Dirab, Dexrabeprazole
- Introduction to Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
- Composition and Formulation of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
- Uses of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
- Off-Label Uses of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
- How Dirab (Dexrabeprazole) Works
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Common and Serious Side Effects of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
- Drug Interactions with Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
- Warnings and Precautions for Use
- Contraindications for Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
- Careful Administration Guidelines
- Administration to Special Populations
- Overdose Management and Treatment
- Important Handling and Safety Precautions
Introduction to Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
Overview of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
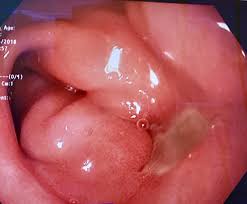
Dirab, the brand name for Dexrabeprazole, is a potent proton pump inhibitor (PPI) designed to mitigate excessive gastric acid production. It is widely prescribed for conditions that involve acid-induced damage to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This medication provides sustained relief for acid-related disorders, improving patient quality of life.
Drug Classification and Mechanism of Action
Dexrabeprazole is categorized as a type of proton pump inhibitor (PPI). Its mechanism involves targeting the H⁺⁄K⁺ ATPase enzyme found in the stomach's cells to decrease the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
Differences Between Dexrabeprazole and Rabeprazole
- Dexrabeprazole is the active enantiomer of Rabeprazole, offering enhanced efficacy and tolerability.
- It demonstrates a higher bioavailability compared to its racemic counterpart.
- Dexrabeprazole has a reduced metabolic burden, making it preferable in individuals with hepatic impairment.
FDA Approval Status and Global Availability
Dirab (also known as Dexrabeprazole) has been given the light in locations for managing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD and peptic ulcers). Nevertheless, the approval process may differ from one country to another; in regions, there might be considerations regarding its usage as a treatment or off-label therapy.
Composition and Formulation of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
Active Ingredients and Excipients
The main component found in Dirab is Dexrabeprazole sodium. It is combined with additives, like lactose monohydrate and magnesium stearate, along with microcrystalline cellulose to maintain its stability and ability to be absorbed by the body effectively.
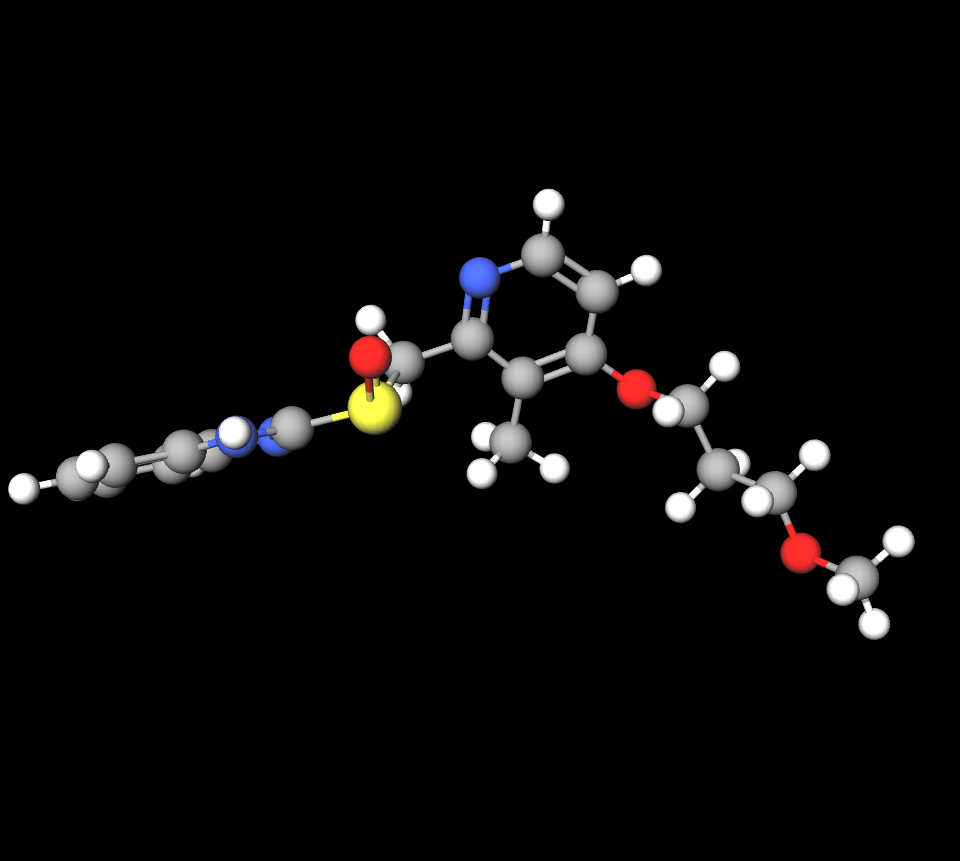
Available Strengths and Pharmaceutical Forms
- Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg
- Capsules: Extended-release formulations for prolonged therapeutic effects
- Injectable: Intravenous formulations for hospital-based administration
Brand Names and Generic Alternatives
Dirab is sold under brand names worldwide. They can be found as generic alternatives in certain areas to provide more affordable treatment options.
