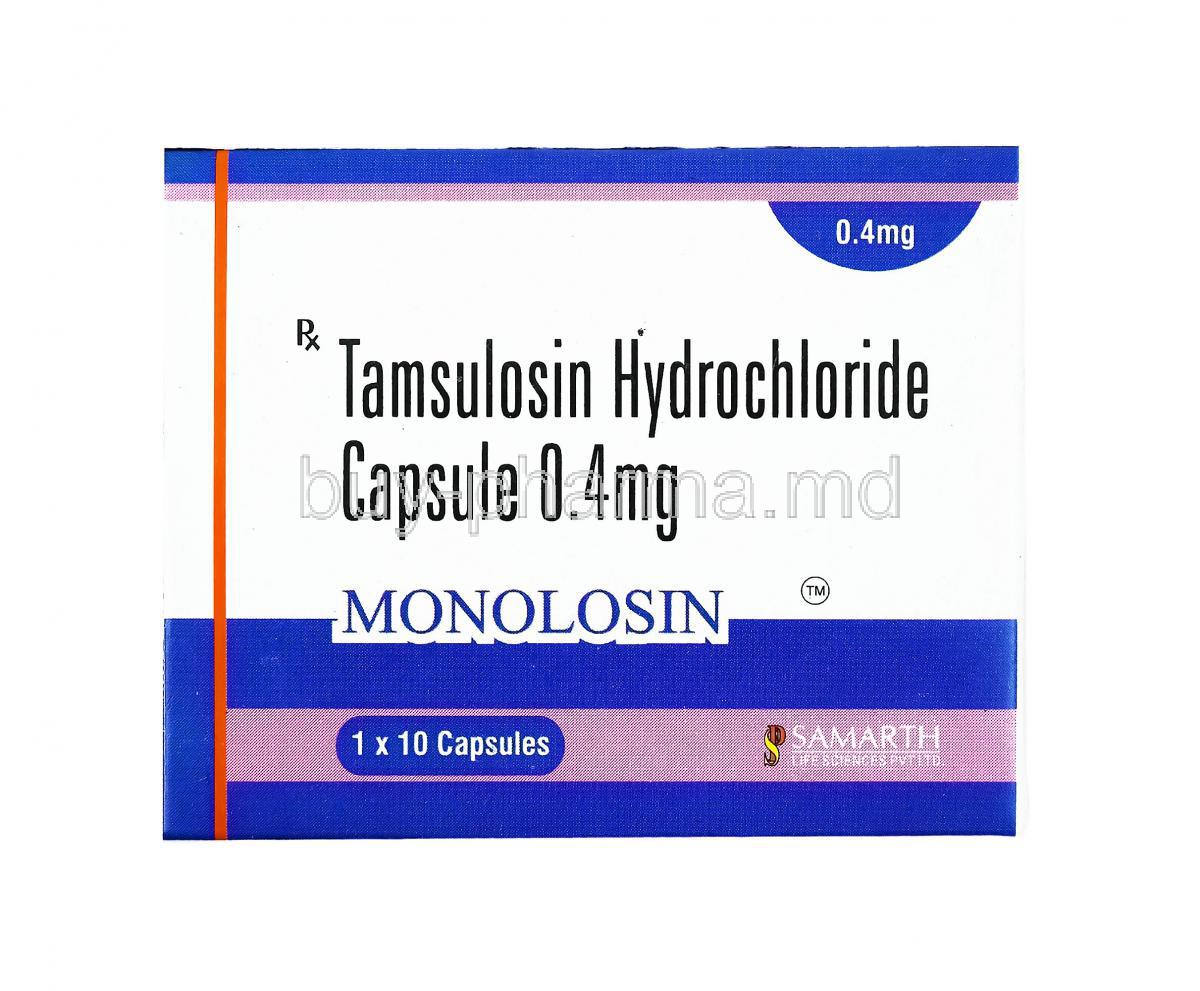
Monolosin, Tamsulosin
Introduction
The field of pharmaceuticals is always. Medicines like Monolosin and Tamsulosin are crucial in modern treatment. These drugs have features and uses that make them essential in addressing certain health issues demonstrating their importance in todays healthcare. Their impact on treatments showcases advancements in science while emphasizing the delicate balance between effectiveness and safety, in drug therapies.
