Retrieve Cream
- Introduction to Retrieve Cream
- Composition and Formulation of Retrieve Cream
- Mechanism of Action: How Retrieve Cream Works
- Approved Dermatological Uses of Retrieve Cream
- Off-Label and Investigational Uses of Retrieve Cream
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Common and Expected Side Effects of Retrieve Cream
- Less Common and Serious Adverse Effects
- Contraindications and Conditions Where Retrieve Cream Should Be Avoided
- Drug and Topical Product Interactions
- Important Warnings and Usage Precautions
- Special Considerations in Elderly Patients
- Use in Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers
- Pediatric Use and Safety in Children
- Overdose and Accidental Ingestion
- Storage and Shelf-Life of Retrieve Cream
- Handling and Application Precautions
- Careful Administration and Monitoring
Introduction to Retrieve Cream
Retrieve Cream is a prescription-grade topical formulation containing tretinoin, a potent derivative of vitamin A. Classified as a retinoid, it is widely used in dermatology for its transformative effects on the skin, particularly in the treatment of acne and signs of aging. Retrieve Cream promotes cellular turnover and revitalizes the skin's surface, making it a cornerstone in both therapeutic and cosmetic dermatologic care.
Initially developed in the 1970s, tretinoin received FDA approval for acne treatment and has since gained regulatory acceptance in numerous countries including Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada. Over time, its use has expanded into cosmetic dermatology for photoaged skin and other pigmentary disorders.
Today, Retrieve Cream is used by dermatologists and aesthetic professionals alike to address concerns such as acne vulgaris, fine lines, uneven texture, and hyperpigmentation.
Composition and Formulation of Retrieve Cream
The active pharmaceutical ingredient in Retrieve Cream is tretinoin, available in varying strengths, 0.025%, 0.05%, and 0.1%, to cater to different skin sensitivities and clinical needs.
- Active Ingredient: Tretinoin (all-trans retinoic acid)
- Inactive Ingredients: Emollient base, alcohol, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), stearic acid, and purified water (varies by formulation)
Retrieve Cream is primarily offered in cream form, which is ideal for drier or mature skin types. Other available formulations of tretinoin include gels (for oily skin) and microsphere formulations, which offer controlled release and reduced irritation.
Azelaic acid and tretinoin
Azelaic acid and retinol are both recognized for their effectiveness in treating acne and hyperpigmentation; however, they work in distinct ways. Azelaic acid boasts inflammatory and antioxidant properties along with its antibacterial effects, whereas retinol mainly accelerates cell turnover as a retinoid compound. When used in combination, the two can amplify their advantages in addressing acne issues and achieving a more even skin tone.
Tretinoin vs retinol
Both Tretinoin and retinol are derived from vitamin A (known as retinoids), commonly used for skin rejuvenation purposes; however, it's important to note that Tretinoin is notably stronger and necessitates a prescription for purchase, whereas retinol is readily available over the counter without any prescription requirements. In terms of effectiveness and speed of results delivery, Tretinoin tends to work with more noticeable outcomes but also poses a greater risk of side effects such as skin irritation and dryness. On the other hand, Retinol is considered gentler in comparison, which makes it a suitable option for individuals who are new to using retinoids or have sensitive skin concerns.
Adapalene vs tretinoin
Adapalene and Tretinoin are both types of retinoids commonly used for treating acne and improving skin quality; nonetheless, their strength levels and tolerability may vary between them. Typically requiring a prescription, for usage Tretinoin is known to be more potent than Adapalene and can cause side effects like dryness and peeling. On the other hand, Adapalene is considered an option as it belongs to a newer generation of retinoids with lower strength variants available over the counter, thus making it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin.
