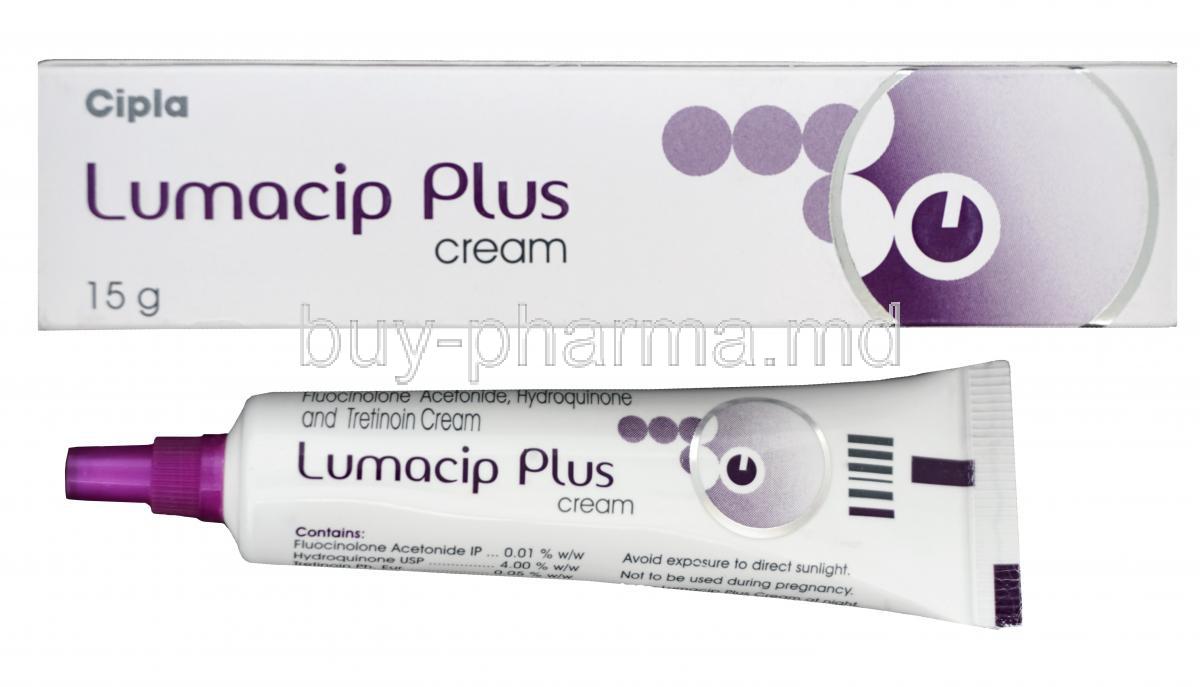
1. Introduction to Lumacip Plus Cream
Lumacip Plus Cream is a multi-component topical formulation categorized under dermatological therapeutics. It combines a high-potency corticosteroid, a broad-spectrum antifungal, and a potent antibacterial agent, making it a comprehensive treatment for inflammatory dermatoses complicated by secondary infections.
The cream is designed to address mixed infections of fungal and bacterial origin, while concurrently reducing inflammation and pruritus. This synergistic effect enhances the efficacy and accelerates symptomatic relief. Lumacip Plus is widely available in regulated pharmaceutical markets as a prescription-only topical medication.
2. Composition and Active Ingredients
Each gram of Lumacip Plus contains a unique combination of three pharmacologically active ingredients:
- Clobetasol Propionate 0.05% w/w: A super-potent corticosteroid that suppresses inflammatory responses, providing rapid relief from erythema, swelling, and pruritus.
- Miconazole Nitrate 2% w/w: An imidazole derivative effective against dermatophytes and yeasts. It inhibits fungal growth by disrupting ergosterol synthesis.
- Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% w/w: A broad-spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis, particularly effective against gram-negative skin pathogens.
