Calcipotriol/ Betamethasone Dipropionate Ointment
- 1. Introduction to Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Dipropionate Ointment
- 2. Comprehensive Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulation
- 3. Dual Mechanism of Action: How the Combination Works
- 4. Indications, Therapeutic Uses, and Off-Label Applications
- 5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Optimal Results
- 6. Careful Administration in Special Populations
- 7. Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Side Effects
- 8. Warnings and Important Precautions for Safe Use
- 9. Contraindications: When the Ointment Should Not Be Used
- 10. Drug and Product Interactions
- 11. Overdosage and Emergency Management
- 12. Storage and Handling Precautions to Maintain Potency
1. Introduction to Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Dipropionate Ointment
Definition and Therapeutic Class
Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Dipropionate ointment is a fixed-dose combination topical medication classified under antipsoriatic agents. It merges a vitamin D analog with a potent corticosteroid, creating a synergistic dual-action therapy used primarily in dermatology for plaque psoriasis management.
Historical Development and FDA/EMA Approval Timeline
This combination was first introduced in Europe in the early 2000s and subsequently approved by the U.S. FDA in 2006. It marked a pivotal shift in psoriasis treatment by simplifying regimens and enhancing adherence.
2. Comprehensive Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulation
Active Ingredients: Calcipotriol 50 µg/g + Betamethasone Dipropionate 0.5 mg/g
The ointment delivers precise microgram and milligram concentrations of both agents to ensure effective local activity with minimal systemic exposure.
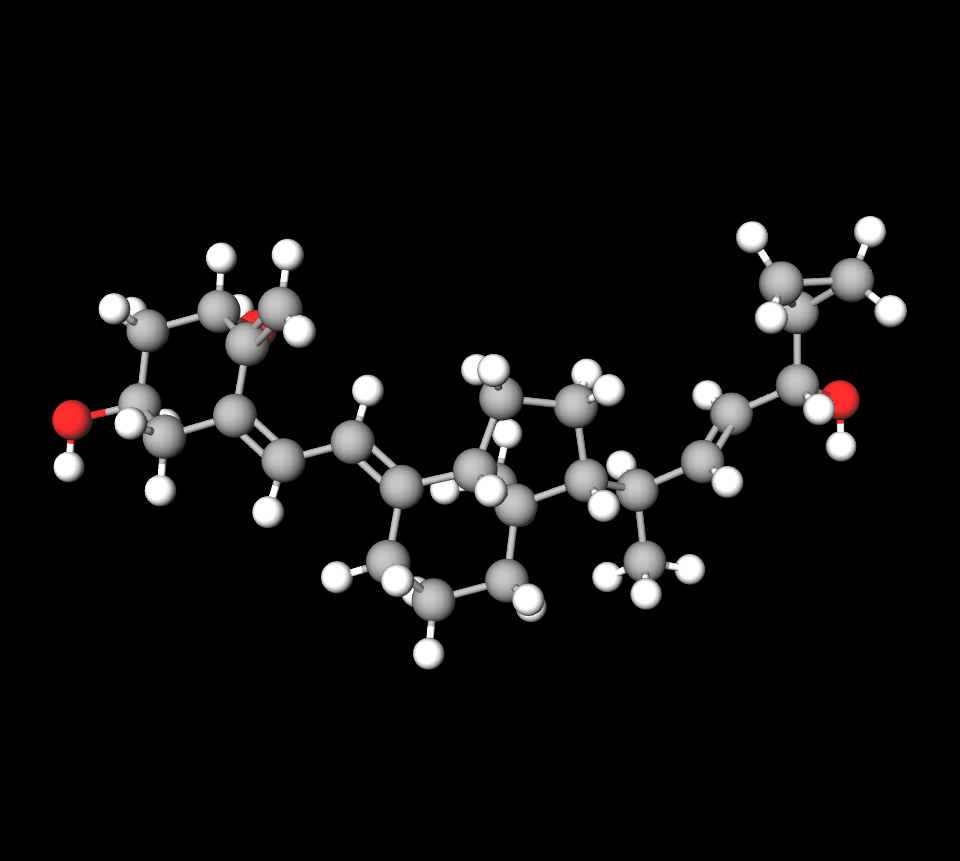
Inactive Excipients and Vehicle Base for Enhanced Skin Penetration
Formulated in an anhydrous, paraffin-based vehicle, the ointment utilizes mineral oils and synthetic esters to enhance dermal absorption and prolong contact time without maceration.