Tazarotene vs tretinoin
Tazarotene and Tretinoin are prescribed topical retinoids derived from vitamin A that are commonly used to address skin issues such as acne breakouts sun damage, and the visible effects of aging, typically considered potent and belonging to a newer generation of retinoids. Tazarotene may lead to quicker improvements in photodamage and specific acne types, although it could result in more initial irritation. On the other hand Tretinoin, an older first-generation retinoid, is usually more readily available and can be a cost-effective choice, offering different strengths suitable for various skin sensitivities
Arazlo vs tretinoin
The brand name Arazlo refers to the medication called Tazarotene, which is classified as a third-generation retinoid, in comparison to Tretinoin, which is categorized as a generation retinoid medicine. Typically viewed as powerful, Tretinoin Arazlo can potentially provide improvements for issues such as photodamage and certain forms of acne—though it might also lead to more initial skin irritation. These are both prescribed treatments that enhance skin cell renewal for managing acne and age-related concerns, such as wrinkles.
Retin a vs tretinoin
Retin A is a brand name for the ingredient called Tretinoin, which is the retinoid (essentially a form of Vitamin A). It works by affecting skin cell turnover and promoting collagen production.
Differin vs tretinoin
Differin (also known as adapalene) and Tretinoin are retinoids commonly utilized for acne treatment; however, they exhibit variations in potency. Differin is categorized as a third-generation retinoid that is often perceived as harsh and can be purchased over the counter in concentrations compared to Tretinoin – a first-generation retinoid that is typically more potent and necessitates a prescription for usage while also being beneficial for addressing signs of aging.
Isotretinoin vs tretinoin
Isotretinoin is taken orally to treat acne that has not improved with treatments by reducing oil production throughout the body systemically. However, Tretinoin comes in the form of a cream or gel. It is commonly used to treat mild to moderate acne, as well as to reduce the appearance of aging by accelerating the skin cell renewal process.
Mechanism of Action: How Retrieve Cream Works
Retrieve Cream works at a cellular level by modulating gene expression and promoting epidermal cell turnover. This accelerates the shedding of dead skin cells and stimulates the growth of new, healthy cells.
- Comedolytic effect: Prevents the formation of microcomedones, the precursors to acne lesions
- Exfoliative action: Enhances desquamation, improving skin texture and luminosity
- Collagen remodeling: Increases fibroblast activity and collagen production, reducing fine lines and wrinkles
- Anti-inflammatory: Downregulates inflammatory mediators, making it useful for inflammatory acne and pigmentary conditions

Tretinoin cream vs gel
Typically, gels are lighter and absorb faster; they work well for acne-prone skin types, whereas creams provide moisture and are beneficial for dry or sensitive skin types.

Approved Dermatological Uses of Retrieve Cream
Retrieve Cream is clinically approved for several dermatologic conditions:
- Tretinoin for acne: Treats both non-inflammatory (comedones) and inflammatory (papules, pustules) lesions
- Tretinoin for wrinkles and Photoaging: Reduces fine lines, surface roughness, and mottled hyperpigmentation
- Melasma: Often used as part of a combination regimen to lighten hyperpigmented patches caused by UV exposure or hormonal changes
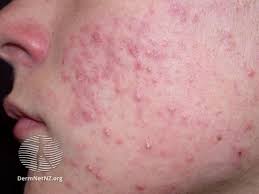
Off-Label and Investigational Uses of Retrieve Cream
Beyond its approved uses, Retrieve Cream has shown efficacy in multiple off-label dermatologic applications:
- Striae distensae: Minimizes the appearance of early stretch marks
- Keratosis pilaris and ichthyosis: Softens rough, keratinized skin and improves texture
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Fades dark spots following acne or skin trauma
- Actinic keratosis: Used adjunctively to treat pre-cancerous skin lesions
- Scar treatment: Enhances collagen remodeling in hypertrophic and atrophic scars

Dosage and Administration Guidelines
How to apply tretinoin
Retrieve Cream should be applied once daily, preferably at night, to clean, dry skin. A pea-sized amount is sufficient for the entire face.
