Etofree, Etodolac
- Introduction to Etofree (Etodolac)
- Composition and Formulation of Etofree
- Mechanism of Action: How Etofree (Etodolac) Works
- Approved Medical Uses of Etofree (Etodolac)
- Off-label and Investigational Uses of Etofree
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Etofree
- Administration in Special Populations
- Etodolac Side Effects
- Serious Adverse Reactions
- Etodolac Interactions
- Contraindications for Etofree Administration
- Etodolac Warnings and Important Safety Precautions
- Careful Administration and Risk Mitigation
- Handling and Storage Instructions for Etofree
- Overdose and Emergency Management of Etofree
- Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Patients
Introduction to Etofree (Etodolac)
Etofree is a known form of etodolac that falls under the category of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It is commonly utilized for its pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory qualities, in the field, and is often recommended by healthcare providers for treating a range of musculoskeletal issues such as osteoarthritis and post-surgery discomfort due, to its distinct pharmacokinetics and specific enzyme preferences that set it apart from typical NSAIDs.
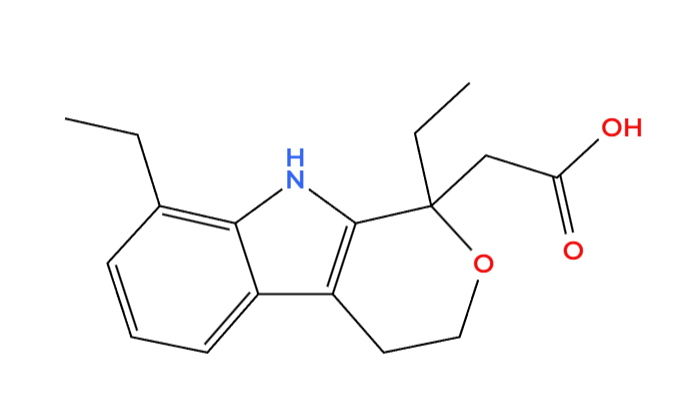
Overview of Etofree as a Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug (NSAID)
Etodolac is the ingredient, in Etofree that helps reduce inflammation by blocking the production of prostaglandins in the body. It works by focusing on cyclooxygenase (COX ) enzymes to control the process. Due to its preference, for COX-2 It leads to stomach-related issues compared to other non-selective NSAIDs.
Classification and Pharmacological Category
In terms of drugs and medications categorization-wise.
- Anti-inflammatory pain relievers known as NSAIDs.
- COX-2 preferential inhibitors
- Enolic Acid Derivatives within the NSAID Spectrum.
It's not classified under opioids or corticosteroids; hence it serves as an option, for managing long-term pain in patients.
Brand Names and Availability in Global Markets
In some areas, around the world it is known as Etofree; however globally etodolac is available, under brand names. In the United States and Canada. It can be obtained with a prescription. Purchased over the counter, in regions, with restricted potencies.
Composition and Formulation of Etofree
Active Ingredient: Etodolac
Each Etofree product includes etodolac as the ingredient, with potent pharmacological effects. This compound has penetration into tissues. Is particularly effective, in inflamed synovial tissues.
Available Strengths and Dosage Forms
Available, in settings, in the following formats;
- Immediate release tablets are available, in two strengths; 200 mg and 300 mg.
- Extended release tablets are available, in strengths of 400 mg 500 mg and 600 mg.
- Capsules of 300 milligrams.
The extended release version ensures round-the-clock protection, with one dose, per day, making it easier for patients to follow their treatment regimen.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Common ingredients found in medications may consist of;
- Lactose Monohydrate
- Magnesium Stearate
- Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
- Titanium dioxide which is used as a coating agent.
These substances act as stabilizers to maintain consistency, in the mixture and serve as binders to keep ingredients together while also controlling absorption levels.

Etodolac vs Ibuprofen
Although they both fall under the NSAIDs category, etodolac stands out for its COX-2 selectivity. This distinction results in;
- Reduced chance of stomach upset.
- An extended period of activity.
- Minimized requirement, for taking medication times a day.
- However, in cases of sudden and short-term pain reduced dosing is required
We would recommend using Ibuprofen for its effectiveness.
Meloxicam vs Etodolac
Both agents, Meloxicam and etodolac exhibit a preference for COX2. Vary in terms of their pharmacokinetic characteristics, with etodolac providing the following benefits;
- Ingestion of the medication leads to quicker attainment of peak plasma levels.
- The duration of action is shorter, for etodolac at 3 hours compared to meloxicam, which lasts, around 10 hours.
- Schedules, with flexibility, for dosing
Etodolac vs Diclofenac
Etodolac causes harm to the heart and stomach than diclofenac does; however, diclofenac is stronger. Can lead to more side effects, as a trade-off.
Etodolac vs Celebrex
Celebrex is a medication known as celecoxib that targets COX-2 inhibitors, with precision compared to etodolac, which has a level of selectivity in this aspect. Celebrex is generally preferred due to its tolerance levels. It is more expensive and requires closer monitoring for cardiovascular risks. On the other hand, Etodolac offers a cost solution by striking a balance, between effectiveness and tolerability levels.
Etodolac and Gabapentin
When etodolac and gabapentin are used together they provide a pain relief approach that works well for nerve pain and after surgery. Combining them boosts their effectiveness; Reduced need for opioids. Enhanced results, for patients dealing with long-term pain management.

Mechanism of Action: How Etofree (Etodolac) Works
Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase (COX) Enzymes
Etodolac blocks COX enzymes, like COX-2, which hinders the production of prostaglandins from acid. Important substances involved in inflammation control and pain relief. Showcasing its effectiveness, in treatment.