Uses of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
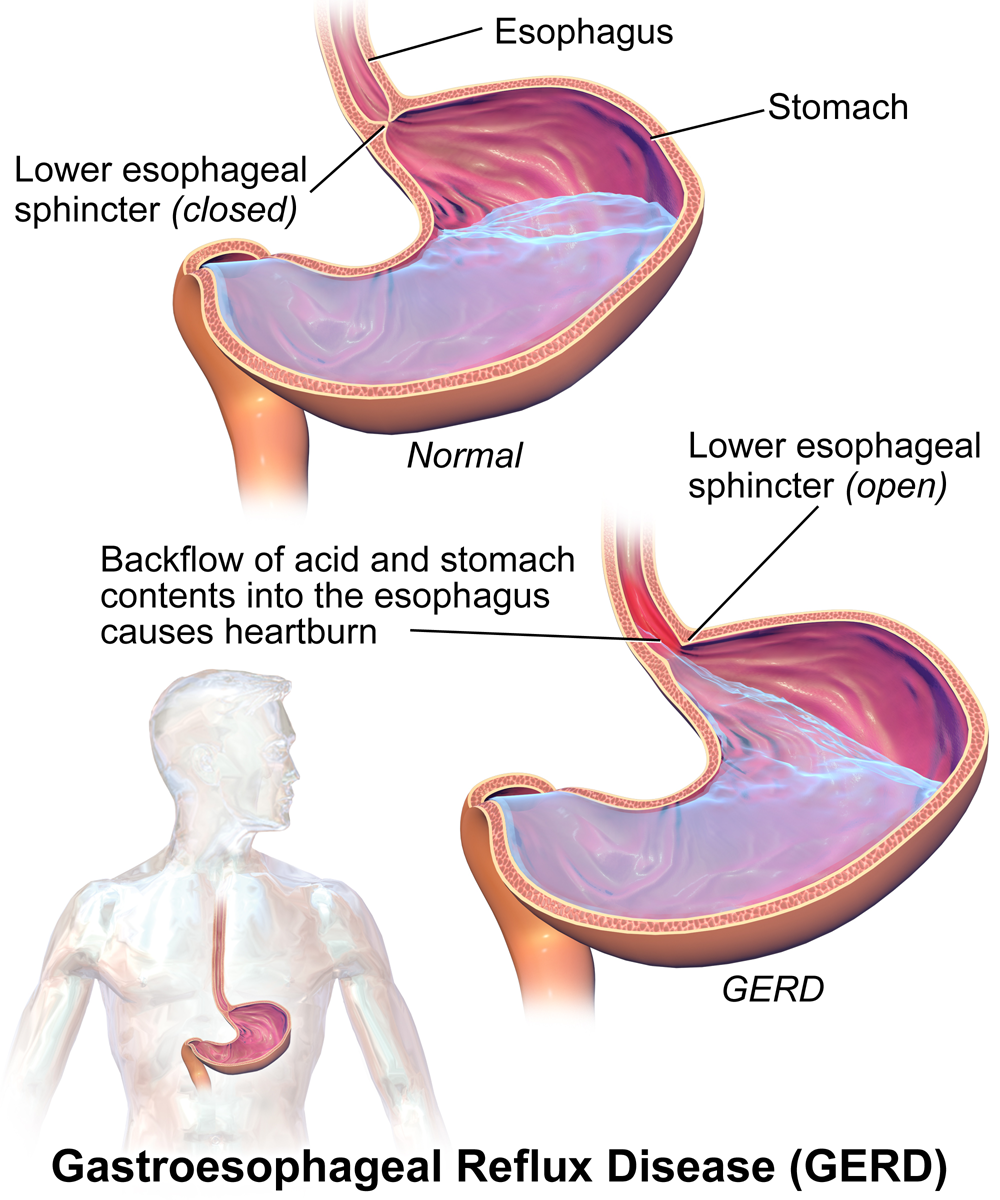
Management of Erosive Esophagitis
Treatment, with Dexrabeprazole is recommended for managing erosive esophagitishttps://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10138-esophagitis—a complication of GERB (gastroesophageal reflux disease). This medication aids in the healing of mucosal tissues. It helps deter the advancement of the condition.
Prevention and Treatment of Peptic Ulcers
Helicobacter Pylori Eradication Therapy
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome and Hypersecretory Conditions
Patients diagnosed with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome find relief through the use of Dirab to manage the overproduction of stomach acid and safeguard against complications.
Off-Label Uses of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia Treatment
Sometimes, doctors recommend using dexrabeprazole to address dyspepsia and alleviate symptoms like bloating, discomfort in the abdomen area (epigastric pain), and feeling full quickly after eating (early satiety).
Reduction of Gastric Acid-Related Symptoms in Non-Erosive Reflux Disease (NERD)
Adjunct Therapy for Barrett's Esophagus Management
Potential Use in Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis
Patients who are severely ill and prone to stress ulcers might find relief with Dexrabeprazole to avoid bleeding and ulcers.
How Dirab (Dexrabeprazole) Works
Inhibition of the Hâº/K⺠ATPase Enzyme
Dexrabeprazole binds permanently to the proton pump. Stops the production of stomach acid at its stage.
Reduction of Gastric Acid Secretion and pH Modulation
