Introduction to S Citadep (Escitalopram Tablet)
Overview of S Citadep as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
S Citadep, formulated with escitalopram, belongs to the class of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). This category of medication is renowned for its precision in modulating neurotransmitter levels, especially serotonin, to alleviate mood-related disturbances. Escitalopram is considered among the most refined SSRIs due to its high selectivity and tolerability profile.
Medical importance of escitalopram in treating psychiatric conditions
Escitalopram has transformed the management of psychiatric illnesses by offering effective treatment with minimal sedative burden. Its medical significance lies in its ability to:
- Stabilize mood in major depressive episodes
- Alleviate pervasive anxiety disorders
- Enhance daily functioning and cognitive clarity in affected individuals
Difference between S Citadep and other SSRIs
Unlike some SSRIs that act on both stereoisomers of citalopram, escitalopram in S Citadep contains only the S-enantiomer. This enhances potency while reducing unwanted pharmacological noise. Consequently, patients may experience therapeutic benefits at lower doses with fewer adverse reactions.
Composition and Formulation
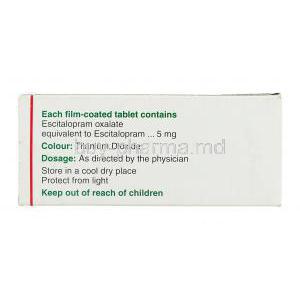
Active ingredient: Escitalopram Oxalate
The primary therapeutic constituent is escitalopram oxalate, which exerts the antidepressant and anxiolytic effects associated with S Citadep.
Available tablet strengths and dosage forms
S Citadep is commercially available in multiple strengths, most commonly 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg tablets. These dose variations allow clinicians to tailor therapy according to symptom severity and patient tolerance.
Inactive ingredients and excipients
In addition to the active compound, tablets may include excipients such as microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, and film-coating agents. These aid in stability, absorption, and patient compliance.
Mechanism of Action: How S Citadep Works
Role of serotonin in mood regulation
Serotonin, a pivotal neurotransmitter, governs emotional equilibrium, sleep cycles, and cognitive sharpness. Deficiency or dysregulation of serotonin often manifests as depression or anxiety.
Escitalopram’s selective action on serotonin reuptake transporters
Escitalopram enhances serotonergic neurotransmission by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin at the presynaptic terminal. This increases serotonin availability in the synaptic cleft, reinforcing positive mood circuits and diminishing pathological worry.
Comparison with citalopram and other antidepressants
Compared to racemic citalopram, escitalopram provides greater efficacy per milligram due to its refined stereochemical purity. In contrast to tricyclic antidepressants, it demonstrates lower anticholinergic load and improved cardiovascular safety.
Approved Medical Uses of S Citadep
- Major depressive disorder (MDD): Effective in reducing core symptoms such as low mood, anhedonia, and cognitive slowing.
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): Relieves chronic, uncontrollable worry and somatic anxiety symptoms.
- Social anxiety disorder (social phobia): Reduces anticipatory fear and performance-related anxiety.
- Panic disorder with or without agoraphobia: Helps decrease the frequency and severity of panic attacks.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): Improves intrusive thought control and reduces compulsive rituals.
Off-Label Uses of S Citadep
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Used to mitigate flashbacks, nightmares, and hyperarousal symptoms.
- Premature ejaculation and sexual dysfunction: Employed for its serotonin-mediated delay in ejaculation.
- Eating disorders such as bulimia nervosa: Assists in reducing binge-purge cycles.
- Fibromyalgia and chronic pain syndromes: May provide relief by modulating central pain perception pathways.
- Menopausal hot flashes and PMDD: Offers symptom relief in hormonally influenced mood and vasomotor disturbances.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard adult dosage for depression and anxiety
The usual recommended starting dose is 10 mg once daily, which may be escalated to 20 mg depending on clinical response.
Titration schedules and maximum recommended doses
Dose increments should be gradual, typically after at least one week of therapy. The maximum advised daily dose is 20 mg.
Dosage adjustments for hepatic or renal impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment often require lower starting doses, such as 5 mg daily. Caution is warranted in severe renal impairment.
Administration instructions: timing, with or without food
Tablets are usually taken once daily, at the same time each day, with or without meals. Consistency improves therapeutic steadiness.
Missed dose and discontinuation protocol
If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is near the time of the next dose. Abrupt discontinuation is discouraged; gradual tapering is recommended to prevent withdrawal phenomena such as dizziness, irritability, or sensory disturbances.
Use in Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients: dose adjustment and monitoring
Elderly patients often exhibit reduced hepatic metabolism and renal clearance. A lower initial dose, commonly 5 mg daily, is advised with careful monitoring for hyponatremia and cardiac conduction abnormalities.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: safety profile, risks, and benefits
While animal studies indicate low teratogenic risk, human data suggest cautious use, especially during the third trimester, due to potential neonatal adaptation syndrome. Minimal quantities are excreted in breast milk, necessitating close observation of breastfed infants.
