Introduction to Trisiden Equine Oral Paste
Overview of Trisiden and Its Dual-Antibiotic Formulation
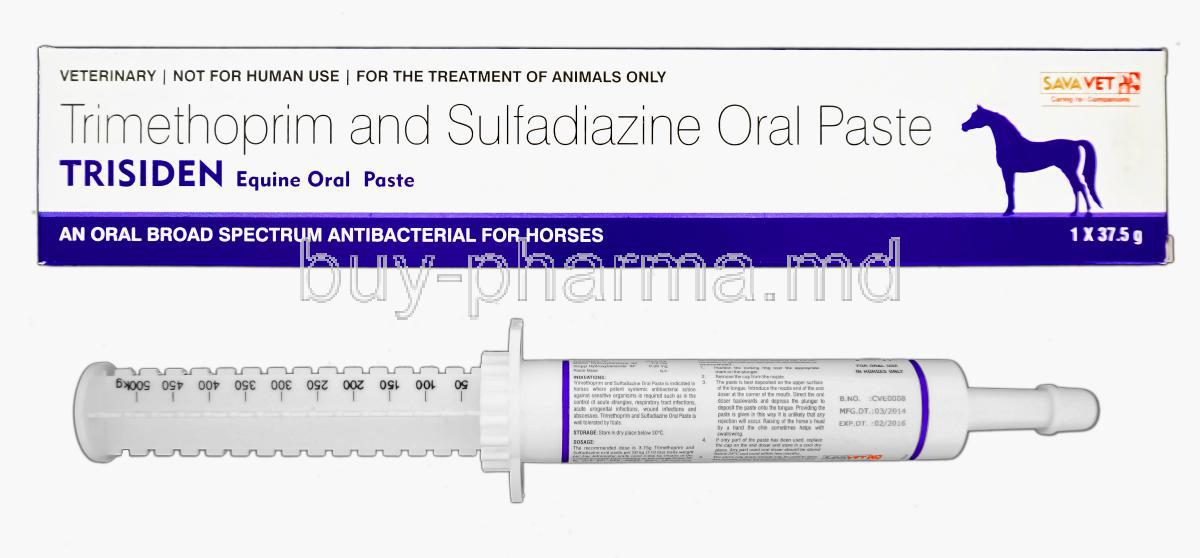
Trisiden is a veterinary-grade antimicrobial oral paste uniquely formulated for equine use. It combines two potent antibiotics—Trimethoprim and Sulfadiazine—to deliver broad-spectrum bactericidal activity. This dual-action approach disrupts bacterial survival mechanisms at multiple levels, enhancing treatment efficacy.
Role in Modern Equine Veterinary Medicine
Widely prescribed in equine medicine, Trisiden plays a pivotal role in treating systemic and localized infections. Its efficacy against a broad array of bacterial pathogens makes it indispensable in the management of infectious diseases affecting racehorses, breeding stock, and pleasure animals alike.
Benefits of Oral Paste Delivery System in Horses
- Easy administration with minimal stress to the horse - Uniform dosing accuracy - Improved compliance in horses reluctant to swallow tablets or capsules
Regulatory Status and Veterinary Prescription Requirement
Trisiden is a prescription-only veterinary medicine (POM-V), approved in numerous jurisdictions for equine use. A licensed veterinarian must assess the horse and issue the prescription prior to administration.
Composition and Formulation Details
Active Ingredients: Trimethoprim and Sulfadiazine
Each gram of Trisiden paste contains a synergistic combination of: - Trimethoprim: a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor - Sulfadiazine: a sulfonamide bacteriostatic agent
Concentration and Ratio of Components
The formulation typically includes a 1:5 ratio of Trimethoprim to Sulfadiazine, a proven combination that ensures maximum bacterial inhibition.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
- Palatable base for oral administration - Stabilizers to maintain antibiotic potency - Viscosity agents to ensure uniform dispersion
Pharmacological Classification and Synergistic Effect
Trisiden belongs to the antimicrobial class of potentiated sulfonamides. The combination achieves a synergistic effect by inhibiting successive steps in the folic acid synthesis pathway, thereby enhancing bacterial kill rates.
