1. Introduction
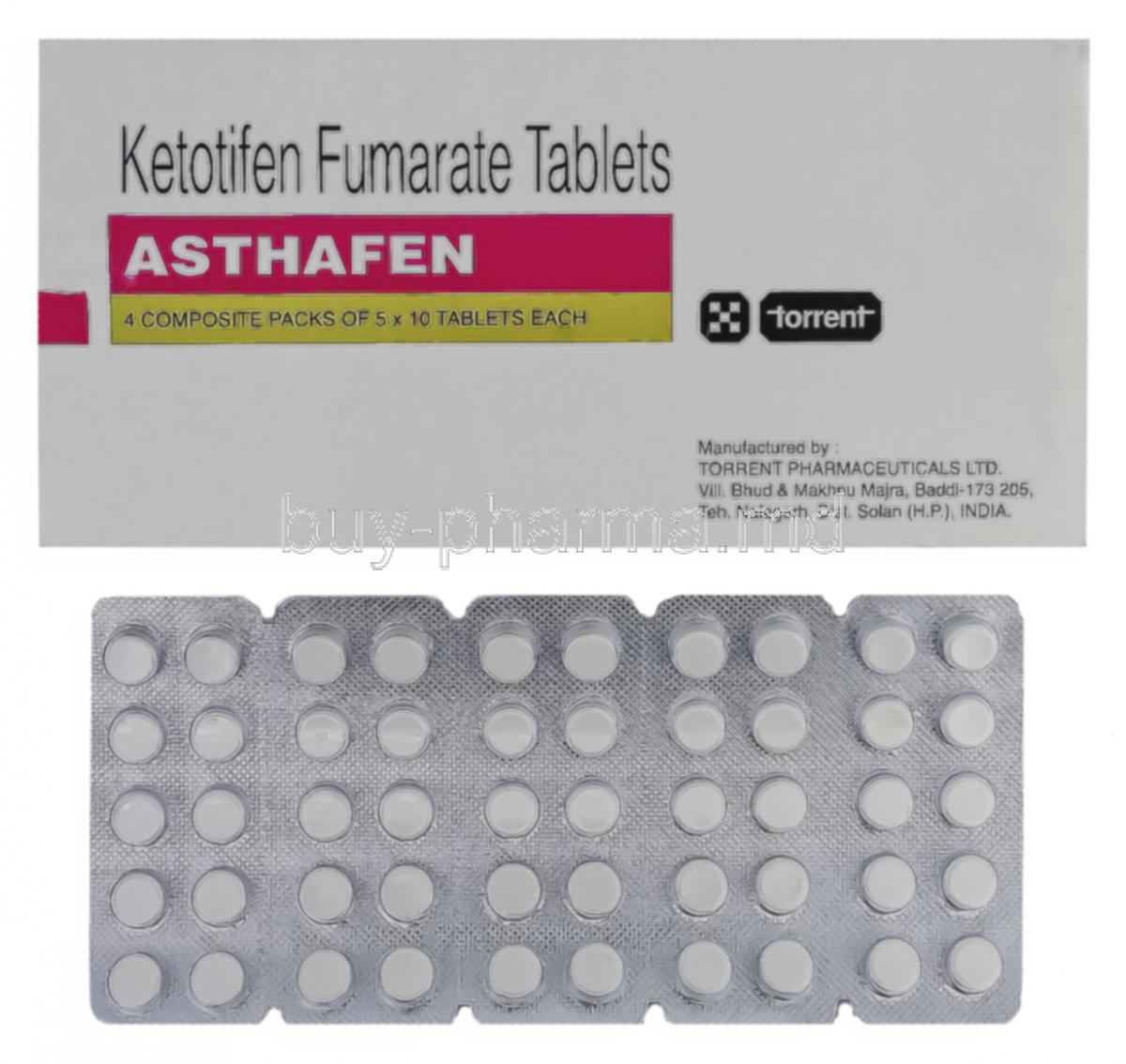
Asthafen, containing Ketotifen Fumarate as its active ingredient, is a well-established medication used in the prophylaxis and long-term management of allergic and asthmatic conditions. Belonging to the class of non-bronchodilator antiallergic agents and mast cell stabilizers, it works by curbing hypersensitivity responses in the respiratory tract and other tissues.
This therapeutic agent has gained recognition for its dual mechanism—antihistaminic and mast-cell-stabilizing properties—making it a cornerstone in allergy prevention strategies. Initially developed in Europe, Asthafen is now marketed worldwide under several trade names such as Zaditen, Ketasma, and Ketotifen. Its efficacy and tolerability have rendered it a preferred adjunct therapy for chronic allergic disorders.
