1. Introduction to Insuman Basal Injection
Insuman Basal Injection contains isophane insulin human, a biosynthetic form of human insulin. Designed for subcutaneous administration, it offers sustained glycemic control for individuals requiring basal insulin coverage. As an intermediate-acting insulin, it bridges the gap between short- and long-acting agents, offering flexibility in diabetes management.
- Classification: Intermediate-acting insulin
- Availability: Prescription-only medication
- Manufacturer: Sanofi-Aventis
- Regulatory Approval: Approved by EMA and widely available in multiple international markets
2. Approved Medical Uses of Insuman Basal Injection
Insuman Basal is clinically approved for glycemic regulation across a spectrum of diabetic conditions:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Essential component of basal-bolus insulin regimens
- Type 2 Diabetes: Indicated when oral hypoglycemic agents fail to achieve adequate control
- Gestational Diabetes: Used under medical supervision when dietary measures are insufficient
- Perioperative Management: Supports blood glucose control before, during, and after surgery
- Steroid-Induced Hyperglycemia: Helps manage elevated blood sugar levels due to corticosteroid therapy
3. Off-label and Investigational Uses of Insuman Basal
While not formally approved, Insuman Basal has shown clinical utility in several additional scenarios:
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Occasionally used with rapid-acting insulin in stabilized patients
- Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA): Administered as part of progressive insulin therapy
- Hospitalized Patients: Supports basal insulin needs during acute illness or fasting
- Metabolic Syndrome: Studied in insulin resistance cases where conventional measures fail
4. How Insuman Basal Works to Regulate Blood Glucose
Insuman Basal mimics the body’s natural basal insulin secretion. Its mechanism includes:
- Hepatic Suppression: Inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis to control fasting glucose
- Peripheral Uptake: Enhances glucose absorption into adipose and muscle tissues
- Pharmacokinetics: Onset occurs in 1–2 hours, peak effect around 4–10 hours, and duration up to 20 hours
- Comparative Action: Less rapid than short-acting insulin, more predictable than long-acting analogs
5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Insuman Basal
Insuman Basal dosage must be customized for each patient based on metabolic requirements and glucose monitoring results:
- Initial Dosing: Typically 0.2–0.4 IU/kg/day for insulin-naïve individuals
- Titration: Adjusted in 2–4 IU increments based on fasting blood glucose targets
- Frequency: Administered once or twice daily, depending on glucose profile