COX-2 Selectivity and Its Relevance to Anti-inflammatory Action
COX-2 is an enzyme that can be activated and is mainly found in areas of the body affected by inflammation and Etodolac shows a preference, for targeting COX-2 in these sites of inflammation. Reduces the formation of prostanoids. Reduces the occurrence of stomach ulcers more, than selective NSAIDs. Allows for application, in cases of osteoporosis and rheumatism.
Impact on Prostaglandin Synthesis and Pain Reduction
Prostaglandins make pain receptors more sensitive, to pain signals. Etodolac reduces the impact by slowing down the production of prostaglandins, leading to a decrease in; Physical discomfort, in muscles. The body's reaction to inflammation, throughout the system. Etofree is recognized as a choice, for managing both acute inflammatory conditions through biochemical modulation.
Approved Medical Uses of Etofree (Etodolac)
Management of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Etodolac (marketed as Etofree) has gained support for its effectiveness, in the extended treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These enduring joint disorders typically involve inflammation and thickening of the membrane, along with gradual cartilage degradation. Etodolac functions as a modifier for disease symptoms, by influencing.
- Relieving swelling and stiffness in the joints.
- Improving movement by adjusting levels.
- Enhancing pain ratings reported by patients over durations.
It is often combined with treatments such as disease-modifying drugs (DMARD), in various treatment plans to help lessen the frequency and intensity of flare ups.
Treatment of Acute Pain and Inflammation
In cases of pain situations Etofree shows effectiveness, in reducing pain signals. Whether caused by tissue injuries, tendon inflammation, sudden bouts of gout, arthritis, etodolac offers relief soon after taking it. Common uses comprise;
- Sporting Muscle strains.
- Sudden onset of back discomfort.
- Inflammatory outbursts unrelated, to term conditions.
Its quick start and moderate duration of action make it suitable, for short term application, without the addiction potential linked to opioid pain relievers.
Relief of Postoperative Pain and Musculoskeletal Disorders
After surgery, procedures are done to alleviate pain and swelling in the area are body reactions that happen physiologically. Etofree is commonly given after surgery to help with the swelling of tissues caused by inflammation and lessen the need for painkillers. Some advantages are;
- Accelerated healing of wounds, through the regulation of fluids.
- Decrease, in areas of increased sensitivity to pain.
- Better results in getting patients up and moving, leading to rehabilitation outcomes.
Its specific anti-inflammatory properties are helpful, for conditions like bursitis. Synovitis is well, as mechanical back pain.

Etodolac for Tooth Pain
Toothache is an area where Etofree shows its effectiveness when linked to pulpitis or gum inflammation conditions. Its capacity to reduce nerve sensitivity through prostaglandin suppression proves beneficial, in relieving pain situations that are not adequately managed by painkillers. In practice, specialists may consider using etodolac for this purpose;
- Mitigating inflammation in the alveolar after extraction
- When treating pulpitis in endodontic procedures.
- As a treatment, for abscesses when used alongside antibiotics.
Its ability to be well tolerated by the system and its minimal sedative effects make it a popular option for use, in procedures done outside the hospital setting especially when managing pain without affecting alertness or daily activities is crucial.

Off-label and Investigational Uses of Etofree
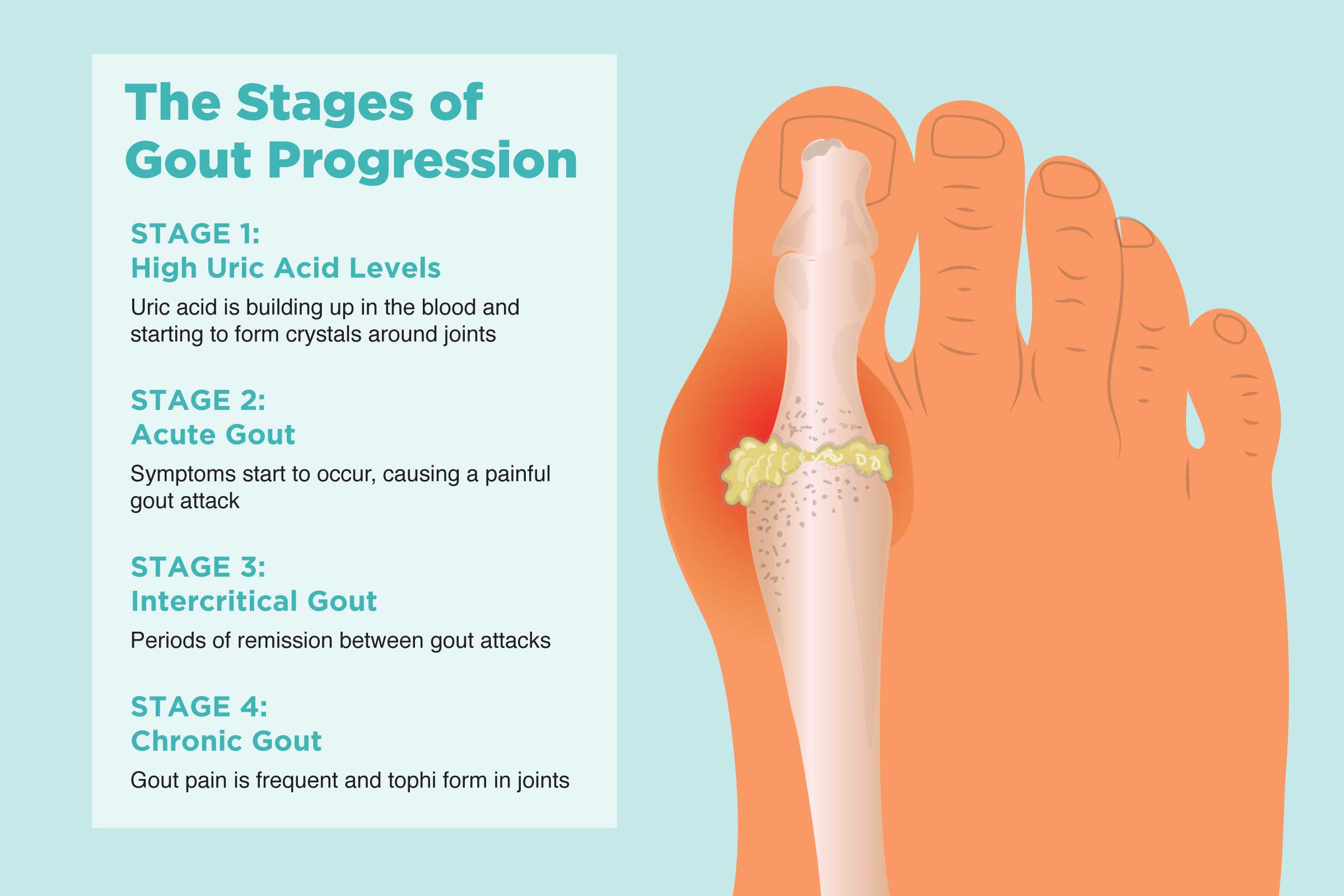
Use in Ankylosing Spondylitis and Gout Flare-ups
While not officially sanctioned for ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Etofree (etodolac) has attracted attention in the community for its effectiveness, in treating spondyloarthropathies. A condition characterized by persistent inflammation of the sacroiliac joints and spine that results in stiffness and restricted movement.The way Etodolac works. Through inhibition. Offers promise, in managing these conditions effectively.
- A decrease in inflammation, in the spine.
