Psorcutan Topical
- 1. Introduction to Psorcutan Topical
- 2. Medical and Off-Label Uses of Psorcutan
- 3. Mechanism of Action: How Psorcutan Works
- 4. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- 5. Composition and Available Formulations
- 6. Storage Conditions and Stability Information
- 7. Side Effects of Psorcutan Topical
- 8. Drug Interactions and Combination Considerations
- 9. Warnings and Precautionary Statements
- 10. Contraindications for Use
- 11. Careful Administration Considerations
- 12. Important Patient Precautions and Counseling Points
- 13. Administration in Elderly Patients
- 14. Administration During Pregnancy and Lactation
- 15. Administration in Pediatric Populations
- 16. Overdose and Toxicity Management
- 17. Safe Handling and Precautions for Use
1. Introduction to Psorcutan Topical
Psorcutan Topical is a dermatological medication formulated to manage various inflammatory skin conditions, with a primary focus on psoriasis. As a topical therapy, it offers localized treatment, minimizing systemic exposure while delivering targeted relief.
Psorcutan belongs to a class of drugs known as vitamin D analogs, designed to regulate the growth and differentiation of skin cells. It is classified under two therapeutic categories: antipsoriatic and anti-inflammatory agents.
The product is commercially available in multiple formulations to suit diverse clinical needs, including ointment, cream, gel, and foam.
2. Medical and Off-Label Uses of Psorcutan
2.1 Approved Uses in Dermatology
- Treatment of plaque psoriasis: Psorcutan is indicated for managing mild to moderate plaque-type psoriasis, reducing erythema, scaling, and thickness of lesions.
- Chronic stable psoriasis vulgaris: It helps control long-term, non-progressive forms of psoriasis with minimal systemic burden.
- Post-remission maintenance: Psorcutan is used to prevent flare-ups after successful induction therapy, sustaining clear skin.
2.2 Off-Label and Investigational Uses
- Scalp psoriasis: Though not always explicitly labeled, Psorcutan is commonly used for scalp involvement due to its anti-proliferative action.
- Vitiligo: In certain cases, it serves as an adjunctive agent in stimulating repigmentation, especially in combination with phototherapy.
- Lichen planus and seborrheic dermatitis: Emerging studies suggest potential benefits due to its immunomodulatory properties, though these uses remain off-label.
3. Mechanism of Action: How Psorcutan Works
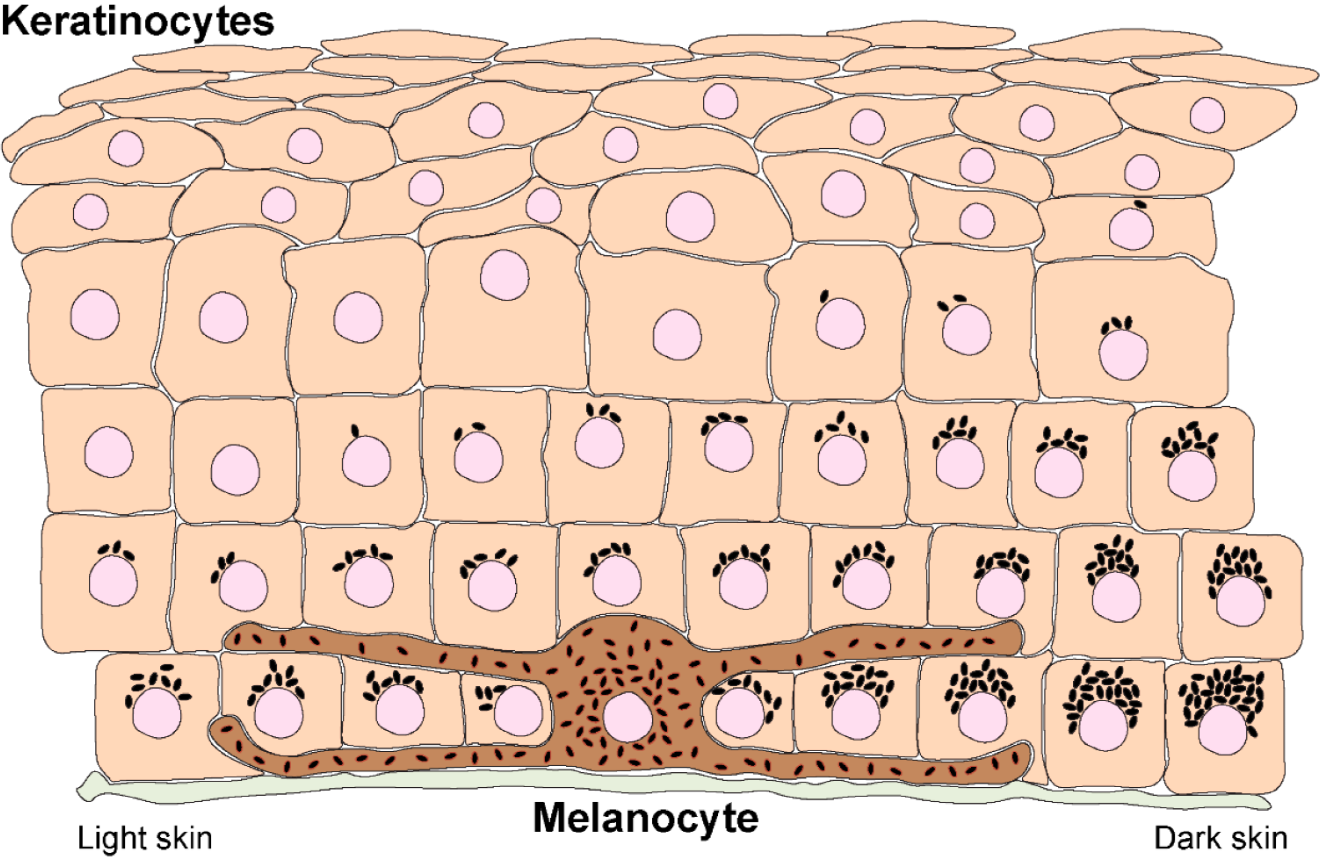
The principal active ingredient in Psorcutan is Calcipotriol (also known as Calcipotriene), a synthetic derivative of vitamin D3. It acts on the skin's immune and cellular pathways to restore normal keratinocyte behavior.