- Injection Sites: Rotate between the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm to avoid lipodystrophy
- Meal Timing: Injection typically 30 minutes before meals
- Combination Use: Can be mixed with short-acting insulins under proper conditions
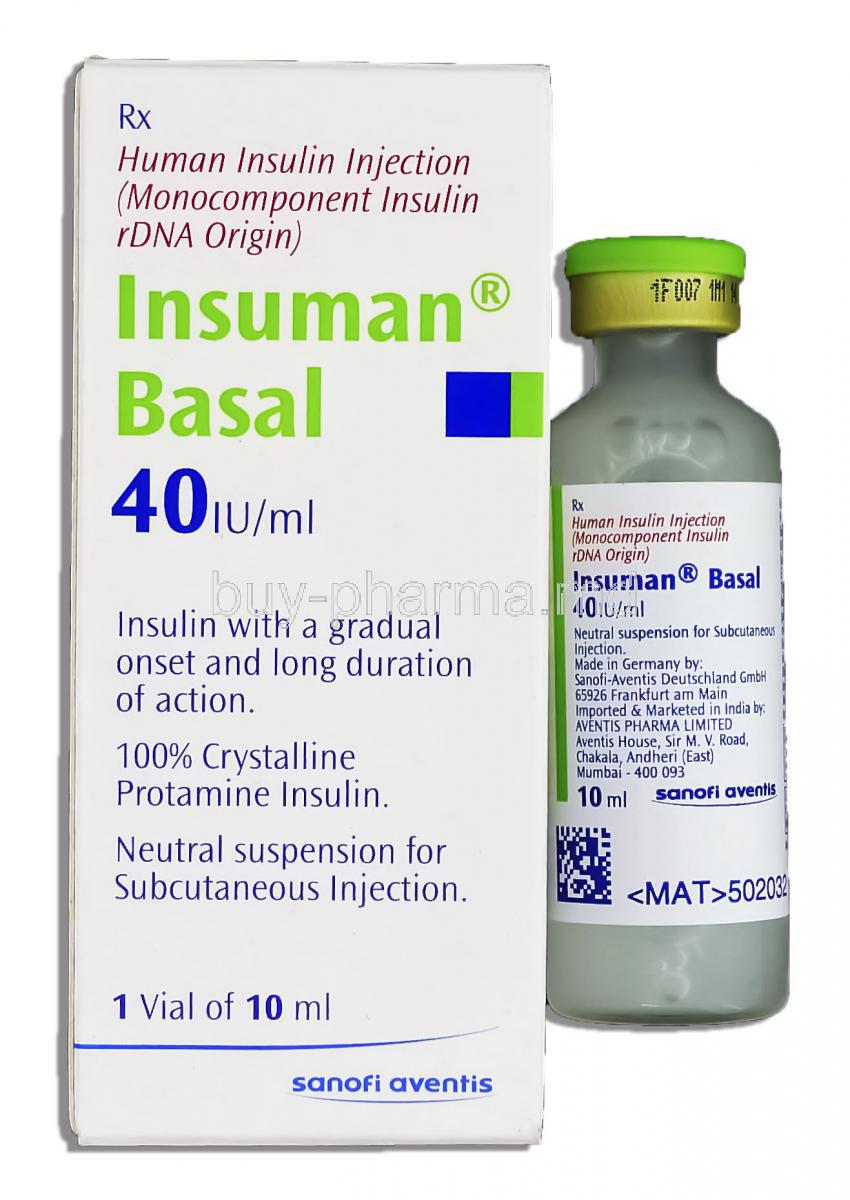
6. Composition and Formulation of Insuman Basal
Each Insuman Basal formulation is designed for reliability and consistency:
- Active Ingredient: Isophane insulin human (recombinant DNA origin)
- Excipients: Includes protamine sulfate, phenol, m-cresol, zinc chloride, and water for injection
- Forms: Supplied in vials, cartridges, or pre-filled SoloStar pens
- Concentration: 100 IU/mL
- Packaging: Available in 3 mL cartridges or 10 mL vials
7. Storage Requirements for Insuman Basal Injection
Proper storage is crucial to maintain insulin potency:
- Unopened: Store in refrigerator at 2°C–8°C; do not freeze
- In Use: Keep at room temperature below 25°C; use within 4 weeks
- Travel Precautions: Use insulated containers; avoid direct heat or cold exposure
- Disposal: Discard used needles and pens in approved sharps containers
8. Common Side Effects of Insuman Basal
Most adverse reactions are mild and manageable with proper guidance:
- Hypoglycemia: The most frequent side effect—monitor for dizziness, confusion, or sweating
- Injection Site Issues: Redness, itching, or mild swelling may occur
- Weight Gain: Linked to anabolic effects and improved glucose uptake
- Lipodystrophy: Fat redistribution due to repeated use of the same injection site
- Edema: Temporary sodium and water retention during dose initiation
9. Other Possible and Serious Adverse Reactions
Though rare, serious events may require medical attention:
- Allergic Reactions: Urticaria, rash, or life-threatening anaphylaxis in sensitized individuals
- Antibody Formation: May alter insulin efficacy over time
- Vision Changes: Temporary disturbances during early glucose normalization
- Localized Infections: Rare cases of abscesses or cellulitis at injection site
10. Drug and Food Interactions with Insuman Basal
Multiple agents may influence insulin action and glycemic control:
- Oral Antidiabetics: Enhanced effect with sulfonylureas or glinides
- Beta-Blockers: Can mask hypoglycemia symptoms such as tachycardia
- Corticosteroids: May counteract insulin and increase glucose levels
- Alcohol: Can potentiate hypoglycemia, especially in fasting states
- Herbal Remedies: Unregulated supplements may unpredictably alter insulin sensitivity
11. Contraindications to Using Insuman Basal
Insuman Basal must not be used in certain clinical situations where risks outweigh benefits. Contraindications are critical to ensure patient safety and prevent life-threatening complications.
