (T4). Levothyroxine requires peripheral conversion to T3 to become active, whereas Tiromel delivers active hormone directly. This makes Tiromel more effective in some patients with impaired conversion, although it also carries a higher risk of side effects.
Historical background and clinical relevance
Liothyronine sodium was introduced in the mid-century as a faster alternative to thyroxine for treating certain thyroid conditions promptly and for diagnostic purposes as well. Today, it is still widely used in personalized thyroid hormone replacement treatments to its pharmacological characteristics.
Composition and Formulation of Tiromel
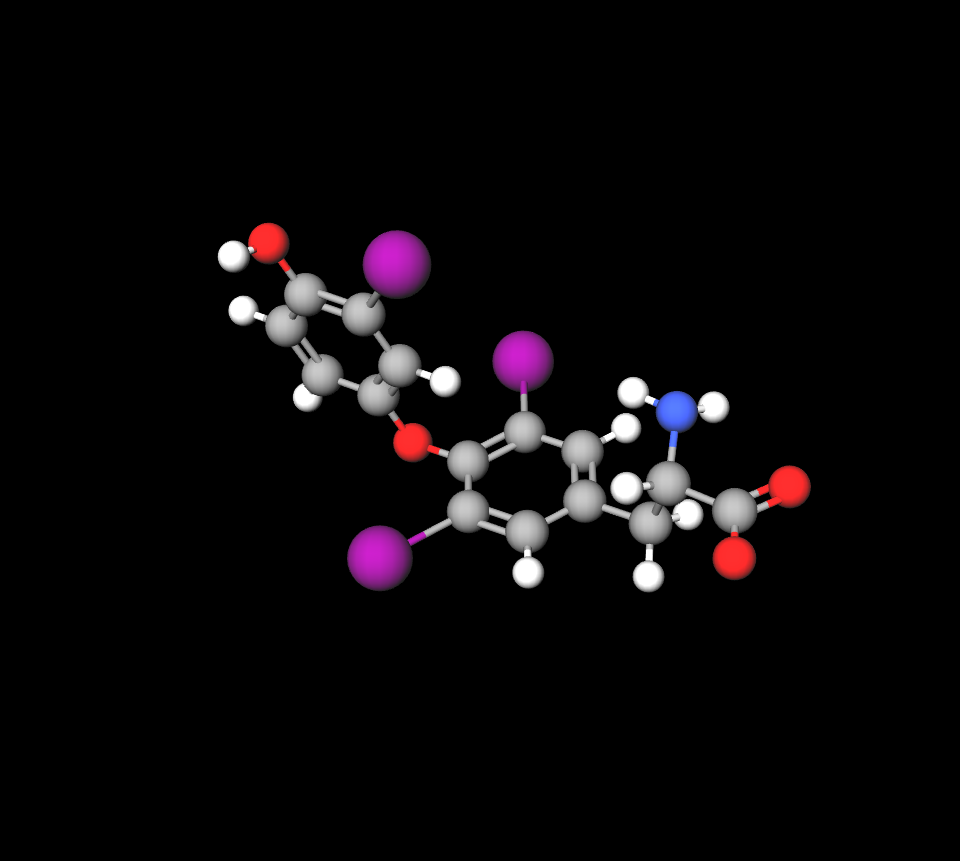
Active ingredient: Liothyronine sodium
Each tablet of Tiromel contains liothyronine sodium, which is a man-made version of the T3 hormone that naturally occurs in the body and acts similarly to the hormone at cell receptors.
Inactive ingredients and excipients
Common ingredients found in medications are monohydrate corn starch, gelatin, and magnesium stearate. These substances help ensure the stability, breakdown, and absorption of tablets.
Bioavailability and pharmacokinetic profile
Tiromel has high oral bioavailability, with peak plasma concentrations typically achieved within 2 to 4 hours. The half-life is shorter than T4, ranging from 1 to 2 days, necessitating multiple daily doses for some patients. It binds loosely to plasma proteins, allowing rapid tissue penetration.
