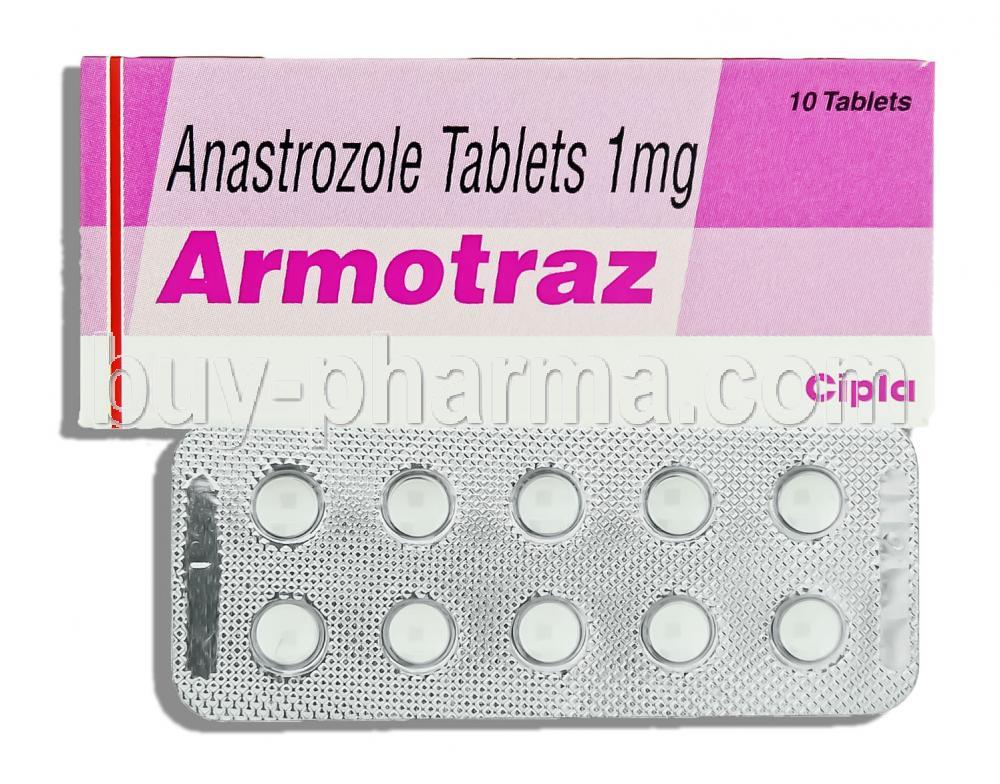
1. Introduction to Armotraz (Anastrozole)
What is Armotraz?
Armotraz is a pharmaceutical preparation containing the active compound anastrozole, a potent aromatase inhibitor utilized predominantly in the treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. It plays a pivotal role in estrogen suppression, making it a cornerstone in the hormonal management of postmenopausal breast malignancies.
Overview of Anastrozole as an Aromatase Inhibitor
Anastrozole functions by blocking the aromatase enzyme, which is responsible for converting androgens into estrogens in peripheral tissues. By inhibiting this enzyme, the medication significantly reduces circulating estrogen levels, thereby limiting the growth stimulus for estrogen-dependent tumors.
Classification and Therapeutic Category
Armotraz falls under the pharmacological class of non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors. It is categorized as an antineoplastic agent, specifically within endocrine therapy for oncology. Its therapeutic application is mainly directed toward breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
Approval Status and Regulatory Background
Anastrozole received regulatory approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for its use in breast cancer treatment. Its efficacy and safety profile have been well-established in numerous clinical trials, resulting in widespread adoption in global oncology guidelines.
2. Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulation
Active Ingredient: Anastrozole
Each tablet of Armotraz contains 1 mg of anastrozole as the primary active component.
Inactive Components and Excipients
The formulation also includes lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, povidone, sodium starch glycolate, and other pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that support tablet stability and bioavailability.
Available Dosage Forms and Strengths
Armotraz is typically available in oral tablet form, with the most commonly prescribed strength being 1 mg per tablet. This standardized dosage facilitates consistent dosing regimens across patient populations.
3. Mechanism of Action: How Armotraz Works in the Body
Role of Aromatase in Estrogen Synthesis
Aromatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the biosynthesis of estrogens. It converts androstenedione and testosterone into estrone and estradiol, respectively, in peripheral tissues.
Estrogen Suppression and Tumor Inhibition
By inhibiting aromatase, anastrozole drastically reduces estrogen levels in the bloodstream. This deprivation halts the proliferation of estrogen-dependent breast cancer cells, effectively slowing disease progression.
Selective Action in Hormone Receptor-Positive Tumors
Armotraz specifically targets tumors expressing estrogen receptors (ER+), minimizing off-target hormonal disruptions. Its selectivity enhances treatment efficacy while reducing systemic side effects associated with broader hormonal therapies.