Tretinoin strengths
0.025%, 0.05%, and 0.1%
- Initiation phase: Start with the lowest strength to assess skin tolerance
- Maintenance: Once tolerance is established, higher strengths may be used for enhanced results
- Application tips: Avoid sensitive areas such as the corners of the nose, mouth, and eyes
Moisturizers and sunscreens should be integrated into the regimen to maintain hydration and prevent photodamage. Daytime SPF use is mandatory.
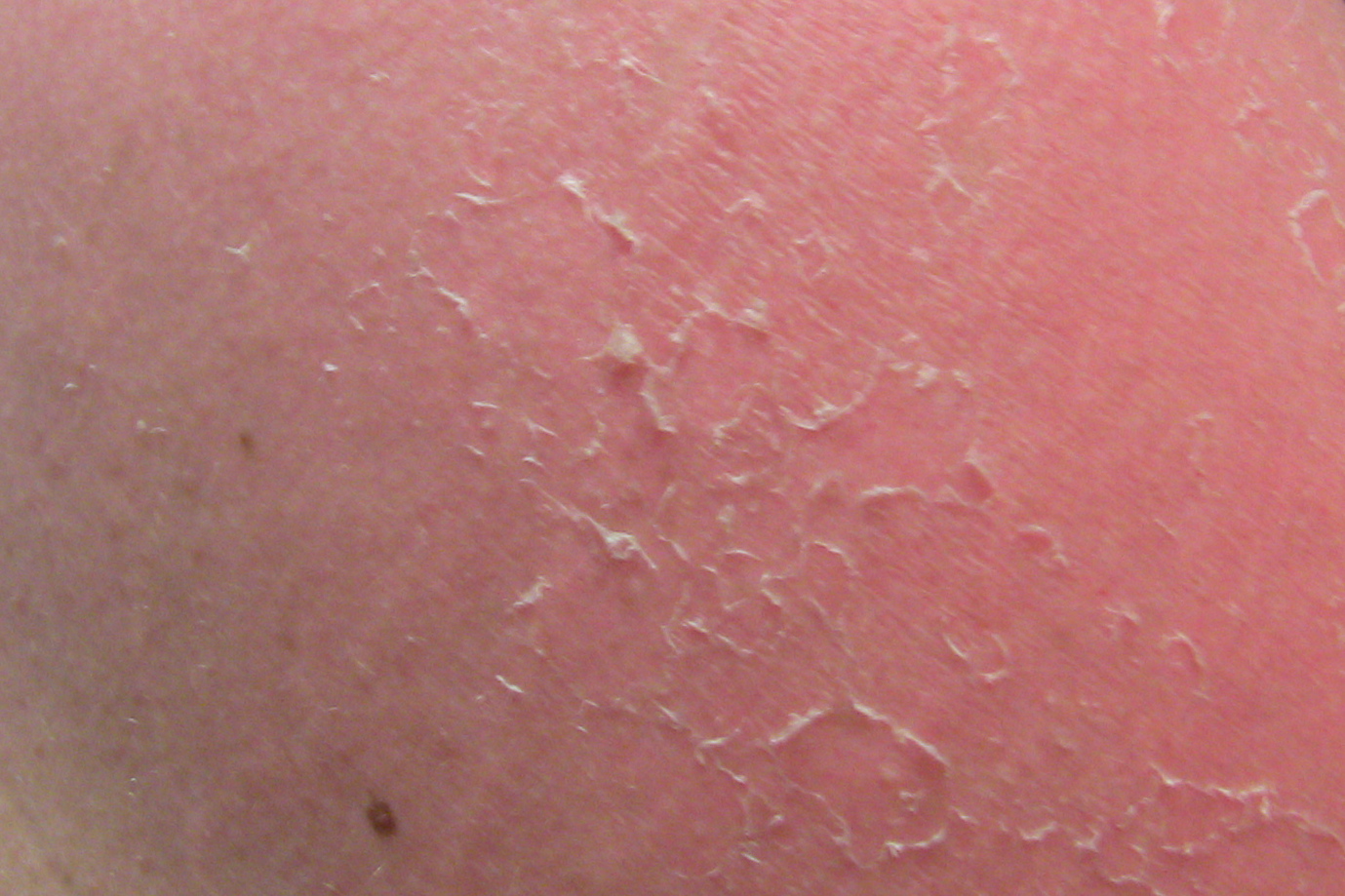
Common and Expected Side Effects of Retrieve Cream
During the initial phase of treatment, many users experience a temporary worsening of symptoms known as the retinoid purge. Expected side effects include:
- Erythema (redness)
- Tretinoin Peeling and flaking
- Dryness or tightness
- Tretinoin Burning or stinging sensation
- Increased sun sensitivity
These symptoms generally subside after 2-4 weeks as the skin acclimates.