- Enhanced alignment, in the phase of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Reducing early morning stiffness and nighttime discomfort.
In cases of gout flare-ups, etodolac can be used to relieve the inflammation caused by uric acid crystals as a supplement or substitution when colchicine is not recommended or causes discomfort.
Cancer Pain Management in Palliative Care
In oncology and palliative care realms, dealing with cancer pain proves to be quite a task. Etofree seems to hold potential as a tool, in managing pain in end-stage illnesses.
- Some of its benefits include:
- Boosting the effectiveness of opioids by focusing on the elements associated with pain.
- Reducing the amount of opioids needed can help alleviate side effects, such as drowsiness and digestive issues.
- Improving the well-being of individuals affected by cancer that has spread to the bones or following complications.
In some cases, in hospice care environments, using NSAIDs like etodolac has been shown to enhance symptom management and reduce instances of pain flares.

Potential Application in Dysmenorrhea
Menstrual cramps that occur due, to increased production of prostaglandins can be effectively managed with COX inhibitors like Etodolac, according to its characteristics, which make it a promising option for those looking for alternatives, to hormonal birth control methods. Some benefits of using Etodolac for period pain relief are;
- The quick decrease, in uterine muscle activity and pain.
- The risk of issues in the digestive tract is lower when using modern NSAIDs compared to traditional ones.
- An alternative choice for teenagers and individuals who cannot use estrogen treatment.
Initial results suggest that etodolac might also reduce symptoms related to menstruation, like tiredness and uneasiness, which could expand its range of applications.
Use in Chronic Low Back Pain and Fibromyalgia
People with back pain or fibromyalgia commonly experience various types of pain that involve both physical and nerve-related aspects. Although still being researched, Etodolac has been considered for use, in treating these conditions. Its purpose encompasses;
- Address the swelling in areas caused by degenerative disc disease.
- As a component of a pain relief approach, working with antidepressants or anticonvulsants.
- Improving patients daily activities by regulating the mechanisms that magnify pain.
- In cases of fibromyalgia characterized by central sensitization dominance
Etodolac could provide some relief from symptoms when paired with medications such, as duloxetine or pregabalin, which may help reduce the risks associated with taking medications.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Etofree
Standard Adult Dosage for Arthritis and Acute Pain
To manage osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in adults using Etofree (etodolac), the usual starting dose ranges, from 300 mg to 500 mg taken twice a day or sometimes a daily dose of 600 mg in cases based on how well the body responds to it and its tolerability levels.
In cases of acute pain episodes when immediate relief is needed, a starting dose of 200 mg, to 400 mg may be given initially followed by doses as required. The aim here is to achieve pain relief while keeping any side effects to a minimum.
Titration should consistently match the assessment and the unique metabolic characteristics of each patient.
Extended-release Versus Immediate-release Dosing
Etodolac is sold in two forms; Release (IR) and extended release (ER). The choice between them varies based on the situation. Quick action formulas that work swiftly and are ideal for intense episodes. ER formulations provide a release of medication into the bloodstream, which is beneficial for managing long-term conditions, such as arthritis. IR tablets can be consumed two to three times a day; however ER tablets are meant to be taken to help with adherence and reduce variations in drug levels in the body.
Renal and Hepatic Impairment Dose Adjustments
Patients, with kidney or liver issues need dosages because their bodies process drugs differently in these conditions. Etodolac is mainly broken down in the liver and eliminated through the kidneys; therefore it is advised to decrease the dose for those, with moderate to severe impairment. In cases of impairment begin treatment, with the effective dose.
