Introduction to Zospar (Sparfloxacin)
Overview of Zospar as a Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic
Zospar, containing sparfloxacin, belongs to the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics. It exerts broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. This makes it a versatile therapeutic option for complex bacterial infections that resist conventional therapy.
Historical Background and Regulatory Approval Status
Sparfloxacin was introduced in the 1990s as part of the second generation of fluoroquinolones. Initially approved for respiratory tract infections, it gained rapid acceptance due to its efficacy and once-daily dosing convenience. However, evolving safety concerns regarding cardiac and dermatological effects have shaped its regulatory standing in different regions.
Clinical Importance in Treating Bacterial Infections
The clinical significance of Zospar lies in its ability to target pathogens responsible for community-acquired pneumonia, chronic bronchitis exacerbations, and resistant sinusitis. In settings where bacterial resistance complicates therapy, sparfloxacin is considered a valuable alternative when prescribed judiciously.
Composition and Formulation
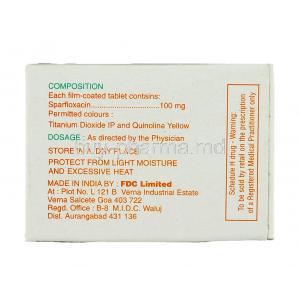
Active Ingredient: Sparfloxacin
Each tablet contains sparfloxacin as the principal active compound. Its chemical structure enhances penetration into tissues and allows for extended antimicrobial activity.
Available Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets typically supplied in 100 mg and 200 mg strengths
- Formulated for oral administration to maximize absorption
- Occasionally compounded in specific clinical scenarios
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Formulations include binding agents, stabilizers, and disintegrants designed to ensure uniform absorption and stability. Excipients may vary slightly between manufacturers but generally remain inert without pharmacological activity.
Mechanism of Action: How Sparfloxacin Works
Inhibition of Bacterial DNA Gyrase and Topoisomerase IV
Sparfloxacin interrupts bacterial DNA replication by binding to DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are essential for DNA supercoiling and repair, making their inhibition fatal for bacterial survival.
Bactericidal Activity Spectrum
The spectrum encompasses:
- Gram-positive organisms such as Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Gram-negative bacilli including Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis
- Atypical pathogens like Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Comparison with Other Fluoroquinolones
Compared to older fluoroquinolones, sparfloxacin demonstrates superior tissue penetration and prolonged half-life. However, it carries a higher risk of QT interval prolongation, necessitating careful selection over safer alternatives in some cases.
Approved Medical Uses of Zospar
Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Effective against common respiratory pathogens, sparfloxacin is used in moderate to severe cases where first-line antibiotics have failed or resistance is suspected.
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis
Zospar reduces bacterial load and inflammation in patients with chronic bronchitis who experience recurrent exacerbations.
Sinusitis and Other Respiratory Tract Infections
Indicated for acute bacterial sinusitis, particularly when resistant organisms compromise the efficacy of standard therapy.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
May be employed in infections caused by susceptible organisms, particularly when oral therapy is preferable to intravenous alternatives.
Urinary Tract Infections (When Indicated)
Though not the first choice, sparfloxacin can be prescribed in complicated or resistant urinary tract infections under physician guidance.
Off-Label Uses of Sparfloxacin
Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis
Sparfloxacin has been studied as part of combination regimens for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Its role is adjunctive, often reserved for resistant cases.
Helicobacter pylori Eradication
Experimental regimens have included sparfloxacin for eradicating H. pylori, though it is not a standard therapy.
Other Resistant Bacterial Infections
In scenarios where conventional antibiotics fail, sparfloxacin may be utilized as an alternative treatment, guided by culture and sensitivity results.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Adult Dosing Regimens
The typical starting dose is a 400 mg loading dose on day one, followed by 200 mg once daily. The regimen may vary depending on infection severity and site.
Dosage Adjustments in Renal Impairment
Since sparfloxacin undergoes renal clearance, dosage adjustments are necessary in patients with compromised renal function to prevent accumulation and toxicity.
Dosing Frequency and Duration of Therapy
Therapy generally lasts between 7 to 10 days. In severe infections, longer durations may be required, though risks of adverse effects must be weighed carefully.
Administration with or without Food
Sparfloxacin may be taken with or without meals. However, it should not be consumed with antacids or dairy products that contain calcium, magnesium, or aluminum, as these reduce absorption.
Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients: Dosage Considerations and Risk Factors
Older patients may have increased susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmias and renal impairment. Dosage must be individualized, and ECG monitoring is advisable when prolonged therapy is required.
Pregnant Women: Safety Profile and Fetal Risk Data
Animal studies suggest potential teratogenic effects, and human data remain insufficient. Use during pregnancy is generally avoided unless no alternatives are available.
Nursing Mothers: Drug Transfer in Breast Milk
Sparfloxacin is excreted in breast milk. Due to the risk of adverse reactions in nursing infants, breastfeeding is not recommended during therapy.
Children and Adolescents: Safety Limitations and Contraindications
Fluoroquinolones, including sparfloxacin, are typically contraindicated in children and adolescents because of the risk of cartilage and joint toxicity. Their use is restricted to life-threatening infections where no safer options exist.
Warnings and Important Precautions
Risk of QT Prolongation and Cardiac Arrhythmias
Sparfloxacin has been associated with prolongation of the QT interval, which can precipitate life-threatening arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes. Patients with underlying cardiac disease or those receiving concomitant QT-prolonging drugs are at elevated risk. Baseline and follow-up electrocardiographic monitoring may be warranted in vulnerable individuals.
