Loceryl Cream
- 1. Introduction to Loceryl Cream
- 2. Composition and Formulation
- 3. Mechanism of Action: How Loceryl Cream Works
- 4. Amorolfine Hydrochloride Cream Uses
- 5. Off-Label and Investigational Uses
- 6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- 7. Common and Serious Side Effects
- 8. Drug Interactions and Product Compatibility
- 9. Warnings and Contraindications
- 10. Precautions for Safe and Effective Use
- 11. Special Considerations in Patient Populations
- 12. Overdose and Accidental Ingestion
- 13. Handling, Storage, and Stability
- 14. Summary and Clinical Guidance
1. Introduction to Loceryl Cream
1.1 What is Loceryl Cream?
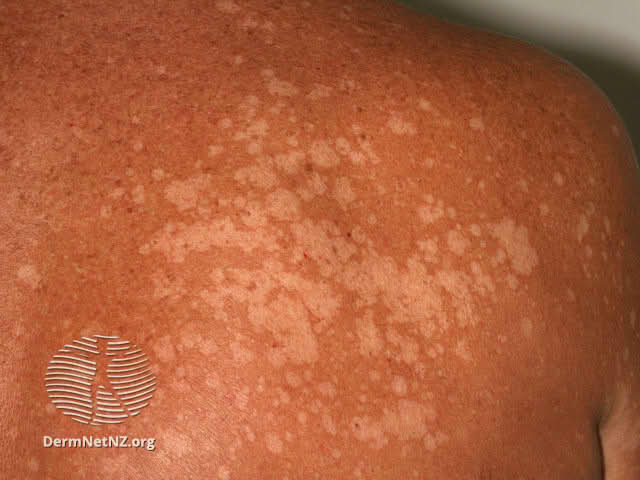
Loceryl Cream is a topical antifungal medication used to treat various superficial fungal skin infections. It contains a broad-spectrum antifungal agent that targets the integrity of fungal cell membranes, providing relief from itching, scaling, and inflammation.
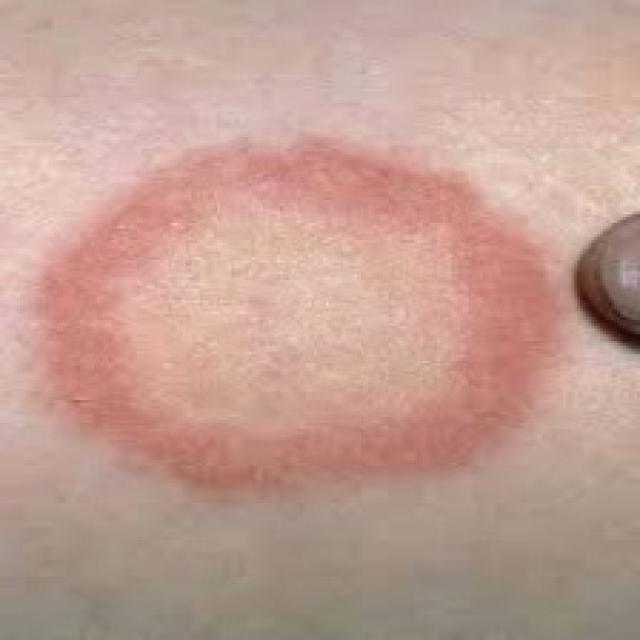
1.2 Classification and Therapeutic Category
Loceryl belongs to the class of topical antimycotics and is categorized under imidazole derivatives. It is specifically indicated for dermatomycoses and candidiasis, offering both fungistatic and fungicidal activity depending on the concentration and treatment duration.
