Zeformin XR, Gliclazide/ Metformin
- Introduction to Zeformin XR
- Overview of Zeformin XR as a Combination Therapy
- Composition of Zeformin XR
- Active Ingredients and Their Strengths
- Pharmaceutical Formulation and Available Dosages
- Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
- Jardiance and Metformin
- Farxiga and Metformin
- Glipizide and Metformin
- Metformin vs Mounjaro
- Rybelsus vs Metformin
- Metformin vs Wegovy
- Glipizide vs Metformin
- Berberine vs Metformin
- Metformin vs Ozempic
- Metformin vs Semaglutide
- Mechanism of Action: How Zeformin XR Works
- Approved Uses of Zeformin XR
- Off-Label and Investigational Uses
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Side Effects of Zeformin XR
- Common and Mild Side Effects
- Serious and Rare Side Effects
- Contraindications of Zeformin XR
- Drug Interactions and Food Interactions
- Warnings and Precautions for Use
- Special Populations: Cautions and Guidelines
- Pediatric Use
- Careful Administration and Monitoring
- Overdose and Emergency Management
- Storage Instructions for Zeformin XR
- Handling Precautions and Patient Education
Introduction to Zeformin XR
Zeformin XR is a significant advancement in oral diabetes treatment. It combines two effective medications in a single, extended-release tablet, tackling two key aspects of managing blood sugar: the body's insulin production and its ability to use insulin effectively.
Because of its slow-release formula, Zeformin XR maintains a steady level of medication in the bloodstream, avoiding the peaks and troughs of standard formulas. This modern approach to diabetes care moves beyond using a single drug and instead focuses on a comprehensive, long-lasting strategy. The combination therapy found in Zeformin XR makes it easier for people to follow their treatment plan, reduces stomach issues, and helps maintain a stable metabolism over time.
Overview of Zeformin XR as a Combination Therapy
Gliclazide and Metformin work in different ways to control blood sugar. Gliclazide, a sulfonylurea, directly stimulates the beta cells in your pancreas to produce and release more insulin. In contrast, Metformin, a biguanide, improves your body's response to the insulin it already has, making it easier for your liver and other cells to absorb glucose.
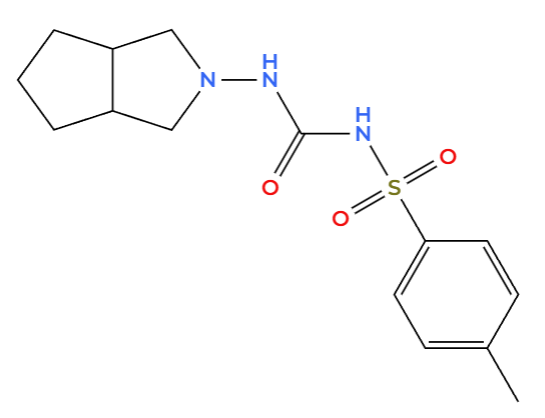
Gliclazide
Zeformin XR combines these two mechanisms into one medication. By both helping your body produce more insulin and improving how your cells use glucose, it effectively lowers high blood sugar. This dual-action approach makes it a powerful treatment for hyperglycemia.
When a single medication isn't enough to manage a condition, a combination therapy like Zeformin XR is often a great solution, especially for patients who need extra help to get their blood sugar under control.
The extended-release formula of Zeformin XR also helps patients stick to their treatment plan. Instead of taking multiple pills throughout the day, they only need to take one, which is much easier to remember. This also helps keep the amount of medication in their bloodstream stable, avoiding the spikes and dips that can occur with immediate-release formulas.
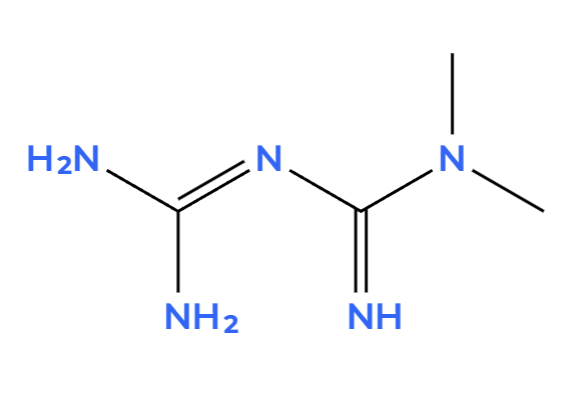
Metformin
Composition of Zeformin XR
Active Ingredients and Their Strengths
Zeformin XR contains a carefully measured combination of two active ingredients:
- Gliclazide, in doses typically ranging from 30 mg to 60 mg.
- Metformin hydrochloride, in controlled-release strengths from 500 mg to 1000 mg.
This blend is specifically designed to meet the varied needs of people with type 2 diabetes while keeping the risk of low blood sugar as low as possible.
Pharmaceutical Formulation and Available Dosages
Zeformin XR tablets have a design that lets the active ingredients slowly get released over an hour. This helps make sure the medicine works and also reduces the stomach problems that can happen with metformin. The way these tablets are made, with a kind of matrix, allows the ingredients to come out gradually which is gentler on the stomach.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
The formulation is a mix of ingredients and other substances, like hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and colloidal silica. These extras help keep the tablet from falling apart, control how the drug is released, and keep everything together when the tablets are stored.
Jardiance and Metformin
Zeformin XR isn't the combination noting. Jardiance, which is empagliflozin, is also often paired with metformin. This combination works by cutting back on glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, which in turn helps the body use insulin effectively. The result is a treatment that not only helps control blood sugar levels but also provides some protection against problems.
Farxiga and Metformin
When you combine Farxiga also known as dapagliflozin with metformin the results can be pretty powerful. Together, they tackle blood sugar levels by helping the kidneys get rid of glucose and adjusting how the liver produces glucose. This combination tends to work for people who are, at a higher risk, for heart or kidney problems.
Glipizide and Metformin
Glipizide is another type of sulfonylurea that can be used in combination with metformin to produce an effect. While its effective, there is a bit of a trade-off. Glipizide has a risk of causing hypoglycemia compared to gliclazide. This difference is important for doctors to consider when deciding which medication to prescribe.
Metformin vs Mounjaro
Mounjaro (tirzepatide) and Metformin work differently to manage blood sugar and weight.
- Mounjaro targets two key receptors in your body, which helps to improve blood sugar control and reduce appetite.
- Metformin primarily works by lowering the amount of glucose your liver produces.
This difference highlights a shift in treatment strategies: from simply adjusting your body's metabolism to using hormone-based approaches that mimic natural processes to regulate blood sugar.
Rybelsus vs Metformin
Rybelsus, a pill form of semaglutide, works in a way that Metformin does. Metformin is still the go-to treatment when someone is first diagnosed. Rybelsus brings some benefits to the table. It can help people lose a lot of weight and feel fuller for longer. This means doctors can now offer treatment plans depending on what each patient needs
Metformin vs Wegovy
Wegovy (semaglutide) is a medication designed primarily for weight management, although it also helps control blood sugar. Metformin, on the other hand, is used mainly to control blood sugar levels. This difference highlights the close connection between treatments for diabetes and obesity. Both medications play important roles in addressing these complex health issues.
Glipizide vs Metformin
While both Metformin and Glipizide are essential diabetes medications, they have different safety profiles. Glipizide stimulates the body to release insulin, which can lead to a higher risk of dangerously low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). In contrast, Metformin works differently by making the body more sensitive to the insulin it already has. This reduces the need for extra insulin production, making it a safer and preferred first-line treatment.
Berberine vs Metformin
Berberine, a compound found in plants, has been getting attention for its potential to help the body respond to insulin. While research has drawn some comparisons between berberine and metformin, a diabetes medication, there is still not clinical evidence to back up its effectiveness, and it hasn't been officially endorsed by regulatory bodies. As things stand metformin has a track record when it comes to scientific proof.
Metformin vs Ozempic
Ozempic or semaglutide has been shown to lower blood sugar levels and trim body weight. Metformin is a staple in diabetes treatment, offering a budget friendly option that most people can tolerate. Typically, doctors start patients on metformin before moving to advanced medications like Ozempic, which works by mimicking a natural hormone in the body.

Metformin vs Semaglutide
Semaglutide comes in two forms. A pill you take by mouth and an injection. It's shown to have a wider range of effects on metabolism than metformin. Metformin remains the line of treatment around the world. This is because it's been proven to work is easy to get, and has a record of being safe, over time.
Mechanism of Action: How Zeformin XR Works
Gliclazide Mechanism: Stimulating Insulin Secretion
Gliclazide, a type of sulfonylurea, works by binding to channels on the surface of pancreatic beta cells. This action triggers a chain reaction that changes the cell's electrical charge, causing it to depolarize. As a result, other voltage-sensitive channels open, allowing calcium to rush into the cell. This influx of calcium is the final trigger that causes the beta cells to release their stored insulin.
By stimulating the pancreas in this way, Gliclazide helps reduce the spikes in blood glucose that occur after meals. This drug is particularly appealing for long-term blood sugar management because it has a lower risk of causing hypoglycemia compared to other sulfonylureas.