In cases of moderate to severe liver or kidney issues, it is advisable to avoid long-term usage unless the advantages clearly outweigh the drawbacks. It's important to check levels of serum creatinine and liver enzymes and keep an eye on the health of these individuals.
Administration Frequency and Duration of Therapy
Administer Etofree with food or milk to reduce stomach discomfort the length of treatment depends on the need;
- Short-term such as, pain after surgery, typically lasts, around 3 to 5 days.
- Chronic illnesses such as, arthritis require monitoring, with checkups to assess progress and make any necessary adjustments as needed.
Extended usage requires monitoring as it may pose risks, to the heart and blood vessels well as the stomach and kidneys.
Administration in Special Populations
Etofree Use in the Elderly
Dosing Considerations for Patients Aged 65 and Older
Elderly patients show sensitivity, to drug effects. Have a slower metabolism rate, which can lead to more adverse reactions if not careful with medication dosages. It is recommended to start with a dose of around 200 mg to 300 mg per day and then slowly increase it while monitoring closely.
Increased Risk of Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Renal Dysfunction
In individuals aged 65 and above, the chances of experiencing complications due, to NSAIDs are notably higher. These complications may include;
- Peptic ulceration and gastrointestinal hemorrhage
- Worsening of an existing kidney condition.
- High blood pressure and Water retention
Long term therapy may require the use of agents, like proton pump inhibitors administered together.
Etofree Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
Safety Classification in Pregnancy (FDA Category)
Etodolac has been categorized as a Class C drug, by the FDA, which suggests that while animal studies have demonstrated effects in fetuses there is data from human studies to draw conclusions regarding its safety, during pregnancy; therefore it should only be used if the benefits outweigh the risks.

Potential Fetal Risk and Third-trimester Contraindication
In the months of pregnancy etodolac should not be used because it has the potential to cause harm. Shutting down the arteriosus duct early
- Sustaining labor for a period.
- Raising the chances of post-delivery bleeding
- Interfere with the growth of the kidneys in the baby.
It is better to use pain relievers that are safer, for women during the later stages of pregnancy.
Breastfeeding Considerations and Excretion in Breast Milk
Etodolac is released in amounts, in breast milk but is not expected to cause harm to nursing infants; however it is recommended to exercise caution when using it in cases. If needed for treatment it's best to use the amount for the briefest period possible while also watching out for any potential negative reactions related to NSAIDs in infants.

Etofree Use in Pediatric Patients
Approved Indications and Age Limitations
Etodolac isn't widely authorized for children's use unless it's for specific situations and age ranges. In the United States it has restricted approval, for managing rheumatoid arthritis in kids aged 6 years and above.
Pediatric Dosing and Safety Concerns
When given as directed by the doctor, children's medication dosing usually depends on their weight.
- It is calculated between 13 to 20 mg per kilogram, per day split into two doses, with important factors to take into account.
- Keep a watch for signs of stomach bleeding or liver issues. It is advisable to avoid using this medication at the same time, as NSAIDs or substances that may harm the kidneys.
- Testing the functions of the kidneys and liver.
Etodolac is typically not advised for use in children under six years old due to a lack of safety information, for neonates and infants.
Etodolac Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Discomfort, Nausea, and Diarrhea
Stomach related issues are commonly experienced as a result of using etodolac due, to its impact, in reducing production in the stomach lining and weakening its barriers. Some common signs of this include;
- Experiencing discomfort in the abdomen and indigestion
- Feeling queasy is common. Usually depends on the amount you take.
- Experiencing stools or diarrhea is more common when taking doses of the medication.
These symptoms could improve if you take etodolac with food or antacids at the same time; however if the issues persist despite this approach it may be necessary to reevaluate the treatment plan.

Dizziness, Headache, and Fatigue
Less frequent side effects affecting the system can impact how patients function at the beginning of treatment. Dizziness and headaches are usually harmless it could sometimes require a dose reduction. Fatigue also could be linked to the nervous system or slight changes, in blood flow, in older individuals.

Etodolac Side Effects Weight Gain
While it is not commonly emphasized as an effect of etodolac use, in settings or discussions among people not in the field of medicine and health care providers (HCPs) there are reports linking this medication to fluid retention, in certain individuals who take it for pain relief or inflammation management purposes.
Slight swelling in the extremities. Gradual weight gain may occur with usage. Exacerbation of existing heart failure or kidney problems It's important to keep an eye out for any signs of fluid in patient's bodies when they're taking blood pressure medications or diuretics at the same time.
Serious Adverse Reactions
Cardiovascular Risks: Myocardial Infarction and Stroke
Etodolac and other NSAIDs come with a warning about the risk of cardiovascular thrombotic events when used for an extended period or in high doses;
This danger is particularly heightened in individuals with existing atherosclerosis or hypertension.
The potential risks encompass;
- Sudden heart attack.
- Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain, leading to decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery to that area of the brain.
- Exacerbation of existing heart failure.
It is crucial to assess risk levels in individuals and those, with various cardiovascular risk factors.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Ulceration
Serious gastrointestinal issues, like ulcers and bleeding may arise suddenly without any warning signs at any moment. Elderly individuals and those with a history of ulcers or those taking corticosteroids and anticoagulants are at a risk of experiencing these complications. Some symptoms to watch out for include;
- Melena or Hematemesis
- Sudden drop in blood pressure
- Having stomach discomfort or indigestion that doesn't improve with antacids.