Less Common and Serious Adverse Effects
Though rare, more significant adverse reactions may occur:
- Contact dermatitis: Allergic reaction requiring discontinuation
- Paradoxical hyperpigmentation: More likely in individuals with darker skin tones if not combined with SPF
- Retinoid dermatitis: Severe irritation from overuse or improper application
- Skin thinning: Typically only seen with prolonged misuse
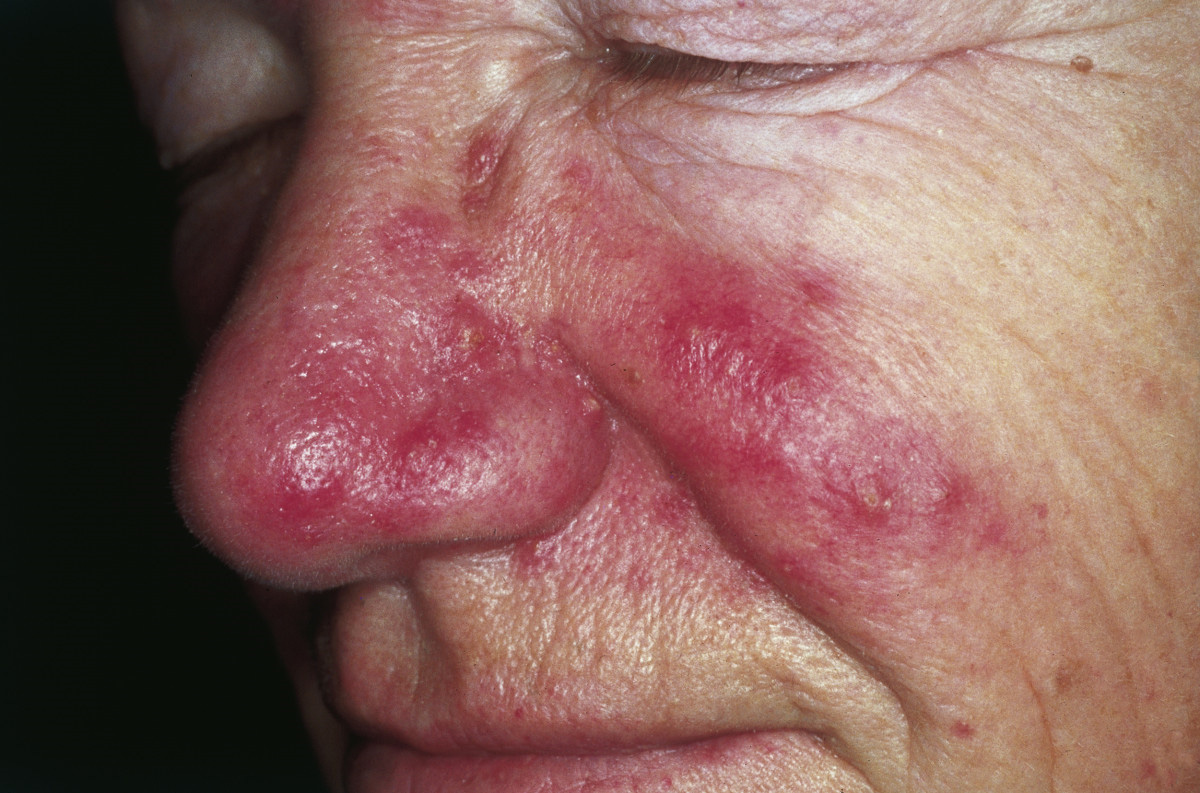
Contraindications and Conditions Where Retrieve Cream Should Be Avoided
Retrieve Cream should not be used in the following scenarios:
- Known allergy to tretinoin or formulation components
- Presence of eczema, open wounds, or active bacterial/fungal/viral infections
- History of rosacea or perioral dermatitis, which may be exacerbated
- Concurrent use of medications or products that increase skin photosensitivity
Patients should undergo a thorough dermatological assessment prior to initiating therapy, especially if there are concerns of hypersensitivity or underlying skin disorders.