Overview of Monolosin and Tamsulosin
Monolosin and Tamsulosin although different in their makeup both serve a similar purpose in treating urological conditions. While Monolosin may not be as well known it has its specific uses whereas, Tamsulosin is renowned for its effectiveness in alleviating symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The widespread use of Tamsulosin in settings demonstrates its success and how well patients tolerate it making it an essential tool, for managing lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
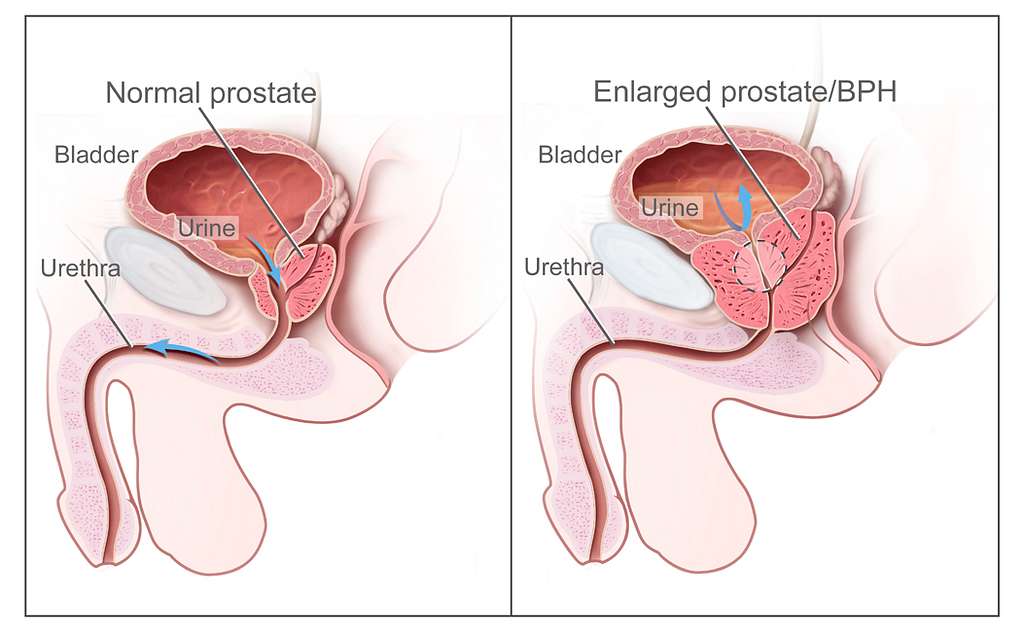
Benign prostatic Hyperplasia
Importance in Modern Medicine
- Monolosin and Tamsulosin play a role in improving the quality of life for individuals dealing with urological issues.
- These medications represent the progress made in targeted treatments providing relief from symptoms while minimizing side effects.
- Their integration into treatment plans showcases a grasp of the underlying causes of diseases demonstrating a move, towards personalized medical approaches.
Composition
Active Ingredients Analysis
The effectiveness of Monolosin and Tamsulosin lies in the components they contain. These medications are designed to work by focusing on particular receptors or pathways to relieve symptoms of diseases. By targeting areas they reduce unintended harm showcasing the move, towards more precise pharmacological treatments.
Excipients and Their Roles
In addition to the components, excipients have a vital yet often overlooked role, in crafting these medicines. These inactive substances are carefully chosen to improve drug effectiveness, absorption, and patient adherence. Including them in drug compositions demonstrates the sector's dedication to improving treatment results using advanced scientific methods and technology.
How It Works
Mechanism of Action for Monolosin
Monolosin works by a method that is still being thoroughly researched and current findings indicate that it is effective, in regulating pathways related to urological conditions. By adjusting muscle tone it helps alleviate symptoms without causing widespread side effects. This targeted approach highlights the effectiveness of the drug in treatment.