- Hypersensitivity: Patients with known allergy to insulin human or any formulation excipient should not receive Insuman Basal due to the potential for severe allergic reactions.
- Active Hypoglycemia: Insuman Basal is contraindicated during episodes of low blood glucose, as administration can exacerbate the hypoglycemic state.
- Insulin Pumps: This preparation is not designed for continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) devices and must not be used in pump therapy.
- Unmanaged Insulin Allergy: In rare cases where desensitization fails, insulin therapy should be discontinued under expert guidance.
12. Important Warnings and Risk Considerations
Several scenarios necessitate heightened vigilance when initiating or maintaining therapy with Insuman Basal:
- Severe Hypoglycemia: A common risk when dosages are miscalculated or administered without proper food intake. Continuous monitoring and patient education are essential.
- Fasting and Physical Activity: Prolonged fasting or strenuous exercise without appropriate insulin adjustment increases hypoglycemia risk.
- Blood Glucose Surveillance: Regular monitoring allows for timely titration and helps prevent glycemic excursions.
- Insulin Transition: When switching from another insulin product, overlapping periods and pharmacodynamic variations must be carefully managed.
- Acute Stress Situations: Conditions such as infections, trauma, or surgery often alter insulin sensitivity and require individualized dose recalibration.
13. Guidelines for Careful Administration and Monitoring
Prudent administration of Insuman Basal involves structured monitoring and disciplined patient behavior:
- Glucose and HbA1c Checks: Periodic blood glucose tracking and quarterly HbA1c evaluations are essential to assess long-term glycemic control.
- Device Training: Proper education on the use of syringes or insulin pens minimizes administration errors and enhances self-efficacy.
- Inspection of Injection Sites: Monitoring for signs of lipodystrophy or infection ensures local tissue health is preserved.
- Consistent Lifestyle Patterns: Stable mealtime and activity routines support predictable insulin response and reduce variability in glycemic outcomes.
- Emergency Preparedness: Patients and caregivers should be instructed on identifying hypoglycemia and using emergency glucagon kits when necessary.
14. Important Precautions Before and During Use
Certain medical and behavioral variables influence insulin effectiveness and safety:
- Impaired Renal or Hepatic Function: Reduced clearance may require dose reduction and closer surveillance.
- Concomitant Injections: When co-administered with agents like GLP-1 receptor agonists, timing and site separation must be observed.
- Exercise Impact: Intensity and duration of physical activity can markedly alter insulin sensitivity.
- Dietary Considerations: Meal composition and carbohydrate timing should be consistent and coordinated with insulin action profiles.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol interferes with glucose metabolism and increases the risk of unrecognized hypoglycemia, especially during fasting.
15. Administration of Insuman Basal to Elderly Patients
Older adults present unique challenges and increased sensitivity to insulin therapy:
- Renal Decline: Decreased kidney function prolongs insulin action and necessitates lower dosages.
- Hypoglycemia Vulnerability: The elderly are more susceptible to both unrecognized and symptomatic hypoglycemia.
- Dose Initiation: Begin with conservative doses and titrate slowly based on response and tolerability.
- Cognitive and Physical Impairment: These may hinder the ability to self-administer injections or recognize symptoms, requiring caregiver involvement.
16. Use of Insuman Basal in Pregnant and Nursing Women
Insuman Basal is suitable for use in pregnancy when clinically indicated, with careful monitoring:
- Placental Transfer: Human insulin does not cross the placenta and is considered safe for fetal development.
- Trimester Adjustments: Insulin requirements typically rise during the second and third trimesters and may rapidly decline postpartum.
- Postpartum Management: Immediate reassessment of insulin needs is crucial following childbirth to avoid hypoglycemia.
- Lactation: Compatible with breastfeeding, as insulin is not excreted in significant quantities in breast milk.