Drug and Topical Product Interactions
Retrieve Cream contains tretinoin, a retinoid that can interact with various other topical agents. These interactions may either reduce its effectiveness or amplify skin irritation.
- Benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and astringents: When used concurrently with tretinoin, these agents may cause excessive irritation, dryness, or peeling. It is advisable to stagger their use one in the morning and one at night or avoid combination unless directed by a dermatologist.
- Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), vitamin C serums, and exfoliants: These products can destabilize the skin barrier and increase the potential for stinging or redness when layered with tretinoin. If used together, they should be introduced slowly and monitored carefully.
- Topical antibiotics and acne therapies: Clindamycin and erythromycin may be compatible when combined with tretinoin, often formulated in fixed-dose combinations for enhanced acne control.
- Corticosteroids or immunosuppressive agents: These may blunt the efficacy of tretinoin or counteract its inflammatory modulation, and their concurrent use should be managed by a physician.
Important Warnings and Usage Precautions
Proper precautions must be observed when using Retrieve Cream to avoid unwanted side effects and maximize therapeutic outcomes.
- Photosensitivity: Tretinoin increases the skin's sensitivity to UV radiation. Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) and protective clothing is essential.
- Skin treatments: Procedures like waxing, chemical peels, or dermabrasion should be avoided during treatment, as they can cause severe irritation or skin trauma.
- Gradual initiation: Start with applications every other night to allow the skin to build tolerance. Escalate frequency only as tolerated.
- Environmental sensitivity: Use caution in harsh climates extreme cold or wind can exacerbate irritation. Protective skincare may be necessary.

Tretinoin purge timeline
During the initial phase of using Tretinoin, known as a purge period where, breakouts and irritation may intensify initially before subsiding over 6 to 12 weeks as the skin adapts to the medication.
Special Considerations in Elderly Patients
Aging skin undergoes physiological changes that may alter the response to topical treatments like tretinoin.
- Altered barrier function: Thinner, more fragile skin in older adults can increase absorption and sensitivity, necessitating gentler regimens.
- Dosing frequency: Application may need to be reduced to two to three times per week to avoid excessive irritation or dryness.
- Monitoring: Routine skin checks for signs of overexfoliation, dryness, or eczema-like symptoms are recommended throughout the treatment period.

Use in Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers
Although topical tretinoin is minimally absorbed, its use during pregnancy and lactation carries potential risks due to its similarity to systemic retinoids.
- Pregnancy category C: Animal studies have shown fetal risk, and controlled human studies are lacking. Retrieve Cream should be avoided during pregnancy unless the potential benefit clearly outweighs the risk.
- Teratogenicity: Due to the teratogenic nature of systemic retinoids, many clinicians recommend discontinuing use in women who are pregnant or planning pregnancy.
- Lactation: Topical use is generally considered safe during breastfeeding when applied to areas away from the chest to prevent accidental ingestion by the infant.
Pediatric Use and Safety in Children
The use of Retrieve Cream in pediatric populations requires cautious assessment due to the skin's increased sensitivity and the limited data available.
- Not recommended for children under 12: Safety and efficacy have not been established for young children.
- Adolescent use: Retrieve Cream may be prescribed for severe acne in adolescents under clinical supervision, with a focus on gradual introduction and monitoring.