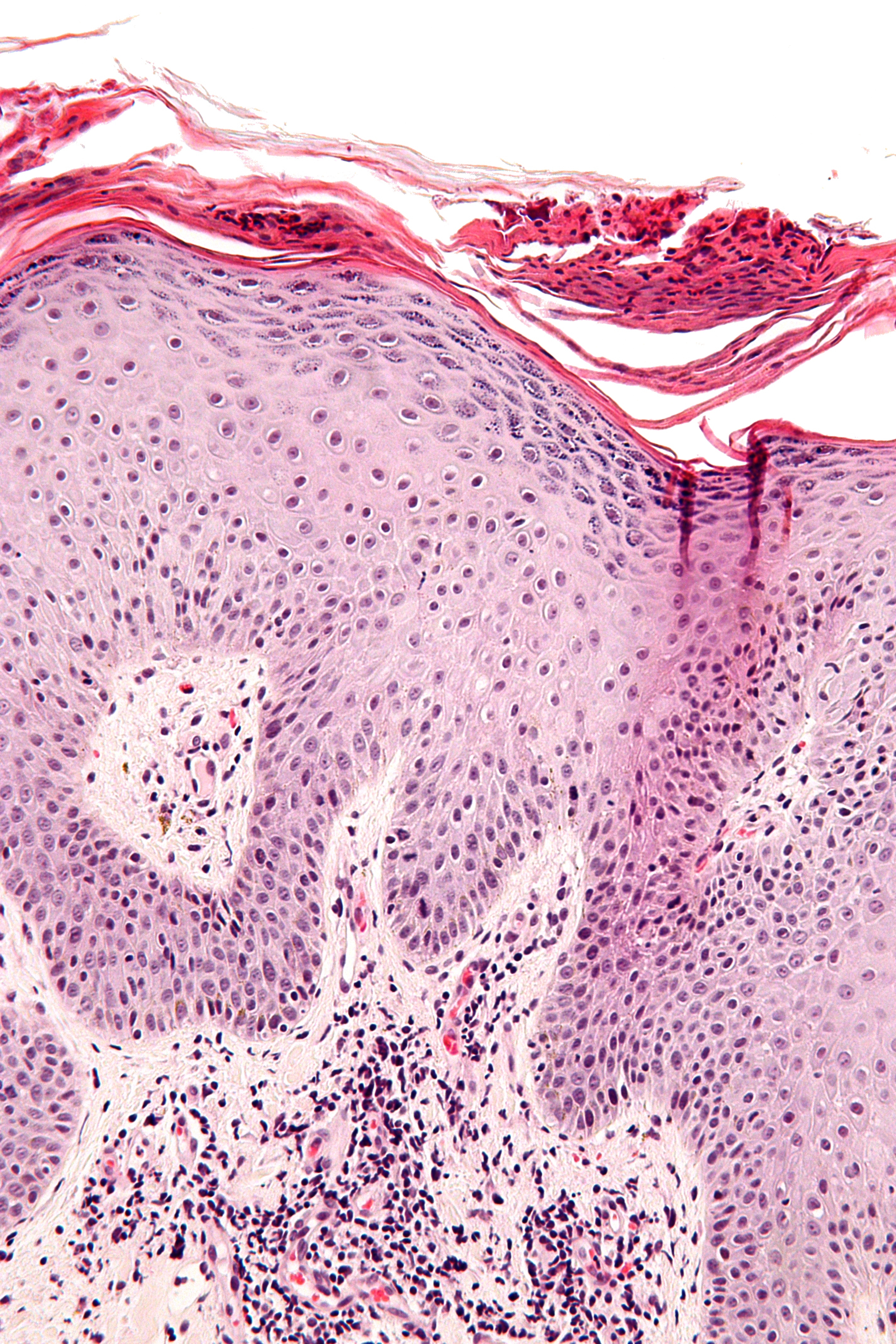
1.3 Overview of Medical Relevance and Regulatory Approvals
Loceryl Cream is approved in multiple countries for topical treatment of fungal skin conditions. It is commonly prescribed in dermatology and general practice settings, with proven efficacy documented in clinical trials and post-marketing studies. Regulatory agencies such as EMA and TGA recognize its use in outpatient settings.