Available Packaging Sizes, Tube Materials, and Child-Resistant Features
Typically dispensed in aluminum or laminate tubes ranging from 15g to 120g, many include tamper-evident seals and safety caps to comply with child-resistant standards.
Fluorouracil and calcipotriol
Fluorouracil and calcipotriol are commonly combined to treat actinic keratosis (AK), a skin condition resulting from sun damage. 5FU-Cal therapy proves effective and faster in treatment duration than using just fluorouracil alone.
Clotrimazole and betamethasone dipropionate
Clotrimazole and betamethasone dipropionate is a treatment that combines an antifungal agent (clotrimazole) with a cortiсosteroid (betamethasone dipropionate). This medication is commonly used to address skin infections caused by fungi such as athletes foot (tinea pedis), jock itch (tinea cruris), and ringworm (tinea corporis). While clotrimazole works against the infection itself, betamethasone helps alleviate inflammation and associated symptoms, such as redness and itching.
Calcipotriol vs calcipotriene
Calcipotriol and calcipotriene are the same drugs. Calcipotriene is the name used in the United States (USAN). They are both derivatives of vitamin D₃ commonly employed in the treatment of psoriasis.
Calcitriol vs calcipotriol
Both calcitriol and calcipotriol are vitamin D analogues commonly used in the treatment of psoriasis; however, they differ in their applications and potential adverse effects. Calcipotriol is mainly administered topically to address plaque psoriasis whereas calcitriol can be administered topically for plaque psoriasis and is also utilized for maintaining calcium balance within the body
Betamethasone dipropionate vs triamcinolone acetonide
Betamethasone dipropionate and triamcinolone acetonide are two types of cortisones commonly prescribed for skin issues, such as eczema and psoriasis. Although they both work well in treating these conditions, betamethasone dipropionate is typically regarded as a steroid compared to triamcinolone acetonide. This implies that it is more efficient in alleviating inflammation, itchiness, and redness; however it also comes with a likelihood of reactions.
Betamethasone dipropionate vs valerate
Betamethasone dipropionate is commonly viewed as stronger than betamethasone valerate because it can penetrate the skin effectively due to its fat solubility level. This characteristic makes it an effective cortisone treatment for a variety of skin issues. On the other hand, betamethasone valerate is considered a cortisone option, suited for less severe conditions or for individuals who may have greater sensitivity to more potent steroids.
Betamethasone dipropionate vs clobetasol