2. Composition and Formulation
The principal constituent of Asthafen is Ketotifen Fumarate, a synthetic benzocycloheptathiophene derivative. It is formulated in multiple dosage forms to suit various therapeutic needs:
- Tablets: 1 mg and 2 mg strengths for oral use.
- Syrup: 1 mg/5 mL, designed for pediatric or sensitive patients.
- Ophthalmic Solution: Used to relieve allergic conjunctivitis.
Inactive components may include lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. Several pharmaceutical manufacturers produce Asthafen globally, ensuring wide accessibility in generic and branded variants.
3. Mechanism of Action: How Asthafen Works
Asthafen exerts its therapeutic effects through multiple biochemical pathways:
- H1 Receptor Blockade: Inhibits histamine binding, preventing allergic symptoms such as itching, sneezing, and nasal congestion.
- Mast Cell Stabilization: Prevents degranulation and release of inflammatory mediators like histamine and leukotrienes.
- Anti-inflammatory Modulation: Suppresses eosinophil activation and reduces bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
Unlike conventional bronchodilators, Asthafen does not relax airway smooth muscles directly. Instead, it targets the underlying allergic process, thereby reducing frequency and severity of asthmatic episodes.
4. Therapeutic Uses
4.1 Approved Medical Uses
- Bronchial Asthma Prophylaxis: Long-term control of allergic asthma when used as maintenance therapy.
- Allergic Rhinitis and Hay Fever: Reduces nasal congestion, sneezing, and rhinorrhea.
- Atopic Dermatitis: Diminishes itch and inflammation in chronic allergic skin conditions.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Relieves redness, tearing, and itching of the eyes.
4.2 Off-Label Uses
- Adjunct in preventing exercise-induced asthma.
- Used for chronic idiopathic urticaria where other antihistamines are ineffective.
- Experimental use in food allergies and idiopathic anaphylaxis.
- Investigational benefits in eosinophilic disorders due to its immune-modulating properties.
5. Dosage and Administration
5.1 Standard Dosage Guidelines
For adults, the standard oral dosage is 1 mg twice daily. In pediatric patients, the recommended dose is 0.05 mg/kg twice daily or as directed by a physician. The therapeutic effect becomes evident gradually, often requiring several weeks for full clinical benefit.
5.2 Administration Instructions
- May be taken with or without meals.
- Consistency is key—take at the same times each day.
- Do not expect immediate relief; its benefits are cumulative with continued use.
5.3 Missed Dose and Dose Adjustment
If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is near the next scheduled dose. Do not double the dose. In patients with hepatic or renal impairment, dosage adjustments should be considered under medical supervision.
6. Pharmacokinetics
Ketotifen is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 2–4 hours. It binds moderately to plasma proteins (~75%) and undergoes hepatic metabolism. The elimination half-life averages 21 hours, allowing twice-daily dosing. Excretion occurs mainly through the kidneys as inactive metabolites.
7. Side Effects of Asthafen
7.1 Common Side Effects
- Drowsiness or mild sedation during initial days of therapy.
- Dry mouth and mild dizziness.
- Increased appetite or modest weight gain.
- Occasional gastrointestinal discomfort such as constipation or nausea.
7.2 Less Common and Serious Adverse Effects
- Allergic skin reactions including rash or urticaria.
- Rare liver enzyme elevations or hepatic dysfunction.
- Nervous system disturbances such as irritability or sleep disturbances in children.
8. Drug Interactions
- Enhanced sedation when combined with alcohol or other CNS depressants.
- Possible potentiation of antihistamines and antidiabetic agents.
- Use caution with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) due to enhanced CNS effects.
- Minor interference with certain laboratory assays measuring serum glucose or hepatic enzymes.
9. Warnings and Precautions
9.1 General Precautions
- Refrain from driving or operating machinery until individual response is known.
- Monitor for excessive sedation, especially during the first few days.
- Observe for weight fluctuations during long-term therapy.
- Discontinue gradually to prevent rebound asthma exacerbation.
9.2 Handling Precautions
- Store tablets and syrup away from direct sunlight and moisture.
- Do not use beyond the expiry date printed on the package.
- Dispose of any unused medication responsibly, following local pharmaceutical waste guidelines.
10. Contraindications
Asthafen (Ketotifen Fumarate) is contraindicated in individuals with known hypersensitivity to Ketotifen or structurally related compounds. Allergic reactions may manifest as rash, urticaria, or severe anaphylactic responses. Patients with a history of epilepsy or seizure disorders should also avoid its use, as Ketotifen may lower the seizure threshold due to its central nervous system activity.