1.4 Summary of Primary and Secondary Indications
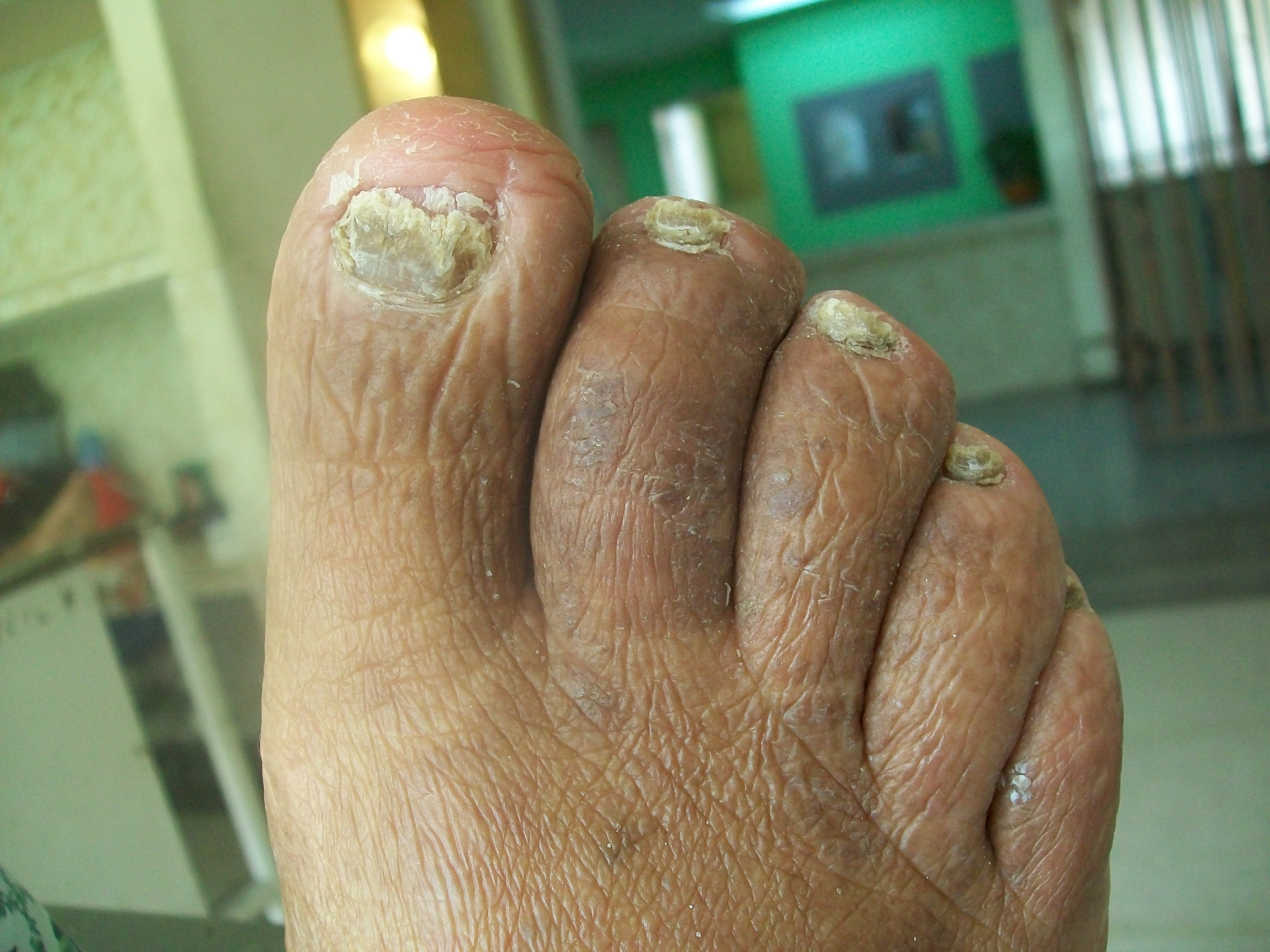
Primary indications include tinea pedis (athlete's foot), tinea corporis (ringworm), and cutaneous candidiasis. Secondary indications encompass off-label applications in onychomycosis (as adjunct therapy) and recurrent fungal conditions in immunocompromised individuals.
2. Composition and Formulation
2.1 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient: Amorolfine Hydrochloride
The therapeutic agent in Loceryl Cream is amorolfine hydrochloride, a morpholine antifungal compound that disrupts fungal cell wall synthesis by targeting sterol biosynthesis.
2.2 Concentration and Available Strengths
Loceryl Cream is typically available in a 0.25% w/w concentration of amorolfine hydrochloride. This formulation ensures localized delivery with minimal systemic absorption.
2.3 Inactive Ingredients and Formulation Excipients
Inactive constituents include purified water, cetostearyl alcohol, glyceryl stearate, and sorbitan stearate. These excipients aid in emulsification, skin hydration, and consistent drug delivery.
2.4 Physical Properties (Cream Texture, Absorption Rate, etc.)
Loceryl Cream has a smooth, non-greasy texture and is rapidly absorbed into the stratum corneum. It forms a transient protective barrier that enables prolonged antifungal activity without residue buildup.
