Atacand
Introduction
Atacand, known by its name Candesartan, is a prime example of an antihypertensive medication that holds great significance in the field of modern medicine. This medication has undergone a history of extensive research and development leading to its esteemed position, in medical records today.
Historical background and development
The story of Atacand begins in the 20th century. It came about through a combination of scientific exploration and the urgent need to tackle growing cardiovascular problems. Over the past few decades, many hypertension medications have been developed, but Atacand stands out as a shining example representing the perfect blend of pharmacological expertise and practical clinical application. The timeline for developing this drug not only involves numerous laboratory tests but also symbolizes the progress made in modern therapeutic approaches.
How It Works
Mechanism of action
When delving into the pharmacodynamics of Atacand, we come across a network of molecular interactions. Essentially, Atacand acts as an antagonist to the Angiotensin II receptor. In terms, this means that Atacand blocks the attachment of Angiotensin II to its receptors, reduces its vasoconstrictive impact, and regulates the secretion of aldosterone. A hormone crucial for maintaining salt and water balance.
Impact on the cardiovascular system
The effects of Atacand on the system are varied and diverse. It helps lower blood pressure by counteracting the impact of Angiotensin II on blood vessels.
- Additionally, it eases the workload on the heart muscle, thus reducing strain.
- Atacand vasodilatory properties can also slow down the progression of heart failure.
- Moreover, it helps maintain perfusion pressures, which in turn reduces the risk of damage to vital organs.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended dosage for various conditions
The effectiveness of a treatment depends not only on the medication itself but also on how precisely it is administered. When using Atacand the recommended dosage can vary based on the condition being treated.
- For hypertension it is typically advised to start with a dose of 8 16 mg and adjust as needed based on individual response.
- In cases of heart failure, a starting dose of 4 mg may be. Adjusted accordingly depending on the specific clinical situation.
It's important to remember that these guidelines are general, and personalized treatment plans tailored to each patients characteristics are of utmost importance.
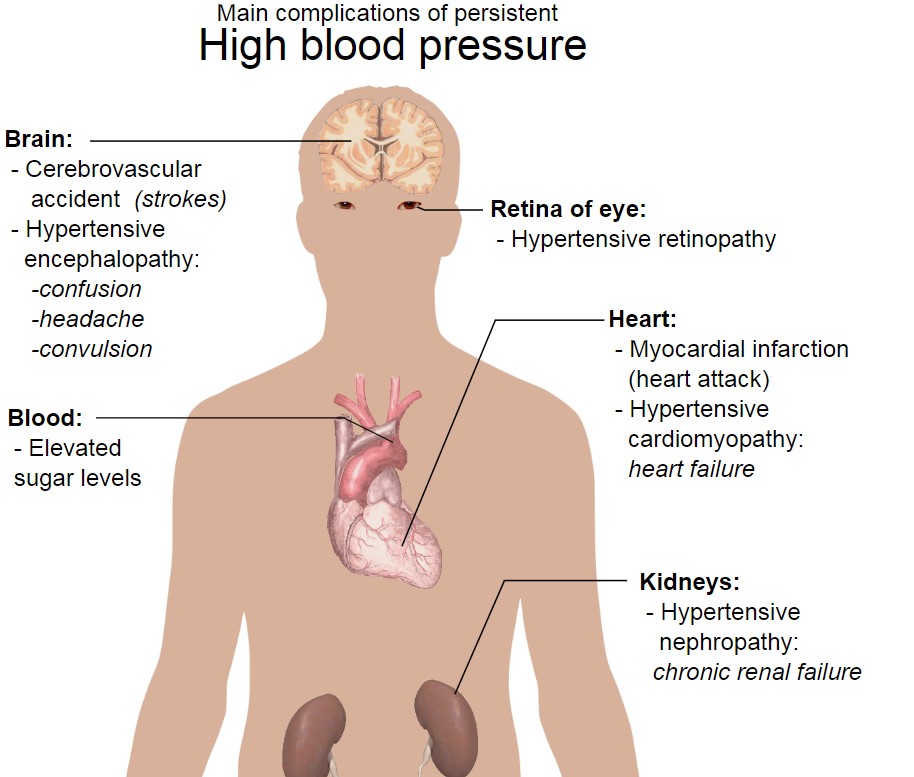
Hypertension
Adjustments based on patient conditions and reactions
Just like a conductor perfecting a symphony, making adjustments to the dosage is vital for achieving therapeutic balance. These adjustments depend on factors such as the patient's function, as the kidneys play a crucial role in drug elimination.