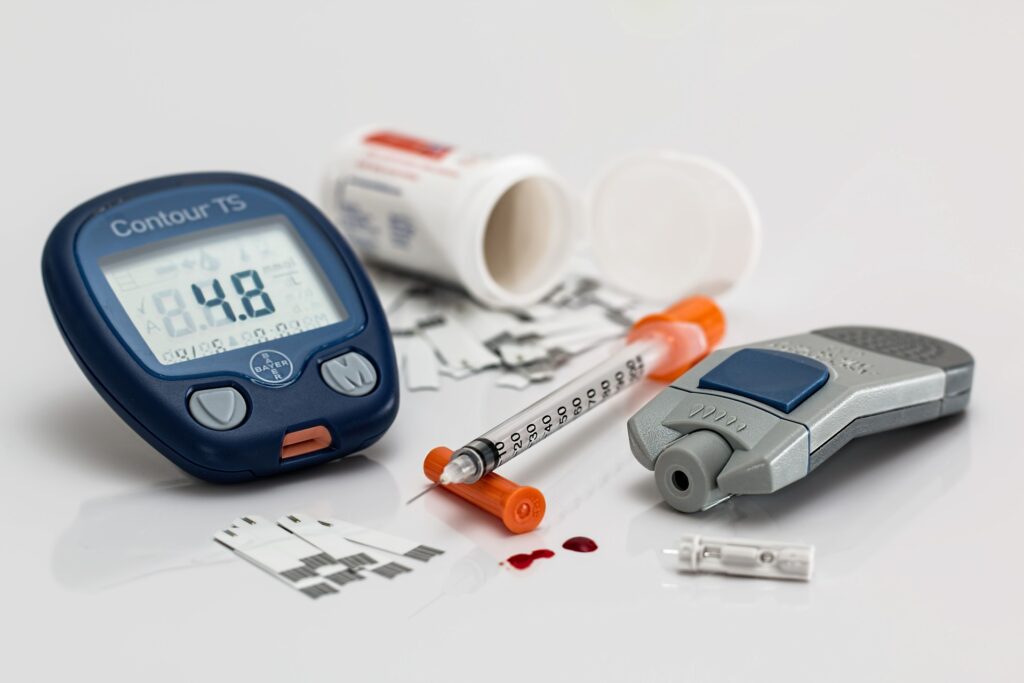
Metformin Mechanism: Reducing Hepatic Glucose Production and Increasing Insulin Sensitivity
Metformin works in a completely different way from other diabetes medications. It activates an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which is like a sensor for your cells' energy levels.
By activating AMPK, Metformin does two key things:
- It reduces the amount of glucose your liver produces.
- It increases how much glucose your muscles absorb from your blood.
This dual action helps to lower both fasting and after-meal blood sugar levels. Because Metformin improves your body's sensitivity to insulin without causing the pancreas to release more insulin, it has a significant benefit: it protects against hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). This makes it a very safe option that's easy for patients to stick with.
Synergistic Effect of Combined Therapy
When combined in Zeformin XR, Gliclazide and Metformin create a more powerful effect than either drug could achieve alone. Gliclazide stimulates the pancreas to release insulin, while Metformin helps the body use that insulin more effectively and reduces the amount of glucose the liver produces. This two-pronged approach tackles the complex causes of type 2 diabetes, leading to:
- Fewer sharp drops in blood sugar.
- A lower chance of the treatment failing compared to using a single medication.
- The ability to achieve the best results with lower doses of each drug.
Impact on HbA1c and Postprandial Glucose Levels
Studies show that Zeformin XR can reduce average blood sugar levels (measured as glycated hemoglobin) by 1-2%, though the exact reduction depends on a patient's initial levels and how consistently they take the medication. Controlling blood sugar spikes after meals it helps prevent the high peaks that can harm blood vessels. Over time, this daily management of blood sugar provides significant long-term benefits for both cardiovascular and overall health.
Approved Uses of Zeformin XR
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults
Zeformin XR is a medication approved for helping adults manage type 2 diabetes. It's particularly useful for those who need to control both their fasting and after-meal blood sugar and who aren't getting the results they need from other medications. One of its key benefits is that its extended-release formula is easier on the stomach, which is a significant factor in helping people stick to their treatment plan for a long-term illness like diabetes.
As Monotherapy or in Combination with Other Antidiabetic Agents
This treatment can be used on its own for patients who can't tolerate other oral medications. However, it's often combined with other anti-diabetes drugs that work in different ways:
- SGLT2 inhibitors, which help the kidneys remove glucose from the body.
- DPP-4 inhibitors, which extend the activity of hormones that control blood sugar.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists, which increase feelings of fullness and promote insulin secretion.
Using these combinations gives doctors the flexibility to customize treatment plans to each patient's specific needs.
Use in Patients Inadequately Controlled on Metformin or Sulfonylurea Alone
For patients whose diabetes isn't well-controlled with either metformin or a sulfonylurea alone, Zeformin XR is an excellent option. By combining these two medications into a single tablet, it simplifies treatment and boosts its effectiveness. This is especially helpful because it prevents treatment from becoming stagnant and can help patients avoid having to quickly escalate to more intensive therapies, such as insulin injections. This makes Zeformin XR a key part of a flexible, step-by-step approach to diabetes care.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses
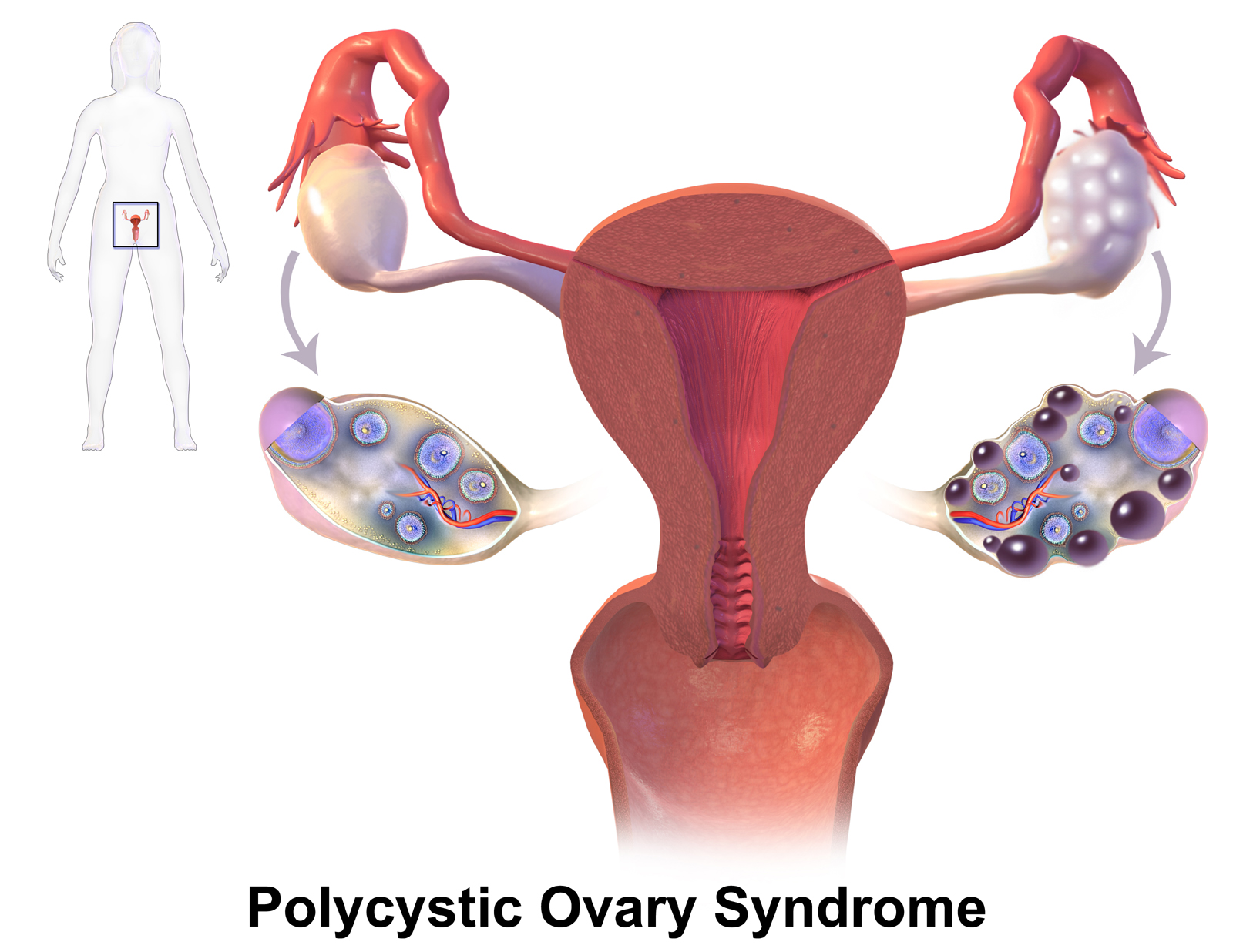
Metformin and PCOS
Metformin is no longer just for diabetes; it's also a common treatment for women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). This condition is often marked by high hormone levels that disrupt menstrual cycles and can make it difficult to get pregnant.
Metformin helps by improving your body's response to insulin, which lowers the amount of insulin in your blood. In turn, this reduces the production of other hormones, which can ease many PCOS symptoms.
For many women with PCOS, taking metformin can lead to:
- More regular periods.
- Improved chances of ovulating.
- Increased fertility.
While Metformin wasn't originally intended to be a fertility treatment, its effects on metabolism can significantly improve the hormone balance that's a key factor in PCOS.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) is a growing global health issue closely tied to insulin resistance and other metabolic problems. Metformin has been studied for its ability to reduce fat in the liver by affecting certain metabolic pathways (AMPK).
While research shows that Metformin can improve liver enzyme levels and insulin sensitivity, its effect on liver scarring (fibrosis) is still not clear. However, its usefulness in managing NAFLD highlights its versatility as a medication that addresses broader metabolic diseases.
Weight Management in Metabolic Syndrome
Within the context of metabolic syndrome, metformin can help stabilize weight and, in some people, lead to a small amount of weight loss. It works by lowering the amount of glucose your liver produces, which can also decrease your appetite and calorie intake.
Although it isn't a primary weight-loss drug, it often supports lifestyle changes. Doctors frequently observe that metformin use leads to:
- Less fat around the waist.
- Better lipid (fat) metabolism.
- Improved response to insulin.
This makes metformin a valuable tool for preventing metabolic syndrome from progressing to full-blown diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes (Limited and Case-Specific)
For pregnant women with diabetes, insulin remains the preferred treatment. However, Metformin is becoming a potential alternative for some patients for the treatment of gestational diabetes. A key advantage of Metformin is that it can be taken orally, and women using it often gain less weight during pregnancy compared to those on insulin.