4. Medical Uses and Indications
4.1 Approved Uses
- Treatment of hormone receptor-positive early-stage breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
- Management of advanced or metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
- Adjuvant therapy following the completion of tamoxifen therapy to reduce recurrence risk.
4.2 Off-Label and Investigational Uses
- Management of gynecomastia in adolescent and adult males.
- Induction of ovulation in women with anovulatory infertility, particularly those with PCOS.
- Treatment of male infertility associated with elevated estradiol levels.
- Preventive use in women with a strong family history of breast cancer or BRCA mutations.
5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Adult Dosage for Approved Indications
The recommended dose is 1 mg taken orally once daily, with or without food.
Duration of Therapy and Treatment Cycles
Treatment duration varies depending on the indication. In early breast cancer, therapy may continue for five years. In metastatic cases, treatment persists until disease progression.
Dose Modifications in Hepatic or Renal Impairment
No initial dose adjustment is necessary; however, patients with severe hepatic or renal dysfunction require closer monitoring due to altered drug metabolism and clearance.
Recommendations for Missed Doses
If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered. Double dosing to compensate for missed doses is discouraged.
When and How to Take the Medication
Armotraz can be administered with or without meals. Consistency in timing daily enhances therapeutic plasma levels.
6. Important Precautions Before and During Use
Monitoring Requirements During Treatment
Routine monitoring includes:
- Bone mineral density assessments
- Liver function tests
- Lipid profile evaluations
Bone Mineral Density Assessment
Due to the risk of osteoporosis, baseline and periodic DEXA scans are recommended to track bone health throughout therapy.
Cardiovascular Risk Management
Anastrozole may elevate cholesterol and increase cardiovascular risks. Regular blood pressure and lipid monitoring are advised.
Managing Lipid Profile and Liver Function Abnormalities
Elevations in liver enzymes and cholesterol may necessitate adjunct therapy or modification of lifestyle interventions.
7. Special Population Considerations
7.1 Administration in Elderly Patients
Pharmacokinetic Considerations in Patients Over 65
Anastrozole pharmacokinetics remain consistent in elderly patients; however, comorbidities necessitate individualized assessment.
Dose Adjustment Recommendations and Monitoring
Although no dose adjustment is typically required, vigilant monitoring for adverse effects, especially bone loss and cardiovascular symptoms, is essential.
7.2 Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Pregnancy Category and Teratogenicity
Classified as Pregnancy Category X. Armotraz is contraindicated in pregnancy due to demonstrated fetal harm in animal studies.
Risks During Breastfeeding and Lactation Transfer
Anastrozole may be excreted in human milk. Its use during lactation is contraindicated due to potential harm to the infant.
7.3 Administration in Pediatric Patients
Lack of Safety and Efficacy Data in Children
Armotraz is not approved for pediatric use. Limited data exist regarding safety and pharmacodynamics in this age group.
Off-Label Use in Adolescent Gynecomastia: Risks and Monitoring
Used cautiously in select cases of pubertal gynecomastia under specialist supervision. Monitoring includes hormone levels and bone development.
8. Contraindications to Armotraz Use
- Known hypersensitivity to anastrozole or formulation components.
- Premenopausal women with functional ovaries.
- Pregnancy and lactation due to teratogenic risks.
9. Warnings and Careful Administration
Pre-Existing Osteoporosis or Low Bone Mineral Density
Anastrozole significantly reduces estrogen levels, accelerating bone resorption. Patients with existing osteoporosis are at higher risk of fractures.
History of Ischemic Heart Disease or Cardiovascular Events
Estrogen depletion may exacerbate cardiovascular conditions. Patients with cardiac histories require careful evaluation before initiation.
Liver Dysfunction or Hepatic Insufficiency
Anastrozole is metabolized in the liver. In cases of hepatic impairment, drug clearance may be reduced, necessitating cautious use and close monitoring.
Potential Mood Disturbances and Cognitive Effects
Reports of anxiety, depression, and memory impairment have been observed in some users. Mental health assessments are recommended during prolonged use.
10. Drug Interactions and Potential Risks
Impact of Estrogen-Containing Products
Concurrent use of estrogen-containing therapies—such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), contraceptive pills, or topical estrogen preparations—can counteract the pharmacological action of Armotraz. As anastrozole functions by suppressing estrogen production, exogenous estrogen administration may diminish its therapeutic efficacy and is therefore contraindicated during treatment.
Interaction with Tamoxifen or Other Hormonal Agents
Tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), has been shown to interfere with the plasma concentrations of anastrozole. Concomitant use reduces the effectiveness of both medications, compromising clinical outcomes. Similarly, the combination of Armotraz with other estrogenic or anti-estrogenic agents should be approached with caution or avoided entirely.