Inactive ingredients may include paraffin, cetostearyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and purified water. Lumacip Plus is supplied in cream form, typically in 15g and 30g laminated tubes.
3. Mechanism of Action: How Lumacip Plus Works
The therapeutic efficacy of Lumacip Plus derives from the targeted mechanisms of its components:
- Clobetasol Propionate binds to glucocorticoid receptors in dermal cells, inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reducing vasodilation and edema.
- Miconazole Nitrate exerts its fungicidal effect by blocking ergosterol biosynthesis, thereby compromising fungal cell membrane integrity and function.
- Neomycin Sulphate impairs bacterial replication by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, leading to erroneous protein translation and bacterial cell death.
Together, these agents act synergistically to combat inflammation, infection, and microbial colonization in complex dermatological conditions.
4. Medical Uses of Lumacip Plus
4.1 Approved Indications
Lumacip Plus is indicated in dermatological conditions with suspected or confirmed fungal and bacterial co-infection, including:
- Dermatophytoses: Tinea corporis (body ringworm), tinea cruris (jock itch), and tinea pedis (athlete’s foot)
- Secondary infected dermatoses: Inflammatory skin disorders complicated by microbial contamination
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Particularly when infection is present
- Eczema with microbial superinfection: Including chronic or acute forms with signs of bacterial/fungal overgrowth
4.2 Off-Label Uses
Although not officially approved, Lumacip Plus is often prescribed off-label for the following conditions under clinical discretion:
- Lichen planus with secondary infection: For reducing inflammation and clearing microbial colonization
- Inflammatory acne lesions: With suspected bacterial contamination or fungal involvement
- Intertrigo: Especially when arising in warm, moist skin folds prone to polymicrobial infection
- Non-specific pruritic dermatitis: With underlying bacterial overgrowth
5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
The standard application involves a thin film applied over the affected area:
- Recommended dosage: Apply twice daily, morning and evening
- Duration: Treatment should not exceed 2 weeks unless directed by a healthcare provider
- Application method: Clean and dry the affected area. Apply sparingly and rub gently until absorbed
- Site-specific caution: Avoid face, axilla, and groin unless advised. Use with extreme caution in areas with thin skin
Treatment tapering may be necessary to avoid rebound effects.
6. Side Effects and Risk Profile
6.1 Common Side Effects
Most adverse reactions are localized and mild. They may include:
- Transient burning or stinging sensation
- Pruritus, dryness, or irritation
- Mild erythema or desquamation (peeling)
- Folliculitis or acneiform eruptions
6.2 Serious or Rare Side Effects
Prolonged use or application over large surfaces may lead to more serious outcomes:
- Cutaneous atrophy, striae distensae, and telangiectasia
- Hypopigmentation in melanated skin
- HPA-axis suppression and adrenal insufficiency
- Allergic contact dermatitis or secondary infection due to immunosuppression
7. Drug Interactions and Incompatibilities
Although topical, Lumacip Plus may interact with systemic and other topical agents:
- Aminoglycosides: Co-administration with systemic aminoglycosides increases the risk of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity
- Topical corticosteroids: Risk of cumulative systemic absorption and local side effects
- Other antifungals: May potentiate or antagonize antifungal effects if not carefully selected
- Occlusive dressings: Significantly enhance systemic absorption, increasing toxicity risk
Patients should inform healthcare providers about all concurrent medications to avoid adverse interactions.
8. Contraindications
Lumacip Plus should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its active components—clobetasol propionate, miconazole nitrate, or neomycin sulphate—or any of the formulation's excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions can manifest as local irritation, urticaria, or in rare cases, systemic anaphylaxis.
The cream is contraindicated in the presence of certain skin infections and dermatologic conditions:
- Viral dermatoses: Including herpes simplex (cold sores, genital herpes) and varicella (chickenpox), as corticosteroids can exacerbate viral replication and dissemination.
- Cutaneous tuberculosis or syphilis: These infectious lesions may worsen with immunosuppressive corticosteroid use.