Tendinitis and Tendon Rupture
Fluoroquinolones, including sparfloxacin, can trigger tendinopathy and tendon rupture, particularly in the Achilles tendon. The risk is heightened in elderly patients, individuals receiving corticosteroids, and those with pre-existing musculoskeletal disorders.
Central Nervous System Effects: Seizures, Confusion, Psychosis
Adverse neurological events such as seizures, acute confusion, agitation, and even psychosis have been reported. Patients with epilepsy or other central nervous system disorders should be monitored closely when prescribed sparfloxacin.
Photosensitivity Reactions and Sun Exposure Risks
Sparfloxacin increases sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. Even minimal exposure to sunlight may provoke exaggerated reactions such as erythema, blistering, and severe rashes. Patients should avoid excessive sun exposure and use protective measures.
Risk of Clostridium difficile–Associated Diarrhea
Disruption of normal gut flora by sparfloxacin can facilitate overgrowth of C. difficile, leading to pseudomembranous colitis. Symptoms range from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colitis requiring immediate medical intervention.
Contraindications
Known Hypersensitivity to Sparfloxacin or Other Quinolones
Patients with a history of allergic reactions to sparfloxacin, fluoroquinolones, or any formulation component should not use this medication.
History of QT Prolongation or Torsades de Pointes
Pre-existing QT prolongation or a documented history of torsades de pointes contraindicates sparfloxacin therapy, given the significant risk of arrhythmias.
Patients on Class IA or Class III Antiarrhythmics
Concurrent use with antiarrhythmic agents such as quinidine, procainamide, amiodarone, or sotalol is contraindicated due to cumulative effects on cardiac conduction.
Severe Hepatic Impairment
Since sparfloxacin undergoes hepatic metabolism, patients with severe hepatic dysfunction may experience elevated drug levels and toxicity, making use contraindicated.
Careful Administration and Monitoring
Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
Those with ischemic heart disease, heart failure, or conduction abnormalities require special caution. ECG monitoring is advised for prolonged therapy.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Reduced renal clearance necessitates dosage adjustments. Accumulation may increase risks of adverse cardiac or neurological effects.
Patients with History of Epilepsy or CNS Disorders
Because sparfloxacin can lower seizure threshold, patients with epilepsy or other CNS disorders need careful monitoring and dose regulation.
Monitoring Requirements During Prolonged Use
Long-term therapy should include periodic assessment of renal and hepatic function, blood counts, and ECG to mitigate adverse effects.
Drug Interactions
Interactions with Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Quinidine, Amiodarone)
Co-administration can synergistically prolong QT interval and precipitate torsades de pointes, thus must be avoided.
Interactions with Macrolides and Tricyclic Antidepressants
Macrolide antibiotics and tricyclic antidepressants also prolong QT interval, compounding cardiac risk when combined with sparfloxacin.
Chelation with Antacids, Iron, and Multivitamins
Concurrent intake of antacids, iron supplements, or multivitamins containing divalent or trivalent cations impairs absorption, reducing bioavailability. A spacing interval of several hours is recommended.
Effects with Theophylline, Warfarin, and Hypoglycemic Agents
- Theophylline: Increased serum levels may cause toxicity.
- Warfarin: Potentiation of anticoagulant effect with increased bleeding risk.
- Hypoglycemic agents: Possible disturbances in blood glucose control.
Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Nausea, Diarrhea, Abdominal Pain
These symptoms are among the most frequently reported and usually self-limiting.
Neurological Symptoms: Headache, Dizziness, Insomnia
Patients may experience transient neurological complaints that resolve upon discontinuation or adaptation to therapy.
Dermatological Reactions: Rash, Pruritus
Mild cutaneous manifestations occur in a subset of patients, typically without systemic involvement.
Photosensitivity and Skin Reactions
Photosensitivity is relatively common and requires strict avoidance of ultraviolet light exposure during therapy.
Serious and Rare Side Effects
QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
Potentially fatal arrhythmias represent the most severe adverse reaction. Early detection via ECG is crucial.
Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis, Stevens–Johnson Syndrome
Though rare, these hypersensitivity reactions necessitate immediate discontinuation and emergency care.
Tendinitis and Tendon Rupture
Sudden onset tendon pain should prompt cessation of therapy to prevent rupture.
Hepatotoxicity and Renal Dysfunction
Isolated cases of liver enzyme elevation, hepatitis, and renal impairment have been documented, requiring monitoring of organ function.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Clinical Features of Sparfloxacin Overdose
Symptoms include severe dizziness, confusion, gastrointestinal upset, and cardiac arrhythmias due to exaggerated QT prolongation.
Supportive Treatment and Gastric Lavage
There is no specific antidote. Early gastric lavage or activated charcoal administration may reduce systemic absorption.
Cardiac Monitoring and Symptomatic Care
Continuous ECG monitoring is recommended in overdose situations. Symptomatic measures such as fluid replacement and electrolyte correction may be required.
Handling and Storage Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions (Temperature, Humidity, Light)
Store sparfloxacin tablets at controlled room temperature, away from excess moisture and direct light to maintain stability.
Safe Handling Practices for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals should avoid crushing or altering tablets unnecessarily. Standard hygiene and safety protocols are sufficient.
Disposal Instructions for Unused or Expired Medication
Unused or expired sparfloxacin should not be discarded in household waste. Proper disposal through pharmacy take-back programs or as directed by local regulations is advised to prevent environmental contamination.