CYP450 Enzyme-Related Drug Metabolism
Anastrozole is metabolized primarily via hepatic pathways involving cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, notably CYP3A4, CYP1A2, and CYP2C8. While it does not significantly inhibit or induce these enzymes, co-administration with strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine) or inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) may alter its pharmacokinetic profile and therapeutic effectiveness.
Effect on Warfarin and Anticoagulants
Limited clinical data suggest that anastrozole does not significantly affect the anticoagulant properties of warfarin. However, due to individual variability in hepatic metabolism and clotting function, patients receiving warfarin or other anticoagulants should undergo regular INR monitoring to avoid bleeding complications or thrombotic events.
11. Common and Serious Side Effects of Armotraz
11.1 Frequently Reported Side Effects
Armotraz is generally well-tolerated, yet several adverse effects occur commonly due to estrogen deprivation:
- Hot flashes, night sweats, and joint pain: Vasomotor symptoms and musculoskeletal discomfort are frequent, often impacting quality of life in postmenopausal women.
- Fatigue and weakness: Generalized lethargy and reduced stamina are reported, particularly in the initial months of therapy.
- Nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort: Mild nausea, abdominal bloating, and occasional constipation or diarrhea may occur but are typically transient.
- Headache and dizziness: These neurologic symptoms are usually self-limiting but should be monitored if persistent.
11.2 Serious Adverse Reactions
Though infrequent, several potentially serious effects require prompt attention:
- Osteoporosis and fracture risk: Prolonged estrogen suppression accelerates bone demineralization, significantly increasing the likelihood of osteoporotic fractures. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans are essential for monitoring bone density.
- Cardiovascular events: Postmenopausal women may face an elevated risk of ischemic heart disease, including angina and myocardial infarction, particularly those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Liver enzyme elevation and hepatotoxicity: Elevations in AST, ALT, or bilirubin levels have been observed, warranting regular hepatic function surveillance.
- Mood changes and depression: Estrogen depletion can influence neurotransmitter balance, occasionally resulting in depression, anxiety, or emotional lability requiring psychiatric assessment.
12. Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Acute Anastrozole Overdose
While data on overdose are limited, large doses may result in:
- Severe nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or syncope
- Somnolence or cognitive dulling
- Electrolyte imbalance due to gastrointestinal losses
Supportive Care and Symptomatic Management
There is no specific antidote for anastrozole overdose. Treatment is largely supportive and may include:
- Activated charcoal administration if within a short time frame post-ingestion
- Monitoring of vital signs and hydration status
- Electrolyte correction and antiemetics as needed
Poison Control and When to Seek Emergency Help
Immediate contact with local poison control centers is advised in any suspected overdose. Emergency medical services should be sought if the patient displays signs of altered consciousness, persistent vomiting, or cardiovascular instability.
13. Storage and Handling Instructions
Recommended Storage Temperature and Conditions
Armotraz tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature, ideally between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect from excessive moisture, heat, and direct light.
Shelf Life and Stability
The product retains its potency and safety profile within its labeled expiration date, typically 24 to 36 months from the date of manufacture when stored properly in original packaging.
Safe Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Unused or expired Armotraz should not be disposed of in household trash or wastewater. Return through local pharmaceutical take-back programs or follow guidelines issued by environmental health agencies for safe disposal.
14. Handling Precautions for Patients and Caregivers
Guidelines for Handling by Non-Patients
Caregivers should minimize direct handling of tablets when not prescribed for themselves. Use of gloves or immediate hand washing after contact is advised to avoid inadvertent exposure.
Avoiding Exposure During Pregnancy
Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant must not handle crushed or broken tablets due to the teratogenic nature of anastrozole. Whole tablets should also be handled with caution by this population.
Personal Hygiene and Safe Disposal Practices
Basic hygiene measures—such as handwashing before and after handling medication—are essential. Tablets should be kept in child-resistant containers and stored out of reach of children and pets. Any discarded medication must be sealed in a secure container to prevent accidental ingestion or environmental contamination.
Armotraz, Anastrozole FAQ
- What is the use of Armotraz tablet?
- What is the dark side of anastrozole?
- What is the drug anastrozole used for?
- What to avoid when taking anastrozole?
- What are the benefits of taking anastrozole tablets?
- Why do men take anastrozole?
- Can anastrozole damage the kidneys?
- What is the best time of day to take anastrozole?
- What happens to your body when you stop taking anastrozole?
- How long do patients stay on anastrozole?
- What does anastrozole do to your brain?
- How does anastrozole affect your teeth?
- What organs does anastrozole affect?
- Who cannot take anastrozole?
- Can I take vitamin D while taking anastrozole?
- What are the long term side effects of anastrozole?