Administration to Children and Adolescents: indications, age restrictions, clinical monitoring
S Citadep may be used in adolescents for depression or anxiety under strict clinical supervision. However, heightened vigilance is necessary as younger populations may experience increased suicidal ideation when initiating therapy. Regular psychiatric evaluation and parental involvement are critical.
Side Effects of S Citadep
Common Side Effects
S Citadep, like other SSRIs, can produce mild yet bothersome reactions in some individuals. These effects often appear within the initial weeks of therapy and may diminish with continued use. Commonly reported symptoms include:
- Nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Insomnia or fragmented sleep patterns
- Headache and mild tension-type pain
- Dry mouth and altered taste sensation
- Sexual dysfunction, including reduced libido or delayed orgasm
Less Common but Significant Side Effects
Beyond the expected effects, some patients experience less frequent but clinically meaningful side reactions:
- Weight changes, with either gain or loss depending on metabolic response
- Persistent fatigue and daytime somnolence
- Fine tremors or involuntary shaking, particularly in the hands
Serious Adverse Effects
Although rare, severe adverse events necessitate immediate clinical evaluation:
- Serotonin syndrome: a life-threatening condition characterized by agitation, confusion, hyperreflexia, and autonomic instability
- Suicidal ideation: increased risk observed in adolescents and young adults during early treatment phases
- QT prolongation: abnormal cardiac electrical activity that may predispose to arrhythmias
- Seizures: exacerbation in patients with pre-existing seizure disorders
Drug Interactions
Interactions with Other Antidepressants
Co-administration with SSRIs, SNRIs, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) can elevate serotonin to dangerous levels, precipitating serotonin syndrome. Such combinations should be avoided or undertaken only under rigorous supervision.
Effects of CYP450 Enzyme Modulators
Escitalopram metabolism is influenced by CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 pathways:
- Inhibitors (e.g., fluconazole, omeprazole) may increase plasma concentrations, heightening toxicity risk
- Inducers (e.g., rifampicin, carbamazepine) can reduce therapeutic efficacy by accelerating clearance
Interaction with Anticoagulants and NSAIDs
When combined with agents such as warfarin or ibuprofen, escitalopram can augment bleeding risk due to impaired platelet aggregation. Monitoring coagulation parameters is advisable.
Alcohol and Recreational Drug Interactions
Concurrent use with alcohol intensifies sedation, cognitive blunting, and may destabilize mood regulation. Recreational drugs such as MDMA pose a severe danger by synergistically elevating serotonin levels.
Herbal Supplements
St. John’s Wort and similar serotonergic herbal preparations potentiate adverse reactions and undermine safe pharmacological balance. Their use alongside escitalopram is discouraged.
Contraindications of S Citadep
- Known hypersensitivity to escitalopram or any excipient in the formulation
- Concomitant administration with MAOIs due to risk of serotonin syndrome
- Patients with congenital long QT syndrome, predisposing them to arrhythmias
- Severe uncontrolled epilepsy where seizure threshold is compromised
Warnings and Important Precautions
- Suicidal behavior risk: heightened vigilance is necessary for adolescents and young adults
- Hepatic or renal impairment: requires dose adjustment and close clinical observation
- Cardiovascular disease and seizure disorders: precautionary monitoring reduces complications
- Monitoring requirements: regular assessments of mental health, liver enzymes, and electrocardiographic parameters are recommended
Careful Administration Guidelines
Specific patient groups necessitate tailored therapeutic strategies:
- Individuals with a history of bipolar disorder or mania, due to risk of manic switching
- Elderly patients and those on diuretics who are prone to hyponatremia
- Patients with bleeding tendencies, particularly when on anticoagulants
- Polypharmacy situations where dose tailoring and interaction checks are crucial
Overdosage and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose
Excessive intake may present with dizziness, tremors, arrhythmias, convulsions, somnolence, and gastrointestinal upset.
First Aid and Supportive Measures
Immediate medical attention is required. First aid involves securing airway, breathing, and circulation. Activated charcoal may be administered if within a safe window post-ingestion.
Gastric Lavage and Symptomatic Management
Gastric lavage may be considered in hospital settings. Symptom-targeted therapies, such as anticonvulsants for seizures or antiarrhythmic measures, are employed.
Importance of Hospital Monitoring
Patients with severe overdose require continuous cardiac monitoring, electrolyte management, and intensive supportive care.
Storage and Handling Precautions
- Store tablets at controlled room temperature, ideally between 20°C and 25°C
- Protect from direct sunlight, excessive heat, and humidity
- Follow safe handling practices and dispose of unused tablets responsibly to prevent misuse
- Keep medication securely out of the reach of children and household pets