Mechanism of Action for Tamsulosin
Tamsulosin's way of working is well explained, mainly acting as a blocker at alpha 1 receptors found in the prostate and bladder neck. This particular blocking leads to the relaxation of muscle tissues helping to ease obstructive symptoms and enhance urinary flow rates. The drug's specificity is crucial for its effectiveness, in treatment reducing the chances of blood pressure compared to less targeted medications.
Comparative Pharmacodynamics
The ways in which Monolosin and Tamsulosin work may be different. They both aim to help with urological issues while causing as few side effects as possible. Monolosins broader approach could be beneficial for some patients while Tamsulosin's specific action is very effective for managing BPH. These medications show the variety of treatment options for urological conditions and emphasize the need, for personalized treatment plans.
Uses
In the field of pharmacotherapy, there are medications designed to treat various health issues. Monolosin and Tamsulosin are notable for their focus on treating urological disorders showcasing the advancements in modern medicine. Despite their differences, in composition, both medications share a goal of relieving symptoms linked to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and similar urological conditions.
Primary Indications for Monolosin and Tamsulosin
Monolosin serves a role in addressing complex urological issues that go beyond the usual scope of BPH treatment. (3)Tamsulosin is widely prescribed due to its targeted impact on α1 adrenergic receptors, in the prostate and bladder which helps reduce the dynamic aspect of urinary blockage.
1. National Library of Medicine - Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Tamsulosin for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
2. NCBI - Tamsulosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia
3. NIH - Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Comparative Analysis of Both Drugs' Efficacy
The effectiveness of Monolosin and Tamsulosin when compared tells a story of the evolution of pharmacology and precise therapy. Monolosin though less researched shows potential in addressing a range of urological issues possibly providing advantages in situations where Tamsulosin's specific mechanism may not be as effective.
Tamsulosin, known for its clinical track record has proven to significantly enhance symptom scores and urinary flow rates in numerous randomized clinical trials highlighting its effectiveness in the targeted population.
Yet the story goes beyond effectiveness. Factors such as safety profiles, patient tolerance, and enhancements in quality of life also play a role in defining the clinical usefulness of these medications.
At the same time, Tamsulosin is praised for its cardiovascular side effects. A feature that sets it apart from other α blockers. Monolosin safety and tolerability are still being investigated through ongoing research to understand their long-term implications.
In summary, both Monolosin and Tamsulosin bring benefits to managing urological conditions; their roles are shaped not only by their pharmacodynamic properties but also by the clinical scenarios where they are utilized.
A comprehensive grasp of their indications, effectiveness, and safety profiles is essential for optimizing outcomes, within the intricate therapeutic realm of urology.
Off-Label Uses
In the field of medicine, the use of medication goes beyond its intended purposes and enters into off-label territory. Despite not being approved by regulatory authorities this practice is crucial in solving treatment challenges when conventional methods fall short. Investigating uses for medications like Monolosin and Tamsulosin showcases the innovative approach of modern medicine utilizing research-backed knowledge to broaden the options, for healthcare providers.
Exploration of Non-Approved Indications
Exploring the realm of off-label use is a process that hinges on real-world observations, personal accounts, and thorough scientific inquiry. Take Monolosin for example initially designated for urological issues but now showing promise in managing chronic pelvic pain syndrome where conventional treatments often fall short.
Likewise, Tamsulosin, known for its role in treating prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) has been studied for its potential to assist in the passage of kidney stones due to its versatile effects on relaxing smooth muscles.
Research into Monolosin's ability to alleviate symptoms of pelvic pain syndrome showcases its versatility beyond its primary purpose. The use of Tamsulosin to help with kidney stone removal underscores its effectiveness, in relaxing muscles beyond just the prostate tissue.
Evidence-Based Support for Off-Label Applications
The approval of using drugs off-label depends on having evidence that proves their effectiveness and safety for uses not officially approved. Various types of studies like randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and meta-analyses form the foundation for practices.
For Tamsulosin there is an amount of research supporting its ability to help pass kidney stones showing significant improvements in stone removal rates and relief from symptoms compared to standard treatment.