Mechanism of Action: How Trimethoprim/Sulfadiazine Works in Horses
Inhibition of Bacterial Folic Acid Synthesis
Trimethoprim targets dihydrofolate reductase, while sulfadiazine inhibits dihydropteroate synthase. Together, they block folic acid synthesis required for DNA replication.
Sequential Blockade of Bacterial Metabolic Pathways
- Sulfadiazine halts the early stage of folate synthesis - Trimethoprim acts on the subsequent step, leading to a cumulative inhibition - This dual blockade prevents bacterial proliferation and survival
Spectrum of Antimicrobial Activity
Effective against: - Gram-positive bacteria such as *Streptococcus equi* - Gram-negative bacteria including *Escherichia coli* and *Salmonella* spp.
Time- and Concentration-Dependent Effects
While sulfadiazine’s effect is concentration-dependent, trimethoprim exhibits time-dependent activity—resulting in sustained antimicrobial pressure across dosing intervals.
Approved Veterinary Uses of Trisiden Paste
Respiratory Tract Infections
Treats bacterial bronchitis, pneumonia, and *Streptococcus equi* (strangles).
Urinary Tract Infections
Indicated in infections of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Gastrointestinal Infections
Used in the treatment of *Salmonella* and *Clostridium* infections causing colitis.
Wound Infections and Abscesses
Supports recovery from infected lacerations and post-traumatic abscesses.
Skin and Soft Tissue Bacterial Infections
Effective in cellulitis, dermatitis, and secondary bacterial skin involvement.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses in Equines
Use in Post-Surgical Prophylaxis
Administered prophylactically to prevent postoperative infections in orthopedic and abdominal surgeries.
Empirical Therapy in Febrile Horses
Used when a definitive pathogen is not yet identified but systemic infection is suspected.
Treatment of Sepsis or Bacteremia in Foals
In certain neonatal sepsis cases, Trisiden is chosen due to its broad antimicrobial coverage.
Potential Application in Protozoal Infections
Though primarily antibacterial, emerging data suggests occasional utility in treating protozoal infections when used adjunctively.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Horses
Standard Dosage Based on Body Weight
Typical dosage: 15-30 mg/kg of combined drug per day, divided into two doses.
Frequency and Duration of Treatment
- Usually administered twice daily - Duration: 5–10 days depending on severity and clinical response
Oral Paste Administration Techniques
- Administer directly into the horse’s mouth using a dosing syringe - Ensure the horse does not spit out the medication
Dosage Adjustment in Foals or Senior Horses
- Foals may require lower or more frequent doses due to immature metabolism - Geriatric horses with reduced renal clearance need adjusted dosing intervals
Missed Dose and Overdose Handling
- If a dose is missed, administer as soon as remembered - In case of overdose: watch for signs of toxicity and contact a veterinarian immediately
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions in Horses
Overview of Known Adverse Reactions
While generally well-tolerated, adverse events may occur with prolonged or high-dose usage.
Common Gastrointestinal Side Effects
- Anorexia - Diarrhea - Mild colic symptoms
Skin Reactions and Hypersensitivity
- Urticaria (hives) - Pruritus (itching) - Rash and localized swelling
Hematological Changes with Prolonged Use
- Thrombocytopenia - Anemia - Leukopenia
Renal Complications and Crystaluria
Sulfadiazine may precipitate in renal tubules, especially in dehydrated horses.
Common and Mild Side Effects to Monitor
Temporary Appetite Suppression
Transient reduction in feed intake may be observed during initial treatment days.
Mild Dehydration Signs
Reduced water intake or dry mucous membranes should be addressed promptly.
Lethargy and Behavioral Changes
Watch for signs such as reduced activity or reluctance to move.
Oral Paste Intolerance and Salivation
Some horses may resist paste administration or exhibit excessive salivation.
Warnings and Contraindications
Contraindicated in Horses with Known Sulfa or Trimethoprim Allergies
Hypersensitive horses should not receive Trisiden due to the risk of severe allergic reaction.
Avoid Use in Horses with Impaired Renal or Hepatic Function
These animals may have reduced drug clearance, heightening toxicity risk.
Risk of Colitis in Adult Horses—Use with Caution
Sulfonamide use has been linked to colitis and enterocolitis in some adult horses.
