Introduction to Victoza Pen Injection
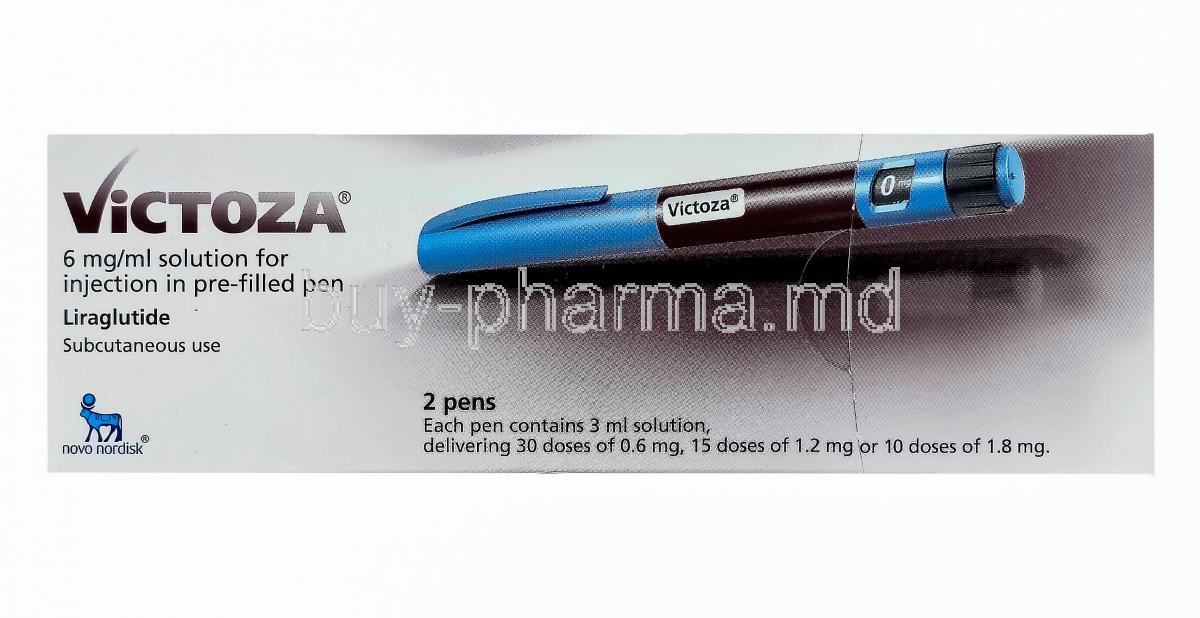
Overview of Victoza (liraglutide)
Victoza is a prescription injectable medication that contains liraglutide, a synthetic glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. It is designed to mimic the activity of the naturally occurring hormone GLP-1, which plays a key role in regulating blood glucose levels and appetite.
Classification: GLP-1 Receptor Agonist
Liraglutide belongs to the pharmacological class of GLP-1 receptor agonists. These agents work by enhancing insulin secretion, suppressing glucagon, and slowing gastric emptying—all in a glucose-dependent manner, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia.
Regulatory Approval and Market Availability
Victoza received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2010 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is currently available in many countries worldwide and is marketed under Novo Nordisk's portfolio of diabetes therapies.
Purpose and Scope of the Victoza Pen Formulation
The Victoza Pen offers a convenient, pre-filled, multi-dose injection device designed for once-daily subcutaneous administration. It allows for precise dose titration and easy self-administration by patients managing chronic metabolic conditions.
Medical and Off-Label Uses of Victoza
2.1 FDA-Approved Uses
- Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults and children aged 10 years and older
- Adjunct therapy to diet and physical activity for glycemic control
- Cardiovascular risk reduction in adults with type 2 diabetes and established heart disease
2.2 Off-Label Uses of Victoza
- Obesity and Weight Loss: Utilized as an appetite suppressant in patients with or without diabetes
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Improves insulin sensitivity and aids in weight reduction
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and NASH: May reduce hepatic fat accumulation and liver enzyme levels
- Pre-diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Helps delay progression to type 2 diabetes and improves cardiometabolic parameters
Composition and Formulation Details
- Active Ingredient: Liraglutide (recombinant DNA origin)
- Concentration: 6 mg/mL in a 3 mL pre-filled injection pen
- Inactive Ingredients: Disodium phosphate dihydrate, propylene glycol, phenol, and water for injection
- Packaging: Supplied as a pre-filled, multi-dose injection pen with dose increments of 0.6 mg, 1.2 mg, and 1.8 mg
Mechanism of Action: How Victoza Works
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonism: Stimulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Glucagon Suppression: Inhibits glucagon secretion from alpha cells, reducing hepatic glucose production
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: Slows gastric motility, helping to stabilize postprandial glucose spikes
- Appetite Regulation: Acts on central nervous system satiety centers to reduce food intake
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Demonstrated reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events in high-risk patients
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
5.1 Recommended Initial and Maintenance Dose
- Initiate at 0.6 mg once daily for at least one week to improve gastrointestinal tolerability
- Increase to 1.2 mg daily; if additional glycemic control is needed, further increase to 1.8 mg daily
5.2 Administration Instructions
- Administer subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm
- Rotate injection sites daily to minimize skin reactions
- Can be injected at any time of day, with or without meals
Handling and Storage Instructions for Victoza
- Unopened Pens: Store in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C. Do not freeze
- In-Use Pens: May be stored at room temperature (below 30°C) for up to 30 days
- Protection: Keep away from direct light and heat
- Disposal: Dispose of used pens and needles safely in a sharps container
Common and Serious Side Effects of Victoza
7.1 Frequently Reported Adverse Effects
- Nausea and vomiting, especially during dose escalation
- Diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal discomfort
- Headache and decreased appetite
- Injection site redness or irritation
7.2 Serious or Rare Adverse Effects
- Pancreatitis: Sudden abdominal pain with vomiting should prompt immediate medical attention
- Gallbladder Disease: Increased risk of gallstones and cholecystitis
- Thyroid C-cell Tumors: Black box warning due to tumor formation in animal studies
- Renal Impairment: Risk of dehydration-related acute kidney injury, particularly with persistent gastrointestinal symptoms