By keeping the gastric acidity level steady, with Dirab's help, it creates a setting for ulcers to heal and symptoms to fade away effectively.
Onset and Duration of Action
The medicine is quickly absorbed in the body. Reaches its levels in the bloodstream after around 2 hours of intake. The effects of reducing acid can last for up to a day, which enables taking it once daily.
Comparison with Other Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
- Faster onset of action than Omeprazole
- Greater acid suppression than Lansoprazole
- Lower potential for drug interactions compared to Esomeprazole
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosing for GERD, Ulcers, and Hypersecretory Conditions
- GERD: 10-20 mg once daily
- Peptic ulcers: 20 mg daily for 4-8 weeks
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome: 40 mg daily, adjustable per patient response
Administration Timing Concerning Meals
For results, it's recommended to take Dexrabeprazole before eating to enhance absorption and effectiveness.
Special Considerations for Long-Term Use
Regular assessment is necessary, for individuals using proton pump inhibitors over a period to monitor risks, like vitamin B12 deficiency and bone density loss.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions
Remember to keep the item in a dry spot, below 25 degrees Celsius, to shield it from dampness and direct sunlight.
Shelf Life and Expiration Date Considerations
Make sure to look at the expiration dates before using any medication and throw away any that have expired to ensure they work effectively.
Proper Disposal Methods
Make sure to get rid of any leftover medication in your area according to the rules to prevent harming the environment.