Additionally, consideration should be given to any medications being taken by the patient, as there may be potential interactions between drugs.
It is also important to take into account the patient's age with elderly individuals who often require extra caution. Regular monitoring and careful clinical judgment are essential when making these adjustments.
Administration guidelines for best results
Atacand's effectiveness, although based on its pharmacology, can be enhanced by following smart administration guidelines. Here are a few recommended practices;
- Take it with or without food to allow for flexibility in incorporating it into your routine.
- Stick to timings to ensure a predictable pharmacokinetic profile.
- Regularly monitor your blood pressure to evaluate how well it is working and make any adjustments.
In summary, by finding the dosage making smart adjustments and being diligent, in administration, we can maximize Atacand's therapeutic potential.
Uses
Indications for use
In the field of pharmacology, certain drugs stand out due to their wide range of uses. The recommended indications for these drugs go beyond suggestions; they represent a combination of empirical evidence, rigorous testing, and clinical experience.
- Hypertension: A condition old as time itself yet as relevant as the latest news headline. In the battle against high blood pressure, medications provide a valuable arsenal. If left untreated, hypertension can lead to complications.(1)
- Management of Heart Failure: This is an area where the weakened and burdened heart seeks relief through interventions. Managing heart failure goes beyond alleviating symptoms; it involves a concentrated effort to rejuvenate, revitalize, and restore cardiac function.(2)
1. WebMD - Atacand - Uses, Side Effects, and More
2. National Library of Medicine - Candesartan in heart failure
Benefits and outcomes
When exploring the realm of benefits and results we discover a tapestry of improved quality of life extended longevity and the sheer satisfaction of achieving therapeutic successes.
- Regarding Hypertension;
Improvement in blood pressure levels to align them with recommended parameters. Preventive advantages that help prevent complications like strokes, kidney problems, and heart attacks. A comprehensive enhancement in vascular health that reduces strain on artery walls.
- For Heart Failure Management;
Increase in output to ensure vital organs receive adequate blood supply. Reduction in symptomatic burdens such as shortness of breath swelling and fatigue. Long-term outcomes that lead to hospitalizations improved functional capacity and an overall enhancement, in quality of life.
Off-Label Use
Common off-label indications
The field of medicine, in its pursuit of providing exceptional care, often explores unconventional approaches. Off-label use, a manifestation of this spirit, refers to the utilization of pharmaceuticals for purposes beyond their approved indications. Although not officially endorsed, these practices arise from observations, anecdotal evidence, and sometimes intuitive medical judgment. Some common examples of off-label use include;
- Psychotropic Medications; Initially developed for conditions like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, they often demonstrate effectiveness in a range of other psychiatric and neurological disorders.
- Anticonvulsants: Apart from treating epilepsy, they have also been employed to manage chronic pain syndromes, psychiatric conditions, and even migraines.
- Beta-blockers; While primarily used for cardiovascular ailments they have found application in anxiety disorders, migraine prevention, and even tremor management.
Efficacy and safety profile for off-label use
When exploring the realm of using drugs off-label, it's crucial to have an understanding of their effectiveness and safety. A drug that proves to be effective in a treatment area should ideally maintain its potency while prioritizing patient safety.
Some key observations to consider are:
- There is a wealth of literature that highlights the effectiveness between off-label use and approved indications as long as the underlying pharmacological mechanism remains relevant.
- The overall safety profile tends to stay consistent. However, specific nuances may arise depending on each patient's physiological responses and any accompanying medical conditions.