- What cancers does anastrozole treat?
- Can you be in the sun while taking anastrozole?
- Does anastrozole cause weight gain?
- Can anastrozole cause erectile dysfunction?
- Is anastrozole a steroid?
- How long is it safe to take anastrozole?
- Is memory loss a side effect of anastrozole?
- Can anastrozole damage your liver?
- How fast does anastrozole kick in?
- Can anastrozole affect your eyesight?
- What are the long-term effects of taking anastrozole?
- How quickly does anastrozole cause bone loss?
- What happens if I don't take anastrozole?
- Does anastrozole cause hair loss?
- Is anastrozole chemo?
- What is the life expectancy of anastrozole patients?
- What are alternatives to anastrozole?
- Does anastrozole affect your bowels?
- How quickly does anastrozole work?
- Does anastrozole cause belly fat?
- How long after starting anastrozole do side effects start?
- Is anastrozole a high risk medication?
What is the use of Armotraz tablet?
The Armotraz Tablet is a treatment option for women with breast cancer. It's often used on its own or alongside treatments like surgery or radiation. For some women, it's the line of defense against breast cancer that's spread to other parts of the body or has taken hold in multiple areas of the breast.
What is the dark side of anastrozole?
The downside of Anastrozole is that it can actually weaken your bones, making them more fragile and at risk of getting osteoporosis or even suffering from bone fractures.
What is the drug anastrozole used for?
Anastrozole is a go-to treatment for early-stage breast cancer that's fueled by hormones. Doctors also prescribe it as a line of defense for advanced breast cancer that has spread and is either hormone receptor positive or its receptor status is unknown.
What to avoid when taking anastrozole?
- Fast food
- Fried chicken
- French fries
- Bacon
What are the benefits of taking anastrozole tablets?
Anastrozole helps prevent breast cancer from coming back.
Why do men take anastrozole?
It is used to treat male infertility with abnormal testosterone-to-estradiol ratio.
Can anastrozole damage the kidneys?
It is a rare ocurrence.
What is the best time of day to take anastrozole?
At night time
What happens to your body when you stop taking anastrozole?
- Nausea
- Hot flashes
- Pain
- Weakness
- High Cholesterol
- Lymphedema
- Osteoporosis
How long do patients stay on anastrozole?
5 to 10 years
What does anastrozole do to your brain?
Decrease in memory retention and concentration
How does anastrozole affect your teeth?
Osteoporosis caused by anastrozole can cause dental problems.
What organs does anastrozole affect?
Liver
Who cannot take anastrozole?
- Pregnant or trying to get pregnant or breastfeeding
- Severe kidney or liver disease
- Osteoporosis
Can I take vitamin D while taking anastrozole?
Yes
What are the long term side effects of anastrozole?
Anastrozole can have some long-term side effects. For one, it increases your risk of fractures. You're also more likely to develop osteoporosis, a condition where your bones become weak and fragile. The problem is that anastrozole blocks estrogen, which is crucial for keeping your bones healthy. When estrogen is low your bones start to thin out making them more prone to breaks.
What cancers does anastrozole treat?
Breast cancer
Can you be in the sun while taking anastrozole?
No
Does anastrozole cause weight gain?
Yes
Can anastrozole cause erectile dysfunction?
No
Is anastrozole a steroid?
No
How long is it safe to take anastrozole?
5 years
Is memory loss a side effect of anastrozole?
Yes
Can anastrozole damage your liver?
Yes
How fast does anastrozole kick in?
Anastrozole kicks in fast, reducing estrogen levels in no time. In fact, some people start noticing side effects within a day of taking it, 24 Hours after their dose.
Can anastrozole affect your eyesight?
Yes
What are the long-term effects of taking anastrozole?
Anastrozole increases the chance of heart problems, including heart attack. It may also decrease bone density when used for a long time.
How quickly does anastrozole cause bone loss?
2 years
What happens if I don't take anastrozole?
If you don't take your therapy as directed, you're taking a risk. Skipping doses, stopping soon, or not starting at all can have serious consequences. It can increase your chances of the cancer spreading to parts of your body or even being fatal.
Does anastrozole cause hair loss?
Yes
Is anastrozole chemo?
Yes
What is the life expectancy of anastrozole patients?
42.3 months
What are alternatives to anastrozole?
letrozole (Femara), tamoxifen (Soltamox), alpelisib (Piqray), everolimus (Afinitor), fulvestrant (Faslodex), palbociclib (Ibrance), abemaciclib (Verzenio)
Does anastrozole affect your bowels?
Anastrozole sometimes causes nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
How quickly does anastrozole work?
24 hours
Does anastrozole cause belly fat?
No results conclusive
How long after starting anastrozole do side effects start?
24 hours
Is anastrozole a high risk medication?
Yes