- Perioral dermatitis and rosacea: These chronic facial dermatoses are known to flare with potent corticosteroid exposure, particularly when applied to the face.
9. Warnings and Precautions
Careful clinical judgment must guide the use of Lumacip Plus. Prolonged or indiscriminate application may lead to systemic corticosteroid absorption, resulting in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, Cushingoid features, or delayed wound healing.
- Avoid applying to large surface areas or under occlusive dressings, as this significantly enhances systemic penetration.
- Neomycin, while effective topically, carries ototoxic and nephrotoxic risks, particularly if absorbed systemically in large quantities or over compromised skin.
- Strictly for external use. Do not apply to mucosal surfaces such as inside the mouth, nose, or near the eyes to prevent irritation or systemic exposure.
Infections unresponsive to the cream after a reasonable duration should prompt discontinuation and further evaluation.
10. Special Considerations for Specific Populations
10.1 Use in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often exhibit diminished dermal integrity. Skin becomes thinner, less elastic, and more susceptible to corticosteroid-induced atrophy.
- Use a reduced frequency of application (e.g., once daily instead of twice).
- Limit the treatment area and duration to mitigate risk of systemic effects.
10.2 Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
Data regarding the systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids during pregnancy is limited. Although systemic exposure is typically low, precaution is advised:
- Use only if clearly necessary, under physician supervision.
- Avoid application to large areas or broken skin, where absorption is likely increased.
- Nursing mothers should avoid applying the cream to the breast area to prevent infant exposure through ingestion.
10.3 Use in Pediatric Patients
Children are particularly vulnerable to the systemic effects of topical corticosteroids due to their higher surface area-to-body weight ratio. Risks include growth retardation and suppression of adrenal function.
- Limit use to short durations (5–7 days) and under strict medical supervision.
- Do not use in children under 12 years unless specifically prescribed by a pediatric specialist.
11. Overdose and Toxicity Management
Topical corticosteroid overdose may present with features of hypercorticism, such as weight gain, facial puffiness, hypertension, and hyperglycemia. Chronic overuse can lead to irreversible skin changes.
Neomycin toxicity, though rare from topical use, may result in ototoxicity or nephrotoxicity if significant systemic absorption occurs, especially in patients with renal impairment or over compromised dermal barriers.
- In suspected overdose: Discontinue the cream immediately and initiate symptomatic treatment.
- Systemic signs: Monitor serum electrolytes, renal function, and perform auditory testing if indicated.
- Prevention: Avoid applying excessive quantities or using beyond recommended durations.
12. Storage Instructions and Stability
- Store below 25°C (77°F) in a cool, dry place.
- Keep away from direct sunlight and excessive moisture to preserve stability.
- Check the expiration date before use. Once opened, the tube should be used within 8–12 weeks depending on manufacturer guidance.
- Discard if the cream changes color, texture, or emits an unusual odor, as this may indicate degradation.
13. Handling Precautions and Usage Instructions
- Wash hands thoroughly before and after application unless hands are the treatment site.
- Avoid contact with eyes, inner nostrils, lips, and other mucosal surfaces.
- Do not apply over broken, ulcerated, or heavily oozing skin unless instructed.
- Dispose of unused or expired medication in accordance with local pharmaceutical waste protocols.
- Store out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or misuse.
14. Important Patient Information and Precautionary Advice
Adherence to the complete prescribed course is crucial, even if symptoms improve before the duration ends. Early discontinuation may result in recurrence or resistance.
- Avoid applying other topical corticosteroids, antibiotics, or antifungals unless explicitly directed by a healthcare provider.
- Watch for signs of allergic reaction (rash, swelling, severe itching) or worsening condition, and discontinue use if these occur.
- Seek medical advice if there is no improvement within 7–10 days.
- Topical therapies should not substitute systemic treatment for severe or widespread infections.
Proper use enhances therapeutic efficacy while minimizing risk. Always follow medical guidance precisely.