Levodopa/ Benserazide
- Introduction
- Composition of Levodopa/Benserazide
- How Levodopa/Benserazide Works
- Approved Uses of Levodopa/Benserazide
- Off-Label Uses of Levodopa/Benserazide
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects of Levodopa/Benserazide
- Common Side Effects of Levodopa/Benserazide
- Drug Interactions with Levodopa/Benserazide
- Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications for Levodopa/Benserazide
- Careful Administration and Monitoring Guidelines
- Administration in Special Populations
- Overdose of Levodopa/Benserazide
- Storage and Handling Precautions for Levodopa/Benserazide
Introduction
Overview of Levodopa/Benserazide:
Levodopa/Benserazide is a medication blend commonly prescribed for managing Parkinson's disease symptoms. It helps restore dopamine levels in the brain to alleviate the movement issues associated with Parkinsonism. Levodopa serves as a dopamine precursor. It works together with Benserazide to prevent the degradation of Levodopa before it reaches the brain through the blood-brain barrier.
Historical development and clinical significance:
The emergence of Levodopa/Benserazide has greatly transformed the treatment options available for individuals with Parkinsons' disease by offering a solution to address conditions characterized by a lack of dopamine in the brain.
Levodopa/Benserazide continues to be the mainstay of treatment for Parkinson's disease due to its proven effectiveness in alleviating symptoms like tremors and stiffness while also being useful for conditions related to parkinsonism in the field of care.
Composition of Levodopa/Benserazide
Active ingredients: Levodopa and Benserazide:
Levodopa acts as the treatment by changing into dopamine; meanwhile Benserazide keeps Levadopa intact until it reaches the brain by inhibiting dopadecarboxylase enzymes.
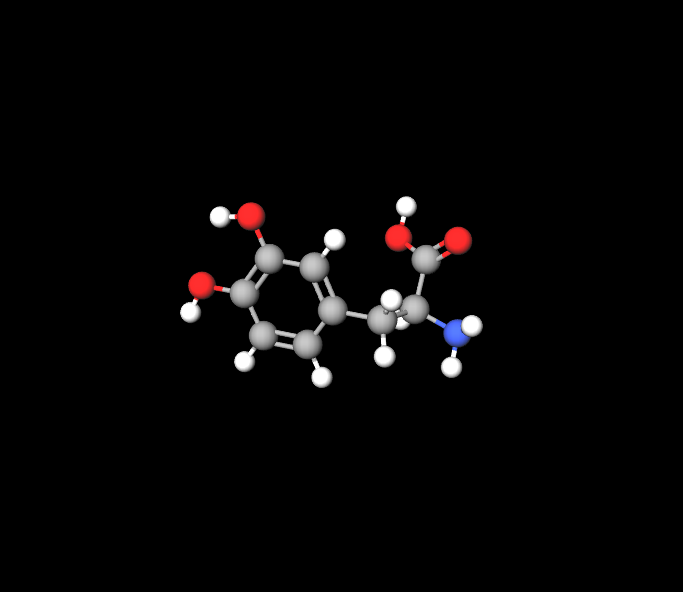
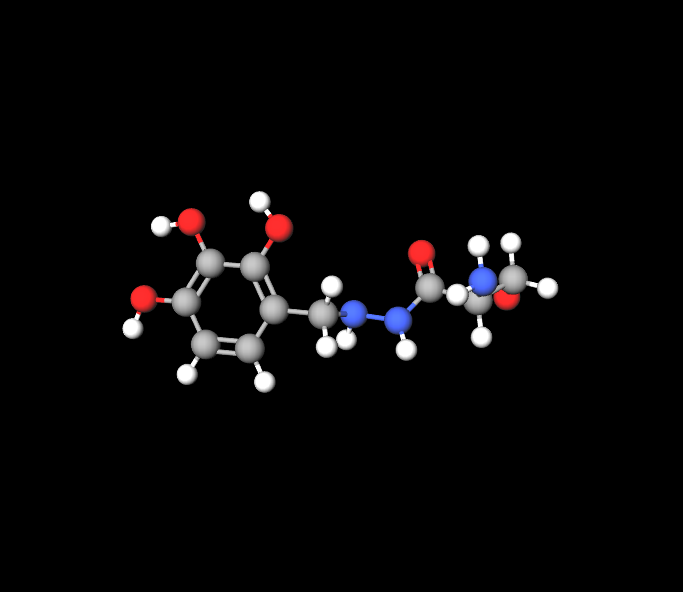
Role of each component:
Levodopa increases dopamine production in the system, while Beneserazide blocks the breakdown of Levopoda outside the brain to ensure it reaches its intended destination effectively.