Amorolfine vs Terbinafine
Amorolfine disrupts the production of sterols, and terbinafine targets squalene epoxidase, an enzyme in building fungal cell walls.
3. Mechanism of Action: How Loceryl Cream Works
3.1 Inhibition of Ergosterol Synthesis in Fungal Cell Membranes
Amorolfine exerts its antifungal effects by inhibiting delta-14 reductase and delta-7-8 isomerase, enzymes essential for ergosterol synthesis. Depletion of ergosterol compromises membrane integrity, leading to cell death.
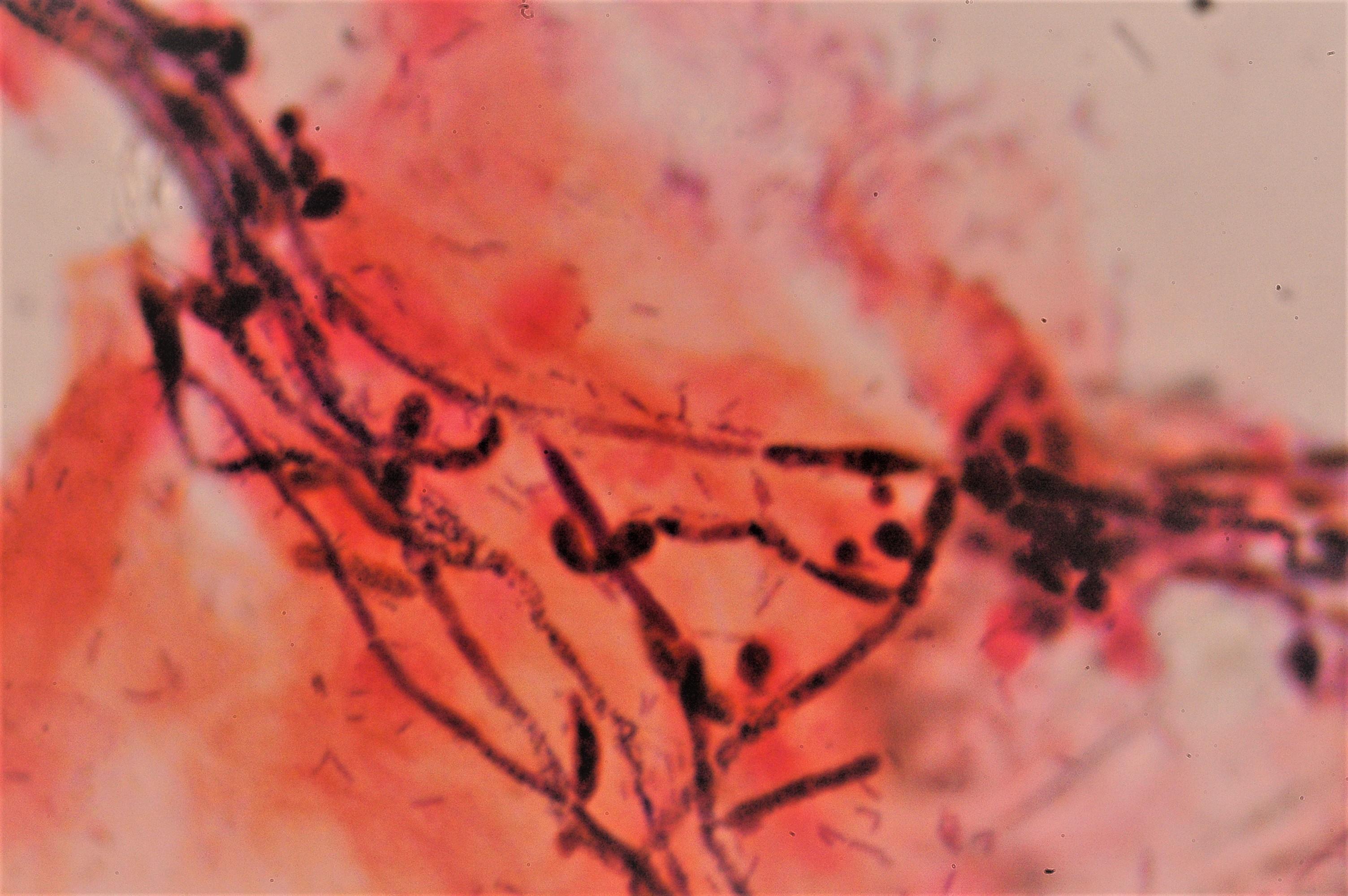
3.2 Spectrum of Antifungal Activity (Dermatophytes, Yeasts, Molds)
Loceryl Cream is active against a broad range of fungi:
- Dermatophytes (Trichophyton spp., Microsporum spp.)