On the other hand, there are concerns about the fetus's exposure to the drug, as Metformin can cross the placenta. Because of this, it is only recommended for pregnant women who cannot or will not take insulin. Even then, its use is carefully monitored and customized for each individual's specific needs.

Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Starting Dose and Titration Recommendations
When you first start taking Metformin, whether alone or with other medications, you typically begin with a low dose to help your body adjust. A common starting point is 500 mg, taken once or twice a day.
The dose is then gradually increased, usually by 500 mg every one or two weeks, as long as you can tolerate it without significant stomach issues. The goal is to reach a daily dose of 1500 mg to 2000 mg, as this range is generally the most effective while still being well-tolerated.
Dosing Frequency and Administration Timing with Meals
To reduce side effects like diarrhea and stomach pain, it's best to take Metformin with food. The immediate-release version is usually taken two or three times a day, while the extended-release version is taken just once a day. Taking the medication with meals helps your stomach handle it better and makes it easier to stay on schedule.
Renal Function-Based Dose Adjustments
The proper dosage of Metformin depends on how well your kidneys are functioning. To determine this, doctors will check your estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) before you start the medication and at regular intervals afterward.
- If your eGFR is 60 mL/min/1.73 m² or higher, you can be given the full dose without concern.
- If your eGFR is between 45 and 59, the medication should be used cautiously, and you should be monitored closely.
- If your eGFR is between 30 and 44, it's generally recommended to take a reduced dose and not increase it.
Metformin is not recommended for people with an eGFR below 30, as this significantly increases the risk of a serious condition called lactic acidosis.
Considering a patient's kidney health is essential for both their safety and the long-term effectiveness of their treatment.
Switching from Other Antidiabetic Regimens
When switching from sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones or insulin to Metformin it's best to phase it in. Using both treatments together for a while can help keep blood sugar levels steady. The dosing will need to be tailored to each person for those who were taking a lot of insulin to prevent blood sugar from dropping low or becoming unstable.
Metformin Dosage for Weight Loss
Metformin, a common diabetes medication, has also been studied for its use in weight management for non-diabetic individuals. The dosage is typically the same as for diabetes, about 1500-2000 mg per day. While the weight loss is usually modest, averaging around 2 to 4 kilograms over several months, it is most effective in those with insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome. It's important to remember that metformin is meant to be used in addition to diet and exercise, not as a replacement.
Side Effects of Zeformin XR
Classification by System: Gastrointestinal, Metabolic, Hematologic
The side effects of Zeformin XR generally affect two main areas of the body.
- First, gastrointestinal issues are common due to the metformin component. Patients often report problems like diarrhea, nausea, and stomach discomfort, and occasionally constipation or indigestion.
- Second, the gliclazide component can lead to low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), especially if you skip or delay meals, because it stimulates your body to produce more insulin.
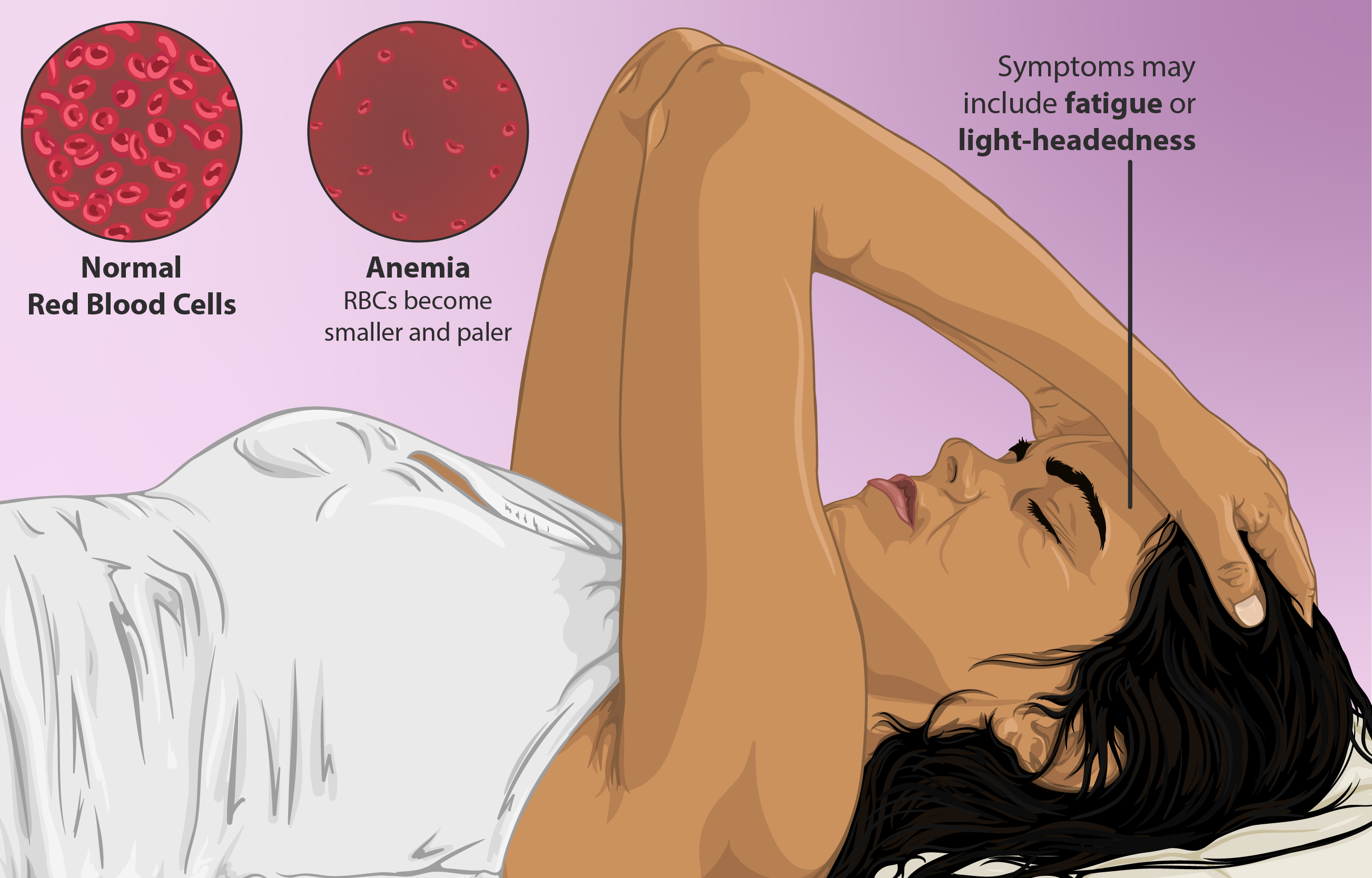
Additionally, a rare long-term side effect of metformin is a vitamin B12 deficiency, which, if left untreated, could potentially lead to anemia.
Frequency Categories: Very Common, Common, Rare
Side effects from this medication can happen at different rates, categorized by how often they occur:
- Common side effects, especially when starting the medication or increasing the dose quickly, include stomach problems like diarrhea and nausea.
- Less common side effects can include a metallic taste in your mouth or constipation. For those who are sensitive, there's also a chance of low blood sugar.
- Rare, but severe side effects can occur, such as extremely low blood sugar, a dangerous buildup of lactic acid, or blood disorders like megaloblastic anemia, which can be caused by a lack of vitamin B12.
Doctors use these classifications to help predict how patients might react to the treatment. This allows them to better prepare patients for potential side effects and provide guidance and support.
Managing Common Side Effects
Dealing with medication side effects can be a challenge, but there are practical ways to manage them:
- Start with a low dose and increase it slowly to help your body adjust and reduce stomach problems from metformin.
- Always take your medication with food to ease stomach discomfort and nausea.

- Consider an extended-release version, like Zeformin XR, as it's less likely to cause stomach issues, such as diarrhea and bloating, than immediate-release tablets.
- Monitor your blood sugar closely and adjust your diet to help manage low blood sugar caused by gliclazide.
When these strategies are combined with the medication, patients are more likely to stick with their treatment and see better results over time.
Common and Mild Side Effects
Nausea, Diarrhea, Abdominal Discomfort
When treatment first starts, some side effects are pretty common. They tend to go on their own after a couple of weeks especially if the dosage is increased slowly. It's worth telling patients that while these symptoms can be a hassle, they're rarely bad enough to make them stop treatment altogether.
Metallic Taste in Mouth
Some people on Metformin may notice a temporary metallic taste in their mouth. While this isn't harmful, it can sometimes affect your appetite and the way food tastes. This sensation usually goes away on its own as your body gets used to the medication or after your dose is stable.
Mild Hypoglycemia (Especially with Missed Meals)
Even with Zeformin XR, patients taking gliclazide should be mindful of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can cause dizziness, sweating, and fatigue. To help prevent this, it's a good idea to eat regular meals, keep glucose tablets with you, and limit alcohol. If your blood sugar starts to drop, catching it early and acting quickly can prevent the situation from getting worse. Being prepared and paying attention to your eating habits can make a big difference in managing this risk.

Serious and Rare Side Effects
Lactic Acidosis: Risk Factors and Symptoms
Lactic acidosis, a very rare but serious side effect of metformin, occurs when the body can't clear lactate, leading to a dangerous buildup. The risk is higher for people with kidney problems, heart failure, sepsis, dehydration, or those who drink a lot of alcohol.
Early symptoms can be subtle but may include:
- Extreme fatigue and muscle weakness.
- Stomach problems, such as abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting.
- Rapid, shallow breathing (tachypnea) or shortness of breath.

- Confusion or an altered mental state.
If these symptoms appear, you must stop taking the medication and seek immediate medical help to prevent potentially deadly consequences.
Severe Hypoglycemia and Its Management
Because this medication contains gliclazide, there's a risk of hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar). This can be triggered by skipping meals, exercising too much, or drinking too much alcohol.
Symptoms can include seizures, fainting, or severe confusion. If a person is awake, they should immediately eat or drink something sugary. In a hospital, doctors can give a sugar solution directly into a vein.