Common and Serious Side Effects of Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
Most Frequently Reported Side Effects

Less Common but Significant Adverse Reactions
- Dizziness and fatigue
- Skin rashes and pruritus
- Elevated liver enzymes
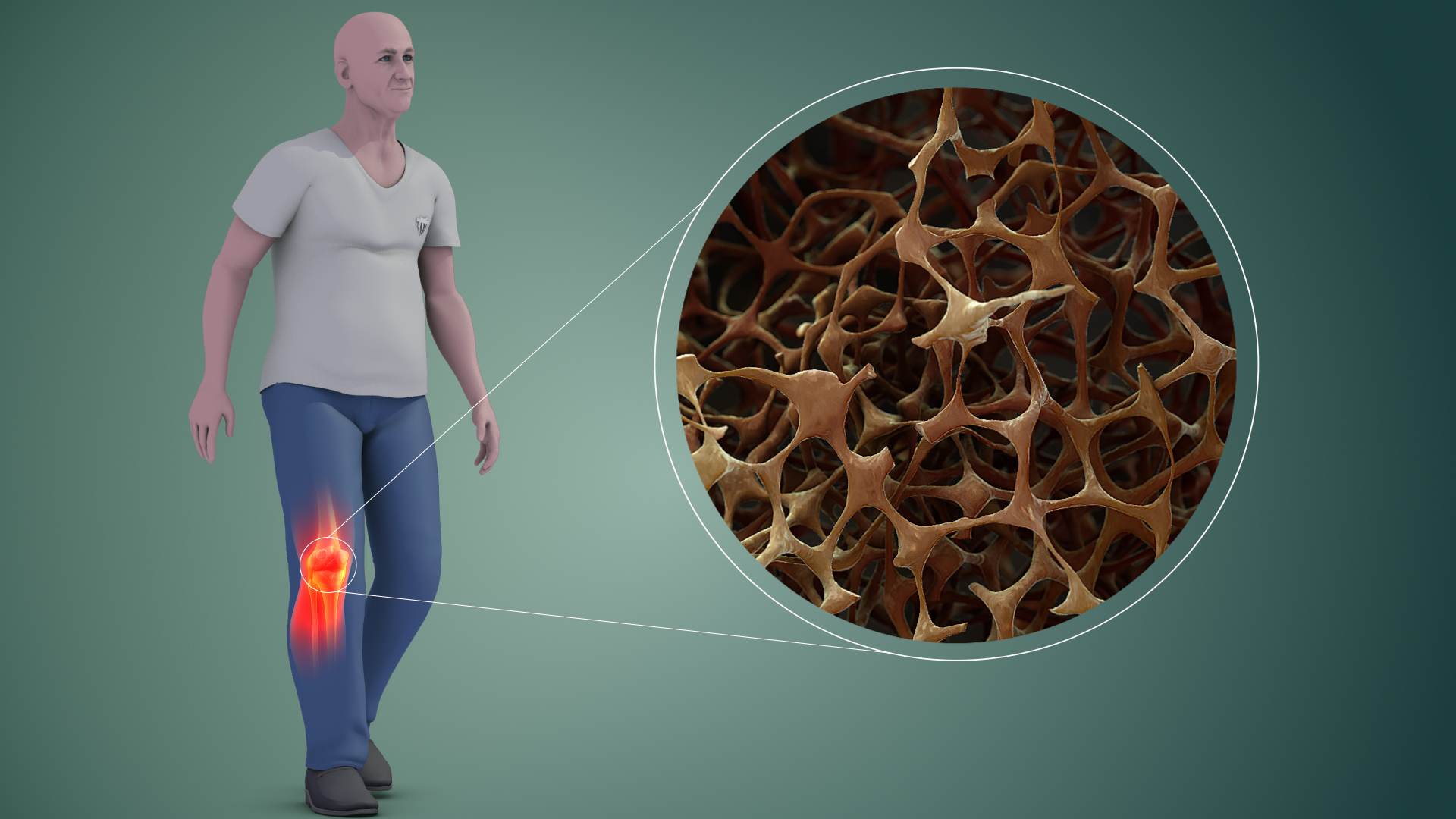
Potential Long-Term Effects
- Increased risk of osteoporosis-related fractures
- Vitamin B12 malabsorption
- Potential kidney function decline
Monitoring and Reporting Adverse Reactions
Patients should report any unusual symptoms to healthcare providers. Regular monitoring is recommended for those on prolonged therapy.