- Yeasts (Candida albicans, Malassezia spp.)
- Molds (Scopulariopsis, Aspergillus spp.)
3.3 Time to Therapeutic Effect and Fungal Eradication
Clinical improvement is typically observed within 7-10 days, while complete eradication may require up to 4-6 weeks depending on the severity and location of infection.
4. Amorolfine Hydrochloride Cream Uses
4.1 Treatment of Superficial Dermatomycoses
Loceryl is effective in managing:
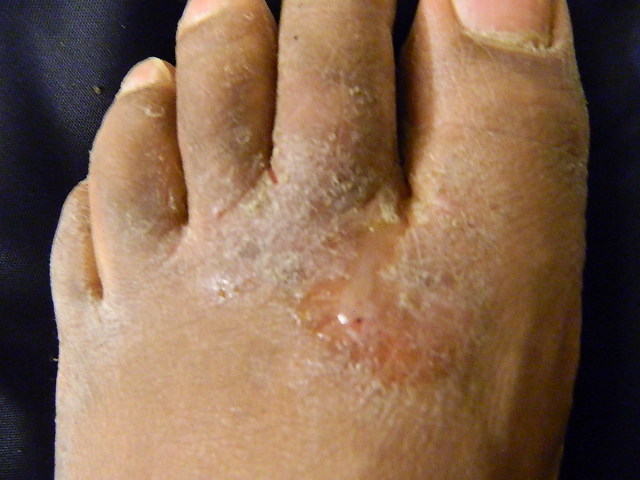
4.2 Candidiasis of the Skin
4.3 Treatment of Pityriasis Versicolor
4.4 Use in Onychomycosis as Adjunctive Topical Therapy
5. Off-Label and Investigational Uses
5.1 Use in Immunocompromised Patients with Recurrent Fungal Infections
5.2 Application in Chronic Paronychia with Suspected Fungal Components
Though not explicitly approved, dermatologists may recommend Loceryl for chronic nail fold inflammation suspected to have a fungal etiology.
5.3 Preventive Use in Recurrent Interdigital Fungal Infections
In patients prone to athlete's foot or toe-web infections, Loceryl may be used prophylactically during high-risk periods such as summer or communal bathing.
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
6.1 Standard Dosing Frequency and Duration by Condition
- Apply once or twice daily to the affected area
- Duration ranges from 2 to 6 weeks depending on severity

6.2 Instructions for Proper Application Technique
Clean and dry the affected area thoroughly. Apply a thin layer of cream, ensuring full coverage beyond the visible margin of infection. Wash hands after application.
6.3 Recommendations for Occlusive Dressing or Secondary Protection
Avoid occlusive dressings unless directed by a physician. In cases of foot involvement, wearing breathable cotton socks is advised.
6.4 Missed Dose Management and Treatment Adherence Tips
If a dose is missed, apply as soon as remembered. Do not double the dose. Adherence is critical to prevent recurrence and resistance.
7. Common and Serious Side Effects
7.1 Amorolfine Side Effects: Itching, Burning, Redness, Dryness
Mild localized reactions are common and usually transient. These include:
- Pruritus
- Burning sensation
- Localized erythema or dryness
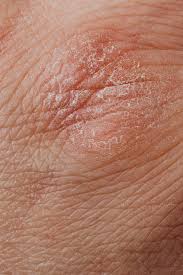
7.2 Localized Hypersensitivity or Contact Dermatitis
7.3 Rare but Serious Events: Allergic Skin Reactions, Swelling, Blistering
Though rare, severe reactions like angioedema or vesiculation warrant immediate medical attention.
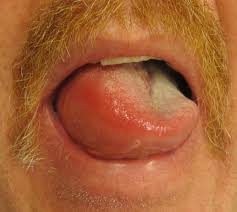
7.4 Reporting Side Effects and Post-Marketing Surveillance Data
Adverse effects should be reported to pharmacovigilance systems. Post-marketing data suggest a low incidence of serious events.