- It's crucial to monitor and diligently practice pharmacovigilance to identify and address any unexpected reactions or outcomes promptly.
Potential risks associated with off-label use
Venturing into the realm of off-label use comes with its share of potential risks. Straying from treatment paths inherently carries certain dangers. Some of these concerns include;
1. Unforeseen Adverse Reactions; The uncharted territory of therapies may lead to unexpected negative reactions that have not been observed in traditional settings.
2. Drug Interactions; When other medications, those outside the scope of the primary indication, are administered simultaneously, unforeseen interactions can arise, jeopardizing patient safety.
3. Efficacy Concerns: Without the foundation of rigorous clinical trials, off-label use sometimes grapples with uncertainties regarding its effectiveness as a treatment option.
In summary, while off-label use embodies the spirit within the medical community, it necessitates a cautious balancing act that weighs therapeutic potential, against safety concerns.
Composition
Active ingredients and their roles
The core of any formulation primarily relies on its active components. These carefully selected, and extensively tested entities play a crucial role in orchestrating the therapeutic effects of the drug. The active ingredients serve purposes including;
1. Therapeutic Modulation: Actively interacting with the body's pathological processes to produce desired therapeutic responses.
2. Target Engagement; Binding with proteins or receptors, ensuring precise and specific actions.
3. Disease Alteration; Modifying the course of diseases often by slowing down their progression or actively reversing certain symptoms.
These roles highlight how active ingredients contribute to the effectiveness and functionality of pharmaceutical formulations.
Inactive ingredients and their purposes
Active ingredients may be the stars of the show. Let's not forget about their quiet counterparts, the inactive ingredients, also known as excipients. These unsung heroes have a role to play in various aspects of medication.
- Firstly, they help with drug delivery by aiding in the absorption or distribution of the ingredient.
- Secondly, they ensure that the active molecules remain stable and effective throughout storage.
- Lastly they contribute to formulation cohesion by binding all the different components of the drug ensuring a consistent and reliable dose delivery.
So while active ingredients grab most of the attention, it's important to recognize and appreciate the role played by these silent but essential excipients.
Side Effects
Overview of side effects
Every medication, regardless of its effectiveness, can have some side effects. These unintended physical reactions can vary from mild and temporary to severe and long-lasting.
Differentiating between common and rare side effects
The occurrence and frequency of side effects can differ across individuals. Typically the side effects commonly seen in settings are mild and resolve on their own. On the other hand, although rare some side effects can be more serious and require immediate medical attention.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects, which are commonly experienced with medications may include;
- Headache; This is usually temporary and can be relieved with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Stomach discomfort; gastrointestinal issues that typically go away on their own without any intervention.
- Feeling drowsy; There might be a sedative effect so it's important to be cautious when engaging in activities that require alertness.
Uncommon/Rare Side Effects
Rare side effects, although not commonly experienced, can have implications in a clinical setting. These include allergic reactions that require immediate medical attention, sudden onset of symptoms such as slurred speech or muscular weakness indicating neurological deficits, and irregular heart rhythms known as cardiac arrhythmias, which can be potentially life-threatening if left untreated.
Interactions
Drug-drug interactions
When multiple drugs are taken together, they can often interact with each other, leading to changes in their effects. There are types of these interactions;
1. Interactions; In this case, one drug cancels out or reduces the effect of another drug.
2. Synergistic Interactions; When drugs are combined their effects can be greater than what they would produce.
3. Pharmacokinetic Interactions; Here, one drug affects how another drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized or excreted from the body.
These interactions highlight the complexities that can arise when multiple medications are used simultaneously.