It must not be employed during acute asthma attacks. The medication functions as a preventive agent, not a bronchodilator. Therefore, it is ineffective for immediate relief of bronchospasm or acute wheezing episodes. In such situations, fast-acting beta-agonists should be used instead.
11. Careful Administration
Asthafen requires cautious administration in patients with underlying metabolic or systemic disorders:
- Liver Impairment: As the drug is extensively metabolized hepatically, impaired hepatic function can lead to prolonged half-life and accumulation. Periodic liver function tests are advised.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Mild weight gain and appetite stimulation are common. For diabetic patients, careful monitoring of blood glucose levels and caloric intake is essential.
- Long-Term Corticosteroid Therapy: Tapering corticosteroids while initiating Ketotifen must be done gradually to prevent adrenal insufficiency. Close observation during therapy transition is imperative.
12. Important Precautions
Continuous clinical supervision ensures optimal therapeutic efficacy and safety of Asthafen. Patients should undergo regular pulmonary assessments and monitoring of lung function, particularly in chronic asthma management.
- Avoid abrupt discontinuation: Sudden cessation may precipitate rebound bronchial hyperresponsiveness or asthma exacerbation.
- Lifestyle measures: A balanced diet, controlled weight, and avoidance of known allergens enhance the therapeutic outcomes.
- Follow-up visits: Periodic evaluation of symptom progression, side effects, and dosage adjustment ensures treatment continuity and safety.
13. Use in Special Populations
13.1 Administration to Elderly
In geriatric patients, physiological changes such as decreased hepatic metabolism and renal clearance necessitate dose adjustments. Lower initial doses may reduce the risk of excessive sedation or psychomotor impairment. Regular cognitive and motor assessments are advisable during long-term therapy.
13.2 Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Animal studies indicate no teratogenicity at therapeutic doses, yet human data remain limited. Therefore, Asthafen should be prescribed during pregnancy only when potential benefits justify the potential risk. During lactation, Ketotifen is excreted into breast milk, possibly inducing mild sedation or irritability in nursing infants. Physicians should consider discontinuing breastfeeding or the medication based on clinical necessity.
13.3 Administration to Children
Ketotifen is generally well tolerated in pediatric populations when administered as 1 mg/5 mL syrup. However, young children may exhibit paradoxical excitation, restlessness, or insomnia. Monitoring appetite and weight is advised since prolonged use can increase caloric intake. The dosage should always be guided by a pediatric specialist to ensure age-appropriate administration.
14. Overdosage and Management
Overdose with Asthafen may result in pronounced drowsiness, disorientation, confusion, or tachycardia. In severe cases, convulsions and hypotension may ensue. Emergency management includes:
- Immediate gastric lavage if ingestion is recent.
- Administration of activated charcoal to limit systemic absorption.
- Supportive measures such as airway maintenance, oxygen therapy, and hemodynamic stabilization.
There is no specific antidote for Ketotifen toxicity. Symptomatic care and continuous monitoring remain the mainstay of treatment until full recovery.
15. Storage and Stability
Asthafen should be stored at a controlled room temperature between 15°C and 30°C. The product must be kept away from direct sunlight, humidity, and extreme heat. Tablets should remain in their original blister packaging until use, while syrup formulations must be tightly closed and refrigerated after opening if recommended by the manufacturer.
- Do not freeze liquid formulations.
- Discard opened syrup bottles after the expiration period indicated on the label.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion.
16. Patient Counseling Information
Patients should receive comprehensive guidance to ensure safe and effective use of Asthafen:
- Take medication consistently at the prescribed times to maintain steady plasma levels.
- Inform physicians of all concomitant medications, including over-the-counter products and supplements, to avoid drug interactions.
- Avoid alcohol and sedative agents to prevent additive drowsiness.
- Seek medical advice if symptoms worsen, or if unusual fatigue, weight gain, or tremors develop.
Educating patients about the preventive rather than curative nature of Ketotifen is vital for compliance and long-term control of allergic disorders.
17. Summary
Asthafen (Ketotifen Fumarate) represents a cornerstone in the management of allergic conditions and asthma prophylaxis. Its unique pharmacological profile, combining antihistaminic and mast cell stabilizing properties, makes it an indispensable therapy in both adults and children. Although generally well tolerated, medical oversight is essential—particularly during prolonged use or in special populations.
When used judiciously under professional supervision, Ketotifen Fumarate offers sustained relief from allergic inflammation, reduces asthma exacerbations, and contributes to improved respiratory well-being over time.