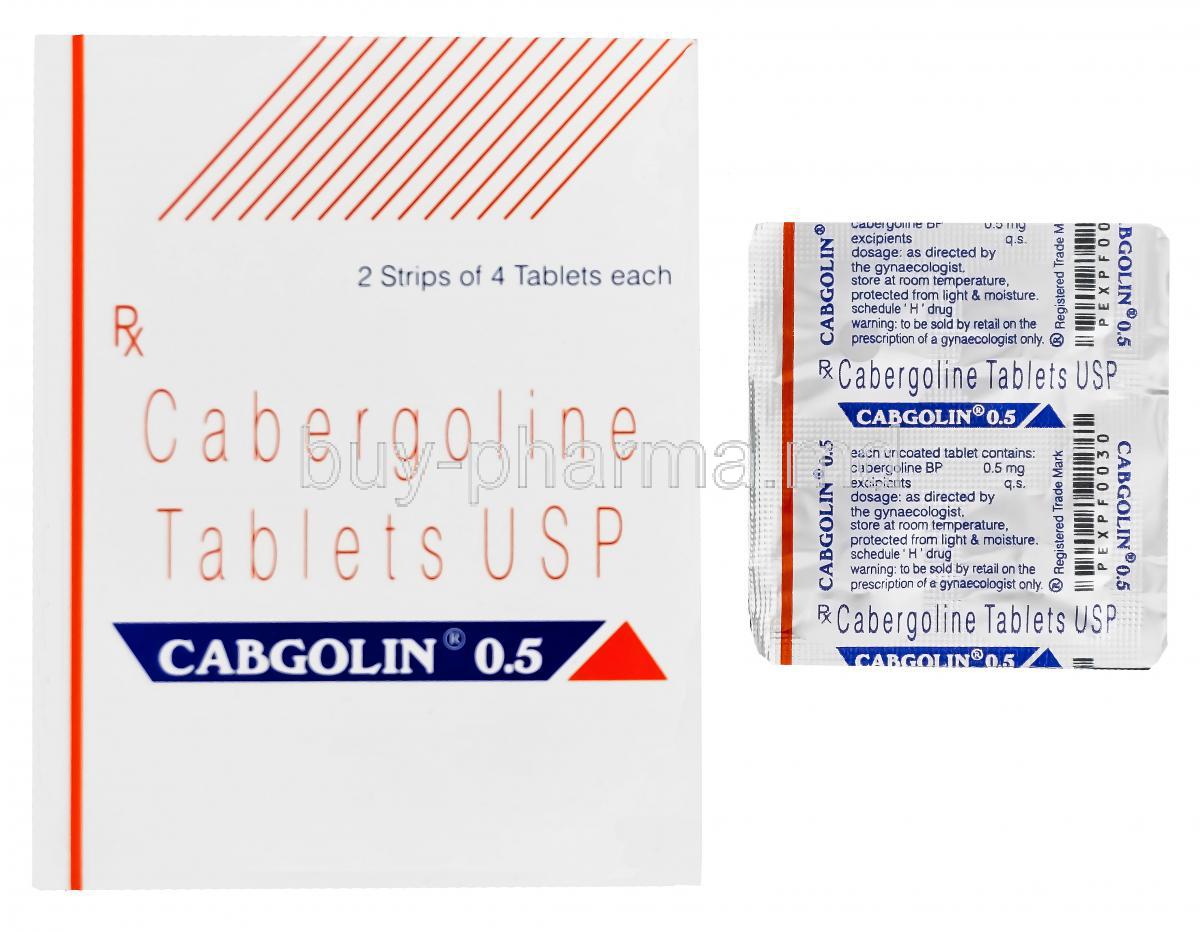
Introduction to Cabgolin (Cabergoline)
Overview of Cabgolin and its Active Ingredient Cabergoline
Cabgolin is a pharmacological agent containing Cabergoline as its active ingredient, primarily prescribed to manage conditions related to elevated prolactin levels in the blood. As a potent dopamine receptor agonist, it exerts a targeted influence on the pituitary gland, restoring hormonal equilibrium and alleviating symptoms caused by hyperprolactinemia. Cabgolin is recognized for its long-lasting effects, allowing for reduced dosing frequency compared to older prolactin-lowering drugs.
History of Development and Approval
Cabergoline was developed in the late 20th century as a refined ergot derivative with enhanced specificity for dopamine D2 receptors. It received regulatory approval in various regions for the treatment of prolactin-related disorders, and its favorable safety profile, combined with extended half-life, has made it a preferred therapy worldwide.