- Skin barrier consideration: Pediatric skin has higher permeability, increasing the likelihood of irritation. Dosing should be conservative.
Overdose and Accidental Ingestion
While topical overdose of tretinoin is uncommon, misuse or accidental ingestion can have consequences.
- Topical overdose: Signs include severe dryness, peeling, burning, and inflammation. Treatment involves cessation of the cream and supportive care with emollients.
- Systemic ingestion: Accidental oral intake though rare, may mimic symptoms of vitamin A toxicity. Medical attention is warranted in such cases.
- Emergency management: Rinse affected skin thoroughly with water, and consult a healthcare provider immediately if ingestion occurs or adverse symptoms are severe.
Storage and Shelf-Life of Retrieve Cream
To preserve the efficacy and stability of Retrieve Cream, proper storage practices should be followed.
- Temperature: Store at 15-25°C (59-77°F). Do not freeze the product.
- Container care: Keep the tube tightly closed and away from moisture or direct light exposure.
- Shelf life: Check the expiration date before use. Discard the cream if it becomes discolored, separated, or emits an unusual odor.
Handling and Application Precautions
Safe application techniques enhance the product's effectiveness and reduce the likelihood of irritation.
- Hand hygiene: Wash hands before and after applying Retrieve Cream to avoid unintentional transfer to mucosal surfaces.
- Application zones: Do not apply to eyes, lips, nostrils, or broken skin. If contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water.
- Product layering: Apply a thin layer of tretinoin first, then wait 20-30 minutes before applying moisturizer. Avoid applying other actives simultaneously unless advised by a healthcare provider.

Careful Administration and Monitoring
Individualized treatment regimens and vigilant monitoring optimize outcomes and minimize complications.
- Initiation protocol: Begin with the lowest concentration on alternate nights for 2-3 weeks. Gradually increase frequency as tolerated.
- Irritation monitoring: Watch for signs of erythema, burning, or excessive peeling. If symptoms persist, reduce application or pause treatment temporarily.
- Intermittent use: In patients with sensitive skin, consider a "retinoid holiday" or intermittent dosing to maintain benefits while minimizing irritation.
Retrieve Cream FAQ
- What is the retrieve cream used for?
- Is retrieve the same as retinol?
- Do you put moisturizer on before or after retrieve cream?
- Can I use retrieve cream every night?
- Can tretinoin remove dark spots?
- Can I use tretinoin daily?
- How long does retrieve take to work?
- What happens if you stop using tretinoin?
- Does tretinoin make skin glow?
- Can I use vitamin C with tretinoin?
- Can tretinoin remove scars?
- How to use retrieve cream?
- What are the side effects of tretinoin?
What is the retrieve cream used for?
Retrieve is employed for managing acne. It is also utilized in the treatment of sun-damaged skin.
Is retrieve the same as retinol?
Tretinoin could be seen as a form of retinol.
Do you put moisturizer on before or after retrieve cream?
Moisturizer first
Can I use retrieve cream every night?
Yes
Can tretinoin remove dark spots?
Tretinoin is known to be effective in diminishing the visibility of spots and hyperpigmentation.
Can I use tretinoin daily?
Yes
How long does retrieve take to work?
2-3 weeks
What happens if you stop using tretinoin?
If you discontinue using Tretinoin cream, there's a possibility that you may notice a reappearance of acne or wrinkles on your skin.
Does tretinoin make skin glow?
Using Tretinoin as part of your skincare routine helps to remove skin cells and promote a youthful appearance to your skin.
Can I use vitamin C with tretinoin?
Not at the same time
Can tretinoin remove scars?
Yes
How to use retrieve cream?
Apply a layer of the medication to the skin area(s) as usual before bedtime, following the specific instructions provided by your doctor or pharmacist diligently.
What are the side effects of tretinoin?
Using Tretinoin may lead to dryness or redness on your skin. It could result in swelling or flaking as well as blistering sensations and discomfort, such as itching or a burning feeling.