Cleocin T Topical Solution
- 1. Introduction to Cleocin T Topical Solution
- 2. Mechanism of Action: How Cleocin T Works
- 3. Approved and Off-Label Uses of Cleocin T Topical Solution
- 4. Composition and Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- 5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- 6. Side Effects of Cleocin T Topical Solution
- 7. Drug Interactions and Compatibility
- 8. Warnings and Important Precautions
- 9. Contraindications for Use
- 10. Careful Administration in Special Populations
- 11. Overdose and Emergency Management
- 12. Storage and Shelf-Life Information
- 13. Handling Precautions and Patient Counseling
1. Introduction to Cleocin T Topical Solution
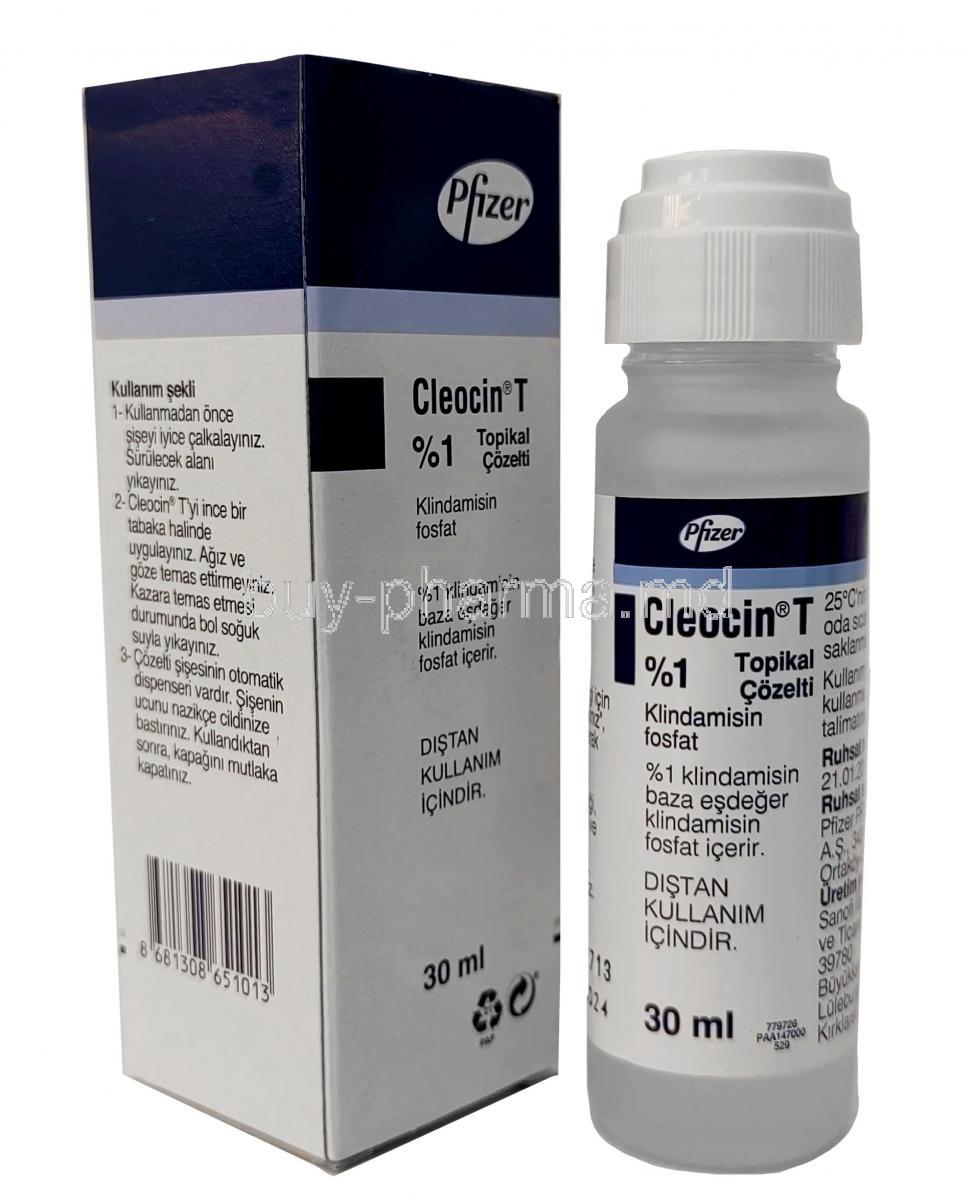
Cleocin T Topical Solution, clinically known as clindamycin phosphate topical solution, is a prescription-strength medication used primarily in the dermatological management of acne. It belongs to the lincosamide class of antibiotics and is designed for topical use, directly targeting bacterial proliferation within the skin's pilosebaceous units.