- Keratinocyte regulation: Calcipotriol binds to vitamin D receptors in the skin, suppressing keratinocyte hyperproliferation and promoting normal differentiation.
- Anti-inflammatory action: It downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2 and TNF-α, thereby reducing erythema and irritation.
- Comparison with corticosteroids: While corticosteroids are more potent in acute inflammation, Psorcutan offers sustained control with fewer long-term risks such as skin atrophy.
4. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
4.1 Recommended Dosage by Indication and Formulation
- Apply once or twice daily, depending on clinical severity and formulation type.
- Maximum weekly dose: Should not exceed 100 grams per week in adults to minimize systemic absorption.
- Application areas: Suitable for trunk, limbs, and scalp, but avoid facial or intertriginous regions unless specifically instructed.

4.2 Step-by-Step Application Instructions
- Clean and gently pat dry the affected skin before application.
- Apply a thin layer and spread evenly without occlusion.
- Do not apply immediately before or after UV therapy unless directed by a healthcare provider.
- For combination therapy (e.g., with topical steroids), alternate morning and evening applications.
5. Composition and Available Formulations
- Active ingredient: Calcipotriol 50 mcg/g
- Formulation-specific excipients:
- Ointment: Soft white paraffin, liquid paraffin
- Cream: Macrogol cetostearyl ether, white soft paraffin
- Gel/Foam: Isopropyl alcohol, butylated hydroxytoluene
- Preservatives and pH: Buffered to maintain skin tolerance
- Packaging: Tubes and cans of 30g, 60g, or 100g, depending on formulation
Calcipotriol betamethasone
Calcipotriol and betamethasone dipropionate are commonly combined as treatments for plaque psoriasis management purposes. Calcipotriol functions as a vitamin D mimic to control the proliferation of skin cells. At the same time, betamethasone acts as a cortisone compound, targeting the reduction of inflammation and easing discomforts such as redness and itchiness.
Fluorouracil/calcipotriol
Fluorouracil and calcipotriol are prescribed medications that are frequently mixed in a cream to manage actinic keratoses (AKs) and specific forms of superficial skin cancer. The function of fluorouracil is to eliminate precancerous skin cells by acting as an antimetabolite; whereas calcipotriol functions as a vitamin D3 analog that controls the growth of skin cells and boosts the immune system's ability to address cancerous cell growth.
6. Storage Conditions and Stability Information
- Store below 25°C (77°F); avoid freezing.
- Protect from light and moisture to maintain potency.
- Once opened, use within the period indicated on packaging (typically 6-12 weeks).
- Keep out of reach of children and store in original container.