Therapeutic Classification: Dopamine Agonist Medication
Belonging to the class of ergoline-derived dopamine agonists, Cabgolin modulates dopaminergic signaling, primarily within the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. This targeted activity allows it to selectively inhibit prolactin synthesis without significantly affecting other pituitary hormones.
Global Brand Names and Generic Availability
Cabgolin is marketed under numerous brand names internationally, including Dostinex, Cabaser, and Prolacton, in addition to its generic form. The widespread availability of generics ensures affordability and accessibility for patients requiring long-term therapy.
Pharmacological Composition of Cabgolin
Active Ingredient: Cabergoline
Each tablet contains Cabergoline as the principal bioactive compound. This molecule is a synthetic ergot alkaloid with high affinity for dopamine D2 receptors.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Cabergoline possesses a complex ergoline ring structure, contributing to its stability and receptor selectivity. Its lipophilic nature aids in efficient absorption and prolonged systemic activity.
Inactive Ingredients and Formulation Details
Common excipients include lactose, leucine, and magnesium stearate. These agents support tablet integrity, enhance stability, and ensure consistent drug delivery.
Available Dosage Strengths and Pharmaceutical Forms
Cabgolin is typically available in 0.25 mg and 0.5 mg oral tablet strengths, allowing for flexible dosing tailored to individual patient needs.
Mechanism of Action: How Cabgolin Works in the Body
Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonist Activity
Cabergoline binds selectively to D2 receptors in the pituitary lactotroph cells, mimicking dopamine's inhibitory effects.
Suppression of Prolactin Secretion from the Pituitary Gland
By activating these receptors, Cabgolin directly reduces prolactin synthesis, normalizing serum levels over time.
Effects on Lactotroph Cells and Hormonal Regulation
Reduced prolactin output alleviates symptoms such as galactorrhea, menstrual irregularities, and infertility, restoring endocrine balance.
Impact on Other Endocrine Pathways
While highly selective, Cabergoline may exert minor influences on growth hormone secretion and hypothalamic neurotransmission.
Approved Medical Uses of Cabgolin
Treatment of Hyperprolactinemia and Related Disorders
Cabgolin is indicated for both idiopathic hyperprolactinemia and cases secondary to pituitary adenomas.
Management of Prolactin-Secreting Pituitary Adenomas (Prolactinomas)
The drug reduces tumor size in many patients, alleviating pressure effects and restoring pituitary function.
Restoration of Menstrual Cycle Regularity in Women with High Prolactin
By lowering prolactin, Cabgolin supports ovulation and menstrual cycle normalization.
Treatment of Infertility Caused by Elevated Prolactin Levels
In reproductive-age patients, prolactin normalization enhances fertility potential.
Suppression of Postpartum Lactation When Medically Indicated
In situations where breastfeeding is contraindicated, Cabgolin effectively halts milk production.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses of Cabgolin
Adjunct Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease Management
Its dopaminergic activity can help improve motor function when combined with other Parkinson’s therapies.
Use in Cushing’s Disease and Pituitary-Dependent Hypercortisolism
Cabergoline may assist in reducing ACTH secretion in certain pituitary disorders.
Potential Role in Acromegaly Management
In some patients, it reduces growth hormone and IGF-1 levels, complementing other treatments.
Investigational Applications in Psychiatric and Metabolic Disorders
Research is ongoing into Cabergoline's effects on mood disorders, compulsive behaviors, and metabolic regulation.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Initial Dosing Recommendations for Hyperprolactinemia
Typically initiated at 0.25 mg twice weekly, adjusted based on serum prolactin and tolerability.
Dose Titration and Maintenance Dosing
Doses may be increased gradually to a maximum of 1 mg twice weekly, as clinically indicated.
Weekly vs. Divided Dose Schedules
Once- or twice-weekly dosing minimizes side effects while maintaining efficacy.
Special Instructions for Patients with Hepatic or Renal Impairment
Lower initial doses and careful monitoring are recommended in patients with reduced organ function.
Administration Tips to Reduce Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Taking Cabgolin with food can reduce nausea and improve tolerability.
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Cabgolin
Classification of Side Effects: Common, Uncommon, and Rare
Adverse effects range from mild gastrointestinal upset to rare but serious fibrotic complications.
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort may occur, especially during dose initiation.
Neurological Effects
Dizziness, headache, and fatigue are reported, often resolving with continued use.
Cardiovascular Effects
Orthostatic hypotension and, rarely, arrhythmias may develop.
Psychiatric Effects
Some individuals experience mood changes, irritability, or compulsive behaviors.