Betamethasone dipropionate and clobetasol are corticosteroid treatments used to address various skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis; however, clobetasol is typically regarded as more potent than betamethasone dipropionate in terms of effectiveness for managing these conditions. Both of these medications function by alleviating symptoms by reducing redness and itching while also diminishing swelling in the areas.
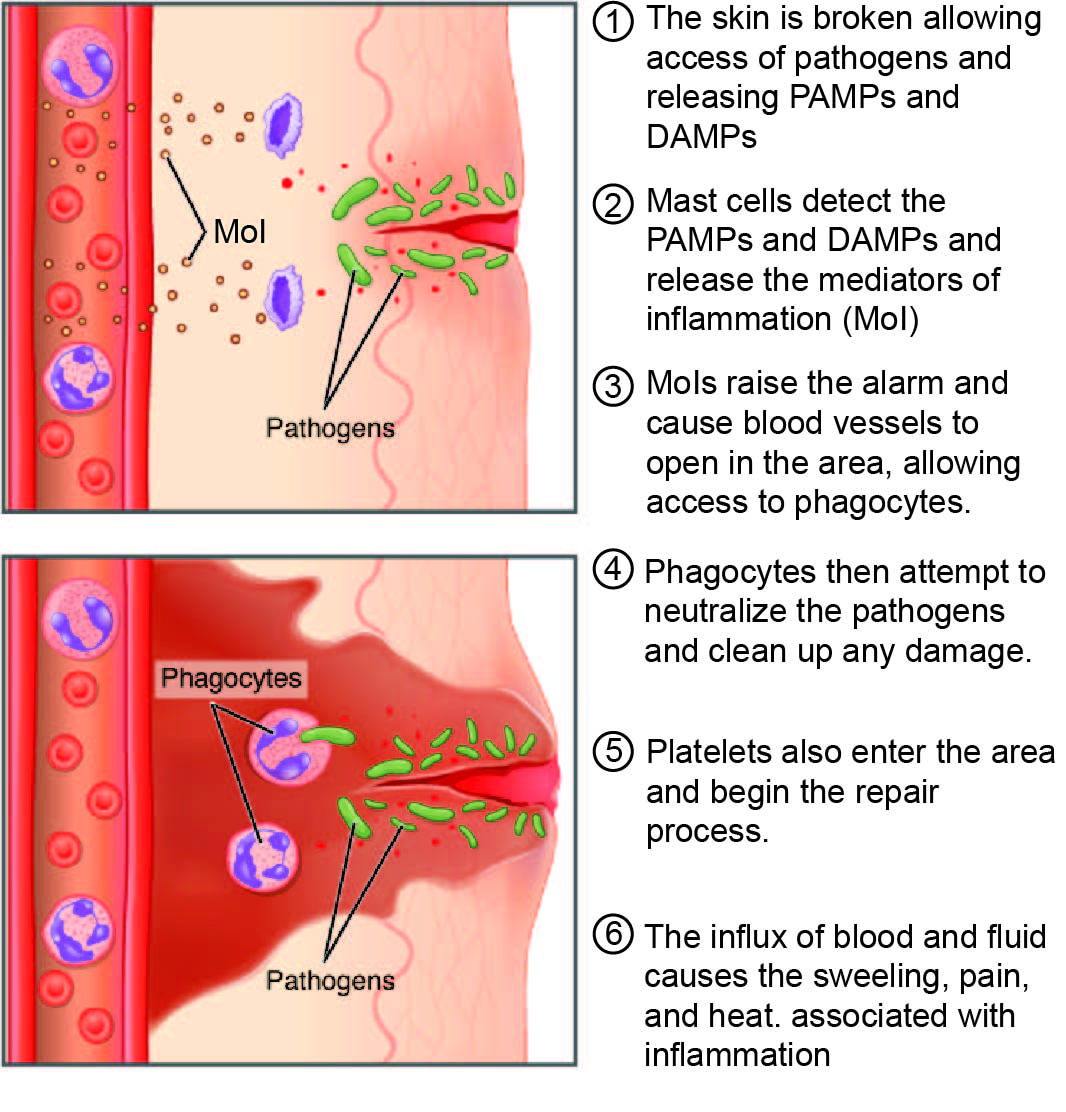
3. Dual Mechanism of Action: How the Combination Works
Calcipotriol: Vitamin D Analog Regulating Keratinocyte Differentiation
Calcipotriol modulates the proliferation and maturation of keratinocytes, directly addressing the hyperproliferative hallmark of psoriatic lesions.
Betamethasone Dipropionate: Potent Corticosteroid Suppressing Inflammatory Cascades
Synergistic Benefit: Reduced Lesion Thickness and Accelerated Plaque Clearance
By combining keratinocyte-normalizing and anti-inflammatory effects, the ointment provides faster resolution of plaques with reduced recurrence risk.
Pharmacokinetics and Systemic Absorption Profile
Minimal systemic absorption under proper usage conditions. Peak plasma levels of both agents remain well below thresholds associated with systemic adverse effects.
4. Indications, Therapeutic Uses, and Off-Label Applications
Primary Indication: Chronic Plaque Psoriasis (Body & Scalp)
Adjunctive Therapy in Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis After Phototherapy or Biologics
Off-Label Use: Nail Psoriasis and Onycholysis Management
Off-Label Use: Inverse/Intertriginous Psoriasis in Sensitive Skin Folds
Used with caution in areas prone to occlusion; dose reduction and frequency adjustment recommended.
Emerging Investigational Uses: Palmoplantar Pustulosis, Seborrheic Dermatitis
Preliminary studies suggest benefit in resistant cases of palmoplantar pustulosis and select seborrheic dermatoses.
5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Optimal Results
Standard Adult Application Frequency and Duration
- Apply once daily, preferably at the same time each day.
- Recommended treatment duration: up to 4 weeks on the body, 8 weeks on the scalp.
Scalp-Specific Protocols and Leave-On Time Recommendations
Gently massage into affected areas; no rinsing necessary unless instructed. Apply to dry hair and scalp.

Maximum Weekly Dose Limits and Body Surface Area Restrictions
- Do not exceed 100g per week.
- Avoid application on more than 30% of body surface area.
Step-Down Maintenance Strategies to Sustain Remission
Transition to every-other-day application or alternate with non-steroidal emollients after lesion clearance.
Missed Dose Procedure and Restart Recommendations
If missed, apply as soon as remembered. Do not double dose. Resume regular schedule promptly.