It may be worth thinking about using preventive proton pump inhibitors for patients, at risk who need long-term NSAID treatment.
Renal Impairment and Liver Enzyme Elevation
Renal damage caused by etodolac can be sneaky. It is especially concerning for individuals, with preexisting kidney issues or low fluid levels in the body due to dehydration or other reasons like illness or medications that cause loss. NSAIDs, like etodolac, can affect kidney function by interfering with prostanglandins that help regulate blood flow in the kidneys. Symptoms of kidney damage may manifest as follows:
- The increase in blood creatinine levels
- The reduced amount of urine produced
- There is a disruption, in the balance of electrolytes, in the body.
Liver enzyme levels may increase without causing symptoms, but could sometimes signal liver cell damage. Regularly checking liver function through tests is advisable when undergoing long-term treatment.
Etodolac Interactions
Interaction with Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Agents
Using etodolac alongside anticoagulants (such as warfarin) or antiplatelet medications (like aspirin or clopidogrel) can raise the chance of bleeding occurrence. Experts suggest monitoring blood clotting factors since etodolac hinders the process of platelet aggregation and extends bleeding duration.
Risk of Nephrotoxicity with Diuretics and ACE Inhibitors
When etodolac is used alongside diuretics or angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, in individuals like those who are dehydrated or elderly, people can lead to an impact on kidney function known as a 'triple whammy' effect, resulting in sudden kidney problems.
- NSAID decreases the vasodilation caused by prostaglandins, in the blood vessels.
- ACE inhibitors work by widening the efferent arteriole.
- Diuretics help decrease the volume of fluid in blood vessels.
It's important to check kidney function when taking medications like this.
Potentiation with Other NSAIDs and Corticosteroids
Using NSAIDs or corticosteroids at the time can cause more severe gastrointestinal issues than using them individually, and it's best to avoid combining them unless absolutely necessary and, under close monitoring with proper protection, for the stomach.
Interaction with Methotrexate and Lithium
Etodolac could lead to decreased kidney function of methotrexate and lithium, which might cause levels, in the blood and lead to effects. There are consequences such as;
- The potential side effects of methotrexate include kidney damage.
- Decreased blood cell production.
Possible effects from using lithium may include reactions such, as tremors or confusion. Regular monitoring of plasma levels is advisable to ensure dosage adjustments as necessary.
Etodolac and Alcohol
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of bleeding when combining etodolac with alcohol as alcohol can independently irritates the stomach lining and worsen etodolac's erosive effects. It's best to steer clear of alcohol while undergoing treatment with etodolac. Please inform a doctor immediately if you experience any discomfort. If you think you'll be consuming a lot of alcohol consider using pain relievers.
Contraindications for Etofree Administration
History of Hypersensitivity to Etodolac or NSAIDs
It's important to note that Etofree (etodolac) should not be given to anyone who has had a reaction to etodolac or other NSAIDs like aspirin due to hypersensitivity issues as it may lead to reactions such as;
- Skin Swelling in tissues beneath the skin.
- Anaphylaxis.
- Stevens-Johnson or Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Such heightened sensitivity can be quite unpredictable. May manifest in individuals who have previously tolerated similar substances well, making it imperative, for sensitized patients to completely avoid exposure to such agents.
Active Peptic Ulcer Disease or Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Etodolac should not be given to individuals, with issues as it hampers the protective function of the mucosa by blocking prostaglandins and raises the possibility of developing ulcers and bleeding complications in that region. Hence, it is important to be cautious, in cases where such conditions are present;
- Recent or present gastrointestinal bleeding.
- A past occurrence of ulcers repeatedly returning or causing a hole, in the tissue.
- In groups of people s preferential consideration should be given to pain relievers or selective COX−2 inhibitors, along with measures to protect the stomach.
Severe Renal or Hepatic Dysfunction
When someone has kidney or liver issues, the way etodolac is broken down and removed from the body is greatly affected. This can result in a build-up. Worsening of organ problems. This warning applies to;
- Creatinine clearance is, than 30 milliliters, per minute.
- Severe liver damage, in Child Pugh Class C.
- Individuals experiencing decompensated cirrhosis or nephrotic syndrome.
With a level of impairment present, in a patient's condition it is necessary to make appropriate adjustments, to the dosage and closely monitor the situation.
Post-Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
Etodolac should not be used for managing pain during heart bypass surgery due, to an increased chance of heart and stroke-related blood clotting issues. It is recommended to consider using pain relievers that are not NSAIDs in such cases.
Etodolac Warnings and Important Safety Precautions
Risk of Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Long-term usage of etodolac is linked to a chance of issues happening when taken in high amounts.
- Heart attack
- Ischaemic stroke.
- Unexpected demise due to a heart attack.
The likelihood of this danger could go up when the treatment is extended to individuals, with existing heart conditions or risk factors, like diabetes or high cholesterol levels.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation Risks
Serious issues, with the stomach are a risk associated with NSAID treatment, and using Etodolac could potentially lead to;
- Ulcers in the stomach or the upper part of the intestine.
- GI bleeding occurring without any warning signs.
- An urgent surgical procedure is needed due to a perforation.
As one grows older and combines the use of corticosteroids with smoking and alcohol consumption, or has a history of ulcers beforehand, can escalate the risk significantly.
Hepatotoxicity and Renal Toxicity Warnings
Changes in liver enzyme levels like ALT and AST have been noted to lead to liver problems, including fulminant hepatitis and liver failure in rare instances, with the use of etodolac potentially affecting kidney function through alterations, in glomerular perfusion dynamics. Watch out for these signs;
- Signs of jaundice include yellowing of the skin or eyes colored urine, and pain or tenderness in the right abdomen.