Medical Uses of Tiromel (Approved Indications)
Treatment of hypothyroidism (primary, secondary, and tertiary)
Tiromel restores deficient T3 levels in patients with various forms of hypothyroidism, particularly when T4 monotherapy is insufficient. It is sometimes combined with levothyroxine for optimal symptom control.
Myxedema and myxedema coma management
In critical cases of severe hypothyroidism, including life-threatening myxedema coma, Tiromel is used intravenously to rapidly increase circulating thyroid hormone levels.
Diagnostic use in suppression tests
Management of congenital hypothyroidism
Off-Label and Experimental Uses of Tiromel
Adjunct therapy in treatment-resistant depression
Tiromel for weight loss
While Tiromel is not explicitly recommended for weight loss purposes, some people wrongly use it due to its effects. Thyroid hormones can boost metabolism and support weight loss.
Management of fibromyalgia symptoms
Preliminary evidence suggests low-dose T3 therapy may alleviate fatigue and cognitive dysfunction in fibromyalgia patients, although data remains inconclusive.
Tiromel 25 mcg bodybuilding
Use in goiter and thyroid suppression protocols pre-surgery
Tiromel might be included as a surgical measure to lower TSH levels in patients with thyroid nodular disease or goiter who are preparing for surgery or radioiodine therapy.
Mechanism of Action: How Tiromel Works in the Body
Role of triiodothyronine (T3) in metabolic processes
Cellular uptake and nuclear receptor binding
After entering cells via specific transporters, T3 binds nuclear thyroid hormone receptors, modulating transcription of genes involved in growth and energy expenditure.

Effects on basal metabolic rate, thermogenesis, and protein synthesis
Tiromel raises the body's metabolic rate (BMR), generates heat within the body, and improves the processing of proteins and fats by aiding in their creation and breakdown processes and resulting in changes to metabolism.
Comparison with T4 (Levothyroxine) in terms of potency and onset
T3 is several times more potent than T4 and acts faster due to its active form, but it also results in more fluctuation in serum hormone levels, necessitating cautious use.
Recommended Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard dosing in hypothyroidism: adult and pediatric considerations
In adults, the usual starting dose is between 5 and 25 micrograms per day, which is then gradually raised over time as needed for effectiveness. For children, the dosage varies based on their age and the seriousness of the deficiency, with monitoring required.
Dosage adjustments based on lab monitoring (TSH, T3, T4)
Serum TSH, free T3, and T4 levels guide dosing adjustments. The goal is symptom control without causing hyperthyroid effects.
Administration timing and food interactions
Tiromel should be taken on an empty stomach, preferably 30 minutes before breakfast, as food may affect absorption.
Titration strategies to minimize side effects
Dosing should be titrated slowly, typically in 5-10 mcg increments every 1-2 weeks, especially in elderly or cardiac patients.
Intravenous versus oral routes (in critical care settings)
Intravenous administration is typically only used in situations such as coma, where oral absorption is limited or too sluggish.
Side Effects of Tiromel: What to Expect
Common Side Effects of Tiromel
- Palpitations
- Anxiety
- Fine tremors
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Increased appetite
- Heat intolerance and profuse sweating

Serious and Rare Side Effects
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Angina pectoris
- Osteopenia or osteoporosis with long-term use
- Menstrual irregularities in women
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Known Drug Interactions
- Potentiation of anticoagulants, leading to increased bleeding
- Reduced efficacy of insulin and oral hypoglycemics
- Enhanced effects of tricyclic antidepressants and sympathomimetics
- Absorption interference by calcium, magnesium, and iron supplements
Contraindications for Tiromel Use
- Untreated adrenal insufficiency
- Active, uncorrected thyrotoxicosis
- Known hypersensitivity to liothyronine
- Recent myocardial infarction or severe cardiac ischemia
Special Warnings and Precautions with Tiromel Therapy
Risk of over-replacement and iatrogenic hyperthyroidism
Overdosing Tiromel can mimic hyperthyroidism, increasing the risk of cardiac arrhythmia, weight loss, and osteoporosis. Regular monitoring is critical.