Drug Interactions with Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
Interactions with Other Proton Pump Inhibitors and H2 Blockers
Combining Dirab (Dexrabeprazole) with other proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2-receptor antagonists (e.g., ranitidine, famotidine) may not provide additional therapeutic benefits and could lead to excessive suppression of gastric acid. This can impair digestion and increase susceptibility to infections such as Clostridium difficile. Concomitant use should be avoided unless clinically justified.
Effects on the Metabolism of Other Medications
Dexrabeprazole affects the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system, particularly CYP2C19 and CYP3A4. This interaction can influence the metabolism of several medications:
- Warfarin: Potential for increased anticoagulant effects, elevating the risk of bleeding complications.
- Diazepam: Prolonged sedative effects due to delayed clearance from the body.
- Digoxin: Increased serum levels, heightening the risk of digitalis toxicity, especially in elderly patients.
Potential Impact on the Absorption of Vitamins and Minerals
By reducing gastric acidity, Dirab may impair the absorption of essential nutrients:
- Vitamin B12: Chronic use can lead to B12 deficiency, resulting in neurological complications and anemia.
- Magnesium: Hypomagnesemia may occur, potentially causing muscle cramps, arrhythmias, or seizures.
- Calcium: Reduced calcium absorption increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Food and Beverage Interactions
Certain foods and beverages may alter the effectiveness of Dexrabeprazole:
- Alcohol: Can exacerbate gastric irritation and counteract the medication's protective effects.
- Caffeinated Drinks May stimulate acid production, reducing the drug's efficacy.
- High-fat Meals: Slows gastric emptying and may delay drug absorption.
Warnings and Precautions for Use
Risk of Clostridium Difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Long-term PPI use, including Dirab, has been linked to an increased risk of Clostridium difficile infection. Patients presenting with persistent diarrhea should be evaluated for this potentially severe complication.
Increased Risk of Osteoporosis-Related Fractures
Prolonged suppression of stomach acid may impair calcium absorption, weakening bone density and a heightened risk of hip, wrist, or spinal fractures. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation should be considered for at-risk individuals.
Considerations for Long-Term Therapy
Chronic Dexrabeprazole use necessitates periodic reevaluation to assess continued necessity. Long-term therapy is associated with:
- Increased susceptibility to enteric infections.
- Gastric hyperplasia due to sustained acid suppression.
- Potential for rebound acid hypersecretion upon discontinuation.
Potential Kidney and Liver Function Impairment
Reports of acute interstitial nephritis have been associated with prolonged PPI use. Additionally, in patients with hepatic impairment, Dexrabeprazole metabolism may be altered, requiring dose adjustments.
Monitoring Requirements for At-Risk Patients
Regular assessment of kidney function, liver enzymes, and electrolyte levels is advised for patients on long-term treatment.
Contraindications for Dirab (Dexrabeprazole)
Known Hypersensitivity to Dexrabeprazole or Other PPIs
Patients with a history of allergic reactions to PPIs, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, or Stevens-Johnson syndrome, should avoid this medication.
Severe Hepatic Impairment and Dose Considerations
Hepatic metabolism of Dexrabeprazole is significantly reduced in patients with severe liver disease. A lower dose or alternative treatment should be considered.
Patients with a History of Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematosus
PPIs have been implicated in drug-induced lupus erythematosus, characterized by arthralgia, rash, and positive ANA titers. Discontinuation should be immediate if symptoms appear.
Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Malignancies
PPIs may mask the symptoms of gastric cancer, delaying diagnosis. Patients with unexplained weight loss, anemia, or persistent dyspepsia should undergo further evaluation before initiating therapy.
Careful Administration Guidelines
Patients with Moderate to Severe Renal Impairment
Though Dexrabeprazole is primarily metabolized in the liver, patients with renal dysfunction may be at increased risk for electrolyte imbalances. Magnesium and creatinine levels should be routinely monitored.
