Cognium Syrup
- Introduction to Cognium Syrup
- Composition and Active Ingredients
- Mechanism of Action: How Cognium Syrup Works
- Cognium Syrup uses
- Off-Label and Alternative Uses of Cognium Syrup
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Cognium Syrup side effects
- Drug Interactions and Substance Incompatibilities
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Special Precautions and Careful Administration
- Administration in Elderly Patients
- Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Pediatric Administration and Considerations
- Overdose Risks and Emergency Management
- Handling, Storage, and Shelf Life
- Handling and Patient Information Precautions
Introduction to Cognium Syrup
What is Cognium Syrup?
Cognium Syrup is a herbal cognitive supplement formulated to support brain function, memory enhancement, and neuroprotection. Designed for both adults and children, it is primarily used in managing cognitive impairment and memory-related issues.
Therapeutic class and general indication
Cognium falls under the class of nootropic or neuroenhancer supplements. It is generally indicated for conditions involving memory decline, mental fatigue, reduced concentration, and early cognitive impairment associated with age or neurological conditions.
Composition and Active Ingredients
Key active ingredient(s) and their standardized extract form
- Shankhapushpi
- Brahmi
- Jyotishmati
- Ashwagandha
- Jalabrahmi




Inactive ingredients and excipients
It contains ingredients like sorbitol and methylparaben, sodium benzoate, and flavored syrups to enhance taste and preserve freshness for periods of time.
Herbal vs Synthetic
Cognium Syrup is completely natural, which helps reduce the risks linked to nootropics. The formula's mix of plant-based chemicals offers a range of advantages with minimal side effects.
Mechanism of Action: How Cognium Syrup Works
Neuroprotective activity and antioxidant properties

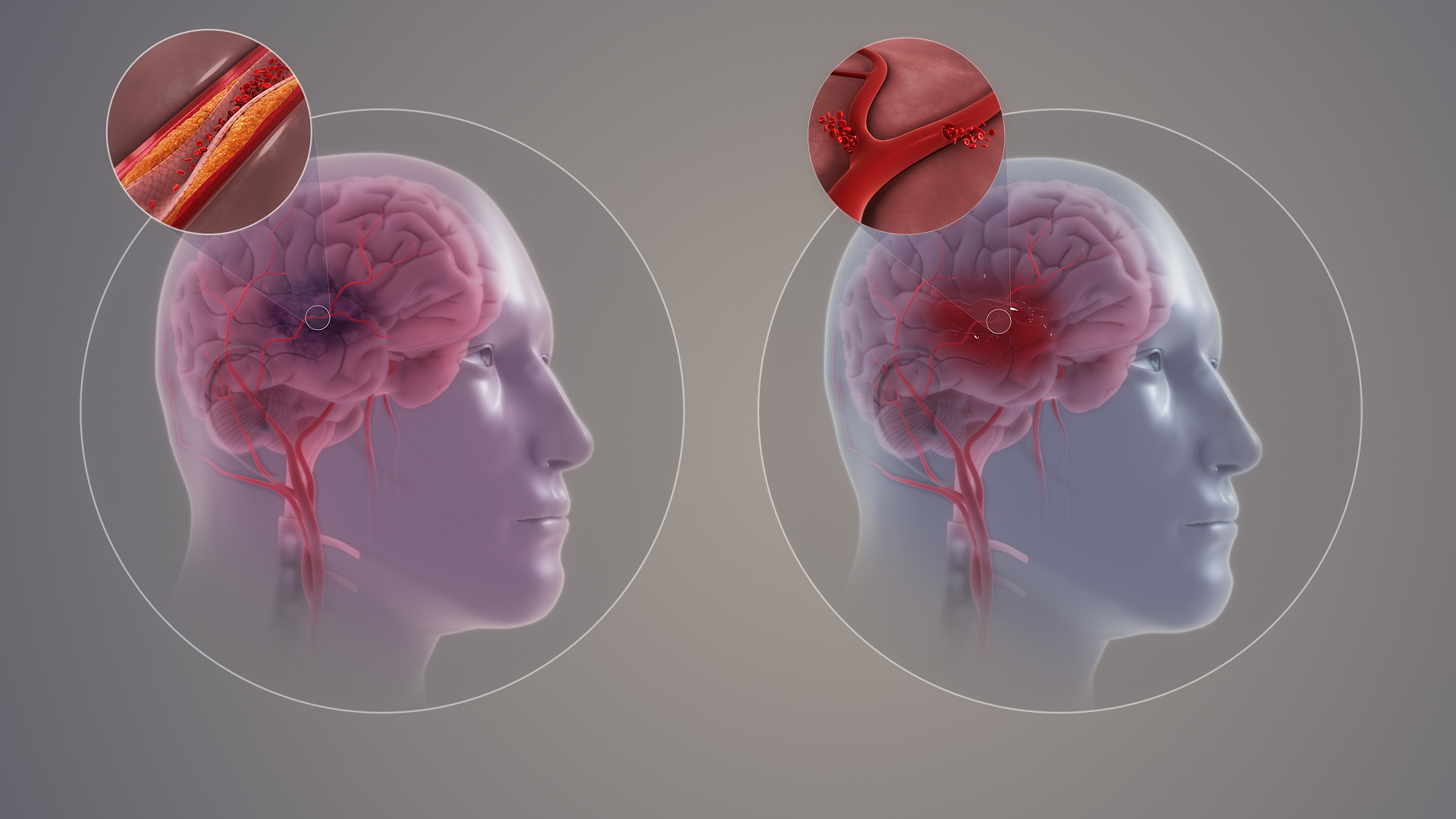
Cognitive enhancement through improved cerebral blood flow
The syrup enhances blood flow in the brain's blood vessels, which helps boost alertness and memory by delivering oxygen and essential nutrients to support cognitive functions.