To prevent these incidents, patients should understand how to manage their condition, eat at regular times, and have their medication dose carefully adjusted by a doctor.

Hematologic Effects: Anemia, Thrombocytopenia
Long-term use of Metformin can lead to a vitamin B12 deficiency, which might cause a type of anemia. In some cases, it has also been linked to thrombocytopenia (low platelets) or leukopenia (low white blood cells), which can increase the risk of bleeding or infections. To prevent these blood-related issues, doctors should regularly monitor their patients' blood counts and vitamin B12 levels during extended treatment.
Allergic Reactions and Dermatological Symptoms
Although rare, allergic reactions to this medication can occur. Symptoms can range from a simple rash or itchiness to severe swelling of the face or throat. Other signs might include hives or red, blotchy patches on the skin.
If you experience a reaction, you should immediately stop taking the medication and see a doctor. A doctor may prescribe antihistamines or corticosteroids to help manage your symptoms, depending on how severe the reaction is.
Contraindications of Zeformin XR
Severe Renal Impairment or End-Stage Renal Disease
Zeformin XR is not safe for patients with kidney problems or kidney failure. Because their kidneys can't properly filter the drug, it can lead to a dangerous condition called lactic acidosis. For this reason, doctors must check a patient's kidney function before starting treatment and continue to monitor it throughout.
Acute or Chronic Metabolic Acidosis, Including Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Zeformin XR should not be used by patients with any form of metabolic acidosis, whether it's acute or chronic. This is particularly important for those with ketoacidosis, which requires immediate treatment with insulin and fluids. Giving Zeformin XR to a person in this state could worsen their condition and potentially lead to life-threatening complications.
Known Hypersensitivity to Gliclazide, Metformin, or Any Excipients
If you have an allergy to any ingredient in Zeformin XR, you should not take it. Even a mild allergic reaction can signal that a future reaction could be much more severe, so the medication should be stopped permanently.
Metformin Contraindications
Metformin is generally not recommended if you have certain health conditions that increase the risk of a serious complication called lactic acidosis. These conditions include:
- Liver problems
- Conditions that affect your blood's ability to carry oxygen
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Other severe health issues like a recent heart attack, a serious infection, or severe dehydration
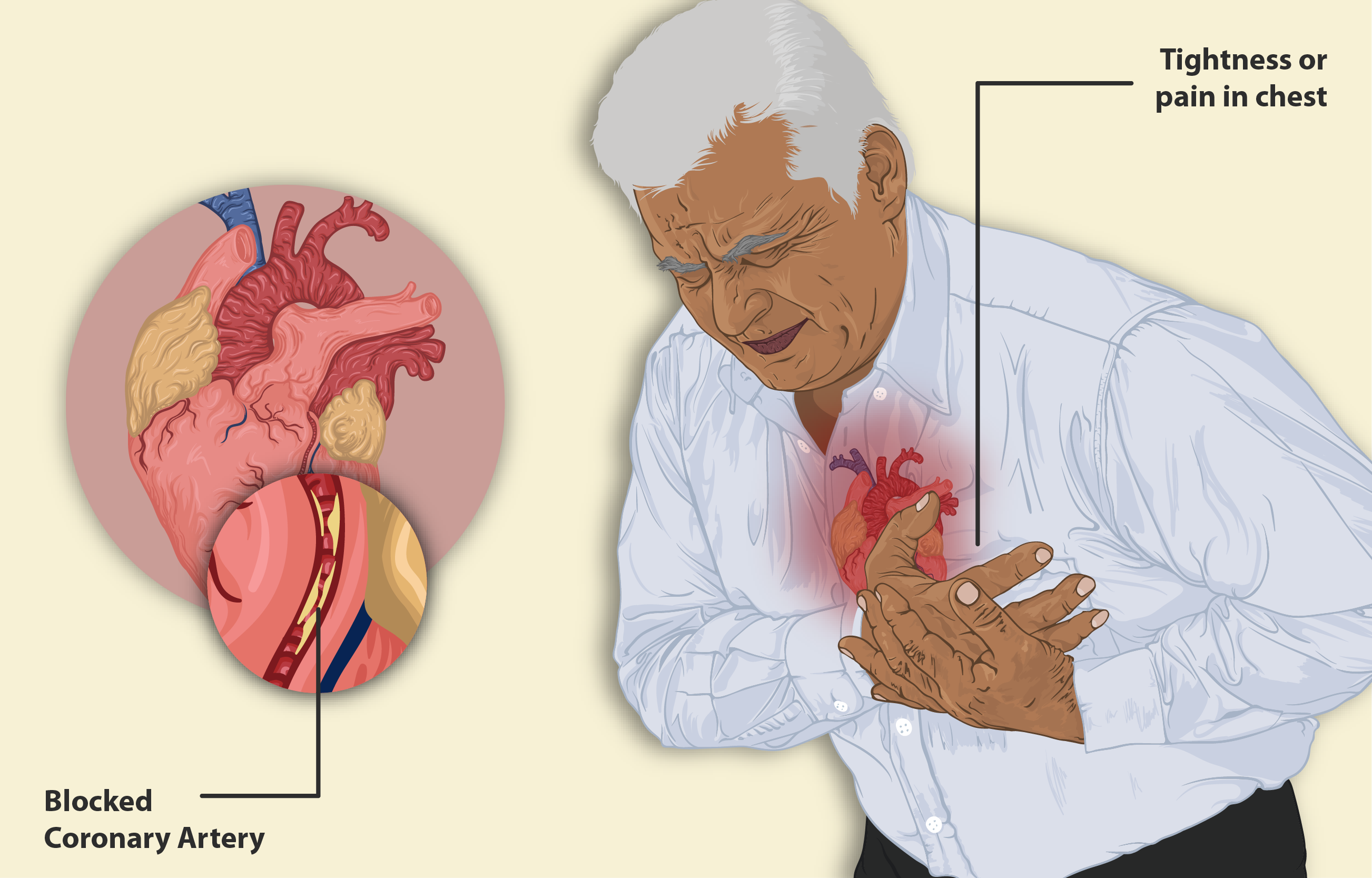
Because these conditions can make you more vulnerable to lactic acidosis, doctors must carefully consider these risks before prescribing metformin.
Drug Interactions and Food Interactions
Interactions with Other Antidiabetic Agents
Combining diabetes medications with insulin, meglitinides, or other sulfonylureas can be very effective at controlling blood sugar, but it also significantly increases the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Because of this, these combinations require careful monitoring and customized dosing to be used safely.
Risk with Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol while on Metformin can increase the risk of a serious condition called lactic acidosis, as alcohol interferes with how your body processes lactate. This risk is especially high with binge drinking or drinking on an empty stomach. For your safety, it's best to limit or completely avoid alcohol while taking this medication.
Impact of Corticosteroids, Diuretics, Beta-Blockers
Several other medications can interfere with Zeformin XR's effectiveness and increase its side effects:
- Corticosteroids can raise blood sugar by increasing glucose production in the liver and reducing your body's response to insulin.
- Diuretics can worsen dehydration and affect kidney function, which increases the risk of lactic acidosis.
- Beta-blockers can hide the symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), making it more difficult to recognize and treat the condition.
Use with Iodinated Contrast Agents
To prevent potential kidney problems caused by iodinated contrast media, doctors typically have patients stop taking metformin before exposure. This precaution is taken to avoid the risk of lactic acidosis if the contrast agent causes sudden kidney issues. Once a patient's kidney function has been checked and is confirmed to be stable, they can safely restart their metformin.
Metformin and Alcohol
Combining Metformin with alcohol is risky because alcohol both slows down the liver's glucose production and makes it harder for the body to clear lactate. This significantly increases the risk of lactic acidosis. Therefore, it's crucial for patients to be advised on limiting their alcohol intake to ensure their safety during treatment.

Warnings and Precautions for Use
Risk of Lactic Acidosis and Preventive Measures
Lactic acidosis is a rare but life-threatening side effect of medications containing metformin, like Zeformin XR. It's a medical emergency caused by a buildup of lactic acid in the body.
To reduce this risk, doctors carefully select patients for these medications, avoiding those with kidney or liver disease. They also stop the treatment if a patient's condition could lead to low oxygen levels or dehydration.
It is crucial for patients to recognize the warning signs of lactic acidosis, such as fatigue, stomach pain, or rapid breathing, so they can get immediate medical help if symptoms appear.

Renal Function Monitoring Protocol
Since the kidneys are responsible for eliminating metformin from the body, doctors must assess a patient's kidney function before starting treatment by checking their estimated filtration rate.
Afterward, kidney function should be rechecked at least once a year for healthy adults. For older patients or those with existing kidney issues, these checks should be more frequent, occurring every three to six months. If kidney function declines, the metformin dose may need to be adjusted or stopped entirely to prevent the drug from accumulating and causing lactic acidosis.
Liver Function Impairment and Drug Metabolism
Although metformin isn't processed by the liver, people with liver problems are still at a higher risk of lactic acidosis because their bodies have trouble clearing lactate. Therefore, Zeformin XR should not be used in patients with liver damage. Doctors must be particularly cautious with patients who drink heavily, have liver scarring (cirrhosis), or have elevated liver enzymes, as these conditions further impair the body's metabolic regulation.