Available formulations and strengths:
Levodopa/Benserazide comes in forms, like tablets and capsules, with strengths typically starting from 100 mg of Levopoda and 25 mg of Benserazide to doses based on treatment needs.
Carbidopa-levodopa
Carbidopa-levodopa addresses Parkinson's disease symptoms by boosting dopamine levels in the brain, which is a component in regulating body movements and coordination. This results in a reduction of symptoms like stiffness and tremors associated with Parkinson's.
How Levodopa/Benserazide Works
Mechanism of action in the brain:
Once Levopoda enters the brain through the blood-brain barrier, it transforms into dopamine, a neurotransmitter that affects motor functions.Benserazide plays a role in preventing Levopoda from breaking down outside the nervous system and helping more of it reach there.
Levodopaâs role in dopamine production:
Dopamine is crucial for smooth, controlled muscle movements. Levodopa compensates for the brain's inability to produce adequate dopamine in conditions like Parkinson's disease.
Benserazideâs function as a decarboxylase inhibitor:
Benserazide acts on peripheral tissues, inhibiting the enzyme dopa decarboxylase. This allows Levodopa to remain intact longer, enabling more of it to enter the brain, where it can be transformed into dopamine.
Impact on motor symptoms in Parkinsonâs disease:
By boosting the dopamine levels in the brain's chemistry through Levodopa/Benserazide treatment, it is able to alleviate the signs of Parkinsons' disease, like tremors and muscle stiffness, while also improving movement speed.

Approved Uses of Levodopa/Benserazide
Parkinsonâs disease:
Parkinsonism secondary to brain injury or encephalitis:
Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) in certain cases:
Off-Label Uses of Levodopa/Benserazide
Potential benefits in treating dystonia:
Use in refractory depression:
Certain studies in the field have looked into using a combination of Levodopa and Benserazide for cases of depression that do not respond well to treatment; however, more research is needed to validate its effectiveness in situations.
Investigational use in Huntingtonâs disease and Touretteâs syndrome:
Levodopa/Benserazide is currently under study for its advantages in neurological conditions like Huntingtons' disease and movement disorders such as Tourettes syndrome that are linked to issues with dopamine levels.
Dosage and Administration
Standard dosing protocols for Parkinsonâs disease:
Starting doses are typically conservative, at 100 mg of Levopoda and 25 mg of Benserazide. They can be adjusted as needed, depending on how the patient responds to the medication.
Titration and individualized dosing:
The dosage should be adjusted based on the patient's requirements to find the balance between effectiveness and possible side effects.It's typical to make changes as the illness advances.
Maximum levodopa dosage
The typical dosage is generally no higher than 525 mg of carbidopa and 2100 mg of levodopa split into up to four doses per day.
Best practices for administration (timing, with or without food):
Levodopa/Benserazide is usually recommended to be taken on a stomach to improve absorption; however, it can also be consumed with food to alleviate any digestive discomfort that may arise. When dealing with patients who have liver or kidney issues, a careful adjustment of the dosage is necessary to prevent any side effects.
In terms of treatment duration and ongoing management plans it is common for Levodopa/Benserazide to be prescribed for the haul with regular adjustments in dosages as the disease advances or as the patients tolerance changes, over time.
Side Effects of Levodopa/Benserazide
Overview of common side effects: Like any medication, Levodopa/Benserazide may cause a variety of side effects, though these often subside as the body adjusts to the treatment.
- Nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal discomfort: These are among the most common side effects, particularly during the early stages of treatment.
- Orthostatic hypotension: Sudden drops in blood pressure upon standing can occur, especially in the elderly or those on high doses.
- Dyskinesia: Involuntary movements, or dyskinesias, may develop with long-term use, often requiring dose adjustments.
Less common side effects: Certain side effects are less frequent but can still impact patients significantly.
- Psychiatric disturbances (hallucinations, confusion): These may occur, particularly in older adults or those with a history of cognitive impairment.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Although rare, arrhythmias can occur, especially in those with pre-existing heart conditions.
Serious side effects requiring medical attention: In rare cases, severe side effects may necessitate immediate medical intervention. These include extreme mental changes, severe chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
Common Side Effects of Levodopa/Benserazide
While Levodopa/Beneserazide is quite effective, in treatment terms, its usage can lead to some commonly reported side effects, such as:
- Feeling sick
- Throwing up
- Feeling dizzy or light-headed
- Mouth feeling parched
- Feeling tired or sleepy
- Orthostatic hypotension refers to a decrease in blood pressure when a person stands up.
- Involuntary muscle movements, also known as dyskinesia, can also occur.
Managing mild side effects:
Some patients may experience side effects that can be easily controlled with simple changes in their routine, like having a light snack with the medication to reduce nausea or standing up slowly to address dizziness from sitting or lying down positions.
Patient education on identifying common side effects early:
Patients should be knowledgeable, about side effects to take action and ensure that their treatment stays effective and manageable by recognizing early signs and communicating openly with healthcare providers to handle these effects effectively
Drug Interactions with Levodopa/Benserazide
Levodopa/Benserazide is recognized for its ability to interact with medications and dietary elements in different ways.
Interaction with other Parkinsonâs medications:
MAO B inhibitors like selegiline and COMT inhibitors like entacapone are commonly prescribed alongside Levodopa/Benserazide to improve their efficacy; nevertheless, careful dosage and monitoring are crucial to prevent complications such as heightened dyskinesia.
Potential interactions with antipsychotics, antihypertensives, and antidepressants:
Some antipsychotic drugs, like haloperidol, could work against Levodopa by blocking dopamine receptors in the body's system and causing interference with its effects on the condition being treated. It is also recommended to be careful when mixing Levodopa/Benserazide with medications for blood pressure or depression because this mix can result in blood pressure or other unwanted reactions.
Dietary interactions:
Consumption of meals high in protein may impact the absorption of Levodopa and decrease its effectiveness for patients taking it as medication.As a result of this interference, between high protein meals and Levodopa absorption rates, persons are frequently recommended to limit their protein intake and try to take it from their Levodopa doses whenever feasible.
Importance of monitoring for drug interactions in polypharmacy patients:
Patients who are prescribed medications, known as polypharmacy, should receive monitoring for potential drug interactions to ensure their treatment is effectively managed and adjusted as needed through regular consultations with healthcare professionals.
Warnings and Precautions
Managing Levodopa/Benserazide treatment necessitates cautious attention due to risks and precautions that need to be taken into account.
Risks of sudden discontinuation:
Stopping Levodopa/Benserazide suddenly can have repercussions such as triggering Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (a critical condition marked by muscle stiffness and changes in mental state). It's crucial to reduce the dosage under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Risk of impulse control disorders:
Some individuals might encounter challenges with managing their impulses, like engaging in gambling or shopping sprees or showing behavior as a possible side effect of the medication's impact on dopamine levels; therefore, close monitoring is recommended.
Worsening of glaucoma:
Patients with narrow-angle glaucoma should be cautious when using Levodopa/Benserazide as it may worsen their symptoms of the condition. It is advisable for individuals, with an occurrence of glaucoma to undergo eye examinations.
Caution in patients with severe cardiovascular or respiratory disease:
Patients who have heart or lung issues should be careful when using this medication because it may worsen their symptoms or have adverse interactions with other treatments.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) risk with abrupt cessation:
When stopping the medication of patients who need to discontinue, it is vital to reduce the dosage to avoid triggering NMS by withdrawal symptoms.