17. Insuman Basal Use in Pediatric Populations
Pediatric use is permitted under specialist supervision with customized dosing:
- Approved Age Groups: Insuman Basal is approved for use in children with Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- Dose Initiation: Calculated based on body weight and metabolic status, typically starting at 0.2–0.4 IU/kg/day.
- Parental Training: Parents and caregivers must be educated in insulin administration and monitoring practices.
- Monitoring Targets: Age-appropriate glucose targets and flexible insulin titration help minimize risk and optimize control.
18. Management of Insuman Basal Overdosage
Overdosage with Insuman Basal may lead to life-threatening hypoglycemia, requiring urgent intervention:
- Initial Signs: Drowsiness, tremors, palpitations, confusion, and sweating signal early-stage hypoglycemia.
- Immediate Action: Oral glucose, sweet snacks, or sugar-containing fluids for conscious patients; injectable glucagon or IV dextrose for unconscious patients.
- Hospital Protocols: Severe cases demand emergency hospitalization with cardiac and neurologic monitoring.
- Long-Term Effects: Repeated hypoglycemic episodes may impair cognitive function and increase the risk of severe complications.
19. Safe Handling and Disposal of Insuman Basal
Proper handling and disposal protocols help prevent injuries, contamination, and environmental hazards:
- Patient and Caregiver Safety: Always check expiration dates and avoid reusing disposable devices.
- Needlestick Prevention: Do not recap used needles; use needle removal devices when applicable.
- Sharps Disposal: Place used syringes and pen needles in designated sharps containers immediately after use.
- Environmental Responsibility: Do not discard insulin pens or containers in household waste; follow local pharmaceutical waste disposal guidelines.
Insuman Basal Injection FAQ
- What is insuman basal?
- How long does Insuman basal last in the body?
- What is a basal injection?
- What is the duration of action of Insuman basal?
- What is the alternative for Insuman basal?
- When is the best time to take basal insulin?
- Where is the best place to inject basal insulin?
- Can you take basal insulin twice a day?
- How many units of insulin is normal per day?
- Where not to inject insulin?
- What happens if insulin is taken after food?
- How many times a day do you take basal insulin?
- What happens if you miss your basal insulin?
- How do you know if your basal insulin is correct?
- Why is basal insulin given at night?
- What is Insuman basal?
What is insuman basal?
Insuman Basal is an intermediate-acting insulin suspension containing isophane insulin
How long does Insuman basal last in the body?
Between 11-20 hours
What is a basal injection?
Lasting insulin, known as basal shot is typically administered twice daily.
What is the duration of action of Insuman basal?
Typically, consumed one or two times daily, it begins to take effect within two hours and remains active for 18 to 24 hours.
What is the alternative for Insuman basal?
Insulin glargine 100 U/mL, insulin glargine 300 U/mL, insulin detemir, or insulin degludec
When is the best time to take basal insulin?
Morning or at bedtime
Where is the best place to inject basal insulin?
The primary injection sites typically include your stomach (in a curve, below your navel), the parts of your thighs, and your buttocks.
Can you take basal insulin twice a day?
Yes
How many units of insulin is normal per day?
40 units
Where not to inject insulin?
It's important to avoid injecting insulin into muscles, near bones, or veins, and refrain from injecting it in areas like the face or scalp. It's best to steer clear of the navel and the hands and feet when administering insulin.
What happens if insulin is taken after food?
The likelihood of experiencing hypoglycemia, where blood sugar levels may drop.
How many times a day do you take basal insulin?
Basal insulins are commonly consumed twice daily.
What happens if you miss your basal insulin?
Might increase your risk of hypoglycemia
How do you know if your basal insulin is correct?
Your blood sugar levels should remain relatively stable throughout the night if the insulin dosage is accurate. If your blood sugar consistently increases overnight, it could mean that your basal insulin dose is too low. However, a consistent decrease in blood sugar overnight may suggest that your basal insulin dose is too high.
Why is basal insulin given at night?
Since intermediate duration basal insulin remains effective, for 8 to 12 hours at a time, the individuals undergoing this treatment do not require insulin during the daytime.
What is Insuman basal?
Insuman Basal is a type of insulin that acts in the range and consists of insulin.