Introduction
Foracort Inhaler is a combination therapy designed to provide comprehensive control of chronic respiratory disorders such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Belonging to the therapeutic class of corticosteroids and long-acting β₂-agonists (LABA), this medication delivers a dual mechanism—reducing airway inflammation and promoting smooth muscle relaxation—to ease breathing and prevent respiratory distress.
Available under several brand names and dosage forms, including inhalers and rotacaps, Foracort is formulated to ensure rapid onset and sustained relief. Manufactured by Cipla Ltd., it is approved by leading global regulatory authorities such as the FDA, EMA, and CDSCO, and is trusted worldwide for its proven efficacy in maintaining long-term respiratory stability.
Foracort holds a vital role in the management of chronic respiratory diseases by preventing exacerbations, improving lung function, and enhancing patients’ quality of life through consistent symptom control and reduced hospitalizations.
Composition and Formulation
Foracort Inhaler contains two active pharmaceutical ingredients: Budesonide and Formoterol fumarate dihydrate. Budesonide acts as a corticosteroid, reducing inflammation and swelling in the airways, while Formoterol functions as a bronchodilator, helping the respiratory muscles relax and air to flow freely into the lungs.
The synergistic mechanism of these two agents enables both immediate and sustained control of symptoms, improving pulmonary function and reducing the risk of acute flare-ups. Foracort is available in different strengths such as 100/6 µg, 200/6 µg, and 400/6 µg, allowing personalized dosing for various severity levels of asthma and COPD.
Inactive ingredients ensure optimal aerosolization and delivery through a precision metered-dose inhaler system, engineered for consistent therapeutic output and minimal drug wastage.
How Foracort Inhaler Works
The mechanism of Foracort is rooted in its dual pharmacologic components. Budesonide, a potent anti-inflammatory corticosteroid, acts by inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and cytokines. This results in reduced airway swelling and mucus formation. Formoterol, a long-acting β₂-adrenergic receptor agonist, binds selectively to β₂-receptors in the bronchial smooth muscle, promoting prolonged bronchodilation and preventing bronchospasm.
Together, these agents deliver a synergistic effect that maintains airway patency while curbing underlying inflammation. The onset of action for Formoterol occurs within minutes, offering rapid symptom relief, whereas Budesonide sustains long-term airway protection through continued anti-inflammatory activity.
- Onset of action: Within 3–5 minutes
- Duration of effect: Up to 12 hours post-inhalation
- Pharmacokinetics: Low systemic absorption minimizes corticosteroid-related side effects while maintaining high pulmonary efficacy
Medical Uses and Indications
Primary Uses
- Asthma maintenance therapy: Controls chronic inflammation, prevents attacks, and reduces the need for rescue inhalers.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Improves airflow, lessens exacerbation frequency, and enhances exercise tolerance.
- Exercise-induced bronchospasm prevention: Provides prophylactic relief before physical exertion to prevent airway constriction.
Off-label Uses
- Eosinophilic bronchitis: Reduces eosinophilic infiltration in the bronchial mucosa, improving persistent cough.
- Cough variant asthma: Targets airway hyperreactivity to suppress chronic cough symptoms.
- Bronchial hyperreactivity: Helps stabilize airway responsiveness to allergens and environmental triggers.
- Step-down therapy: Used to minimize dependence on systemic corticosteroids in controlled asthma cases.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Foracort varies according to age, disease severity, and therapeutic response. It is typically administered as two inhalations twice daily, though the exact regimen should be determined by a physician.
- For Asthma: Standard adult dose is one to two inhalations twice daily, adjusted based on symptom control.
- For COPD: Usually one inhalation twice daily for maintenance therapy.
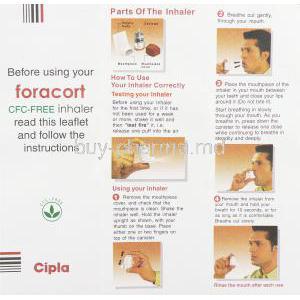
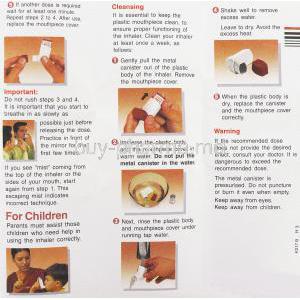
Foracort should be inhaled deeply through the mouthpiece to ensure optimal lung deposition. Regular cleaning of the inhaler is recommended to prevent blockage. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it’s close to the next dose. Patients should avoid double dosing.
A stepwise approach—starting from a low dose and titrating upward—ensures optimal balance between efficacy and safety.
Administration in Special Populations
Administration to Elderly
Elderly patients may exhibit heightened sensitivity due to comorbid cardiovascular or hepatic conditions. Dose adjustment is usually not necessary, but monitoring for systemic effects is advised.
Administration to Children
Foracort can be prescribed for children aged six years and older under medical supervision. Pediatric doses are generally lower, and proper inhalation training is crucial to ensure therapeutic benefit.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
During pregnancy, Foracort should only be used when the potential benefits outweigh the possible fetal risks. Budesonide is considered relatively safe compared to other corticosteroids, though prolonged exposure should be avoided. Minimal drug transfer into breast milk has been reported, but clinical significance remains low when used as prescribed.
Side Effects
Foracort Inhaler is generally well-tolerated, but certain local and systemic adverse reactions may occur. Most side effects are mild and transient, resolving with continued use or dosage adjustment.
Common Side Effects
- Throat irritation or dry cough
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Oral candidiasis (fungal infection of the mouth)
- Headache, dizziness, or mild tremor
- Palpitations or nervousness
Less Common and Serious Adverse Effects
- Hypokalemia (low potassium levels)
- Adrenal suppression due to chronic corticosteroid exposure
- Paradoxical bronchospasm (sudden airway tightening)
- Increased risk of pneumonia in COPD patients
To minimize side effects, patients are advised to rinse their mouth with water after each inhalation and maintain regular follow-up visits for monitoring lung function and systemic tolerance.