Contraindications for Levodopa/Benserazide
Known hypersensitivity:
Patients who have a sensitivity to Levopoda or Benserazide should steer clear of this medication.
Narrow-angle glaucoma:
Levodopa/Benserazide should not be used by people with narrow-angle glaucoma as it can make their eye pressure worse.
History of severe psychiatric disorders:
Individuals who have previously experienced health conditions, like schizophrenia or psychosis, are advised against using Levodopa/Benserazide as it may worsen their psychiatric symptoms.
Concurrent use of non-selective MAO inhibitors:
It's not recommended to mix Levodopa/Benserazide with selective MAOI drugs because it can cause a dangerous increase in blood pressure, known as a hypertensive crisis. Make sure to stop taking MAOI medications least two weeks before starting on Levodopa/Benserazide treatment.
Careful Administration and Monitoring Guidelines
Ensuring the safety and effectiveness of Levodopa/Benserazide therapy requires management and consistent monitoring.
Monitoring blood pressure during initial treatment:
Levodopa/Benserazide may lead to hypotension particularly at the beginning of treatment phase.It is essential to check blood pressure to prevent any negative effects.It is important to assess motor function and symptom management in patients.They should be checked regularly for any changes, in motor function either positive or negative.Dosage adjustments may be required as the condition evolves.
Liver and kidney function monitoring:
Regular examinations to evaluate the functionality of the liver and kidneys are advised for individuals, with existing liver or kidney issues.
Periodic psychiatric evaluations:
Patients should have health checkups due to the possible psychiatric side effects they may experience – especially those with a background of mental health conditions.
Administration in Special Populations
13.1 Administration to Elderly Patients
When prescribing Levodopa/Beneserazide to adults, care may be needed as they are more sensitive to its effects and may need smaller doses to prevent severe side effects like orthostatic hypotension and cognitive changes. Due to common concerns in this patient group, it is important to monitor decline and the risk of falls in patients taking Levodopa/Beneserazide. Periodic evaluations can assist in reducing these dangers.
13.2 Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Risks associated with use during pregnancy:
There isn't information about the safety of Levodopa/Benserazide when used during pregnancy, so it's important to consider both the possible risks to the fetus and the advantages for the mother.
Recommendations for breastfeeding mothers:
It is possible for Levodopa to transfer to breast milk; however, the impact it may have on nursing infants is not well understood yet, so it is advisable, for mothers who are breastfeeding, to seek advice from their healthcare provider before taking this medication.
Alternative therapies for pregnant patients with Parkinsonâs disease:
Sometimes, pregnant women might explore treatments to reduce risks to the baby.
13.3 Administration to Children
While Levodopa/Benserazide is mainly intended for adults, as per use guidelines; there are situations where healthcare providers might consider prescribing it to patients, off label.
Off-label use in pediatric patients:
Sometimes, Levodopa/Benserazide is prescribed for treating conditions like dopamine-responsive dystonia in kids in uncommon instances.
Dosing considerations for children:
Dosage, for children, should be. Closely observed to prevent any adverse reactions.
Safety data and clinical trials in pediatric populations:
The safety and effectiveness of Levodopa/Benserazide, in children are not fully proven yet; more research is required to understand its effects, over the term.
Overdose of Levodopa/Benserazide
An overdose of Levodopa/Benserazide can result in health issues that necessitate prompt medical attention.
Signs and symptoms of overdose:
Signs of taking much of a substance could entail intense feelings of sickness and throwing up uncontrollably as well as experiencing sudden body movements without your control or feeling disoriented and restless along, with irregular heartbeats.
Emergency treatment protocols:
In case of an overdose occurrence, it is necessary to provide care, which might involve lavage treatment using activated charcoal and addressing symptoms accordingly.
Long-term consequences of overdose:
Extended exposure to medication, may result in long-term neurological harm or heart-related issues, so it's important to carefully watch over patients for any enduring consequences.