Not for Use in Animals Intended for Human Consumption
Residues from Trimethoprim/Sulfadiazine may pose a health hazard in meat-producing animals.
Drug Interactions and Compatibility
Interaction with Other Sulfonamides or Antifolate Agents
Concurrent use of Trisiden with other sulfonamide antibiotics or antifolate compounds can potentiate toxicity or lead to overlapping adverse effects. Such combinations may amplify hematologic suppression or hypersensitivity reactions, necessitating vigilant monitoring.
Reduced Efficacy When Combined with Antacids or Certain Feed Supplements
Administration alongside calcium, magnesium, or aluminum-based antacids, as well as iron supplements or mineral-rich feeds, may interfere with the gastrointestinal absorption of Trisiden. This may result in subtherapeutic serum levels and reduced antimicrobial efficacy.
Potential Antagonism with Local Anesthetics or Methotrexate
- Certain local anesthetics may compete with sulfonamides at the enzymatic level, diminishing antibacterial activity. - Methotrexate, a folate antagonist, can synergize with Trimethoprim, increasing the risk of pancytopenia and nephrotoxicity.
Monitoring When Used Concurrently with Nephrotoxic Drugs
Combining Trisiden with nephrotoxic agents such as aminoglycosides or NSAIDs increases the likelihood of renal impairment. Creatinine and BUN levels should be regularly monitored during coadministration.
Precautions and Careful Administration Considerations
Necessity of Culture and Sensitivity Testing When Possible
Prior to initiating treatment, bacterial culture and antibiotic sensitivity testing are advisable to confirm the organism’s susceptibility. This promotes judicious antimicrobial stewardship and minimizes the risk of resistance.
Importance of Hydration to Avoid Crystal Formation in Urine
Sulfadiazine can precipitate in renal tubules, particularly in dehydrated horses. Adequate water intake or supplemental fluid therapy is essential to maintain renal perfusion and prevent crystalluria.
Monitoring of CBC and Renal Parameters During Extended Use
- Complete blood count (CBC) should be monitored periodically to detect anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia. - Serum chemistry panels are necessary for evaluating renal function during prolonged therapy.
Adjustments for Horses with a History of Colic or Metabolic Disorders
Horses with predisposing gastrointestinal or metabolic conditions may require reduced dosing or closer observation, as they may be more vulnerable to drug-induced GI upset or electrolyte imbalances.
Use in Special Equine Populations
12.1 Administration in Elderly Horses
Age-Related Pharmacokinetic Considerations
Aging horses often exhibit decreased hepatic metabolism and renal clearance, potentially altering the pharmacokinetics of Trimethoprim/Sulfadiazine.
Adjusted Dosing Based on Renal Clearance
Dose frequency or quantity should be reduced in geriatric horses with suboptimal renal filtration to avoid drug accumulation and toxicity.
Increased Susceptibility to Dehydration and Toxicity
Older equines may be less efficient at maintaining hydration, which can compound the risk of sulfonamide-induced renal damage. Hydration status must be assessed regularly.
12.2 Administration in Pregnant and Lactating Mares
Risk Assessment Based on Trimester
While limited data is available, use in early gestation is generally avoided due to potential interference with embryonic folate metabolism. Risk-benefit evaluation should be individualized.
Potential Teratogenicity and Placental Transfer
Both active compounds can cross the placental barrier. Though rare, teratogenic effects are possible, particularly if administered during organogenesis.
Residue Risk in Milk and Suckling Foals
Trace residues may be excreted in mare’s milk, posing a potential risk to nursing foals. Veterinary oversight is essential if treatment during lactation is unavoidable.
12.3 Administration in Foals and Juvenile Horses
Safety Profile in Neonatal and Weanling Foals
Trisiden should be used cautiously in foals under two months of age due to immature liver enzyme systems and developing renal function.
Recommended Starting Age and Dosage Adjustments
Veterinarians typically initiate therapy in foals older than four weeks, adjusting the dose based on body weight and metabolic maturity.
Monitoring Growth and Development During Treatment
Long-term or repeated courses may necessitate evaluation of weight gain, bone density, and general growth parameters to ensure no adverse developmental effects.