This solution is formulated for external application and is classified as a topical antibiotic, offering a localized antibacterial action without significant systemic absorption under normal use.

Cleocin generic name
Cleocin T is most commonly available in a concentration of 1% clindamycin phosphate and is dispensed in solution form with applicators for ease of use across facial and truncal areas. Its indications span the management of inflammatory acne lesions, pustules, and papules, helping reduce the count and severity of active breakouts.
- Concentration: 1% clindamycin phosphate
- Form: Topical solution in 30 mL and 60 mL bottles
- Primary use: Acne vulgaris treatment
2. Mechanism of Action: How Cleocin T Works
Cleocin T operates by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis at the 50S ribosomal subunit, effectively halting the propagation of Propionibacterium acnes (now reclassified as Cutibacterium acnes), a gram-positive anaerobe implicated in acne pathogenesis.
Rather than outright bactericidal action, clindamycin demonstrates a bacteriostatic effect, suppressing bacterial growth and diminishing the inflammatory cascade associated with acne lesions. This dual mechanism, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory, contributes to its therapeutic benefit.
Noticeable improvement in lesion count and inflammation typically begins within 2 to 6 weeks of consistent application, with optimal outcomes visible after 8-12 weeks.
3. Approved and Off-Label Uses of Cleocin T Topical Solution
3.1 Primary Indication: Treatment of Acne Vulgaris
Cleocin for acne
For enhanced efficacy, it is frequently used in combination therapy with:
- Benzoyl peroxide
- Topical retinoids (e.g., adapalene, tretinoin)
These combinations provide a synergistic approach, attacking acne from multiple angles microbial, keratolytic, and anti-inflammatory.
3.2 Off-Label Dermatological Uses
Beyond its approved indication, Cleocin T has demonstrated clinical utility in several off-label applications, including:
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa: as part of a combined regimen with topical benzoyl peroxide or oral antibiotics
- Rosacea: particularly in papulopustular subtypes where inflammation dominates
- Folliculitis: superficial infections involving hair follicles caused by susceptible bacteria
- Secondary Infections: used adjunctively in atopic dermatitis where bacterial colonization exacerbates inflammation
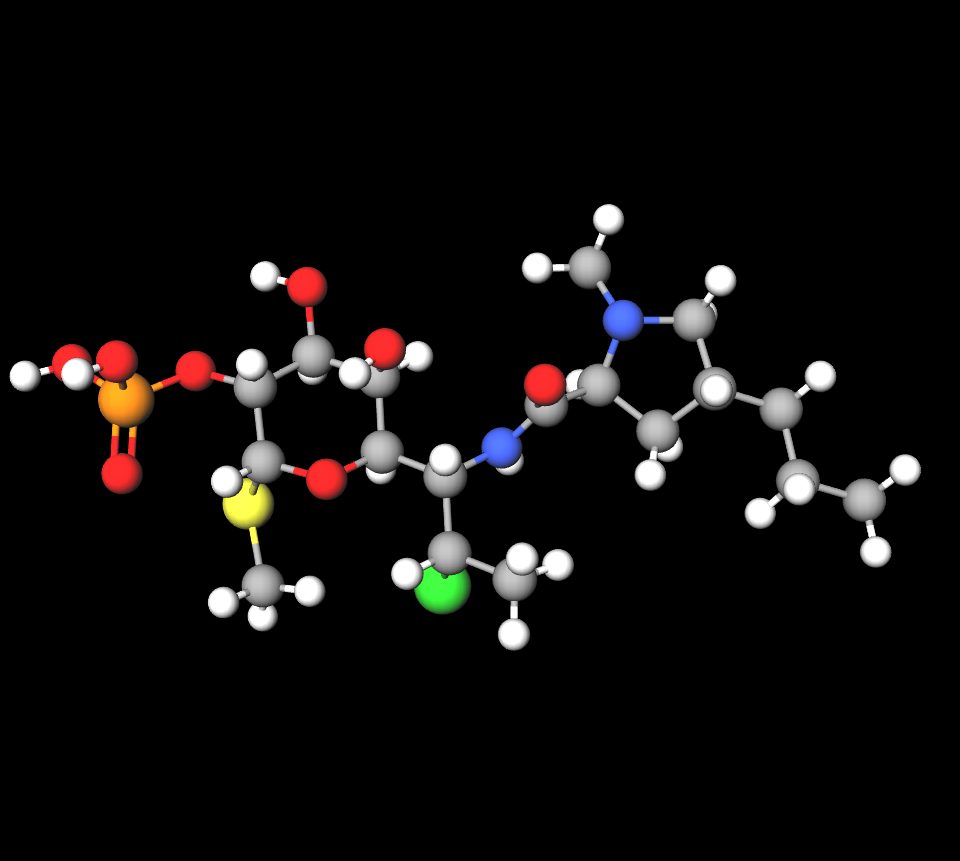
4. Composition and Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Each milliliter of Cleocin T Topical Solution contains:
- Clindamycin Phosphate 10 mg (1%)
- Isopropyl alcohol: serves as a solvent and antibacterial agent
- Propylene glycol: enhances skin penetration
- Water: solvent base
The solution is typically colorless to slightly yellowish, with a distinctive alcohol scent. Its lightweight and quick-drying texture ensures ease of application without leaving a greasy residue.