8. Drug Interactions and Product Compatibility
8.1 Potential Interaction with Other Topical Agents
Avoid simultaneous use with other topical treatments unless prescribed, as this may alter absorption or efficacy.
8.2 Use with Corticosteroids or Combination Antifungals
Co-administration with mild topical steroids may be considered in inflammatory fungal infections, but only under medical supervision.
8.3 Cosmetic and Personal Care Product Compatibility
Avoid applying cosmetics, moisturizers, or deodorants immediately over treated areas to prevent interference with antifungal action.

8.4 Risk of Systemic Absorption and Systemic Drug Interactions
Systemic absorption is negligible; thus, interactions with oral medications are extremely rare but should still be monitored in cases of prolonged use.
9. Warnings and Contraindications
9.1 Contraindications: Known Allergy to Amorolfine or Excipients
Loceryl Cream is contraindicated in individuals with known hypersensitivity to amorolfine or any component of the formulation.
9.2 Cautions in Broken or Ulcerated Skin
Application on broken, weeping, or ulcerated skin should be avoided due to risk of enhanced absorption and irritation.
9.3 Risk of Misuse in Bacterial or Viral Skin Infections
Loceryl is ineffective against bacterial or viral pathogens. Misapplication may delay appropriate therapy and worsen symptoms.
9.4 Warning Against Ophthalmic or Mucosal Use
The cream is intended strictly for external dermatologic use. Avoid contact with eyes, mouth, and mucous membranes.
10. Precautions for Safe and Effective Use
10.1 Skin Sensitivity Testing Recommendations
Before initiating full-scale application, patients with a history of dermal sensitivity should undergo a patch test. Apply a small amount of Loceryl Cream to an inconspicuous area, such as the inner forearm and monitor for erythema, pruritus, or vesiculation over 24 hours. Absence of reaction typically indicates tolerability, but clinical vigilance remains essential.
10.2 Hygiene and Prevention of Cross-Contamination
Maintaining stringent hygiene is paramount during antifungal treatment.
- Clean affected areas with mild soap and water before application
- Use separate towels and clothing for infected areas
- Disinfect or replace contaminated footwear or socks regularly
- Wash hands thoroughly after each application to prevent transfer

10.3 Avoiding Occlusive or Irritating Environments
Fungal growth is potentiated by moisture and occlusion. Patients should avoid:
- Wearing tight, non-breathable clothing or synthetic fabrics
- Prolonged sweating without ventilation
- Use of topical irritants or abrasive exfoliants near treated areas
Airy, dry conditions are conducive to faster resolution of cutaneous mycoses.
10.4 Guidance on Patient Education and Adherence
Educating patients about fungal pathophysiology, treatment expectations, and adherence is crucial. Clinicians should reinforce:
- The importance of completing the full treatment duration, even if symptoms resolve early
- Visible improvement timelines (typically 1-2 weeks)
- The role of prevention and post-treatment monitoring to avoid recurrence
11. Special Considerations in Patient Populations
11.1 Use in the Elderly
Aging skin exhibits reduced barrier function and increased permeability, potentially enhancing drug absorption. Considerations include:
- Monitoring for local irritation, atrophy, or delayed epithelial healing
- Avoiding use near fragile or thin skin zones
- Extended dosing intervals if adverse effects are observed
11.2 Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
11.2.1 Safety Profile During Pregnancy: Current Data and Risk Assessment
Data on amorolfine use during pregnancy is limited. Animal studies suggest low systemic absorption, and teratogenic risk appears minimal. Nevertheless, topical antifungals should only be used when clearly indicated, and systemic exposure must be minimized.

11.2.2 Lactation Considerations and Breast Area Application Restrictions
Amorolfine's excretion into breast milk remains unconfirmed. Avoid application to the breast or chest area of lactating mothers to prevent infant exposure. If use is necessary, apply only to small, localized skin regions away from the nipple.
11.3 Use in Pediatric Patients
Loceryl Cream is not universally approved for pediatric use under a certain age.
- Recommended minimum age varies by region typically +12 years
- Consultation with a pediatric dermatologist is advisable for off-label use
- Smaller application areas and close monitoring are required to mitigate absorption-related risks
12. Overdose and Accidental Ingestion
12.1 Symptoms of Topical Overdose or Misuse
Topical overuse may result in:
- Increased local irritation
- Desquamation or burning sensation
- Rarely, systemic symptoms in compromised skin
Discontinue use temporarily and reassess treatment.