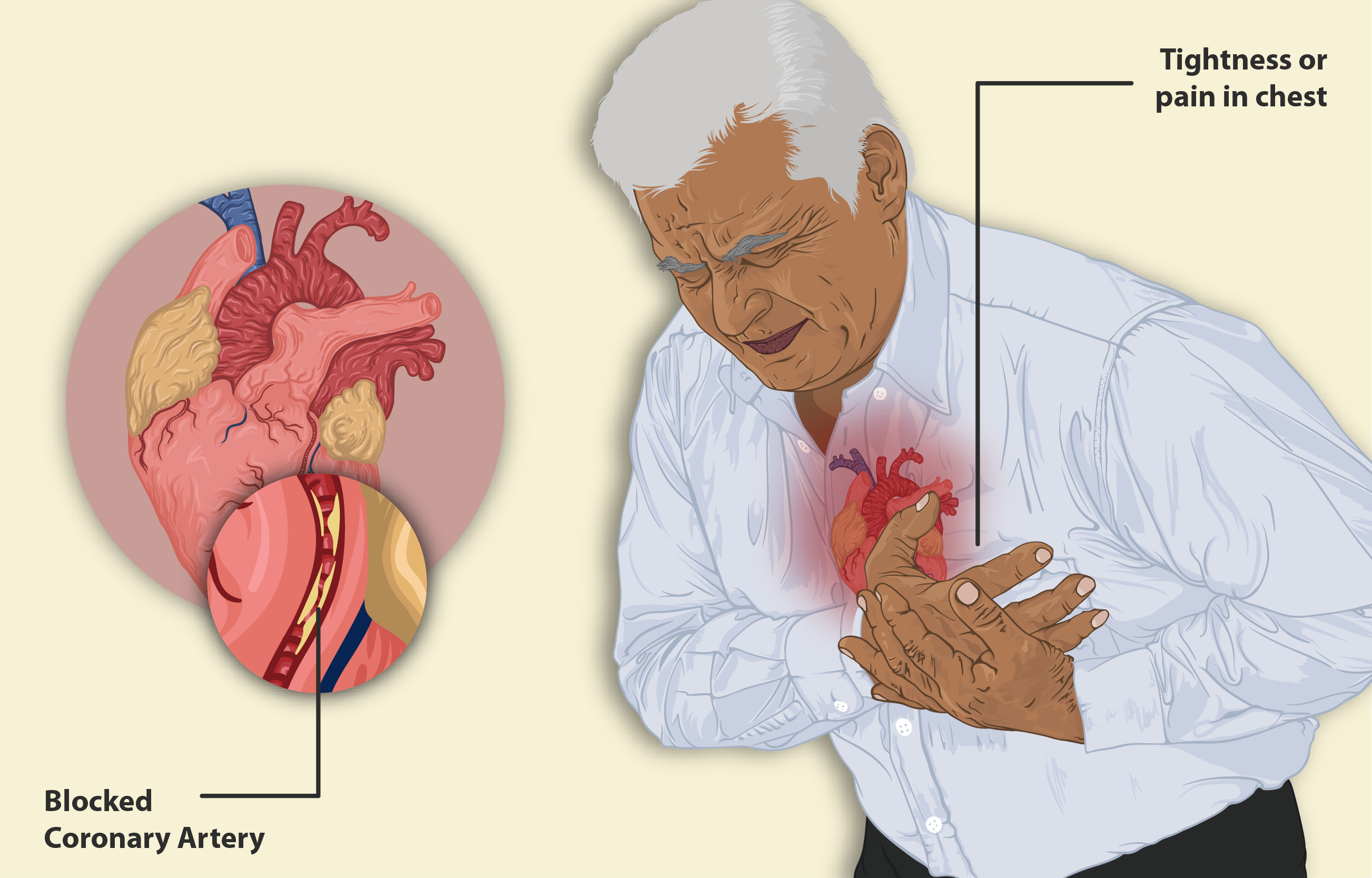
Monitoring cardiac function in at-risk patients
Patients with underlying cardiovascular disease must be monitored closely with ECG and clinical assessments during dose escalation.