- Signs of decreased urine output, like oliguria along with increasing levels of creatinine in the blood, or noticeable fluid buildup.
It's essential to stop the medication if there are signs of liver or kidney problems.
Monitoring Requirements During Prolonged Therapy
Patients who need to take etodolac for a period should undergo check-ups to ensure their safety, and the effectiveness of the treatment plan includes closely monitoring various key factors, such as
- Kidney function tests include measuring the levels of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
- Liver function tests include ALT (alanine aminotransferase) ALT, AST (aspartate aminotransferase), and alkaline phosphatase.
- Perform a blood test to check for anemia or bleeding issues in the hematologic profile.
Before starting any treatment plan or procedure, it's important to conduct tests followed by check-ups every 3 to 5 months or as needed based on your medical condition.
Careful Administration and Risk Mitigation
Use in Patients with Pre-existing Cardiovascular Disease
For individuals, with confirmed artery disease or conditions like disease or peripheral artery disease etodolac should only be considered if there are no other options available and even then it is advised to use the lowest effective dose for the shortest time possible based on the situation, at hand and consulting with a cardiologist may be beneficial.
Caution in Patients with Hypertension or Fluid Retention
Etodolac might worsen blood pressure. Causes water retention, which could make conditions, like congestive heart failure and chronic kidney disease, more complicated due, to certain mechanisms involved. Reduced production of kidney prostaglandin results, in the accumulation of sodium. Disruption of the effectiveness of diuretics. It's important to check blood pressure and monitor electrolyte levels in people with high blood pressure.
Liver and Kidney Function Monitoring Recommendations
Etodolac treatment should always include monitoring of liver and kidney function, in at-risk groups such as the elderly and those with existing conditions. A recommended guideline, for this monitoring involves;
- Baseline tests for liver and kidney function before starting treatment.
- Remember to conduct follow up tests after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment.
- Then every three months. Seek assessment if you experience symptoms such as yellowing of the skin (jaundice), tiredness (fatigue), swelling (edema,) or decreased urine production.
Act early to avoid harm to internal organs in individuals who use etodolac for an extended period of time.
Handling and Storage Instructions for Etofree
Ideal Storage Temperature and Humidity Conditions
It's important to store Etofree (etodolac) in a controlled room setting to keep its properties intact. The recommended storage temperature should be kept between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), allowing for excursions between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Ensuring chemical stability is crucial, for maintaining its effectiveness.
Remember to keep the medication from humidity and steer clear of storing it in bathrooms or near kitchen sinks. Remember to seal the container when you're not using it. Be sure to steer clear of sunlight or UV rays. High humidity levels exceeding 60 percent can speed up the breakdown of the ingredient in a medication. It may reduce its effectiveness, for treatment purposes.
Shelf Life and Packaging Information
Each pack of Etofree comes with a manufacturers expiry date, typically lasting for 24 to 36 months from the production date. It is enclosed in tamper-proof blister packs or durable HDPE bottles to shield against contamination and oxidation.
Storage guidelines also advise on storage methods; Remember to store the medicine in its packaging until it's time to take it. Steer clear of transferring items into packages.
It's not safe to use medication because its effectiveness and safety may not be reliable, after the expiration date listed on the package.
Safe Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Improperly discarding Etofree can lead to dangers and increase the chances of accidental ingestion occurring, so it is important to follow proper disposal methods such as;
- Utilizing pharmacy take back programs, for returning.