Poison control recommendations:
It's important to get in touch with poison control centers if there's been an overdose so they can offer advice on what steps to take next.
Storage and Handling Precautions for Levodopa/Benserazide
Storing and handling Levodopa/Benserazide correctly is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Proper storage conditions (temperature, humidity):
Be sure to keep Levodopa/Benserazide in a dry place at room temperature to maintain its effectiveness and quality over time.
Instructions for patients on medication handling:
Patients are encouraged to use dry hands when handling their medication and store it in the original container to prevent any risk of contamination.
Disposal of unused or expired medications:
Make sure to get rid of any leftover or expired Levodopa/Benserazide by following the rules and using a take back program if possible to protect the environment from contamination.
Safety considerations for caregivers:
Care providers need to be cautious when dealing with the medication. Particularly if they are expecting a baby or have any health issues that could be influenced by coming into contact with the medication.
Levodopa/ Benserazide FAQ
- What are the side effects of too much carbidopa/levodopa?
- What happens if you take levodopa and you don't have parkinson's?
- How long does it take levodopa/carbidopa to take effect?
- What if i take a double dose of carbidopa/levodopa?
- What is a low dose of levodopa?
- What happens if you miss a dose of carbidopa levodopa?
- How to stop carbidopa-levodopa?
- What happens when you stop taking carbidopa/levodopa?
- How long does carbidopa levodopa stay in your system?
- What happens if you take too much carbidopa levodopa?
- How long does it take for carbidopa levodopa to work?
What are the side effects of too much carbidopa/levodopa?
Experiencing discomfort in the stomach area · experiencing an unpleasant taste · frequent belching · altered sense of taste · sweating darker than usual · seeing two images at once · pupils appearing larger, than normal.
What happens if you take levodopa and you don't have parkinson's?
Taking levodopa without having Parkinson's' Disease should not cause any consequences.
How long does it take levodopa/carbidopa to take effect?
The time it takes for a dose to become varies among individuals but generally ranges from 30 minutes to an hour.
What if i take a double dose of carbidopa/levodopa?
Adverse reactions consisted of an onset of blood pressure followed swiftly by low blood pressure lasting for a few hours and prolonged symptoms of dizziness upon changing posture.
What is a low dose of levodopa?
Starting the treatment, with doses is advisable. The suggested daily dosage ranges from 300, to 1200 mg ( if well tolerated) split into 3 to 12 doses throughout the day.
What happens if you miss a dose of carbidopa levodopa?
If you forget to take a dose of this try to take it as soon as you remember. However if its nearly time, for your dose it's better to skip the missed one.
How to stop carbidopa-levodopa?
Please consult with your healthcare provider before discontinuing the use of levodopa and carbidopa to avoid any risks associated with cessation of these medications, such as feverishly rigid muscles that trigger unusual bodily movements and confusion; gradually tapering off the dosage is typically recommended by medical professionals.
What happens when you stop taking carbidopa/levodopa?
Remember to keep taking your levodopa and carbidopa medications even if you're feeling fine. Don't discontinue these medications without consulting your doctor. Stopping suddenly could lead to a condition with symptoms like fever and muscle stiffness along, with unusual body movements and confusion.
How long does carbidopa levodopa stay in your system?
Patients diagnosed with Parkinsons disease experience peak levels of levodopa in their bloodstream within one hour after taking extended release carbidopa–levodopa (known as Rytary or IPHX66 [ER CD LD]) and these levels remain stable for a duration of 4 to 5 hours.
What happens if you take too much carbidopa levodopa?
Signs of taking medication can lead to serious symptoms, like extreme lightheadedness and irregular heartbeats, as well as changes in mental state, such as agitation. Should be watched out for diligently when using this drug treatment regimen is ongoing; be sure to attend all scheduled medical appointments and tests as recommended by your healthcare provider including blood tests and assessments of heart,k idney and liver function in addition, to monitoring blood pressure levels regularly.
How long does it take for carbidopa levodopa to work?
The time it takes for a dose to take effect varies from person to person; however, it generally ranges from 30 minutes to an hour.