6. Careful Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients:Dermal Thinning Considerations and Titration Tips
Use with caution due to age-related skin fragility. Monitor for steroid-induced atrophy and adjust frequency as needed.

Generally not recommended for patients under 12 years of age. Use only under strict supervision in adolescents.
Pregnant Women: Risk Category, Placental Transfer, and Lactation Advice
Classified as Category C. Use only if potential benefit outweighs fetal risk. Avoid breast application during lactation.

Nursing Mothers: Minimizing Infant Exposure During Breastfeeding
Ensure application sites are not in contact with the infant's skin. Avoid using near the breast or clean the area thoroughly before feeding.

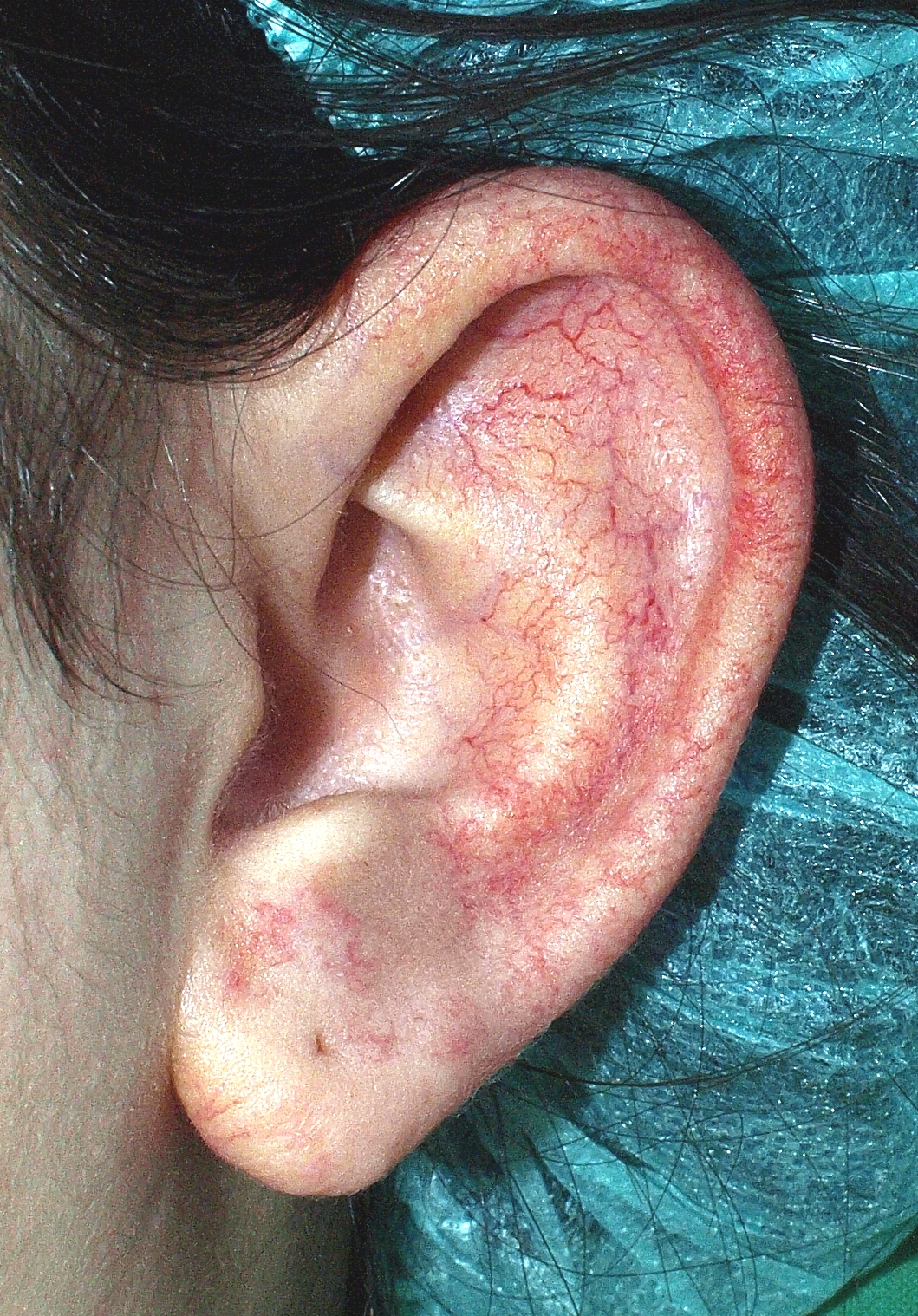
7. Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Side Effects
Common Side Effects: Pruritus, Burning, Mild Folliculitis
Most reactions are localized, transient, and resolve upon discontinuation or dose reduction.