Caution in patients with diabetes or cardiovascular disease
Tiromel could worsen blood sugar fluctuations and trigger chest pain or irregular heartbeats, so it might be necessary to consult with an endocrinologist or cardiologist for management.
Not intended for weight loss in euthyroid individuals
Using weight loss medication in individuals with thyroid function is dangerous. Not recommended, as it can cause serious health problems linked to an overactive thyroid gland.
Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals exhibit heightened cardiovascular sensitivity to liothyronine, often manifesting as palpitations, tachycardia, or angina even at modest doses. To minimize adverse events:
- Initiate therapy with significantly reduced doses, typically 5 mcg daily.
- Employ cautious titration, increasing only in 5 mcg increments every 2-4 weeks.
- Conduct regular cardiovascular evaluations, including ECGs and symptom assessments.
Clinical prudence is paramount in geriatric care, as the risks of cardiac arrhythmias, bone demineralization, and polypharmacy interactions are elevated.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Pregnancy category and fetal safety considerations
Tiromel is typically not suggested as the treatment option for individuals due to its classification in pregnancy category A/B based on regulatory standards; however, the effectiveness of levothyroxine makes it the preferred treatment for maternal hypothyroidism.

Placental transfer and implications
When Liothyronine passes through the barrier during pregnancy, it may impact the thyroid function of the fetus. This can result in tachycardia or a restriction in growth if the mother is exposed to excessive amounts of the substance.
Breastmilk excretion and infant thyroid function
Although small quantities of T3 may be excreted into breast milk, the amounts are typically insufficient to suppress the infant's thyroid function. Nonetheless, lactating mothers receiving high doses should be monitored to ensure infant safety and appropriate neurodevelopment.
Pediatric Population
Age-appropriate dosing and monitoring
In children, especially neonates and infants, precise dosing is essential. Pediatric doses are weight-based, beginning at 0.5 mcg/kg/day and adjusted gradually. Overcorrection can lead to premature cranial suture closure or hyperactivity.
Growth and development considerations
Thyroid hormones play a role in the development of the nervous system (CNS), skeletal growth, and maintaining metabolic balance in the body. It is important to closely monitor the progress of linear growth, bone age, and developmental milestones when undergoing treatment.
Use in congenital hypothyroidism
Tiromel is used in select cases of congenital hypothyroidism, often as an adjunct when T4 monotherapy is suboptimal. Regular thyroid function tests (TSH, Free T3, Free T4) are indispensable to avoid overtreatment or under-replacement.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of acute or chronic overdosage
Toxic levels of Tiromel can precipitate both acute and insidious symptoms:
- Severe anxiety, tremors, and agitation
- Tachycardia, arrhythmias, and elevated blood pressure
- Hyperthermia and diaphoresis
- Excessive weight loss and insomnia
Management strategies: beta-blockers, gastric lavage, supportive care
Emergency interventions include:
- Administration of beta-adrenergic blockers (e.g., propranolol) to manage tachycardia and tremors
- Gastric lavage if ingestion was recent
- Activated charcoal in appropriate cases
- Supportive care including IV fluids, electrolyte management, and sedation
Risk of thyroid storm in massive overdose scenarios
Massive T3 overdose may induce thyroid storm, a life-threatening endocrine emergency characterized by high fever, delirium, cardiovascular collapse, and potential multi-organ failure. Rapid hospitalization and intensive care support are required.