Warnings and Important Precautions
Foracort Inhaler should not be used for the immediate relief of acute asthma attacks or sudden episodes of breathing difficulty. It is designed as a maintenance therapy to prevent exacerbations and manage chronic symptoms. In the event of acute distress, a rapid-acting bronchodilator must be used instead.
Prolonged use of inhaled corticosteroids such as Budesonide carries potential systemic risks, including adrenal suppression and decreased bone mineral density. Patients with prolonged therapy may experience delayed recovery from stress and trauma, emphasizing the need for periodic evaluation of adrenal function.
Monotherapy with long-acting β₂-agonists (LABAs) has been associated with an increased risk of asthma-related death. Foracort mitigates this risk by combining Formoterol with Budesonide, ensuring anti-inflammatory coverage while maintaining bronchodilation. This balanced approach underpins the rationale for combination therapy in chronic airway diseases.
Continuous monitoring of respiratory function, peak expiratory flow rate, and symptom variability is essential to determine treatment efficacy. Adjustments to dosage or adjunct therapies may be necessary depending on individual response. Patients should be educated on recognizing worsening symptoms early.
To prevent oral infections such as Candida albicans-induced thrush, mouth rinsing and gargling with water after each inhalation are strongly advised. This simple precaution minimizes fungal overgrowth without compromising therapeutic benefits.
Contraindications
Foracort Inhaler is contraindicated in individuals with known hypersensitivity to Budesonide, Formoterol, or any component of the formulation. Hypersensitivity reactions may present as rash, angioedema, or bronchospasm and necessitate immediate discontinuation.
It must not be used as the primary treatment for acute bronchospasm or sudden-onset asthma attacks. Patients with severe cardiovascular disorders, including arrhythmias, ischemic heart disease, or heart failure, should avoid its use due to potential sympathomimetic effects from Formoterol. Likewise, uncontrolled hypertension and thyrotoxicosis can be exacerbated by β₂-adrenergic stimulation and require careful exclusion before initiating therapy.
Careful Administration
Special attention should be exercised in patients with cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, or seizure disorders. The β₂-agonist component may cause transient increases in blood glucose and heart rate, necessitating monitoring in susceptible populations.
Individuals with a history of tuberculosis, fungal, or viral infections of the respiratory tract require cautious use, as corticosteroid-induced immunosuppression may facilitate reactivation or progression of infections. Prophylactic or concurrent antimicrobial therapy may be warranted in such cases.
Patients with hepatic or renal impairment may exhibit altered drug metabolism, potentially elevating systemic Budesonide concentrations. Periodic evaluation of hepatic enzyme levels and renal function is recommended during prolonged use.
When discontinuing therapy, abrupt withdrawal should be avoided. A gradual tapering of dose is essential to prevent adrenal insufficiency and disease rebound, particularly after long-term corticosteroid use.
Drug Interactions
Foracort may interact with several classes of medications, influencing its safety and efficacy profile:
- CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and ritonavir can significantly increase plasma Budesonide levels, heightening the risk of systemic corticosteroid effects.
- β-blockers (both selective and non-selective) may counteract the bronchodilatory effects of Formoterol, potentially leading to bronchoconstriction in asthmatic patients.
- Antiarrhythmics that prolong the QT interval, such as amiodarone or quinidine, can produce additive effects, increasing the risk of cardiac arrhythmia when used concurrently.
- Diuretics and xanthines (e.g., theophylline) may enhance the risk of hypokalemia when used with β₂-agonists, requiring electrolyte monitoring.
- Concurrent use with systemic corticosteroids can augment adrenal suppression and metabolic disturbances.
- Caffeine and other stimulants may potentiate tremor and palpitations due to synergistic sympathetic activation.
Overdosage
Excessive inhalation of Foracort may produce symptoms consistent with β₂-agonist overstimulation, including tachycardia, tremors, hypokalemia, and hyperglycemia. Systemic corticosteroid toxicity may also develop after chronic overuse, manifesting as Cushingoid features or adrenal suppression.
Management of acute overdose involves supportive care and close cardiovascular monitoring. Electrocardiogram (ECG) evaluation is recommended to detect rhythm disturbances. Beta-blockers may be cautiously administered to reverse severe cardiac symptoms, though with careful consideration in asthmatic individuals.
Chronic overuse should be managed by gradual dose reduction under medical supervision, addressing systemic effects such as bone density loss or adrenal dysfunction.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Foracort Inhaler should be stored below 30°C in a dry environment, away from direct sunlight and excessive humidity. Extreme temperatures may compromise the stability of the propellant and drug formulation.
The canister should never be punctured, incinerated, or exposed to open flame, even when empty. Contact with water must be avoided to maintain proper aerosol function. Used or expired inhalers should be disposed of responsibly according to local pharmaceutical waste regulations.
Proper storage ensures consistent drug delivery and extends the usability of the inhalation device.
Summary
Foracort represents a cornerstone in the long-term management of asthma and COPD through its synergistic dual-action formula. By combining the potent anti-inflammatory activity of Budesonide with the prolonged bronchodilatory effect of Formoterol, it ensures comprehensive control over respiratory symptoms and prevents disease exacerbations.
The inhaler’s clinical value lies in its ability to reduce hospitalization rates, improve quality of life, and maintain stable pulmonary function when used correctly and consistently. Adherence to dosage instructions, proper inhalation technique, and regular follow-up are imperative for achieving optimal outcomes.
With careful administration and ongoing monitoring, Foracort remains an effective and safe option for patients requiring long-term respiratory management.