Less Common Reactions: Skin Atrophy, Telangiectasia, Striae
Rare but Serious Events: Hypercalcemia, Systemic Steroid Effects
Excessive application may lead to calcium metabolism disturbances and systemic adrenal suppression.
Long-Term Safety Data and Post-Marketing Surveillance Findings
Post-market surveillance indicates a favorable long-term safety profile when used within prescribed limits.
8. Warnings and Important Precautions for Safe Use
Phototoxicity Risk and UV Exposure Management
Limit intentional sun exposure. Use sunscreen or protective clothing when outdoors.

Avoidance of Occlusive Dressings Unless Directed by Physician
Occlusion may enhance systemic absorption and increase the risk of adverse effects. Only use under medical advice.
Rebound Psoriasis and Tapering Strategies
Abrupt discontinuation may trigger flares. Gradual tapering is recommended after improvement.
Guidance on Concomitant Topical Therapies and Cosmetics
Allow at least 30 minutes between application of other topical agents. Avoid concurrent irritants or astringents.
9. Contraindications: When the Ointment Should Not Be Used
Hypersensitivity to Calcipotriol, Betamethasone, or Any Excipient
Patients with known hypersensitivity to calcipotriol, betamethasone dipropionate, or any component of the ointment base must not use this product. Hypersensitivity reactions may manifest as localized urticaria, angioedema, or contact dermatitis. In rare cases, systemic allergic responses can occur, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Viral, Fungal, or Tubercular Skin Infections at Treatment Site
The ointment should not be applied to skin affected by viral conditions (e.g., herpes simplex, varicella), fungal infections (e.g., candidiasis, tinea), or cutaneous tuberculosis. Use in these contexts may exacerbate infection, suppress local immunity, and delay wound healing.
Disorders of Calcium Metabolism or Hypercalcemia
Because calcipotriol is a vitamin D analog, it can influence systemic calcium levels. Patients with pre-existing hypercalcemia, hyperparathyroidism, or chronic kidney disease with calcium-phosphate imbalance should avoid this treatment due to the risk of exacerbating calcium dysregulation.
Ulcerated, Atrophic, or Thinned Skin Areas
Application to ulcerated skin, areas of severe dermal atrophy, or thin-skinned zones (e.g., face, groin, axillae) should be avoided. These areas are more susceptible to corticosteroid-related side effects such as striae, telangiectasia, and dermal fragility.
10. Drug and Product Interactions
Combined Use with Other Topical Corticosteroids or Vitamin D Analogs
Concurrent use of additional topical corticosteroids or vitamin D derivatives should be avoided unless specifically directed. This can increase the risk of cumulative adverse effects such as skin thinning, tachyphylaxis, or systemic absorption leading to adrenal suppression or hypercalcemia.
Systemic Calcium-Elevating Agents (Thiazides, High-Dose Vitamin D)
Use caution in patients taking thiazide diuretics, high-dose vitamin D, or calcium supplements. These agents may compound the calcium-elevating effect of calcipotriol, potentially leading to clinically significant hypercalcemia or vascular calcification in susceptible individuals.
Sequential vs. Concurrent Phototherapy: Best-Practice Protocols
When using phototherapy (e.g., UVB or PUVA) in conjunction with this ointment, phototoxicity and efficacy must be considered. Sequential application, where the ointment is applied after UV exposure, is generally safer. Applying before phototherapy can reduce treatment efficacy and heighten skin sensitivity.
Biologic Immunomodulators and Systemic Retinoids: Overlap Safety Considerations
While no direct contraindication exists, caution is advised when using this ointment alongside systemic agents such as TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 blockers, or systemic retinoids. Immunomodulatory overlap may alter disease dynamics, and patient monitoring should include periodic assessment for systemic side effects or reduced topical responsiveness.
Betamethasone dipropionate alternative
11. Overdosage and Emergency Management
Signs of Topical Steroid Overuse and Systemic Absorption
Excessive use, especially over large surface areas or under occlusion, may result in systemic corticosteroid effects such as adrenal suppression, Cushingoid features, hypertension, and hyperglycemia. Cutaneous signs include severe skin thinning, bruising, and striae distensae.