7. Side Effects of Psorcutan Topical
7.1 Side Effects of calcipotriol
- Mild irritation: Transient burning or stinging may occur post-application.
- Dryness and redness: Common in the initial weeks of therapy, particularly in sensitive skin areas.
- Pruritus: Mild itching may be observed but usually subsides with continued use.
7.2 Serious or Rare Side Effects
- Hypercalcemia: Rare systemic absorption may alter serum calcium levels, especially with excessive application.
- Contact dermatitis: Allergic reactions to the vehicle or active compound are possible.
- Psoriasis exacerbation: In rare instances, improper use may trigger worsening or transformation into pustular psoriasis.
8. Drug Interactions and Combination Considerations
- Calcium supplements or systemic vitamin D: Risk of additive hypercalcemia; monitor levels when used concurrently.
- Topical corticosteroids: When used together, they may offer synergistic benefits but require timing separation to avoid interaction.
- UV therapy: Psorcutan may either enhance or interfere with phototherapy depending on timing; always coordinate with dermatologic guidance.
- Other topical agents: Avoid simultaneous application with irritating or acidic products to reduce cumulative skin irritation.
9. Warnings and Precautionary Statements
Psorcutan Topical should be used with caution to avoid complications stemming from inappropriate application or excessive dosing. Adherence to recommended guidelines ensures both efficacy and safety during treatment.
- Facial, perioral, and mucosal avoidance: Application on the face, near the mouth, eyes, or mucosal membranes may lead to irritation or adverse dermatologic reactions.
- Photosensitivity risk: The treated skin may become more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation. Direct sun exposure and artificial UV therapies should be minimized unless medically supervised.
- Systemic absorption caution: Although Psorcutan is a topical agent, overuse, particularly on large surface areas, can lead to systemic absorption and disturbances in calcium homeostasis.
- Occlusive dressings warning: Occlusion increases percutaneous absorption and should only be employed under clinical instruction to avoid unwanted systemic effects.

10. Contraindications for Use
There are specific clinical scenarios where Psorcutan Topical should be strictly avoided to prevent adverse events or treatment failures.
- Hypersensitivity: Patients with known allergies to calcipotriol or any formulation excipients should not use this product.
- Calcium metabolism disorders: Conditions such as hypercalcemia or hyperparathyroidism render the use of Psorcutan unsafe due to its vitamin D analog action.
- Organ dysfunction: Individuals with severe hepatic or renal impairment may be at elevated risk of altered calcium regulation, making Psorcutan relatively contraindicated.
- Pediatric surface area limitations: Use on large surface areas in young children may lead to systemic exposure and is not recommended.
11. Careful Administration Considerations
In certain dermatological presentations and patient profiles, Psorcutan should be administered with clinical prudence.
- Erythrodermic and pustular psoriasis: These severe subtypes may not respond well to topical vitamin D analogs and can worsen with inappropriate use.
- Fragile or atrophic skin: Use should be limited or adjusted in areas with compromised skin barrier to reduce the risk of irritation or absorption.
- Combination with systemic agents: Concurrent use with immunosuppressants or systemic antipsoriatics requires monitoring for cumulative side effects.
- Long-term treatment protocols: For extended use, periodic reassessment of serum calcium levels and therapeutic effectiveness is recommended.
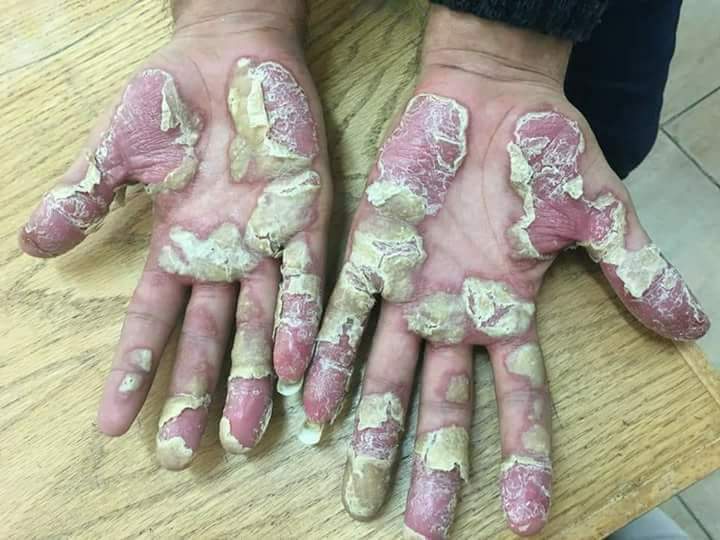
12. Important Patient Precautions and Counseling Points
Effective use of Psorcutan relies heavily on patient education and compliance with safe application practices.