Overdose and Toxicity Management in Horses
Symptoms of Trimethoprim/Sulfadiazine Overdose
Clinical signs may include: - Severe anorexia - Ataxia or incoordination - Oral ulceration - Hematuria and dehydration
Emergency Veterinary Procedures
Immediate discontinuation of the drug is essential. Activated charcoal or gastric lavage may be considered if ingestion was recent. Early intervention improves prognosis.
Supportive Care and Fluid Therapy
- IV fluids to promote renal excretion - Electrolyte balancing and monitoring of acid-base status - Antihistamines or corticosteroids in cases of hypersensitivity
Prognosis Following Acute or Chronic Overdose
Mild cases typically resolve with supportive care, while severe toxicity may lead to renal failure or death if untreated. Prognosis depends on the promptness of care.
Storage Instructions and Product Stability
Recommended Storage Temperature Range
Store Trisiden at 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Avoid freezing or exposure to extreme heat.
Protection from Light and Moisture
Keep the paste in its original packaging, away from direct sunlight and humidity, to preserve potency and prevent degradation.
Shelf Life and Expiration Considerations
Do not use beyond the expiration date indicated on the label. Compromised paste may exhibit changes in consistency, color, or odor.
Safe Handling and Disposal of Expired Product
Dispose of unused or expired medication in accordance with local veterinary pharmaceutical waste regulations. Do not flush or incinerate without guidance.
Handling Instructions and Owner Safety Precautions
Safe Administration Techniques for Horse Handlers
- Use an appropriate dosing syringe - Stand to the side of the horse’s head to avoid injury - Gently insert the paste behind the molars
Hygiene Practices After Handling Medicated Paste
Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water. Avoid contact with mucous membranes, especially eyes and mouth.
Protective Gear Recommendations
Gloves are recommended for individuals with sensitive skin or when prolonged exposure is anticipated.
Environmental Precautions for Paste Residues
Clean up any spilled paste immediately. Do not allow residues to contaminate water sources or feed troughs to prevent environmental and animal exposure.
Trisiden, Trimethoprim/ Sulfadiazine Equine Oral paste FAQ
- What is sulfadiazine trimethoprim used for?
- What is trimethoprim used for in veterinary medicine?
- Is trimethoprim sulfa used in animals?
- What is trimethoprim paste for horses?
- Is trimethoprim and sulfadiazine for horses?
- What is the purpose of trimethoprim?
- Can trimethoprim treat a wound infection?
- What kind of bacteria does trimethoprim treat?
- What does sulfadiazine do?
- Is trimethoprim sulfadiazine safe for cats?
- What are the side effects of trimethoprim for horses?
- What bacteria does sulfadiazine treat?
- What organisms are sensitive to the trimethoprim sulfadiazine combination?
- Is trimethoprim a strong antibiotic?
- Is trimethoprim an anti-inflammatory?
- Is trimethoprim used for skin infections?
- Which class of antibiotic is trimethoprim?
- What are the contraindications for trimethoprim?
- Is sulfadiazine an antibiotic or not?
- What is the antibiotic trimethoprim for horses?
- What is sulfadiazine trimethoprim used for?
- What is trimethoprim used for in veterinary medicine?
- Is trimethoprim sulfa used in animals?
- What is trimethoprim paste for horses?
- Is trimethoprim and sulfadiazine for horses?
- What is the purpose of trimethoprim?
- Can trimethoprim treat a wound infection?
- What kind of bacteria does trimethoprim treat?
- Is trimethoprim sulfadiazine safe for cats?
- What are the side effects of trimethoprim for horses?
- What bacteria does sulfadiazine treat?
- What organisms are sensitive to the trimethoprim sulfadiazine combination?
- Is trimethoprim a strong antibiotic?
- Is trimethoprim an anti-inflammatory?
- Is trimethoprim used for skin infections?
- Is sulfadiazine an antibiotic or not?
What is sulfadiazine trimethoprim used for?
A powerful sulfonamide antibiotic is used to treat infections, such as those affecting the bladder and prostate, or caused by Nocardia or parasites.
What is trimethoprim used for in veterinary medicine?
The medication Sulfa/trimetoprim is commonly prescribed to combat infections.
Is trimethoprim sulfa used in animals?