Drug Interactions and Incompatibilities
Potential Interactions with Insulin and Sulfonylureas
When Victoza is used concurrently with insulin or insulin secretagogues such as sulfonylureas, there is a heightened risk of hypoglycemia. Careful dose adjustment and frequent blood glucose monitoring are advised to mitigate this risk.
Effect on Absorption of Oral Medications
Victoza delays gastric emptying, which may influence the absorption kinetics of orally administered medications. This effect is particularly relevant for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index, such as warfarin or digoxin, necessitating close clinical supervision during co-administration.
Risk When Combined with Other GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
The concomitant use of Victoza with other GLP-1 receptor agonists is contraindicated. Such combinations may result in cumulative effects and elevate the risk of gastrointestinal disturbances, excessive weight loss, or hypoglycemia without added therapeutic benefit.
Alcohol and Gastrointestinal Agents Interaction Profile
Alcohol consumption may amplify gastrointestinal side effects and interfere with glycemic control. Similarly, antacids or agents that alter gut motility may modulate Victoza’s efficacy and tolerability, necessitating clinical judgment on concurrent use.
Contraindications and Populations at Risk
- Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC) or MEN2: Victoza is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2) due to increased risk of thyroid C-cell tumors.
- Hypersensitivity: Individuals with known hypersensitivity reactions to liraglutide or any component of the formulation should avoid use.
- Pancreatitis or Severe Gastrointestinal Disorders: A history of pancreatitis or severe gastroparesis is a contraindication, as Victoza may exacerbate these conditions.
Warnings and Important Safety Precautions
- Black Box Warning: Victoza carries a boxed warning regarding the risk of thyroid C-cell tumors based on rodent studies. The relevance to human risk remains undetermined but is of clinical significance.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Persistent nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain may signal serious underlying issues like pancreatitis and require immediate medical evaluation.
- Cardiovascular Monitoring: Although Victoza has shown cardiovascular benefits in high-risk populations, patients with a history of heart failure or arrhythmia require routine monitoring.
- Hepatic and Renal Considerations: Caution is warranted in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Dose modification may not be required, but regular function assessments are essential.
Careful Administration in Special Populations
11.1 Use in the Elderly
Elderly patients may have reduced renal clearance and a higher sensitivity to adverse effects. Regular assessment of renal function and glucose levels is recommended, especially in those taking concurrent nephrotoxic medications.
11.2 Use in Pregnant and Nursing Women
Victoza is categorized as Pregnancy Category C. Animal studies have shown adverse fetal effects, and there are no well-controlled human studies. It is not recommended during pregnancy unless the potential benefit outweighs the risk. Use during breastfeeding is also not advised, as it is unknown whether liraglutide is excreted in human milk.
11.3 Pediatric Use and Restrictions
Victoza is approved for use in adolescents aged 10 years and older for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Safety and efficacy in children under 10 years have not been established, and its use in this population is not recommended.
Overdose Risk and Management
- Signs of Overdose: Symptoms may include severe nausea, profuse vomiting, and episodes of hypoglycemia.
- Emergency Protocol: Supportive treatment is indicated. Hospitalization may be necessary in cases of persistent symptoms or suspected complications.
- Clinical Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of glucose, electrolytes, and hydration status is crucial. Activated charcoal is not routinely indicated due to delayed gastric emptying.
Handling Precautions and Patient Education
- Safe Use of the Pen: Educate patients on proper pen use, including priming, dosing, and needle disposal.
- Disposal Protocols: Used pens and needles should be discarded in approved sharps containers. Never reuse needles.
- Dosage Adherence: Patients must adhere strictly to their prescribed schedule to maintain glycemic stability.
- Self-Administration Counseling: Teach patients about injection site rotation, recognizing signs of hypoglycemia, and managing mild adverse effects at home.