Common Side Effects of Cabgolin
- Mild nausea and digestive discomfort
- Lightheadedness and orthostatic hypotension
- Headache and drowsiness
- Nasal congestion
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
Drug Interactions and Compatibility Considerations
Interactions with Dopamine Antagonists (Antipsychotics)
These agents may counteract Cabgolin’s therapeutic effects, necessitating careful co-management.
Risk of Additive Hypotensive Effects with Antihypertensive Drugs
Concurrent use may lower blood pressure excessively, requiring monitoring.
Impact of Macrolide Antibiotics on Cabergoline Metabolism
Macrolides can elevate Cabergoline plasma levels, increasing the risk of side effects.
Alcohol Consumption and Central Nervous System Effects
Alcohol may amplify dizziness and sedation, thus moderation is advised.
Monitoring When Combined with Ergot Derivatives
Concurrent ergot use may heighten the risk of fibrotic reactions and vascular effects.
Warnings and Safety Alerts for Cabgolin Use
Risk of Heart Valve Disorders and Need for Echocardiographic Monitoring
Cabgolin, like other ergot-derived dopamine agonists, has been associated with valvular heart disease. Long-term use can lead to valvular thickening or regurgitation, necessitating vigilant monitoring. An echocardiogram before initiating therapy is strongly recommended, with periodic follow-up scans to detect early changes.
Potential for Pulmonary, Retroperitoneal, and Pericardial Fibrosis
Fibrotic reactions, although rare, can affect the lungs, retroperitoneum, or pericardium. Symptoms such as persistent cough, unexplained abdominal pain, or swelling in the extremities should prompt immediate investigation. Early detection through imaging and clinical evaluation is crucial for preventing irreversible damage.
Hypotension and Risk of Fainting, Especially at Treatment Initiation
Cabgolin can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, particularly within hours of the first dose or after dosage increases. This orthostatic hypotension may lead to dizziness, fainting, or falls. Patients should be advised to rise slowly from sitting or lying positions.
Psychiatric Side Effects: Hallucinations, Impulse Control Disorders
In rare instances, dopaminergic therapy can precipitate hallucinations, delusional thinking, or compulsive behaviors such as gambling, hypersexuality, or excessive spending. Monitoring mental health status is an essential aspect of safe treatment.
Caution in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
Those with pre-existing heart conditions, arrhythmias, or history of myocardial infarction require careful risk assessment. Cardiovascular status should be stabilized before initiating Cabgolin therapy.
Contraindications to Cabgolin Therapy
Hypersensitivity to Cabergoline or Other Ergot Derivatives
Patients with a history of allergic reactions to ergot alkaloids should avoid Cabgolin due to the risk of severe hypersensitivity.
History of Fibrotic Disorders (Pulmonary, Retroperitoneal, Cardiac)
Pre-existing fibrosis can be aggravated by Cabgolin, making its use unsafe in such cases.
Uncontrolled Hypertension
Elevated blood pressure increases the risk of cardiovascular complications, and therapy should be postponed until hypertension is controlled.
Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension (Pre-eclampsia, Eclampsia)
Cabgolin should not be used in women experiencing pregnancy-related hypertensive disorders, as it may worsen maternal and fetal outcomes.
Severe Hepatic Impairment
Impaired liver function can alter drug metabolism, increasing the risk of toxicity. Such patients require alternative therapies.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Baseline Cardiovascular Evaluation Before Starting Therapy
Cardiac examination, including echocardiography, should be conducted to rule out pre-existing structural heart disease.
Regular Monitoring of Blood Pressure During Treatment
Frequent blood pressure checks are necessary, especially during the early treatment phase and dose escalations.
Periodic Prolactin Level Checks to Guide Therapy Adjustments
Serum prolactin levels should be monitored to assess therapeutic response and determine the need for dose modifications.
Echocardiogram Recommendations for Long-Term Users
Annual or semi-annual echocardiographic evaluations are advised for patients on prolonged Cabgolin therapy.
Gradual Discontinuation to Avoid Withdrawal Effects
Stopping Cabgolin abruptly can cause symptom rebound. Tapering under medical supervision is preferred.
Special Population Considerations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly patients may have diminished organ function and higher comorbidity rates. Dosing should be conservative, and blood pressure should be closely monitored to reduce fall risk.
Administration to Pregnant Women
Cabgolin should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit outweighs possible fetal risks. Decisions should be based on clinical necessity and available safety data.
Administration to Nursing Mothers
Cabgolin suppresses lactation and is not recommended for breastfeeding women. The safety of the drug in infants exposed through breast milk has not been established.