Individuals with Risk Factors for Gastric Malignancies
Long-term acid suppression has been associated with gastric polyps and potential malignant transformation. Patients with a history of gastric lesions should be monitored closely.
Patients with a History of Gastrointestinal Infections
Reduced stomach acidity can facilitate bacterial overgrowth, increasing the likelihood of infections such as salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis.
Administration to Special Populations
Elderly Patients
Dosage Adjustment Considerations
Geriatric patients may exhibit reduced drug clearance, necessitating lower doses to prevent excessive plasma drug accumulation.
Risk of Drug Accumulation and Adverse Effects
Older adults are more susceptible to PPI-associated complications, including fractures, cognitive decline, and kidney injury. Treatment duration should be minimized.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Profile During Pregnancy
Dexrabeprazole is categorized as a pregnancy Category B drug, indicating no known teratogenic effects in animal studies, though human data remain limited.

Excretion in Breast Milk and Lactation Concerns
Minimal drug transfer into breast milk has been observed, but caution is advised in lactating women.
Pediatric Patients
Approved Age Groups for Use
Pediatric use is limited, with approval generally restricted to children aged 12 years and older for GERD treatment.
Clinical Trial Data on Safety and Efficacy
Studies indicate that Dexrabeprazole is effective in pediatric populations, though long-term safety data remain inconclusive.
Overdose Management and Treatment
Symptoms of Overdose
- Dizziness and confusion
- Tachycardia
- Profound hypotension in severe cases
Recommended Emergency Interventions
In cases of overdose, symptomatic management is key. Supportive care, including fluid replacement and electrolyte monitoring, should be initiated.
Role of Activated Charcoal and Symptomatic Treatment
Activated charcoal may be administered in cases of recent ingestion. No specific antidote exists for Dexrabeprazole overdose.
Important Handling and Safety Precautions
Guidelines for Pharmacists and Healthcare Providers
Proper patient counseling regarding dosage, adherence, and potential adverse effects is crucial for therapeutic success.
Safe Dispensing and Repackaging Considerations
Tablets should be stored in their original blister packaging to prevent degradation. Exposure to excessive moisture can compromise drug stability.
Handling Instructions for Patients to Avoid Misuse
- Do not crush or chew delayed-release tablets.
- Adhere strictly to prescribed dosing schedules.
- Report any unusual symptoms or side effects promptly.
Dirab, Dexrabeprazole FAQ
- What is the use of Dirab tablet?
- What is dexrabeprazole used for?
- What is the difference between rabeprazole and dexrabeprazole?
- What is the use of dexrabeprazole and domperidone capsules?
- What is the use of Dexrabeprazole sodium and Levosulpiride capsules?
- What is the use of Dexrabeprazole?
- Is dexlansoprazole safe for kidneys?
- How long should I take dexlansoprazole?
- What is Dexlansoprazole with domperidone?
- How does dexlansoprazole work?
- What happens when you stop taking dexlansoprazole?
- What is the drug dexrabeprazole used for?
- Does dexlansoprazole affect kidneys?
- When is the best time to take dexlansoprazole?
- How long does it take for dexlansoprazole to start working?
- What is the advantage of dexlansoprazole?
- Can you take dexlansoprazole on an empty stomach?
- What is the mechanism of action of dexrabeprazole?
- How safe is dexlansoprazole?
- Can you take omeprazole and dexlansoprazole together?
- Can I take dexlansoprazole at night?
- Who should not take dexlansoprazole?
- What is an alternative to dexlansoprazole?
- Is dexlansoprazole better than pantoprazole?
- Do you need a prescription for dexlansoprazole?
- What is the brand name for dexlansoprazole?
What is the use of Dirab tablet?
Dirab 10 mg Tablet is a medication that helps decrease the acid levels in your stomach to manage conditions like heartburn and peptic ulcer disease by regulating the production of stomach acid.
What is dexrabeprazole used for?