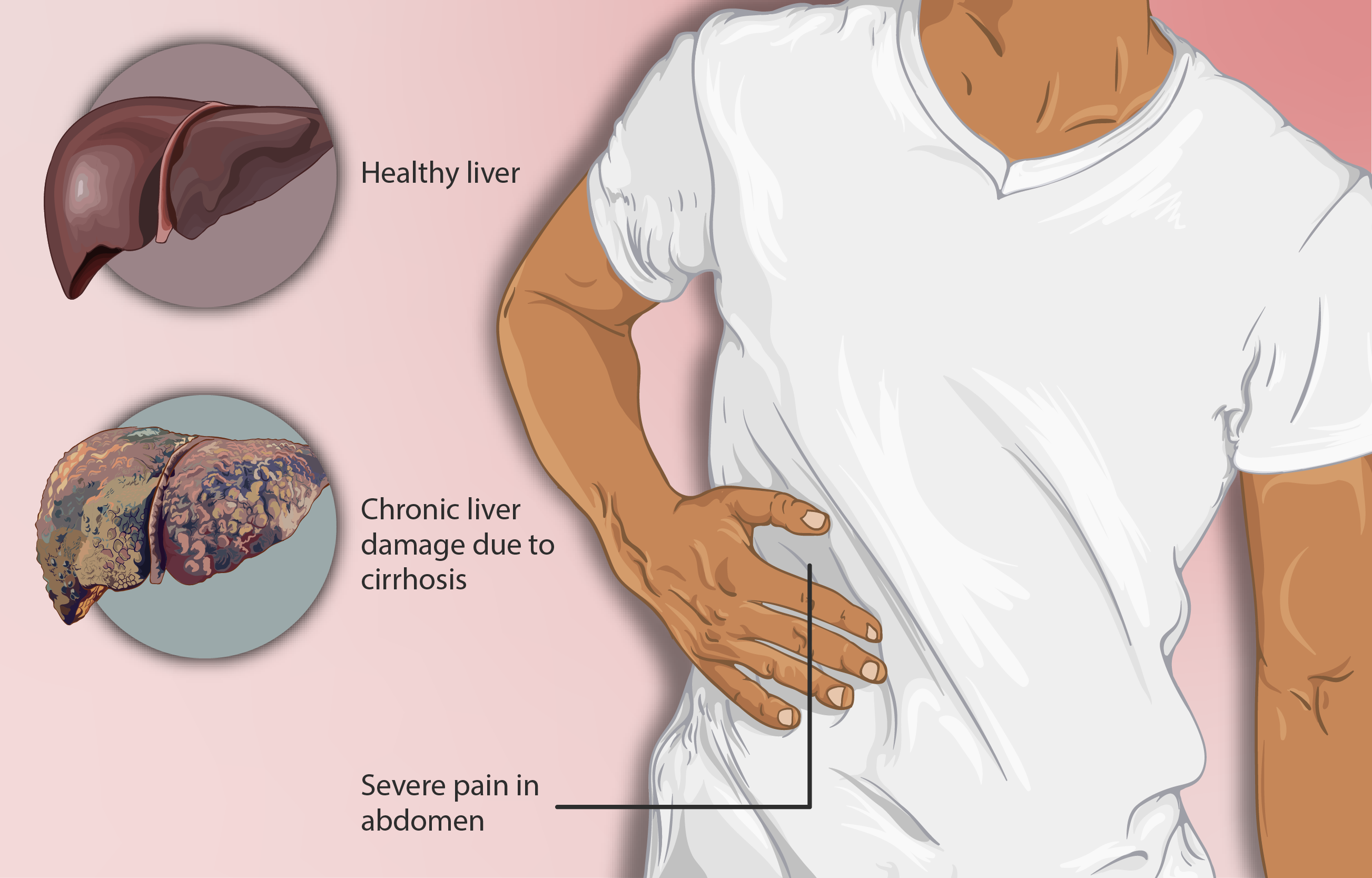
Avoidance of Dehydration and Infections
If you're dehydrated from conditions like vomiting, diarrhea, or not drinking enough fluids, your kidneys can be affected. This, along with severe infections like pneumonia or a UTI, can significantly increase the risks associated with metformin. If you become seriously ill or dehydrated, you should temporarily stop taking Zeformin XR. Do not restart the medication until you have recovered and your doctor has confirmed that your kidney function is back to normal.
Side Effects of Stopping Metformin Suddenly
Suddenly stopping Metformin can cause a rapid and dangerous rise in blood sugar. Patients may experience high fasting and after-meal glucose levels, and over time, classic symptoms of high blood sugar, like increased thirst and frequent urination, can appear. For those who have been on the medication for a long time, abruptly stopping could worsen their diabetes more quickly. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a doctor before discontinuing Metformin. A physician can help by safely transitioning you to another medication or creating a plan to maintain stable blood sugar levels.

Special Populations: Cautions and Guidelines
Elderly Patients
Age-Related Decline in Renal Function and Risk Mitigation
As people age, their kidneys naturally become less efficient, which increases the risk that a diabetes medication could build up to dangerous levels and lead to a life-threatening condition. To reduce this risk, doctors should be cautious with the dosage, regularly monitor the patient's kidney function, and watch for any new illnesses. The best approach is to consider the patient's overall health and any existing medical conditions when deciding on a treatment plan.
Starting Dose and Monitoring Parameters
When starting a patient on this medication, it is best to begin with a low dose, typically 500 mg once daily, to reduce side effects. As treatment continues, the dose should be increased slowly and carefully. It's essential to monitor the patient's kidney and liver function, as well as their ability to tolerate the medication. Additionally, a review of all other medicines the patient is taking is important to avoid interactions that could affect blood sugar control.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Use in Pregnancy: Risks and Benefits
While insulin is the standard treatment for managing health conditions during pregnancy, metformin may be an option for some women with polycystic ovary syndrome or gestational diabetes, provided they are closely monitored by a doctor. Using metformin in these cases could offer benefits like helping to control weight gain and reducing the need for insulin injections. However, research is still ongoing to fully understand the effects of metformin on the baby.

Category C Classification and Recommendations
Zeformin XR, which contains metformin, is not clearly categorized for use during pregnancy. While animal studies have shown some potential risks, there is not enough data from human trials to confirm its safety. Therefore, doctors must carefully weigh the benefits for the mother against the potential risks to the fetus. The medication is typically only prescribed when insulin is not a suitable option or when the potential benefits are considered to be far greater than the risks.
Breastfeeding Considerations and Excretion in Breast Milk
Metformin can pass into a mother's breast milk in small amounts. While studies have not shown any harm to babies, it is still important to be cautious. Doctors usually recommend monitoring the baby's growth and development if the mother is breastfeeding while taking metformin. In cases where the mother is on high doses or has been on the medication for a long time, it may be safer to consider alternative feeding methods, such as formula, if the risks appear to outweigh the benefits.
Pediatric Use
Safety and Efficacy in Children and Adolescents
The use of Zeformin XR in children is limited because most research has focused on adults. While metformin alone is approved for children over ten in some regions, the combination with gliclazide has not received the same widespread regulatory approval for pediatric use. There is not enough safety data, and a major concern is that the gliclazide component could cause dangerously low blood sugar in teenagers. Doctors are still investigating its long-term benefits for children, and they must be very cautious when deciding whether to prescribe it.

Off Label Considerations for Pediatric Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes, doctors may prescribe a medication for a purpose that hasn't been officially approved, a practice known as "off-label" use. This might be considered for adolescents with type 2 diabetes that is difficult to manage with a single drug.
When making this decision, doctors must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of side effects, particularly those related to metabolism and blood disorders. Close supervision is essential, and the dosage must be adjusted based on the patient's weight, stage of development, and organ function.
For these complex cases, it's best to involve a team of experts, including endocrinologists and dietitians, to ensure all aspects of the patient's care are considered before beginning treatment.
Recommended Monitoring in Pediatric Use
When children and teenagers are on Zeformin XR, they need to be carefully monitored to ensure the drug is both effective and safe.
- Blood Sugar Control: Regular checks of their fasting blood sugar and long-term HbA1c levels are crucial to track how well their glucose is being managed.
- Growth and Development: It's important to monitor their height and weight, as well as the timing and progression of puberty, to ensure they are growing as expected and to catch any potential issues early.
- Organ Function: Regular check-ups on their kidney and liver function are necessary to ensure these organs are working correctly.
- Hypoglycemia Awareness: Caregivers must be educated on the signs of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) so they can recognize and quickly respond to a potential drop, which is especially important for young patients who may not be able to identify the symptoms themselves.
This close monitoring is essential to prevent undertreatment and reduce the risk of side effects in this vulnerable patient group.
Careful Administration and Monitoring
Baseline Lab Tests: Renal, Hepatic, Hematologic
Before starting a patient on Zeformin XR, doctors need to perform a baseline evaluation to understand the patient's current health. This includes a series of tests to:
- Assess kidney function, which shows how well the body can remove the drug.
- Check liver enzymes, which provide insight into how the body processes it.
- Review blood tests to look for potential issues like anemia or low blood cell counts.
By considering all of these factors, doctors can safely prescribe the medication and catch any potential problems early, ensuring the treatment gets off to a good start.
Periodic Follow-Up and Glycemic Control Markers
To monitor your progress, doctors typically check your HbA1c levels every three months and may ask you to regularly track your own blood sugar. Other tests are done on a case-by-case basis. For instance, kidney and liver function tests are usually performed once a year, but they may be done more often for high-risk patients. Additionally, if you've been on certain treatments for a long time, it's a good idea to have your vitamin B12 levels checked periodically to prevent anemia.
Dose Modification in Illness or Stress Conditions
When patients become severely ill, undergo surgery, or experience significant stress, their body's ability to manage glucose can be disrupted. This may require a temporary adjustment in their medication. In certain cases, such as with dehydration or infection, it is best to temporarily stop the treatment to prevent a serious complication called lactic acidosis. Once they have recovered and their lab tests are back to normal, they can safely resume the medication. The main goal is to ensure their safety during these high-risk periods.
Foods to Avoid While Taking Metformin
Certain foods and drinks can negatively interact with this medication, either reducing its effectiveness or increasing side effects.
- Alcohol consumption can significantly increase the risk of developing lactic acidosis.
- High-fat meals can slow down drug absorption and cause stomach discomfort.
- Foods high in sugar or simple carbohydrates can make it much harder to control your blood sugar levels.
To get the best results and minimize side effects, you should focus on a balanced diet rich in complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and high-fiber vegetables. This approach helps the medication work smoothly and reduces the chance of unwanted side effects, helping you feel more in control of your health.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose: Hypoglycemia, Lactic Acidosis
Taking Zeformin XR can lead to two serious conditions: dangerously low blood sugar (from the gliclazide) or a buildup of lactic acid (from the metformin). Both can cause severe symptoms.