5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
5.1 Cleocin Dose and Application
Cleocin T is generally applied twice daily, once in the morning and once in the evening. The typical application steps include:
- Cleanse the affected area with a gentle cleanser
- Pat dry thoroughly
- Apply a thin layer of solution using the provided applicator or cotton pad
The treatment duration is often determined by clinical response, with reassessment recommended after 8 to 12 weeks of therapy.

5.2 Special Application Considerations
- Avoid contact with eyes, mouth, mucous membranes, or broken skin
- Hands should be washed after each application
- May be combined with other topical agents under medical supervision
Alcohol-based products may increase irritation if used simultaneously.
6. Side Effects of Cleocin T Topical Solution
6.1 Common Side Effects
- Localized skin dryness, flakiness, or desquamation
- Transient stinging or burning sensation upon application
- Erythema (redness) and mild pruritus (itchiness)
- Altered sebum production: dryness or oily skin
6.2 Less Common or Serious Adverse Reactions
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Pseudomembranous colitis: rare but potentially severe gastrointestinal reaction due to systemic absorption
- Systemic effects such as abdominal pain or diarrhea
Any persistent or worsening side effects warrant immediate medical consultation.
7. Drug Interactions and Compatibility
Several pharmacological interactions should be considered:
- Erythromycin: antagonistic interaction; avoid concurrent use
- Neuromuscular blocking agents: enhanced blockade may occur
- Concurrent systemic antibiotic therapy may increase the risk of adverse effects
- Use with caution alongside alcohol-based toners, exfoliants, or cosmetics

8. Warnings and Important Precautions
- Though topical, systemic absorption may occur and lead to serious gastrointestinal side effects
- Discontinue immediately if severe or bloody diarrhea develops
- Do not use on sunburned, eczematous, or abraded skin
- Patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease, especially colitis, should use with extreme caution
Monitoring and regular follow-up are recommended during extended therapy to ensure safety and efficacy.
9. Contraindications for Use
Cleocin T Topical Solution should not be used in certain clinical contexts due to the potential for serious adverse effects or treatment failure.
- Hypersensitivity: Individuals with a known allergy to clindamycin or its structural analog, lincomycin, must not use this medication. Hypersensitivity reactions may manifest as urticaria, angioedema, or anaphylaxis.
- History of Antibiotic-Associated Colitis: Patients who have experienced antibiotic-associated colitis, including pseudomembranous colitis, should avoid this product. Even topical clindamycin has been implicated in gastrointestinal adverse events due to systemic absorption.
- Presence of Open Wounds or Systemic Infection: Application over compromised skin barriers or in areas with systemic infections increases the risk of systemic uptake and subsequent toxicity. Alternative treatment strategies should be employed in such cases.
10. Careful Administration in Special Populations
10.1 Use in Elderly Patients
No specific dosage adjustment is typically required for geriatric patients. However, age-related changes in skin integrity and immune response necessitate vigilant observation. Practitioners should monitor for:
- Delayed cutaneous healing
- Exaggerated skin irritation
- Signs of systemic absorption such as gastrointestinal discomfort
10.2 Use in Pregnant Women
Cleocin T falls under the FDA Pregnancy Category B. Animal reproductive studies have not demonstrated a risk to the fetus, but well-controlled studies in pregnant women are lacking. Therefore, the use of Cleocin T in pregnancy should be limited to instances where:
- Topical treatment is deemed necessary
- Potential benefits outweigh potential fetal risks
Clinical discretion and physician oversight are imperative.