- If the tablets are not accessible, you can mix them with materials, like coffee grounds or cat litter in a sealed bag before disposing of them in the regular household trash bin.
It's important not to dispose of the medication, in the toilet unless regulatory guidance advises you to do so. Local environmental and pharmaceutical waste regulations must be followed when disposing of materials to reduce risks to health.
Overdose and Emergency Management of Etofree
Symptoms of Etodolac Overdose: Lethargy, Drowsiness, Nausea
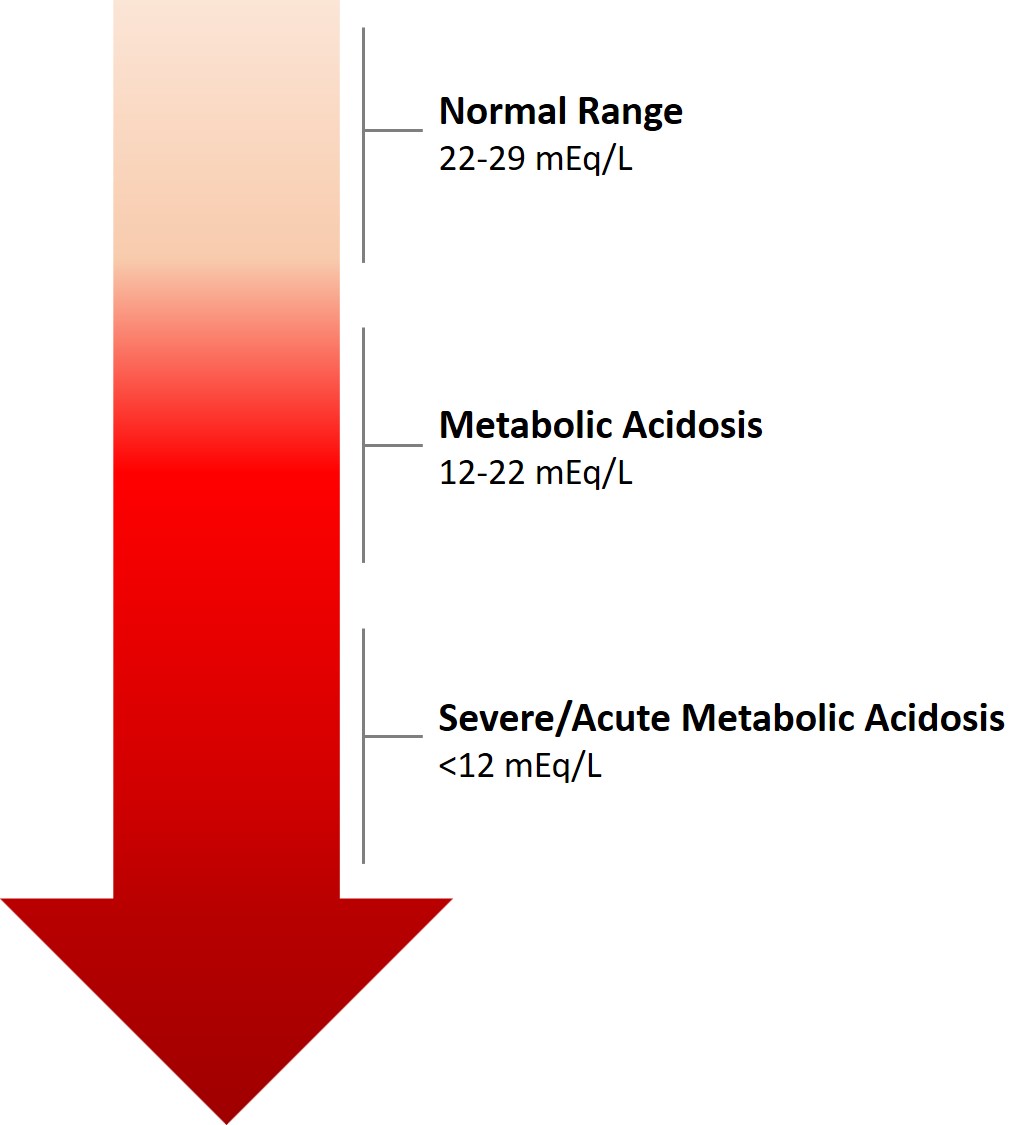
An accidental or intentional overdose of etodolac may lead to gastrointestinal symptoms that usually manifest shortly after ingestion. Feeling extremely sleepy or tired. Feeling sick to your stomach and experiencing discomfort in the abdomen. Feeling dizzy in some situations, the issues could worsen to metabolic acidosis, kidney failure, or depression of the nervous system.
Recommended Supportive Measures and Emergency Interventions
In the case of an overdose of etodolac there is no antidote, for treatment purposes and management focuses on providing support and addressing symptoms as they arise in a timely manner, which may include emergency actions.
- Administering lavage or activated charcoal within 1 to 02 hours of consumption is performed in a hospital environment.
- Promoting clearance through IV hydration. Keeping an eye on indicators, like signs and kidney function.
Patients need to be monitored for 4 to 5 hours after taking the medication orally or even longer if they have been exposed to a sustained release formula.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
It is important to seek attention if you suspect an overdose, and it is crucial to get emergency care without delay if the patient shows signs of the following symptoms;
- Changes in behavior or confusion may indicate a problem.
- Experiencing stomach pain or indications of bleeding in the tract.
- Manifestations of anaphylaxis could include challenges, with breathing or swelling of the face.
Intervening greatly enhances the outlook in cases of situations.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Patients
Proper Handling of Tablets and Capsules
To avoid contamination when handling Etodolac tablets and capsules make sure your hands are dry and clean. Follow these precautions;
- Remember not to crush or break prolonged release tablets.
- Please ensure that the item is kept out of the reach of children and pets.
- Avoid moving items, between containers without the assistance of a trained expert.
Ensuring the stability of the medication form is crucial, for drug delivery and absorption.
Instructions for Missed Doses and Accidental Ingestion
If you forget to take a dose of the medication and remember later, but the next dose is coming up soon anyway;
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it unless it's almost time for your scheduled dose. It's important not to take doses to make up for a missed one if you forget.
In some situations where accidental ingestion occurs, in children it's crucial to seek medical advice even if symptoms haven't appeared yet.
Safe Use Guidelines to Prevent Adverse Effects and Misuse
In order to reduce the chances of results occurring, patients are advised to follow these guidelines when using the medication;
- Remember to consume the medication along, with a meal or some milk to lower the chances of experiencing discomfort.
- Please refrain from using NSAIDs unless advised by a healthcare provider.
- It's best to avoid drinking alcohol while undergoing treatment.
- Remember to inform your healthcare provider if you experience any unfamiliar symptoms or side effects.
- Using information wisely leads to results.
Reduces the chances of negative reactions, to medication or treatment not working effectively.
Etofree, Etodolac FAQ
- Why is Etodolac discontinued?
- How Etodolac works?
- Is Etodolac like Tramadol?
- What is Etodolac used for?
- What is Etodolac?
- Is Etodolac a muscle relaxer?
- Is Etodolac a narcotic?
- Is Etodolac stronger than Ibuprofen?
- How long does Etodolac stay in the body?
- How long after taking Etodolac can i drink alcohol?
- What pain reliever can i take with Etodolac?
- Is Etodolac a controlled substance?
- What are Etodolac pills for?
- Are Etodolac and Etoricoxib same?
- Can Etodolac be taken with Tylenol?
- Can Etodolac cause constipation?