Modulation of neurotransmitters and memory pathways
Evidence-based pharmacological mechanisms
Preclinical trials have demonstrated increased BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor) expression and reduced inflammation markers in models of cognitive decline.
Cognium Syrup uses
Cognitive decline in elderly patients
Dementia and mild cognitive impairment
Adjunctive therapy in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia
Off-Label and Alternative Uses of Cognium Syrup
Pediatric cognitive development and focus improvement
Cognitive fatigue and attention deficit in adults
Post-stroke cognitive rehabilitation
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard dosage for adults
Typically, 5-10 ml of Cognium Syrup is administered twice daily after meals or as directed by a physician.
Cognium syrup dosage for child
For kids who are older than 6 years old, it is recommended to take 2 to 4 teaspoons two times a day based on their age and weight.
Dosage adjustment for elderly and hepatic/renal impairment
Begin treatment using the dose range and regularly assess for any issues with tolerability. While under supervision, make dosage adjustments as needed for patients with liver or kidney impairment.
Duration of therapy and tapering considerations
Most regimens last 8-12 weeks. Tapering is typically unnecessary but should be assessed individually based on response.
Administration timing (with meals, bedtime, etc.)
It's best to take it after eating to reduce stomach issues and improve how well the body absorbs it.

Cognium Syrup side effects
Frequently reported side effects (e.g., headache, gastrointestinal upset)
- Nausea
- Mild abdominal discomfort
- Headache
- Drowsiness in sensitive individuals

Allergic reactions and hypersensitivity manifestations
Rare cases of skin rash, urticaria, or facial swelling may occur in individuals with plant-based allergies.

Long-term use complications (if any)
There have not been any impacts noted from extended usage; however, it is recommended to undergo routine assessments.
Reporting adverse events and pharmacovigilance
Adverse reactions should be reported to national pharmacovigilance centers or the manufacturer as per local guidelines.