10.3 Use in Nursing Mothers
Clindamycin is known to be excreted in breast milk following systemic administration. While systemic absorption from topical application is minimal, it cannot be ruled out. As a precautionary measure:
- Avoid application to the chest area to prevent direct exposure to the nursing infant
- Discontinue breastfeeding temporarily if extensive body surface application is required
10.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of Cleocin T have been established in children aged 12 years and older. Below this age threshold, clinical data remain insufficient. Therefore:
- Use only in pediatric patients 12 years or older
- Supervision by a pediatric healthcare provider is strongly recommended
- Monitor for signs of irritation, hypersensitivity, or poor therapeutic response
11. Overdose and Emergency Management
Although topical overdose is rare, excessive application or misuse can lead to:
- Severe erythema, burning, or desquamation
- Secondary bacterial infections due to compromised skin barrier
In the event of accidental oral ingestion:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea may occur
- Activated charcoal may be considered in early stages
- Seek emergency medical attention for persistent symptoms or suspected overdose
12. Storage and Shelf-Life Information
To maintain potency and stability, Cleocin T should be stored under the following conditions:
- Temperature: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Short excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C.
- Light and Moisture Protection: Keep the container tightly closed and away from direct sunlight or humidity.
- Expiry Monitoring: Do not use beyond the printed expiration date on the label. Discard if physical properties (odor, color, clarity) change.
13. Handling Precautions and Patient Counseling
Proper handling and adherence protocols are critical to achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
- Always wash hands before and after applying the solution to reduce contamination and unintentional spread.
- Use sterile applicator pads or cotton for each application and dispose of them appropriately after single use.
- Do not share the medication, even among individuals with similar symptoms, to prevent cross-contamination and misuse.
- Educate patients on the importance of adherence to dosage and timing.
- Discuss the use of a gentle, non-comedogenic skincare routine to support healing and avoid additional skin irritation.

Cleocin T Topical Solution FAQ
- Can Cleocin treat yeast infections?
- What STD does Cleocin treat?
- What is the drug Cleocin used for?
- What is Cleocin cream used to treat?
- How fast does Cleocin work?
- Is Cleocin a good antibiotic?
- How long can I use Cleocin?
- Is Cleocin safe for kidneys?
- Does Cleocin treat UTI?
- Does Cleocin make you sleepy?
- What infections does Cleocin treat?
- What is Cleocin used for?
- What is cleocin?
- How does cleocin-hcl-1 work?
- Is Cleocin a penicillin?
- How long does cleocin take to work?
Can Cleocin treat yeast infections?
No
What STD does Cleocin treat?
Cleocin could prove effective in the treatment of Chlamydia infections.
What is the drug Cleocin used for?
Cleocin is a type of medication used to address infections.
What is Cleocin cream used to treat?
Bacterial infection and acne
How fast does Cleocin work?
1-3 days
Is Cleocin a good antibiotic?
Clindamycin proves to be an antibiotic for treating a range of infections.
How long can I use Cleocin?
Months
Is Cleocin safe for kidneys?
Yes
Does Cleocin treat UTI?
In some situations, it might be employed to address urinary tract infections in individuals allergic to traditional UTI treatments.
Does Cleocin make you sleepy?
No
What infections does Cleocin treat?
The FDA has approved Clindamycin for treating conditions such as septicemia, infections in the abdomen, lower respiratory infections, gynecological infections, bone and joint infections, and skin and skin structure infections.
What is Cleocin used for?
Skin infections such as cellulitis; lower respiratory tract infections, like pneumonia and bronchitis; stomach infections; pelvic and genital tract infections; bloodstream infections; bone and joint infections.
What is cleocin?
Skin infections such as cellulitis; lower respiratory tract infections, like pneumonia and bronchitis; stomach infections; pelvic and genital tract infections; bloodstream infections; bone and joint infections.
How does cleocin-hcl-1 work?
Cleocin HCL (clidamycin hydrochloride) a functions, by halting the growth process.
Is Cleocin a penicillin?
No
How long does cleocin take to work?
6 weeks