- Can Etodolac and Tramadol be taken together?
- How Etodolac works?
- Etodolac how long can i take it?
- When to stop Etodolac before surgery?
- Etodolac which group of drug?
- Which is stronger Etodolac or Ibuprofen?
- Will Etodolac help with headaches?
- Will Etodolac help toothache?
- Will Etodolac cause diarrhea?
- Will Etodolac make me sleepy?
- How long does it take for Etodolac to kick in?
- What not to take with Etodolac?
- Is Etodolac like Tramadol?
- What is the danger of Etodolac?
- Is Etodolac a strong painkiller?
Why is Etodolac discontinued?
Etodolac is still in use in some regions. Its availability may vary depending on market decisions by manufacturers or the introduction of alternative options or regulatory modifications— not necessarily linked to safety issues.
How Etodolac works?
Etodolac functions by blocking the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX-20 Enzymes), which decreases the generation of prostaglandins that cause inflammation, pain, and reduce swelling.
Is Etodolac like Tramadol?
Etodolac belongs to a class of medications known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), whereas Tramadol is categorized as a centrally acting opioid pain reliever, with unique mechanisms of action and associated risk factors.
What is Etodolac used for?
Etodolac works best for relieving mild to moderate pain and managing osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis by reducing inflammation and enhancing movement abilities.
What is Etodolac?
Etodolac is a medication prescribed for treating inflammation and pain related to conditions.
Is Etodolac a muscle relaxer?
Etodolac is not for muscle relaxation but rather for reducing pain and inflammation.
Is Etodolac a narcotic?
Etodolac is not categorized as a narcotic but rather falls under NSAIDs and lacks the qualities commonly associated with opioids.
Is Etodolac stronger than Ibuprofen?
In situations and for conditions treated with them both Etodolac might offer extended relief compared to Ibuprofeneven though their potency is similar and can vary based on the ailment being addressed.
How long does Etodolac stay in the body?
Etodolac has a life that typically lasts around 6 to 8 hours; however, its anti-inflammatory benefits may persist for, up to 24 hours, depending on the dose.
How long after taking Etodolac can i drink alcohol?
It's usually recommended to wait at a day after finishing your Etodolac medication before drinking alcohol to prevent any stomach or liver issues.
What pain reliever can i take with Etodolac?
It is generally safe to combine Acetaminophen (Tylenol). Always seek advice, from a doctor before taking Etodolac for pain relief.
Is Etodolac a controlled substance?
Etodolac is not classified as a controlled substance. Is not considered to have the potential, for abuse according to the Controlled Substances Act.
What are Etodolac pills for?
Etodolac tablets are prescribed for reducing inflammation and easing pain to enhance functionality in cases such, as arthritis.
Are Etodolac and Etoricoxib same?
Etodolac and Etoricoxib are not the kind of NSAIDs. Etoricoxib is specifically a COX-2 inhibitor, while Etodolac has some selectivity towards COX-2 inhibition well.
Can Etodolac be taken with Tylenol?
You can mix Etodolac, with Tylenol for pain relief since they operate in ways to manage pain.
Can Etodolac cause constipation?
Constipation may sometimes arise as a side effect of Etodolac; however gastrointestinal problems such, as nausea or heartburn are more commonly experienced.
Can Etodolac and Tramadol be taken together?
Etodolac and Tramadol can be prescribed together with monitoring to effectively address moderate, to severe pain levels.
How Etodolac works?
Etodolac how long can i take it?
Etodolac can be used for periods to alleviate pain or for extended periods to manage ongoing health issues; however, continuous use should be overseen due, to potential gastrointestinal and heart related concerns.
When to stop Etodolac before surgery?
Its usually recommended to discontinue Etodolac 3 to 7 days before surgery to reduce the risk of bleeding; however; the exact timing should be determined based on the procedure and guidance, from your doctor.
Etodolac which group of drug?
Etodolac is categorized as a Nonsteroidal Anti Inflammatory Drug (NSAID).
Which is stronger Etodolac or Ibuprofen?
Etodolac might provide benefits in terms of duration but comparing strengths relies heavily upon the dosage and individual reactions. Both are proving to be effective, as NSAIDs.
Will Etodolac help with headaches?
Etodolac might help with tension or inflammatory headaches. Its not usually the go to choice, for migraines.
Will Etodolac help toothache?
Etodolac has the ability to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation linked to problems such, as toothaches.
Will Etodolac cause diarrhea?
Diarrhea can occur as a side effect of Etodolac; however, it is not frequently observed compared to other symptoms associated with NSAIDs.
Will Etodolac make me sleepy?
Etodolac is typically not associated with causing drowsiness according to information. If a feeling of sleepiness does arise in some cases, for individuals or in combination, with other medications used concurrently.
How long does it take for Etodolac to kick in?
Etodolac usually starts easing pain within 30 to 60 minutes after taking it.
What not to take with Etodolac?
Be cautious not to mix NSAIDs or blood thinners with corticosteroids and specific antidepressants unless a doctor prescribes them together to prevent a chance of bleeding and stomach problems.
Is Etodolac like Tramadol?
Etodolac and Tramadol are quite distinct – one is an anti-inflammatory medication while the other is an opioid pain reliever.
What is the danger of Etodolac?
The primary concerns associated with Etodolac involves the possibility of stomach bleeding,g issues, kidney problems and allergic responses.
Is Etodolac a strong painkiller?
Etodolac is considered a NSAID that works well for reducing inflammatory pain; however it is not as effective, as opioids, for treating intense acute pain.