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim (SMX TMP) is a prescription antibiotic for dogs with infections; this combination of two antibiotics fights off the bacteria effectively. It can also be administered to cats on rare occasions.
What is trimethoprim paste for horses?
The use of this medication is recommended for treating infections in horses that are caused by microorganisms and is available in the form of an oral paste, which appears as a creamy white substance, for administering orally.
Is trimethoprim and sulfadiazine for horses?
Yes
What is the purpose of trimethoprim?
Trimethoprim, an antibiotic, is commonly prescribed for the treatment and prevention of urinary tract infections, like cystitis.
Can trimethoprim treat a wound infection?
Yes
What kind of bacteria does trimethoprim treat?
E. coli., K. pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., P. mirabilis, and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species.
What does sulfadiazine do?
Sulfonamide antibiotics are used to treat or prevent infections, with a medicine called sulfonamide antibiotics that prevent the growth of bacteria effectively. But are ineffective against flu viruses.
Is trimethoprim sulfadiazine safe for cats?
Yes
What are the side effects of trimethoprim for horses?
This medication may lead to effects such as diarrhea and allergic reactions. Additionally, it can affect the blood by reducing the count of blood cells (anemia), platelets (thrombocytopenia), and white blood cells (leucopenia).
What bacteria does sulfadiazine treat?
- Management of chancroid and urinary tract infections.
- Addressing Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis
- UTI
What organisms are sensitive to the trimethoprim sulfadiazine combination?
E. coli, Haemophilus spp., Pasteurella spp., Salmonella spp., Staphylococcus spp. and Streptococcus spp.
Is trimethoprim a strong antibiotic?
Yes
Is trimethoprim an anti-inflammatory?
Yes
Is trimethoprim used for skin infections?
Yes
Which class of antibiotic is trimethoprim?
Sulfonamides
What are the contraindications for trimethoprim?
Patients who have experienced a response to the medication.
Is sulfadiazine an antibiotic or not?
Antibiotic
What is the antibiotic trimethoprim for horses?
Various diseases caused by both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria are treated using combinations of trimethoprim/sulfonamide drugs, such as TMPS; these conditions include infections affecting the urogenital tract, alimentary tract, skin, joints, and wounds.
What is sulfadiazine trimethoprim used for?
Potentiated sulfonamide antibiotic is commonly prescribed for treating infections, like those affecting the bladder and prostate well as Nocardia and parasitic infections.
What is trimethoprim used for in veterinary medicine?
Sulfa and trimethoprim are medications commonly prescribed for bacterial infections.
Is trimethoprim sulfa used in animals?
SMX TMP medication is prescribed for dogs to combat infections effectively by combining sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim antibiotics that work in unison against infections susceptible to them. It's also recommended for cats, although less frequently.
What is trimethoprim paste for horses?
The treatment of infections in horses caused by microorganisms is shown through the use of oral paste, which comes in the form of a creamy white substance meant for oral consumption.
Is trimethoprim and sulfadiazine for horses?
Yes
What is the purpose of trimethoprim?
Trimethoprim functions as an antibiotic that is commonly prescribed for the treatment and prevention of urinary tract infections, specifically targeting conditions like cystitis.
Can trimethoprim treat a wound infection?
Yes
What kind of bacteria does trimethoprim treat?
E. coli., K. pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., P. mirabilis, and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species.
Is trimethoprim sulfadiazine safe for cats?
Yes
What are the side effects of trimethoprim for horses?
Side effects of this drug include diarrhea, allergic reactions, and effects on the blood, including decreased number of red blood cells (anemia), decreased number of platelets (thrombocytopenia), and decreased number of white blood cells (leucopenia).
What bacteria does sulfadiazine treat?
The management of chancroid, along with Toxoplasma gondii urinary tract infections, as well as various other infections.
What organisms are sensitive to the trimethoprim sulfadiazine combination?
E. coli, Haemophilus spp., Pasteurella spp., Salmonella spp., Staphylococcus spp. and Streptococcus spp.
Is trimethoprim a strong antibiotic?
Yes
Is trimethoprim an anti-inflammatory?
Yes
Is trimethoprim used for skin infections?
Yes
Is sulfadiazine an antibiotic or not?
Antibiotic