Laboratory and ECG monitoring guidelines
Monitor:
- Serum T3 and T4 levels
- TSH suppression status
- Electrocardiogram for arrhythmic patterns
- Serum electrolytes and liver function
Continuous reassessment is crucial until stabilization is achieved.
Storage and Handling Instructions for Tiromel
Recommended storage temperature and moisture precautions
Remember to store Tiromel in a dry place, at temperatures below 25°C (77°F). It's best to avoid areas, like bathrooms to prevent moisture from affecting the effectiveness of the tablets.
Proper sealing and protection from light
Remember to store the item in its original blister packaging or in an amber-colored container to shield it from oxidation caused by exposure.
Handling expired or damaged tablets
Please refrain from consuming expired or damaged tablets; instead, kindly dispose of them appropriately by utilizing a pharmacy take-back program or adhering to the regulations concerning disposal in your area.
Safe disposal methods
Please avoid disposing of medication by flushing it down the toilet or pouring it into a drain; instead, put expired tablets in a sealed bag. Mix them with something unwanted, like coffee grounds before throwing them away in the household trash if there is no return program available.
Handling and Dispensing Precautions
Use of gloves in compounding pharmacies (if necessary)
Pharmacists who are splitting or compounding tablets might choose to wear gloves to avoid absorbing substances through their skin or contaminating themselves while dealing with high-strength doses.
Make sure to have equipment for handling Tiromel in pharmaceutical environments to avoid mixing it with other drugs.
Labeling and patient counseling protocols
Dispensers must clearly label dosage instructions and warnings. Counseling should emphasize:
- Adherence to prescribed timing
- Avoidance of abrupt discontinuation
- Recognition of overdose symptoms
Storage in childproof containers
Tiromel should always be stored in child-resistant packaging to mitigate accidental pediatric ingestion, which could lead to severe toxicity.
Tiromel FAQ
- What is Tiromel 25 used for?
- What is Tiromel 25?
- What is Tiromel used for in bodybuilding?
- What is Tiromel T3?
- What is Tiromel?
- Where to buy Tiromel?
- When to take Tiromel?
- How long does Tiromel take to work?
- How much Tiromel to take?
- How does Tiromel work?
- What are Tiromel tablets for?
- What is Tiromel 25 used for?
- Does T3 make you lose weight?
- What does taking T3 do for you?
- What happens when you stop taking T3?
- Is T3 good or bad for you?
- What to avoid when taking T3?
- Should I take T3 in the morning or at night?
- Is T3 bad for your heart?
- What are the benefits of taking T3?
- How much T3 is safe?
- How long does it take for T3 to work?
- What is the purpose of T3?
What is Tiromel 25 used for?
For individuals grappling with a sluggish thyroid that isn't producing adequate amounts of vital hormones Tiromel 25 can prove highly beneficial. As one of its central applications in medicine entails treating hypothyroidism effectively doctors often recommend this drug when other treatments fall short. However beyond just addressing low hormone levels in patients Tiromel 25 can also aid those struggling with select forms of goiters or those grappling with metastasized cancer impacting their thyroid gland.What is Tiromel 25?
When we talk about Tiromel 25 we're referring to a specific formulation that contains liothyronine sodium in an amount of 25 micrograms. This synthetic version of T3 thyroid hormone is prescribed by doctors to effectively treat various health conditions stemming from low or unbalanced thyroid hormone levels.What is Tiromel used for in bodybuilding?
In the realm of bodybuilding, certain folks make use of Tiromel in ways not approved by doctors to boost their metabolism and shed pounds. This is because thyroid hormones have a huge role regulating metabolic rates. Nevertheless, these actions come with sizable risks.What is Tiromel T3?
Liothyronine sodium is the active ingredient in Tiromel T3 - a drug designed to mimic triiodothyronine one of our thyroid glands natural hormones. Doctors often prescribe Tiromel T3 as part of therapy for people suffering from hypothyroidism characterized by insufficient levels of thyroid hormone production.What is Tiromel?