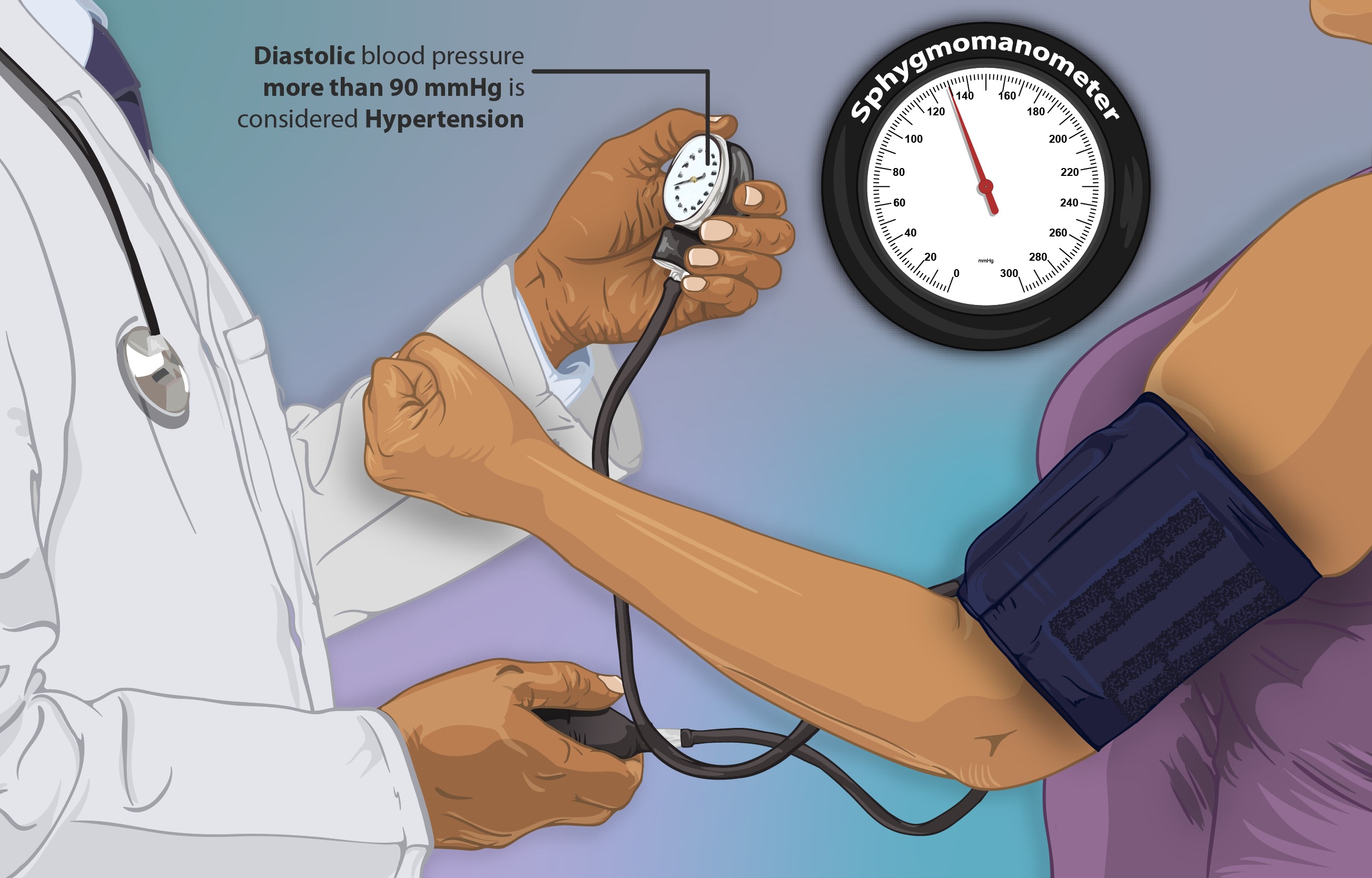
Hypertension
Drug-food interactions
The interaction between medications and food can have varying effects on the effectiveness of the drugs.
- For instance, Grapefruit juice is known to disrupt the breakdown of medications, which could potentially result in elevated levels of these drugs in the bloodstream reaching toxic levels.
- Dairy products have the ability to bind with specific antibiotics, which may reduce their absorption and overall effectiveness.
- High fiber foods might slow down the absorption process of certain medications.