12.2 Management of Accidental Oral Ingestion
Ingestion of Loceryl Cream is rare but may occur in pediatric patients or in error. Symptoms may include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or a bitter taste. Recommended actions:
- Do not induce vomiting
- Rinse the mouth with water immediately
- Seek medical attention if more than a small amount was ingested
12.3 Emergency Procedures and Medical Interventions
For symptomatic ingestion or adverse systemic reaction:
- Monitor vital signs and perform symptomatic treatment
- Activated charcoal may be considered in significant ingestion
- Contact poison control center for specific toxicological advice
13. Handling, Storage, and Stability
13.1 Recommended Storage Temperature and Light Exposure
Store Loceryl Cream below 25°C (77°F). Protect from excessive heat and direct sunlight, which can degrade active compounds and affect efficacy.
13.2 Tube Hygiene and Contamination Prevention
To maintain sterility:
- Close the cap tightly after each use
- Do not touch the tube tip directly to the skin
- Avoid shared use between individuals
13.3 Shelf Life After Opening and Expiration Precautions
Once opened, the cream should be used within 3-6 months, depending on packaging instructions. Discontinue use after the expiry date even if contents appear unaltered.
13.4 Safe Disposal of Unused or Expired Product
Unused or expired cream should be disposed of via pharmaceutical take-back programs. Avoid discarding into household waste or drainage systems to prevent environmental contamination.
14. Summary and Clinical Guidance
14.1 Key Takeaways for Healthcare Professionals
- Loceryl Cream is an effective topical treatment for superficial fungal infections
- Its safety profile is favorable, with minimal systemic absorption
- Patient selection and adherence are crucial to therapeutic success
14.2 Patient Counseling Points
Healthcare providers should emphasize:
- Proper application technique and hygiene
- Duration of treatment and importance of adherence
- Early signs of irritation or allergic reaction to report
14.3 When to Refer to a Dermatologist or Specialist
Referral is advised in the following scenarios:
- Refractory or recurrent infections
- Uncertain diagnosis (e.g., differentiating between fungal, bacterial, or inflammatory dermatoses)
- Suspected systemic involvement or co-existing immunodeficiency
Timely specialist involvement ensures optimal outcomes in complex or resistant cases.
Loceryl Cream FAQ
- What is Loceryl cream used for?
- Can I use Loceryl every day?
- What are the side effects of using Loceryl?
- Is Loceryl effective?
- How long does it take Loceryl to work?
- Do you need a prescription for Loceryl?
- Is Loceryl a steroid?
- Can I apply Loceryl daily?
- What are the side effects of Loceryl cream?
- What is the generic name for Loceryl?
- Is Loceryl waterproof?
- Is Loceryl prescription only?
- How to apply Loceryl cream?
- What are the ingredients in Loceryl cream?
What is Loceryl cream used for?
Loceryl cream contains Amorolfine as its active ingredient, classified under the topical antifungal medication group. It is commonly prescribed to treat various skin fungal infections including athletes foot (tinea pedis), jock itch (tinea cruris), ringworm (tinea corporis), and fungal infections of the hands (tinea manuum). Additionally, it is used for treating candidiasis and pityriasis versicolor on the skin.
Can I use Loceryl every day?
Once or twice weekly
What are the side effects of using Loceryl?
- Blisters
- Redness
- Skin irritation
- Rash
Is Loceryl effective?
After undergoing treatment for half a year, approximately 70-80 percent of individuals are likely to see improvement in their condition; furthermore, a complete recovery is anticipated in one out of every three cases.
How long does it take Loceryl to work?
1 to 3 months
Do you need a prescription for Loceryl?
Yes
Is Loceryl a steroid?
No
Can I apply Loceryl daily?
Once or twice a week
What are the side effects of Loceryl cream?
- Itching
- Stinging sensation
- Redness
What is the generic name for Loceryl?
Amorolfine
Is Loceryl waterproof?
No
Is Loceryl prescription only?
Yes
How to apply Loceryl cream?
Apply a coat of this medication on the area thats affected and softly massage it into the skin.
What are the ingredients in Loceryl cream?
Amorolfine