Low blood sugar can result in:
- Confusion, sweating, or shaking
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
A buildup of lactic acid might be indicated by:
- Slow, deep breathing
- A drop in blood pressure
- A decrease in body temperature
Immediate Interventions and Supportive Care
Treating this condition promptly is key. Giving glucose orally or through a vein can quickly correct blood sugar levels. Making sure the person gets plenty of fluids helps their kidneys remove the metformin, from their system. Care for these patients also involves fixing any imbalances keeping an eye on their heart rhythm and providing oxygen constantly if they need it.
Hospitalization and Dialysis Indications
In cases of overdose or signs of lactic acidosis, a patient must be hospitalized. Doctors may use dialysis to quickly remove excess metformin from the body and correct the acid-base imbalance. Being in an intensive care unit allows for close monitoring and specialized care until the patient's condition is stable.
Storage Instructions for Zeformin XR
Recommended Temperature and Humidity Conditions
To maintain the effectiveness of Zeformin XR, store the tablets at room temperature, ideally between 20 to 25 degrees Celsius. This helps ensure they remain stable over time. You should also protect them from moisture and direct sunlight.
Shelf-Life and Packaging Integrity
To protect this medication from contamination or damage, it's best to keep it in its original packaging until you're ready to use it. The medication's effectiveness is guaranteed only until the expiration date. You should never take tablets that have expired and should dispose of them properly.
Safe Storage Away from Children and Moisture
Storing medications safely is crucial. To prevent accidents it's essential to keep tablets in containers that kids can't open and make sure they are, out of reach of both children and pets. You wouldn't want to store them in a bathroom or kitchen where the humidity can change a lot. That could affect how well they work. A better idea is to find a spot, like a cabinet, where they'll be protected and remain effective.
Handling Precautions and Patient Education
Safe Handling and Disposal
To dispose of unused tablets, you should do so responsibly by using pharmacy take-back programs. It's important not to crush or split tablets, especially the slow-release kind, as this can change how the medication is absorbed and increase the risk of side effects. Always handle the tablets carefully and only when they are still whole.
Importance of Adherence and Consistent Timing
To keep blood sugar levels under control, it's crucial to take Zeformin XR at the time every day. Taking it with meals is an idea as this can help ease any stomach discomfort and make it easier to stick to the routine. By doing the amount of the medication, in the bloodstream stays steady which is important, for managing diabetes.
Patient Counseling on Symptom Recognition and Lifestyle Integration
When patients receive proper counseling, they feel more in control of their health. It's essential that they learn to recognize the signs of potential problems like low blood sugar, lactic acidosis, or stomach issues.
Adopting a proactive lifestyle is also key. Making smart choices like eating a healthy diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and limiting alcohol can significantly improve treatment effectiveness and reduce the risk of future complications.

Zeformin XR, Gliclazide/ Metformin FAQ
- Are Gliclazide and Glipizide the same?
- Are Gliclazide and Diamicron the same?
- What are Gliclazide tablets for?
- What are Gliclazide tablets used for?
- Are Metformin and Gliclazide the same?
- Are Glimepiride and Gliclazide the same?
- Can Gliclazide cause weight gain?
- Can Gliclazide cause hypoglycemia?
- Can Gliclazide cause weight loss?
- Can Gliclazide and Glimepiride be taken together?
- Can Gliclazide cause pancreatitis?
- Can Gliclazide and Glibenclamide be taken together?
- Can Gliclazide cause constipation?
- Can Gliclazide cause liver damage?
- Can Gliclazide be crushed?
- Can Gliclazide cause headaches?
- Can Gliclazide be used with insulin?
- Can Gliclazide cause blurred vision?
- Can Gliclazide be taken without food?
- Can Gliclazide and Dapagliflozin be taken together?
- Can Gliclazide cause dizziness?
- How Gliclazide works?
- How Gliclazide works in the body?
- Gliclazide how to take?
- Gliclazide how many times a day?
- Gliclazide how fast does it work?
- How does Gliclazide work in the body?
- How does Gliclazide cause hypoglycemia?
- How is Gliclazide excreted?
- What Gliclazide is used for?
- Gliclazide what time to take?
- Gliclazide what type of drug?
- Gliclazide when to stop before surgery?
- When should Gliclazide be stopped?
- Does Metformin cause weight loss?
- How to lose weight fast on Metformin?
- Does Metformin help with weight loss?
- Does Metformin cause diarrhea?
- How long does it take for Metformin to work?
- How does Metformin help you lose weight?
- Why does Metformin cause diarrhea?
- What is the lowest dose of Metformin you can take?
- Can Metformin cause weight loss?
- Does Metformin help you lose weight?
- How long does Metformin take to work?
- Does Metformin make you sleepy?
- Is Metformin used for weight loss?
- When is the best time to take Metformin?
- Metformin dosage for weight loss in non diabetics?
- Does Metformin cause weight gain?
- What happens if you take too much Metformin in one day?
- How long does Metformin stay in your system?
- Does Metformin cause hair loss?
- How long does it take Metformin to work?
- Best time to take Metformin for weight loss?
- What is the lowest dose of Metformin you can take for PCOS?
- Can Metformin cause diarrhea?
- Can I stop taking Metformin when my sugar back to normal?
- What is Metformin used for other than diabetes?
- How fast does Metformin work?
- Does Metformin cause constipation?
- How does Metformin work for weight loss?
- What does Metformin do for PCOS?
- Can you take Metformin and Ozempic together?
- How much is Metformin without insurance?
- How long for Metformin to work?
- Does Metformin make you lose weight?
- How to stop Metformin diarrhea?
- Can you take Metformin while pregnant?
- Can Metformin cause weight gain?
- What happens if you take Metformin and don't need it?
- Can you take Berberine with Metformin?
- Can you drink on Metformin?
- Can Metformin cause constipation?
- Side effects of missing a dose of Metformin?
- Does Metformin make you tired?
- Does Metformin cause kidney damage?
- How much Metformin for weight loss?
- Can you lose weight on Metformin?
- Is there a better drug for type 2 diabetes than Metformin?
- When to take Metformin before or after meals?
- Can I miss taking Metformin one day?
- How does Metformin help PCOS?
- Is Metformin bad for your kidneys?
- Can you take Ozempic and Metformin together?
- Is Jardiance better than Metformin?
- Is Metformin safe during pregnancy?
- Will Metformin help me lose weight?
- How to take Metformin for weight loss?
- When to start Metformin for prediabetes?
- Does Metformin make you pee?
- How much Metformin can you take in a day?
- How quickly does Metformin work?
- Metformin kidney damage?
- Can Metformin cause hair loss?
- How much weight can you lose on Metformin?
- Can Metformin cause hypoglycemia?
- Why does Metformin smell like fish?
- Metformin for weight loss in non diabetics?
- Can you drink alcohol while taking Metformin?
- How long does it take for Metformin to get out of your system?
- Can you drink alcohol with Metformin?
- Foods to avoid when taking Metformin for PCOS?
- Why take Metformin and Ozempic together?
- Can you take Jardiance and Metformin together?
- Does Metformin fatigue go away?
- Can Metformin be used for weight loss?
- Will Metformin cause weight loss?
- Is Metformin the same as Ozempic?
Are Gliclazide and Glipizide the same?
It's common to mix up Gliclazide and Glipizide, but they are two distinct drugs. Although both are in the sulfonylurea class used for managing type 2 diabetes, their different chemical structures mean they are absorbed and processed differently by the body. This affects how they are used in medical practice and the specific effects they have on patients.
Are Gliclazide and Diamicron the same?
Diamicron and Gliclazide are one and the same. Diamicron is the brand name.
What are Gliclazide tablets for?
People with type 2 diabetes are often given Gliclazide tablets to help control their condition, when changing their diet and getting exercise isn't enough to bring their blood sugar levels down.
What are Gliclazide tablets used for?
People with type 2 diabetes rely on these treatments to keep their blood sugar levels under control. The stakes are high. If left unchecked, the condition can lead to complications. Kidney damage is a concern as is the threat of vision problems that can severely impact life.. Then there's the increased risk of disease, which can be devastating. By managing blood sugar, patients can significantly reduce their chances of developing these issues.
Are Metformin and Gliclazide the same?
Metformin and Gliclazide are not the same thing. The way they work is actually quite different. Metformin belongs to a class of drugs called biguanides. It helps by reducing the amount of glucose made by the liver. On the other hand, Gliclazide is a type of sulfonylurea which means it works by stimulating the pancreas to release insulin.
Are Glimepiride and Gliclazide the same?
Glimepiride and Gliclazide are drugs, even though they're both classified as sulfonylureas. The main differences lie in their potency dosing requirements and the side effects they can cause. Each has its own profile in these areas.
Can Gliclazide cause weight gain?
Gliclazide can lead to weight gain, which is thought to be related to the way it boosts insulin levels and helps the body use glucose effectively.
Can Gliclazide cause hypoglycemia?
Gliclazide can lead to hypoglycemia in situations where meals are missed or if the dosage is too high. It's also possible for this to happen when it is taken with medications that lower blood sugar levels.
Can Gliclazide cause weight loss?
Can Gliclazide and Glimepiride be taken together?
You typically shouldn't combine Gliclazide and Glipizide because they're both from the same drug class, sulfonylureas, and work in a very similar way. Using them together won't offer any additional benefits and could significantly increase your risk of experiencing low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
Can Gliclazide cause pancreatitis?
It's worth noting that pancreatitis has been known to occur, albeit rarely in patients taking Gliclazide. There have been a handful of instances where this has happened.
Can Gliclazide and Glibenclamide be taken together?
It's not an idea to take Gliclazide and Glibenclamide together. Both of these medications belong to a group called sulfonylureas, and using them in combination can lead to a drop in blood sugar levels causing a condition known as hypoglycemia.
Can Gliclazide cause constipation?
Not many people taking Gliclazide experience constipation but for some it can be a problem.
Can Gliclazide cause liver damage?