Administration to Children and Adolescents
There is limited data on Cabgolin use in pediatric populations. Dose adjustments should consider age, weight, and developmental status.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Overdose may manifest as severe hypotension, hallucinations, confusion, or gastrointestinal distress. Prompt medical evaluation is required.
Immediate Medical Intervention Protocols
Emergency care includes airway stabilization, cardiovascular monitoring, and correction of blood pressure abnormalities.
Supportive Care and Symptomatic Treatment
Intravenous fluids, vasopressors, and other supportive measures should be administered as needed.
Role of Gastric Lavage and Activated Charcoal in Recent Ingestion
In cases of recent ingestion, gastric lavage or activated charcoal administration may help reduce drug absorption.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Temperature and Conditions
Cabgolin should be stored at room temperature, away from excessive heat and humidity.
Protection from Moisture and Direct Light
Tablets should remain in their original blister packaging until use to protect from moisture and light degradation.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
Expired medication should not be used, as potency and safety cannot be guaranteed.
Safe Handling Practices to Maintain Drug Stability
Hands should be clean and dry when handling tablets to avoid contamination and degradation.
Disposal Guidelines for Unused or Expired Medication
Unused or expired Cabgolin should be disposed of according to local pharmaceutical waste guidelines, avoiding flushing or improper disposal methods.
Cabgolin, Cabergoline FAQ
- What is cabergoline used to treat?
- When is the best time to take Cabgolin?
- How long does it take for cabergoline to regulate your period?
- How much weight will I lose on cabergoline?
- How long does it take for cabergoline to shrink a tumor?
- How fast can cabergoline work?
- What are the side effects of cabergoline?
- What to avoid when taking cabergoline?
- Does cabergoline thin your hair?
- What happens if you suddenly stop taking cabergoline?
- What organ does prolactin affect?
- Can cabergoline cause hypersexuality?
- What is the warning for cabergoline?
- What are the benefits of taking cabergoline?
- What are the mental effects of cabergoline?
- Does cabergoline make it hard to sleep?
- Who cannot take cabergoline?
- How long can you stay on cabergoline?
- Is cabergoline hard on the kidneys?
- How fast does cabergoline start working?
- How do you feel after taking cabergoline?
- What to avoid while on cabergoline?
- Can cabergoline make you angry?
- Is cabergoline bad for the heart?
- How quickly does cabergoline reduce prolactin?
- What are the risks of cabergoline?
- Does cabergoline weaken your immune system?
What is cabergoline used to treat?
Cabergoline is a medication that's really good at tackling issues that happen when your body produces too much of a hormone called prolactin. For women, it can help with menstrual problems and fertility issues. On top of that, it's used to treat tumors in the gland, which is a small gland in your brain that produces prolactin. These tumors are called prolactinomas.
When is the best time to take Cabgolin?
At night time
How long does it take for cabergoline to regulate your period?
2 months
How much weight will I lose on cabergoline?
1.2% body weight
How long does it take for cabergoline to shrink a tumor?
6 months
How fast can cabergoline work?
within 3 hours after ingestion
What are the side effects of cabergoline?
nausea, constipation, and headaches
What to avoid when taking cabergoline?
Alcohol
Does cabergoline thin your hair?
Yes
What happens if you suddenly stop taking cabergoline?
Prolactin levels can remain high
What organ does prolactin affect?
mammary alveoli
Can cabergoline cause hypersexuality?
Rarely
What is the warning for cabergoline?
Cabergoline can cause some people to have strong, unusual, and uncontrolled urges (compulsions), including gambling, sex, shopping, or eating
What are the benefits of taking cabergoline?
Cabergoline is used to treat hyperprolactinemia (high levels of prolactin, a natural substance that helps breast-feeding women produce milk but can cause symptoms such as infertility, sexual problems, and bone loss in women who are not breast-feeding or men).
What are the mental effects of cabergoline?
- Mood changes
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Psychosis
Does cabergoline make it hard to sleep?
Yes
Who cannot take cabergoline?
People with heart issues
How long can you stay on cabergoline?
6 months
Is cabergoline hard on the kidneys?
Yes
How fast does cabergoline start working?
Within 3 hours after ingestion
How do you feel after taking cabergoline?
It can leave you feeling dizzy, queasy or even give you a headache.
What to avoid while on cabergoline?
Alcohol
Can cabergoline make you angry?
Yes
Is cabergoline bad for the heart?
It's worth noting that cabergoline has been linked to a risk of heart problems.
How quickly does cabergoline reduce prolactin?
2-5 days
What are the risks of cabergoline?
- Heart valve problems
- Fibrosis
Does cabergoline weaken your immune system?
A bit