Drug Interactions and Substance Incompatibilities
Interactions with CNS stimulants or depressants
May potentiate or reduce the efficacy of sedatives, anxiolytics, or psychostimulants when co-administered.
Impact on patients taking anticoagulants or antiepileptics
Caution is warranted due to potential herb-drug interactions that may influence clotting time or seizure threshold.
Alcohol and herbal supplement considerations
Avoid concurrent use with alcohol or unknown herbal products to prevent unpredictable CNS effects.
Clinical significance of potential pharmacokinetic changes
Limited evidence exists, but metabolic interference with hepatic enzymes may alter plasma levels of co-administered drugs.
Warnings and Contraindications
Situations requiring medical supervision
Patients experiencing issues due to brain injuries or mental health conditions should consult a doctor for a diagnosis before proceeding with any treatment options.
Pre-existing neurological or psychiatric conditions
Please consult a psychiatrist before using in cases of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder or active seizures.
Contraindicated with concurrent MAOI or sedative use
Potential risk of additive CNS depression or hypertensive crisis necessitates caution.
Special Precautions and Careful Administration
Monitoring requirements during long-term use
It is advisable to perform evaluations every 4 to 6 weeks throughout extended periods of administration.
Precautionary use in hepatic or renal impairment
Adjust dosage and closely monitor for drug accumulation or hepatic stress markers.
Caution in patients with seizure history or concurrent antipsychotic therapy
Neuroexcitatory properties could potentially reduce the seizure threshold in groups that are more susceptible to such effects.
Recommendations for gradual discontinuation
The stoppage might happen suddenly. For patients who are also using medications that affect the central nervous system, it is recommended to slowly reduce the intake.
Administration in Elderly Patients
As people age, their liver and kidney functions may slow down, which means that dosage adjustments need to be considered when prescribing medication like Cognium Syrup. It's best to start with a low dose and increase it gradually depending on how well the person responds to the treatment and how well they can tolerate it.
Monitoring for increased sensitivity to side effects
Elderly individuals might have a response to ingredients that could result in higher chances of feeling dizzy or experiencing stomach discomfort and slight drowsiness. It is advised to check for any reactions to address them promptly.
Use in elderly with comorbidities (e.g., cardiovascular or hepatic diseases)
In individuals with concurrent medical conditions such as chronic liver disease, hypertension, or ischemic heart disease, Cognium Syrup should be administered under close clinical supervision. Interactions with existing medications and organ function status should be evaluated periodically.
Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety data in pregnancy: animal vs. human studies
Available data from animal models suggest a favorable safety profile; however, comprehensive human studies are lacking. Therefore, its use during pregnancy should be considered only if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks.

Placental transfer and teratogenicity risk assessment
Due to limited data on placental transfer and embryotoxic potential, Cognium Syrup is not routinely recommended in the first trimester. Teratogenicity risk remains undetermined and should be approached conservatively.
Breastmilk excretion potential and infant safety
The excretion of Cognium's active components into breast milk has not been fully established. Nursing mothers should avoid use unless deemed necessary by a healthcare provider, especially in neonates or premature infants.
Physician guidance on use during lactation
Medical consultation is essential before initiating Cognium Syrup during breastfeeding. If used, close observation of the infant for any signs of hypersensitivity, gastrointestinal disturbance, or behavioral changes is advised.
Pediatric Administration and Considerations
Age suitability and evidence of efficacy in children
According to studies that show focus and memory retention in children facing learning challenges, it's generally safe for kids aged five and up to use Cognium Syrup.
Cognitive development applications
The syrup helps with brain development processes in situations involving attention issues, school performance struggles, and language development delays by improving how neurons communicate and encouraging changes in connections vital for learning.
Pediatric dosing and risk-benefit analysis
Standard dosages for children usually range from 2 and a half to 3 teaspoons twice a day, depending on their weight and health condition, to minimize any risks.