It's worth noting that Gliclazide can have some side effects. For instance, it may lead to abnormalities, in liver enzymes or even hepatitis, although this is quite rare. Because of this doctors often recommend keeping an eye on liver function while someone is taking the medication.
Can Gliclazide be crushed?
If a Gliclazide tablet needs to be broken down, the immediate-release kind can be crushed. However it's crucial not to crush the modified release tablets as this can change how the drug is released and affect how well it works.
Can Gliclazide cause headaches?
Headaches can be an effect of Gliclazide. Typically they're not too severe and don't last long.
Can Gliclazide be used with insulin?
In cases, people with type 2 diabetes may take Gliclazide at the same time as insulin particularly when a single treatment isn't doing the job.
Can Gliclazide cause blurred vision?
Blurred vision can be a problem. It's usually more about the ups and downs of blood sugar levels than the medicine causing it.
Can Gliclazide be taken without food?
To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia it's best to take Gliclazide with a meal.
Can Gliclazide and Dapagliflozin be taken together?
For treating type 2 diabetes, a combination of Gliclazide and Dapagliflozin can be used, as they work differently but complement each other to lower blood sugar. However, it's very important to monitor this combination closely. Gliclazide can increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), so regular monitoring is essential to make sure the treatment is safe and effective.
Can Gliclazide cause dizziness?
Gliclazide can sometimes cause dizziness, which is often a result of blood sugar episodes. If this happens, it's an idea for patients to be careful when they are, behind the wheel or using machinery.
How Gliclazide works?
Gliclazide basically helps your body produce insulin, which in turn brings down blood sugar levels in people, with type 2 diabetes. It does this by prompting the pancreas to step up its insulin release. The end result is that it helps keep blood glucose in check.
How Gliclazide works in the body?
Gliclazide works by attaching to receptors on the beta cells in the pancreas, which triggers a boost in insulin production. As a result the body can use glucose efficiently. This is how it helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Gliclazide how to take?
To minimize the chance of blood sugar levels dropping too low it's best to take Gliclazide by mouth when you eat. Be sure to follow the dosage and timing your doctor recommends.
Gliclazide how many times a day?
The usual dose of immediate release Gliclazide is twice a day. On the hand the modified release version is a bit different. Is generally taken just once a day.
Gliclazide how fast does it work?
Gliclazide starts taking effect an hour after it's taken and its impact on blood glucose levels typically peaks around 6 to 8 hours later.
How does Gliclazide work in the body?
Gliclazide works by boosting the release of insulin from the pancreas. At the time, it increases the responsiveness of tissues in the body to insulin. The end result is blood sugar levels.
How does Gliclazide cause hypoglycemia?
Taking Gliclazide and then skipping or delaying a meal, or not eating enough, can lead to hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar). This happens because Gliclazide prompts the pancreas to release insulin. If you don't eat enough to match that insulin, your blood sugar levels will drop too low. Essentially, your body is producing more insulin than it needs for the food you've consumed.
How is Gliclazide excreted?
The liver plays a role, in breaking down gliclazide which is then eliminated from the body via the urine. The byproducts of this process are no longer active.
What Gliclazide is used for?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus can be a condition to manage. Certain medications, like Gliclazide, have been shown to help. The main goal of this treatment is to get blood glucose levels under control, which in turn reduces the risk of some complications that can come with diabetes. By managing blood sugar, people with type 2 diabetes can lower their risk of developing these problems.
Gliclazide what time to take?
To get control over blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, it's an idea to take Gliclazide with breakfast or the first big meal of the day.
Gliclazide what type of drug?
Gliclazide belongs to a group of medicines called sulfonylureas which are used to lower blood sugar levels. It's taken by mouth to help manage diabetes.
Gliclazide when to stop before surgery?
To prevent low blood sugar during fasting for surgery, Gliclazide is typically stopped on the day of or the day before the procedure. Other medications, like insulin, can be used instead if necessary.
When should Gliclazide be stopped?
If someone's blood sugar keeps dropping or if their kidneys or liver aren't working properly, that's usually a sign to stop taking Gliclazide. The same goes if they're allergic to it. Sometimes people need to switch to insulin or a different treatment,and in those cases Gliclazide would typically be discontinued.
Does Metformin cause weight loss?
Metformin can lead to a bit of weight loss in some people, likely because it helps their bodies respond better to insulin and curbs their appetite.
How to lose weight fast on Metformin?
Losing weight on Metformin tends to happen over time. To get the most out of it, it's an idea to eat a diet watch your portions and get moving regularly. Trying to shed pounds isn't usually the best approach. A steady pace, supported by habits, is often the way to go.
Does Metformin help with weight loss?
Metformin appears to have an impact on weight loss for those who are overweight and struggle with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. The weight loss effect is generally not drastic. It's still a benefit, for people taking the medication.
Does Metformin cause diarrhea?
Diarrhea is often an effect of Metformin, especially when you're just starting out with the medication or taking it in large amounts.
How long does it take for Metformin to work?
Metformin typically starts to bring down blood sugar levels within a days. It takes one to two weeks of using it to see the full benefits.
How does Metformin help you lose weight?
Metformin seems to help with weight loss in a ways. For one, it can curb your appetite. It also lowers insulin resistance, which is a plus. On top of that it reduces the amount of glucose your body absorbs from the gut.
Why does Metformin cause diarrhea?
The way metformin works can lead to diarrhea because it changes how the gut moves, increases the amount of glucose in the intestines and disrupts the balance of bacteria that live there.
What is the lowest dose of Metformin you can take?
The usual starting dose is 500 mg taken once a day. To make it easier, on the stomach it's often best to take it with food.
Can Metformin cause weight loss?
Taking Metformin can lead to weight loss for some people. This usually happens slowly and isn't very dramatic.
Does Metformin help you lose weight?
Metformin can help with weight loss to some extent. It does this by improving how the body processes nutrients and reducing hunger, which in turn lowers calorie intake. However it's not a solution for losing weight on its own.
How long does Metformin take to work?
Metformin takes hold quickly, starting to make a difference in blood sugar levels within a few days. It typically takes around two weeks, though for the benefits to kick in.
Does Metformin make you sleepy?
Sleepiness isn't typically an effect of Metformin. However, some people taking the medication might feel tired, especially if their blood sugar levels are up and down a lot.
Is Metformin used for weight loss?
Metformin isn't typically given to people just to help them lose weight. However doctors might prescribe it for conditions, like insulin resistance or polycystic ovary syndrome, where shedding a pounds can make a difference.
When is the best time to take Metformin?
Taking metformin with food helps cut down on stomach upset. Makes the medicine easier to absorb. Generally having it with meals is the way to go.
Metformin dosage for weight loss in non diabetics?
Metformin hasn't been officially approved for weight loss in people without diabetes. When it's used in studies the dosage can vary widely. Anywhere from 500 mg to 2000 mg per day. But here's the thing; if you're considering taking it, you should only do so under the supervision of a doctor.
Does Metformin cause weight gain?
Generally, Metformin isn't known to cause weight gain. Instead people often experience weight loss when they take it. This is because the drug affects how their body handles insulin, and it can also help curb their appetite a bit.
What happens if you take too much Metformin in one day?
If someone takes Metformin, it can cause some very serious problems. They might develop acidosis, a condition where the body makes much lactic acid, or experience nasty symptoms, like nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. On top of that their blood sugar could drop to levels. If any of this happens, they need to get to a hospital.
How long does Metformin stay in your system?
Metformin doesn't stick around in the body for long. Its half life is six hours. Generally its completely cleared out in a day or two with the kidneys doing most of the work to get rid of it.
Does Metformin cause hair loss?
Metformin doesn't usually cause hair loss. It can happen in some cases and often this is because of an underlying condition, like ovary syndrome rather than the medication itself.
How long does it take Metformin to work?
Metformin tends to start doing its job of bringing down blood sugar levels within just a few days. However it generally takes a couple of weeks of using it for the medication to have its effect.
Best time to take Metformin for weight loss?
Taking your medication with meals, like breakfast and dinner, seems to work. It helps cut down on stomach problems. Keeps your blood sugar levels steady which can be a plus if you're trying to manage your weight.
What is the lowest dose of Metformin you can take for PCOS?
For women with PCOS, a good starting point is often 500 milligrams taken once a day. This dose can be increased bit by bit to help the body get used to it and to make it work better.
Can Metformin cause diarrhea?
Diarrhea is an issue for people taking Metformin especially when they first start or if their dose is on the higher side.
Can I stop taking Metformin when my sugar back to normal?
Don't stop taking metformin without talking to your doctor. It's often crucial, for keeping blood sugar levels in check, and quitting can disrupt the progress you've made with diet and other habits.
What is Metformin used for other than diabetes?
Metformin has uses too. Doctors sometimes prescribe it to help women with syndrome. It's also useful for people who have trouble with insulin resistance. Some studies even suggest it can help with weight loss and overall metabolic health.
How fast does Metformin work?
It doesn't take long for metformin to start making a difference. You can see a drop in glucose levels within a few days. What's really noticeable is the improvement in blood sugar control, which typically becomes apparent after about one to two weeks of taking the medication.
Does Metformin cause constipation?
Constipation isn't all that typical for people taking Metformin. Some folks might still experience it. Diarrhea is generally more of an issue. Constipation can show up for an individual.
How does Metformin work for weight loss?
Metformin can contribute to weight loss through several mechanisms. It improves your body's sensitivity to insulin, a hormone that controls blood sugar. When insulin works more efficiently, your body produces less of it, which seems to reduce feelings of hunger. Additionally, Metformin affects how your body stores fat, making it slightly easier to lose weight. These combined effects can lead to a modest but noticeable reduction in body weight.
What does Metformin do for PCOS?
Women with PCOS often find that metformin can be a help. For one thing, it improves insulin resistance, which in turn can lead to periods. It also supports ovulation. That can be a boost to fertility. Overall, the medication seems to nudge the body's systems towards a more normal rhythm.
Can you take Metformin and Ozempic together?