Dexrabeprazole is prescribed for managing acidity issues such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (acid reflux) and peptic ulcer disease.
What is the difference between rabeprazole and dexrabeprazole?
Dexrabeprazole is expected to show more effectiveness in improving symptoms than Rabeprazole, even when administered at half the usual dosage, while maintaining a comparable level of safety and efficacy.
What is the use of dexrabeprazole and domperidone capsules?
The combination of Dexrabeprazole and Domperidone is a medication used to address stomach-related issues such as acidity problems and indigestions, among others like heartburn and peptic ulcers well as nausea and vomiting symptoms in individuals who might have ailments like Zollinger Ellison syndrome or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What is the use of Dexrabeprazole sodium and Levosulpiride capsules?
Dexrabeprazole, with Levosulpiride, is mainly prescribed to address issues with acidity and movement in the system.
What is the use of Dexrabeprazole?
Dexrabeprazole works by inhibiting the activity of proton pumps for generating stomach acid, which helps decrease production in the stomach and prevents excessive acid reflux into the esophagus, thereby alleviating heartburn symptoms associated with acid reflux.
Is dexlansoprazole safe for kidneys?
Dexlansoprazole can cause kidney problems.
How long should I take dexlansoprazole?
8 weeks
What is Dexlansoprazole with domperidone?
By blocking the function of proton pumps that create stomach acid and preventing acid from returning to the esophagus, it helps decrease the production of stomach acid.
How does dexlansoprazole work?
It functions by decreasing the acid levels in the stomach. It is classified under a group of drugs known as PPIs.
What happens when you stop taking dexlansoprazole?
Occasionally, individuals might encounter a situation called 'heartburn rebound,' where their symptoms resurface once they discontinue the medication.
What is the drug dexrabeprazole used for?
Dexrabeprazole is commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms related to stomach acidity issues, like reflux and peptic ulcers.
Does dexlansoprazole affect kidneys?
Yes
When is the best time to take dexlansoprazole?
Remember to follow your doctor's instructions when taking this medication orally. Once a day, with or, without food is recommended by healthcare professionals to ensure results based on your symptoms and meal schedule.
How long does it take for dexlansoprazole to start working?
3 days
What is the advantage of dexlansoprazole?
Key benefits of the medication comprise its safety record and minimal chance of reactions when used alongside other medicines concurrently.
Can you take dexlansoprazole on an empty stomach?
The FDA has given the light for dexlansoprazole to be taken once a day regardless of meals.
What is the mechanism of action of dexrabeprazole?
Dexrabeprazole functions by inhibiting the activity of proton pumps in generating stomach acid.This results in a decrease in the production of acid in the stomach. It helps prevent an overflow of acid into the food pipe.
How safe is dexlansoprazole?
Individuals using proton pump inhibitors like dexpansoprazole might have a risk of experiencing fractures in their wrists, hips, or spine compared to individuals who do not use medications. Additionally people taking proton pump inhibitors may also potentially develop fundic gland polyps which're a form of growth on the lining of the stomach.
Can you take omeprazole and dexlansoprazole together?
No
Can I take dexlansoprazole at night?
Yes
Who should not take dexlansoprazole?
Low levels of calcium or magnesium in the bloodstream can sometimes be an issue to watch out for when considering dexlansoprazole or other medications for lupus treatment or management before or during pregnancy if you're planning on conceiving.
What is an alternative to dexlansoprazole?
Rabeprazole (Aciphex), prescription-only esomeprazole, pantoprazole (Protonix) and lansoprazole (Prevacid)
Is dexlansoprazole better than pantoprazole?
While there wasn't a difference, in the 0 to 12 hour timeframe, dexlansoprazole showed consistently higher pH levels during the final 12 to 24 hours compared to pantoprazole (with a significance level of P = 0·001) and esomeprazole (with a significance level of P=0·044) although not with rabeprazole (, with a significance level of P=0·075).
Do you need a prescription for dexlansoprazole?
Yes
What is the brand name for dexlansoprazole?
Dirab