Impact of other medical conditions
Certain medical conditions can influence how a drug works. For example;
- Liver diseases can change how the body processes the drug, which could increase the chances of experiencing side effects.
- Cardiac conditions may indicate that certain medications affecting heart rhythm or blood pressure should be avoided.
- Kidney problems can affect how drugs are eliminated from the body, requiring adjustments in dosage.
It's important to consider these medical conditions when prescribing or taking medication.
Warnings and Contraindications
Warning
The world of pharmaceuticals is filled with treatments, but it requires careful attention. We must make sure to maximize the benefits while minimizing any harmful effects.
Situations in which caution is advised
The use of Atacand with other medications should be approached with caution in certain clinical situations;
1. Concurrent Medications; Taking Atacand alongside drugs that have the potential to harm the kidneys can increase the risk of kidney problems.
2. History of Angioedema; Patients who have experienced angioedema in the past are more likely to have it happen again while using Atacand.
3. Procedures; Extra care should be taken during the perioperative period especially for major surgeries as there is a possibility of experiencing worsened low blood pressure.
Adverse reactions to monitor
It is crucial to monitor patients after taking Atacand to detect any early indications of potential health issues, such as;
1. Hyperkalemia: This refers to levels of potassium in the blood which could lead to cardiac complications.
2. Renal Dysfunction; This occurs when there are changes in the levels of serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output.
3. Hypotension; This is particularly noticeable in patients who have depleted volumes of fluids.
By staying vigilant and observing these signs, we can promptly identify and address any concerns.
Contraindication
There are situations where it is not recommended and even discouraged to use Atacand;
1. Bilateral Renal Artery Stenosis; Due to the increased risk of kidney problems.
2. History of Anuric Reaction; Patients who have experienced a lack of urine production after taking this medication
3. Known Hypersensitivity: This may result in reactions or swelling.
It's important to be aware of these conditions and discuss them with your healthcare provider before considering the use of Atacand.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Careful Administration
Administering drugs, ones like Atacand requires precise and personalized approaches akin to an intricate ballet.
In patients with renal impairments
Patients with kidney problems require consideration when it comes to medication dosage, as there may be an increased risk of drug effects. Close monitoring is necessary. Adjustments to the dosage might be required.
With other antihypertensive drugs
Using medications together can enhance the effects of low blood pressure, so it is crucial to carefully examine the medication schedule and regularly monitor blood pressure.
Important Precautions
Ensuring the well-being of patients requires precautions that cannot be compromised.
It is important to monitor liver functions as any changes in the liver can affect how medications are metabolized and cleared from the body.
Additionally, it is crucial to check for electrolyte imbalances in order to identify any abnormalities and prevent potential complications.
Special Population Considerations
Administration to Elderly
The older population, due to changes in their functions and the presence of other health conditions, requires a customized approach to their treatment.
Dosing considerations
Due to changes in the body's physiology, such, as decreased kidney function it is important, to begin with dosage and adjust it based on how the person responds.
Monitoring for adverse reactions
The elderly population is often more prone to experiencing effects from the medication so it is important to carefully observe them for any possible kidney problems, imbalances in electrolytes, or significant drops, in blood pressure.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Ensuring the well-being of both mother and child requires a thorough assessment and careful consideration when making decisions.
Potential risks to fetus and infants
There is a possibility that Atacand may cause harm to the baby, such as kidney problems, low levels of amniotic fluid, or even fetal death. It is also important to note that nursing babies could be exposed to the medication through breast milk.
Recommendations and alternatives
It is recommended to stop using this treatment if pregnancy is detected. It's important to consider options that are safer for both pregnancy and breastfeeding if available.
Administration to Children
Children undergoing treatment due to their distinct physical characteristics require specific considerations.
Age-appropriate dosing
The dosing schedules should be tailored according to the child's age, weight, and overall well-being. Begin with the range of dosages and make adjustments based on how well it works and how well the child tolerates it.
Efficacy and safety profile
Clinical trials and observational studies conducted on children help us understand how effective and safe a treatment is. It is crucial to monitor for any possible negative reactions.