For treating hypothyroidism and certain other disorders linked to the thyroid gland Tiromel medication is often administered owing to its key ingredient liothyronine sodium - an artificial form of T3 hormone.Where to buy Tiromel?
You can acquire Tiromel from different internet pharmacies or even from nearby ones. But remember, it's necessary to acquire it only with the guidance and prescription of a healthcare expert because of its possible hazards and adverse reactions.When to take Tiromel?
Tiromel is a medication that is often suggested for once daily use based on your doctors recommendations or prescription guidelines. Its best taken before breakfast with no food in your stomach for about thirty minutes up to an hour as this can increase the benefits of this drug according to health professionals.How long does Tiromel take to work?
Within a few days, Tiromel's effects may be apparent, but achieving complete therapeutic benefits could take several weeks. Because every patient reacts differently, maintaining frequent check-ins to review progress and modify the dosage if necessary is critical.How much Tiromel to take?
When taking Tiromel determining the correct dosage requires careful consideration of various patient specific factors. These may include age, weight, and response to treatment. To avoid any potential complications or negative side effects from improper use of this medication its critical that patients closely follow all instructions given by their healthcare provider regarding dosage adjustments or titration.How does Tiromel work?
Tiromels mechanism involves supplementing or substituting for the thyroid hormones that the body naturally creates. These particular hormones are vital for maintaining energy and metabolic regulation within the body. By supplying synthetic alternatives to these hormones Tiromel is able to reinstate typical metabolic function and natural energy levels.What are Tiromel tablets for?
Those who suffer from hypothyroidism or certain types of goiters may benefit from using Tiromel tablets. In addition individuals who have thyroid cancer may also find them helpful for management purposes. By offering a synthetic form of T3 these tablets work to restore balance to this hormone within the body.What is Tiromel 25 used for?
Individuals facing challenges, with a thyroid that doesn't produce essential hormones, may find Tiromel 25 to be very helpful in their situation. It is commonly used in medicine to treat hypothyroidism when other therapies are not effective. Apart from correcting low hormone levels, Tiromel 25 can also assist individuals dealing with types of goiters or those affected by cancer that has spread to their thyroid gland.
Does T3 make you lose weight?
Higher baseline free T3 and free T4 levels were significantly associated with a greater weight loss during the first 6 months
What does taking T3 do for you?
Substitute the thyroid hormone in your body by imitating the functions of your hormones.
What happens when you stop taking T3?
Stopping your thyroid medication abruptly can cause the symptoms of hypothyroidism to resurface easily since leaving hypothyroidism untreated can result in health issues, like mood swings and slowed thinking processes, alongside irritability.
Is T3 good or bad for you?
Elevated levels of T3 could indicate hyperthyroidism due to excessive thyroid hormone production.
What to avoid when taking T3?
Medications that reduce acidity levels in the stomach, dairy products and supplements containing calcium, supplements with iron content, foods rich in fiber, like bran flakes and fiber bars, iodine-rich food items, and foods made from soybeans.
Should I take T3 in the morning or at night?
Morning
Is T3 bad for your heart?
Decreases T4 vascular resistance, which includes tone, and boosts the growth of coronary arterioles.
What are the benefits of taking T3?
It offers a supply of thyroid hormone for individuals who may have a production deficiency.
How much T3 is safe?
Children 6 to 10 years old: 104 – 183 ng/dL. Children 11 to 14 years old: 68 – 186 ng/dL. Adolescents 15 to 17 years old: 71 – 175 ng/dL. Adults 18 to 99 years old: 79 – 165 ng/dL.
How long does it take for T3 to work?
After starting your thyroid medication regimen, it may take around 4 to 6 weeks for you to begin feeling better and notice an improvement in your symptoms.
What is the purpose of T3?
Managing the metabolism of the body and overseeing functions, like heart rate regulation, facilitating digestive processes, and coordinating muscle activity.