It's not uncommon for Metformin and Ozempic to be prescribed together. This combination can be pretty effective when it comes to managing type 2 diabetes and helping with weight control.
How much is Metformin without insurance?
The cost of metformin is usually pretty low, typically running, between $4 and $15 a month at pharmacies even without insurance.
How long for Metformin to work?
Once you start taking metformin, it usually begins to have an effect within a matter of days. However, it's often a couple of weeks before the full benefits become apparent given that you're taking it as directed and consistently.
Does Metformin make you lose weight?
Metformin can be helpful for weight loss in some cases. The impact is usually pretty modest. To really see results, it tends to work when combined with a diet and regular exercise.
How to stop Metformin diarrhea?
To help prevent diarrhea while taking Metformin, try starting with a low dose and always take it with your meals. If the issue continues, your doctor might recommend switching to an extended-release version or adjusting your current dose. There are several ways to manage this side effect and reduce your risk.
Can you take Metformin while pregnant?
Metformin can be prescribed to women. This is typically only done in specific situations, like when they have gestational diabetes or a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS for short. In these cases, the woman would need to be monitored by her doctor.
Can Metformin cause weight gain?
Metformin isn't typically associated with weight gain. In fact most people who take it tend to either maintain their weight or experience an amount of weight loss.
What happens if you take Metformin and don't need it?
Using Metformin when you don't really need it can cause some side effects, like stomach problems and diarrhea. There's also a chance of something serious happening like lactic acidosis. The thing is, if you're not supposed to be taking it you're not going to get any health benefits, from it.
Can you take Berberine with Metformin?
When taking berberine and metformin together, it's crucial to have a doctors guidance. This is because both substances can lower blood sugar levels, which may lead to a risk of hypoglycemia. Without oversight, combining these two could potentially cause more harm than good.
Can you drink on Metformin?
When taking Metformin, it's an idea to keep an eye on your alcohol intake. Drinking too much can raise the risk of a condition called lactic acidosis. This is a life-threatening complication, so it's worth being cautious and limiting how much you drink.
Can Metformin cause constipation?
Constipation is a side effect. It's not as likely as diarrhea.
Side effects of missing a dose of Metformin?
If you miss a dose, your blood sugar might spike for a while. As long as it doesn't become a habit it usually won't have serious consequences. Skipping doses every now and then probably won't cause harm but doing it regularly can lead to more significant problems.
Does Metformin make you tired?
Some people taking Metformin might feel tired. This can happen for a few reasons. It could be because their blood sugar is too low, or they might be lacking vitamin B12. Occasionally the gastrointestinal side effects that can come with Metformin, like a stomachache can also leave people feeling drained.
Does Metformin cause kidney damage?
Metformin typically doesn't harm the kidneys on its own. Doctors are wary of prescribing it to people, with poor kidney function. The concern is that it could lead to a buildup of acid in the body a serious condition.
How much Metformin for weight loss?
Typically people start to see the effects of weight loss when they're taking somewhere, between 1500 and 2000 milligrams a day. That being said the right dose can vary a lot from person to person. Its crucial to work with a doctor to figure out what's best, for each individual.
Can you lose weight on Metformin?
A lot of people who take Metformin notice they lose a bit of weight especially if they're also eating healthier and getting exercise.
Is there a better drug for type 2 diabetes than Metformin?
Metformin is usually the first choice for treating type 2 diabetes because it's effective, safe, and inexpensive. However, it's not the right fit for everyone. For instance, people with heart or kidney issues may benefit more from a GLP-1 receptor agonist like Ozempic, while those who need to lose weight might be better suited for an SGLT2 inhibitor like Jardiance. The best medication always depends on the individual patient's specific health needs.
When to take Metformin before or after meals?
To minimize stomach upset and make the medication easier to take, Metformin is best taken with food either during meals or afterward. This helps the body get used to it. Reduces the risk of side effects.
Can I miss taking Metformin one day?
If you happen to miss a dose of Metformin it's probably not going to cause any harm, though your blood sugar levels might spike for a while. The best thing to do is just get back on track with your schedule. Don't try to make up for the missed dose by taking one; just take the next dose as planned.
How does Metformin help PCOS?
For women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), metformin can be very helpful. It makes the body more responsive to insulin, which in turn helps regulate hormonal balance. This can lead to several benefits:
- More regular menstrual cycles.
- A reduction in high levels of androgen, a hormone that is often elevated in women with PCOS.
- The potential to encourage ovulation, which can significantly improve fertility for women who have difficulty conceiving.
Is Metformin bad for your kidneys?
Metformin doesn't directly damage the kidneys, but doctors generally avoid prescribing it to people with kidney disease. This is because poor kidney function can increase the risk of lactic acidosis, a serious condition where too much lactic acid builds up in the body.
Can you take Ozempic and Metformin together?
Doctors often prescribe a combination of Ozempic and Metformin for people with type 2 diabetes. This pairing can be highly effective at controlling blood sugar levels and helping with weight management, as both medications are well-established treatments for the condition.
Is Jardiance better than Metformin?
Jardiance isn't meant to take the place of Metformin as the treatment option. However it might be a choice, for patients like those dealing with heart failure or kidney disease. In some cases it could also offer benefits, such, as reducing glucose levels and improving cardiovascular health.
Is Metformin safe during pregnancy?
Metformin is sometimes prescribed during pregnancy for women with diabetes or polycystic ovary syndrome. In these cases it's crucial that the treatment is closely monitored by a doctor to ensure everything goes smoothly.
Will Metformin help me lose weight?
Metformin can help with weight loss at a bit for people who are overweight. It's not a diet pill though. It's one of those added benefits.
How to take Metformin for weight loss?
When treating with metformin it's crucial to be under the care of a doctor. The typical approach is to begin with a dose, taking it with meals to help reduce the risk of any reactions. As the body adjusts, the dose can be slowly increased to find the balance and support metabolic health.
When to start Metformin for prediabetes?
In some cases doctors may prescribe metformin to people with prediabetes if they're not getting results, from lifestyle changes. This is particularly true for individuals with risk factors, like being overweight younger or having a family history that puts them at risk.
Does Metformin make you pee?
Metformin doesn't act like a diuretic. So when it helps regulate blood sugar levels, people with diabetes might notice they're not running to the bathroom as often. The reason is pretty straightforward; getting blood sugar under control can make a difference in reducing urination, a common issue for those, with diabetes thats not well managed.
How much Metformin can you take in a day?
The usual rule of thumb is that adults shouldn't take than 2000 to 2550 milligrams per day. This can vary, though ,depending on the formula and how well the person taking it can handle the dose.
How quickly does Metformin work?
It doesn't take long for metformin to start bringing down blood sugar levels. A few days. The full effect typically kicks in within a week or two. Thats when you can expect to see the difference.
Metformin kidney damage?
Metformin usually doesn't hurt your kidneys. Doctors are careful, about prescribing it to people with kidney problems. The reason is that it can lead to a buildup of acid, which is particularly risky for those with poor kidney function.
Can Metformin cause hair loss?
Losing hair doesn't usually happen to people taking Metformin. However a few folks have said it's happened to them. When it does it's often because of some condition they have, rather than the medication causing the problem.
How much weight can you lose on Metformin?
Losing weight with Metformin tends to be a process. On average, people might drop around 2 to 5 kilograms over a period of months. This, of course, varies from person to person. Largely depends on their lifestyle and how their body reacts to the medication.
Can Metformin cause hypoglycemia?
Metformin is not usually a cause of high blood sugar when taken by itself. However, the likelihood of this happening goes up when it's taken with diabetes medications or when someone skips meals.
Why does Metformin smell like fish?
Some people notice that metformin tablets have a fishy smell. This is because of how they're made. Its nothing to worry about. The smell doesn't mean the tablets have gone bad. It's a side effect of their chemistry.
Metformin for weight loss in non diabetics?
For some people, without diabetes like those with insulin resistance or polycystic ovary syndrome, metformin is sometimes used to help with weight loss.. It's essential to take this medication only if a doctor has prescribed it, as they can help determine if it's the right choice and monitor its effects.
Can you drink alcohol while taking Metformin?
You should limit how much alcohol you drink while taking Metformin. Drinking too much can increase your risk of developing lactic acidosis, a rare but serious condition.
How long does it take for Metformin to get out of your system?
The body gets rid of metformin within a day or two. 24 To 48 hours. This timeframe can vary quite a bit though. Largely depends on how your kidneys are working.
Can you drink alcohol with Metformin?
It's fine to have a drink then. Going overboard isn't a good idea. For one thing it can raise your risk of getting acidosis, which is a serious condition. So it's best to keep your drinking in check.
Foods to avoid when taking Metformin for PCOS?
For the results, it's an idea to steer clear of foods that are highly processed and packed with carbs, as well as sugary drinks and too much alcohol. What works better is eating meals that complement the effects of Metformin. This way you can get the most out of the medication.
Why take Metformin and Ozempic together?
When these two things are used together they work better to control blood sugar levels. They also help people lose weight and lower their risk of heart problems, which is more than either one can do on its own.
Can you take Jardiance and Metformin together?
Jardiance and metformin are commonly used together to get a handle on blood sugar levels. This combination also offers protection for the kidneys and heart which is a big plus.
Does Metformin fatigue go away?
Sometimes fatigue can kick in from the start of treatment. More often than not it fades away as your body gets used to it. If the tiredness just won't quit, it's probably an idea to get it checked out by a doctor.
Can Metformin be used for weight loss?
The drug Metformin can help some people lose weight. Its main use is for treating metabolic problems, not as a way to shed pounds. It's typically prescribed for health issues, not as a weight loss solution.
Will Metformin cause weight loss?
A lot of people who take Metformin tend to lose a bit of weight. This effect is more noticeable when they're also eating well and staying active.
Is Metformin the same as Ozempic?
Metformin and Ozempic are not the thing. For one metformin is a pill, a type of biguanide that you take by mouth. Ozempic, on the hand is a shot, a GLP 1 receptor agonist thats injected. The way they work is also completely different.