Monitoring for behavioral or physiological changes
Children who are taking Cognium need to be checked for signs of hyperactivity or irritability, and any changes in their sleep patterns or behavior that seem unusual should be closely monitored. Parent input and evaluations by healthcare providers play a role in assessing the situation.
Overdose Risks and Emergency Management
Symptoms of acute overdose
Taking too much Cognium Syrup could lead to symptoms like feeling sick to your stomach, throwing up, feeling dizzy or overly sleepy, or having discomfort in your belly. In some cases, you might also have reactions or tremors.
Immediate first aid and supportive care
If overdose is suspected, discontinue the product immediately. Provide supportive measures including hydration, rest, and monitoring of vital signs. Activated charcoal may be administered if ingestion is recent.
When to seek emergency medical attention
Medical attention should be sought immediately if the patient shows signs of respiratory depression, altered consciousness, persistent vomiting, or severe allergic reactions such as facial swelling or rash.
Antidote availability and treatment protocols
There is no specific antidote for Cognium Syrup overdose. Management remains symptomatic and supportive. In severe cases, hospitalization and monitoring of renal and hepatic functions may be necessary.
Handling, Storage, and Shelf Life
Ideal storage conditions (temperature, light, humidity)
Remember to keep your Cognium Syrup in a dry place at temperatures below 25°C to maintain its properties intact. Shield it from direct sunlight and moisture.
Shelf life and expiration indicators
Make sure to inspect the packaging for the expiration date and lot number before use; avoid using the syrup after its shelf life expires, which is around 24 months from the manufacturing date when stored correctly.
Disposal of unused or expired syrup
Make sure to dispose of any leftover Cognium Syrup according to the guidelines for waste disposal in your area. Refrain from pouring it down drains or flushing it down the toilet.
Child-proof packaging and storage recommendations
Remember to store the item in its child packaging and keep it away from children at all times to avoid any accidental swallowing incidents.
Handling and Patient Information Precautions
Instructions for accurate measuring and dispensing
Remember to use the measuring spoon or oral syringe that comes with the product when you dose it out. Don't just eyeball it with regular kitchen spoons, as this can result in incorrect doses, either too little or too much.
Counseling points for caregivers and patients
- Ensure you follow the recommended dosage and schedule closely.
- Make sure to let your healthcare provider know about any side effects or uncommon symptoms you experience.
- Please avoid combining this medication with any remedies or over the counter drugs of origin.
Importance of adherence to prescribed regimen
To ensure the outcomes, it is important to take Cognium Syrup for the recommended period of time. Missing doses or not taking it consistently could reduce its ability to enhance functions.
When to discontinue and consult a physician
If the patient experiences side effects or allergic reactions or does not see any improvement within 4 to 6 weeks of using the syrup, it is recommended that they stop using it. It is always advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional before making any decisions to discontinue or resume the syrup.
Cognium Syrup FAQ
What is the use of cognium syrup?
Charak Cognium Syrup enhances your ability to concentrate and stay focused while working by enhancing brain function and improving memory retention and recall processes to combat fatigue.
Is cognium safe to take?
Yes
How long does it take for Cognium to work?
1 week
Is Cognium good for ADHD?
Yes
What is Cognium made of?
Shankhapushpi, Brahmi, Arjuna, Jyotishmati, Ashwagandha, Jalabrahmi
What is composition of Cognium?
Shankhapushpi, Brahmi, Arjuna, Jyotishmati, Ashwagandha, Jalabrahmi
What is the work of Cognium?
Many people turn to this supplement to enhance memory retention, focus, and support abilities. It also reduces mental exhaustion and promotes brain well-being while increasing attention and alertness levels. This is particularly beneficial for those managing stress or preparing for exams, seeking to boost cognitive clarity.
Is Cognium better than Prevagen?
There were improvements in age groups with Cognium, while Prevagen did not show significant results across the population as a whole. Patients typically see results with Cognium within 3 to 4 weeks, whereas Prevagen suggests a timeframe of 90 days for expected outcomes.