- Eye safety: Patients must avoid applying Psorcutan near the eyes to prevent severe ocular irritation or injury.
- Broken or infected skin: Application on lesions with compromised integrity may lead to enhanced absorption or secondary infection.
- Sunlight precautions: Patients should avoid UVB therapy or direct sunlight on treated areas unless directed, as photosensitivity may occur.
- Dosing compliance: Strict adherence to prescribed application frequency and total weekly dose is critical to prevent toxicity.
13. Administration in Elderly Patients
Older adults may present with skin sensitivity and comorbidities that necessitate careful consideration when using Psorcutan.
- Skin evaluation: Prior to initiation, the skin should be assessed for thinning, dryness, or other age-related vulnerabilities.
- Increased sensitivity: Aging skin may react more strongly to topical medications, warranting gradual introduction and observation.
- No standard dosage changes: While dose adjustment is generally not required, heightened clinical monitoring is advised.
14. Administration During Pregnancy and Lactation
Use of Psorcutan in pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should be approached with caution due to limited human safety data.
- Pregnancy classification: Psorcutan should only be used if clearly necessary and under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
- Animal data: Reproductive toxicity was noted in some animal studies, but human evidence remains inadequate.
- Breastfeeding precautions: If used during lactation, avoid application on the breast area to prevent infant exposure via nursing.

15. Administration in Pediatric Populations
Pediatric use of Psorcutan must be limited and carefully supervised to prevent systemic complications.
- Age restrictions: Safety and efficacy data for children under 12 years are limited, necessitating specialist supervision.
- Lower maximum dose: Children are more susceptible to systemic absorption; therefore, a lower maximum dose should be adhered to.
- Monitoring requirements: Periodic serum calcium measurements may be warranted during prolonged or extensive use.
16. Overdose and Toxicity Management
Over-application or accidental ingestion of Psorcutan can lead to clinically significant toxicity, particularly involving calcium metabolism.
- Symptoms of overdose: Manifestations include hypercalcemia, nausea, fatigue, muscle weakness, and confusion.
- Immediate intervention: Discontinue the product and assess serum calcium levels without delay.
- Supportive care: Ensure adequate hydration and symptomatic treatment based on clinical severity.
- Hospitalization: In cases of severe toxicity, inpatient management and intravenous therapy may be required.
17. Safe Handling and Precautions for Use
Proper storage and hygienic handling of Psorcutan are essential for maintaining its effectiveness and preventing secondary complications.
- Prevent contact with sensitive areas: Always avoid contact with the eyes, oral mucosa, or nasal passages.
- Hand hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly after application to prevent inadvertent transfer to unintended areas.
- Disposal: Expired or unused medication should be disposed of in accordance with local pharmaceutical waste guidelines.
- Healthcare settings: In institutional environments like nursing homes, staff should use gloves and follow standard infection control protocols during application.
Psorcutan Topical FAQ
- What is Psorcutan Topical?
- What is Psorcutan Topical used for?
- What is the drug calcipotriol used for?
- Is calcipotriene a steroid?
- How long can you use calcipotriol?
- What are the side effects of calcipotriol?
- When to stop calcipotriol?
- Is calcipotriol good for wound healing?
- What is a substitute for calcipotriol?
- How long is the calcipotriol treatment?
What is Psorcutan Topical?
Calcipotriol is a type of Vitamin D used to manage plaque psoriasis by regulating the proliferation of skin cells.
What is Psorcutan Topical used for?
Calcipotriol is a type of Vitamin D used to manage plaque psoriasis by regulating the proliferation of skin cells.
What is the drug calcipotriol used for?
Calcipotriol is a prescription drug primarily employed in the treatment of psoriasis.
Is calcipotriene a steroid?
No
How long can you use calcipotriol?
4 weeks
What are the side effects of calcipotriol?
- Thirst
- Loss of appetite
- Dry mouth
- Metallic taste
- Weakness
When to stop calcipotriol?
Once your skin is better
Is calcipotriol good for wound healing?
Yes
What is a substitute for calcipotriol?
- Clobetasol topical
- Humira
- Methotrexate
- Triamcinolone topical
- Cosentyx
- Ustekinumab.
How long is the calcipotriol treatment?
4 weeks