Hypercalcemia Recognition: Symptom Checklist and Lab Monitoring
- Nausea and vomiting
- Polyuria and polydipsia
- Muscle weakness and confusion
- Serum calcium levels above 10.5 mg/dL
These indicators necessitate immediate biochemical evaluation and medical intervention.
Immediate Interventions: Discontinuation, Supportive Care, Endocrinology Referral
Upon suspicion of overdose, discontinue the ointment immediately. Initiate supportive measures such as hydration, electrolyte correction, and consultation with an endocrinologist for adrenal or calcium metabolism assessment. Hospitalization may be required in severe cases.
Reporting Requirements to Poison Control and Regulatory Bodies
Healthcare professionals are encouraged to report overdose events to national poison control centers and relevant pharmacovigilance authorities. This supports post-marketing safety surveillance and risk management strategies.
12. Storage and Handling Precautions to Maintain Potency
Recommended Storage Temperature and Humidity Parameters
Store at a controlled room temperature, typically between 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Avoid exposure to excessive humidity, as it may compromise the stability of active ingredients and vehicle components.
Stability Concerns: Light, Heat, and Air Exposure Effects
Keep the tube tightly closed when not in use. Exposure to light and air can degrade calcipotriol, while heat accelerates the breakdown of betamethasone. Do not store near windows, heaters, or in vehicles during warm weather.
Safe Disposal of Partially Used Tubes to Prevent Accidental Ingestion
Unused or expired product should be disposed of following local pharmaceutical waste protocols. Avoid discarding in household trash or sinks. Accidental ingestion, particularly in children, can lead to toxicity.
Travel and Transportation Tips for Climate-Sensitive Medication
When traveling, store the ointment in a cool, insulated container. Avoid packing it in checked luggage where temperature fluctuations are common. Use desiccant packets if stored in humid climates for extended periods.
Calcipotriol/ Betamethasone Dipropionate Ointment FAQ
- What is calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate ointment used for?
- How long should you use calcipotriol betamethasone?
- Where should you not apply betamethasone?
- How long does it take for calcipotriol ointment to work?
- How do you apply calcipotriol ointment?
- How do you know if betamethasone is working?
- What medical conditions are treated by betamethasone dipropionate?
- Is calcipotriol ointment safe?
- How many times a day can you use betamethasone ointment?
- Is it safe to use betamethasone everyday?
- What is the danger of betamethasone?
- Can I put calcipotriol on my face?
- Is calcipotriene cream itchy?
- How long does betamethasone dipropionate stay in your system?
- What are the side effects of calcipotriol betamethasone?
- What are the side effects of calcipotriol ointment?
What is calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate ointment used for?
Betamethasone and calcipotriene are often combined to treat plaque psoriasis on the skin and scalp by alleviating symptoms such as redness, pain, itching, swelling, and other skin-related discomforts.
How long should you use calcipotriol betamethasone?
4 weeks
Where should you not apply betamethasone?
Steer clear of applying the product in areas like the rectal regions, as well as in skin folds and underarm areas, unless specifically advised by your healthcare provider.
How long does it take for calcipotriol ointment to work?
12 weeks
How do you apply calcipotriol ointment?
Apply the ointment to the areas of your skin affected by psoriasis by either squeezing it onto the skin or applying it to your finger first before spreading it. Ensure not to exceed the recommended amount. Then gently rub it in to cover the psoriasis.
How do you know if betamethasone is working?
Your skin is likely to show improvement within a few days of using betamethasone.
What medical conditions are treated by betamethasone dipropionate?
Eczema, contact dermatitis, and psoriasis
Is calcipotriol ointment safe?
Yes
How many times a day can you use betamethasone ointment?
1 to 2 times per day
Is it safe to use betamethasone everyday?
Make sure to limit the use of betamethasone skin treatments to a few weeks or a day or two each week.
What is the danger of betamethasone?
Extended use of betamethasone, without interruption, may result in the medication entering your bloodstream inadvertently. This can lead to adverse effects like adrenal gland issues or complications, with blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) and vision impairment being a remote possibility.
Can I put calcipotriol on my face?
No
Is calcipotriene cream itchy?
Yes
How long does betamethasone dipropionate stay in your system?
36-54 hours
What are the side effects of calcipotriol betamethasone?
- blistering
- burning
- crusting
- dryness
- flaking
- itching
- scaling
- severe redness
- soreness
- swelling of the skin
What are the side effects of calcipotriol ointment?
- Dry mouth or metallic taste
- Weakness or pain
- Headache
- Stomach pain