On the other hand, while there is promising evidence for the off-label use of Monolosin it is still in its early stages and requires further investigation to fully understand its potential benefits.
In summary, exploring uses for medications like Monolosin and Tamsulosin demonstrates how medical practice evolves with a combination of evidence-based knowledge and clinical expertise to enhance patient care.
This approach showcases the adaptability of pharmacotherapy while emphasizing the importance of research to validate and improve these unconventional uses so that they are effective and safe, for patients.
Dosage and Administration
Ensuring the dosage and administration of medications is crucial in medical practice to guarantee effectiveness and safety for patients.
This is particularly important when it comes to drugs such as Monolosin and Tamsulosin where the results of treatment and potential side effects are directly linked to getting the dosage.
The discussion below outlines the suggested doses, for conditions including modifications needed for certain groups of people highlighting the importance of tailoring pharmacotherapy to individual patients.
Recommended Dosage for Different Conditions
The recommended dosages for Monolosin and Tamsulosin are customized according to the condition being treated aiming to strike a balance between maximizing therapeutic effects and minimizing potential risks.
Tamsulosin, commonly prescribed for prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) typically begins at a daily dose of 0.4 mg with the possibility of adjustments depending on how the patient responds to treatment.
On the other hand, Monolosin, known for its wide range of off-label uses requires a more individualized approach to dosing that takes into account the patient's condition and response.
- Tamsulosin; Initial dose is 0.4 mg per day for BPH, with modifications.
- Monolosin; Dosage varies based on the specific condition underscoring the importance of clinical judgment.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly
Elderly individuals frequently come with a range of health issues and bodily changes that require careful dosing considerations. When it comes to Tamsulosin starting with a dose might be wise due to their heightened sensitivity and the risk of side effects, like orthostatic hypotension. Similarly, Monolosin calls for a strategy of adjusting doses according to kidney function existing health conditions, and the medications being taken concurrently.
Dosage Adjustments and Considerations
Customizing treatment to meet the needs of each patient is crucial, particularly for groups, like older individuals, whose bodies' way of processing and reacting to medications may differ. It's important to check and adjust medication doses based on how well they work and any negative effects that may arise for successful treatment.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The use of Monolosin and Tamsulosin in women and breastfeeding mothers is approached with caution requiring a careful evaluation of the potential risks and benefits. Although there is information available regarding the effects of these medications, during pregnancy and breastfeeding it is typically recommended to avoid their use unless deemed essential and closely monitored by medical professionals.
Administration to Children
The use of Monolosin and Tamsulosin in treating children is an area that lacks research evidence. It's crucial to determine the dosage for different age groups while facing a shortage of data that often restricts their usage.
When it comes to Tamsulosin it might be used for pediatric kidney stones with expert guidance. Careful attention to proper dosing and monitoring is essential.
To sum up, giving Monolosin and Tamsulosin involves dealing with the complexities and responsibilities of treatment. Setting the dosages for various conditions and making adjustments, for specific groups highlights the importance of tailoring treatment individually.
This not only ensures these medications work effectively but also helps prevent potential side effects reflecting the core principles of sound medical practice.
Side Effects
The use of medications although they can save lives or greatly enhance quality of life may bring about a range of side effects that could impact how well patients follow their treatment and the overall success of therapy. It is essential in care to understand, anticipate and address these negative reactions. This conversation gives an overview of the side effects linked to drugs such, as Monolosin and Tamsulosin explores how often they occur, and suggests ways to manage them. It also highlights the importance of recognizing and safeguarding high-risk patients by taking precautions.
Overview of Common Side Effects
Both Monolosin and Tamsulosin medications come with a range of side effects that can vary in severity. The common adverse reactions are typically linked to how they interact with receptors in the body. When it comes to Tamsulosin, a medication primarily prescribed for prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) patients might experience dizziness, headaches, and orthostatic hypotension due to its impact, on alpha-adrenergic receptors. On the other hand, Monolosin depending on its usage may share some of these side effects but could also present unique adverse responses based on its mode of action and the specific condition being addressed.
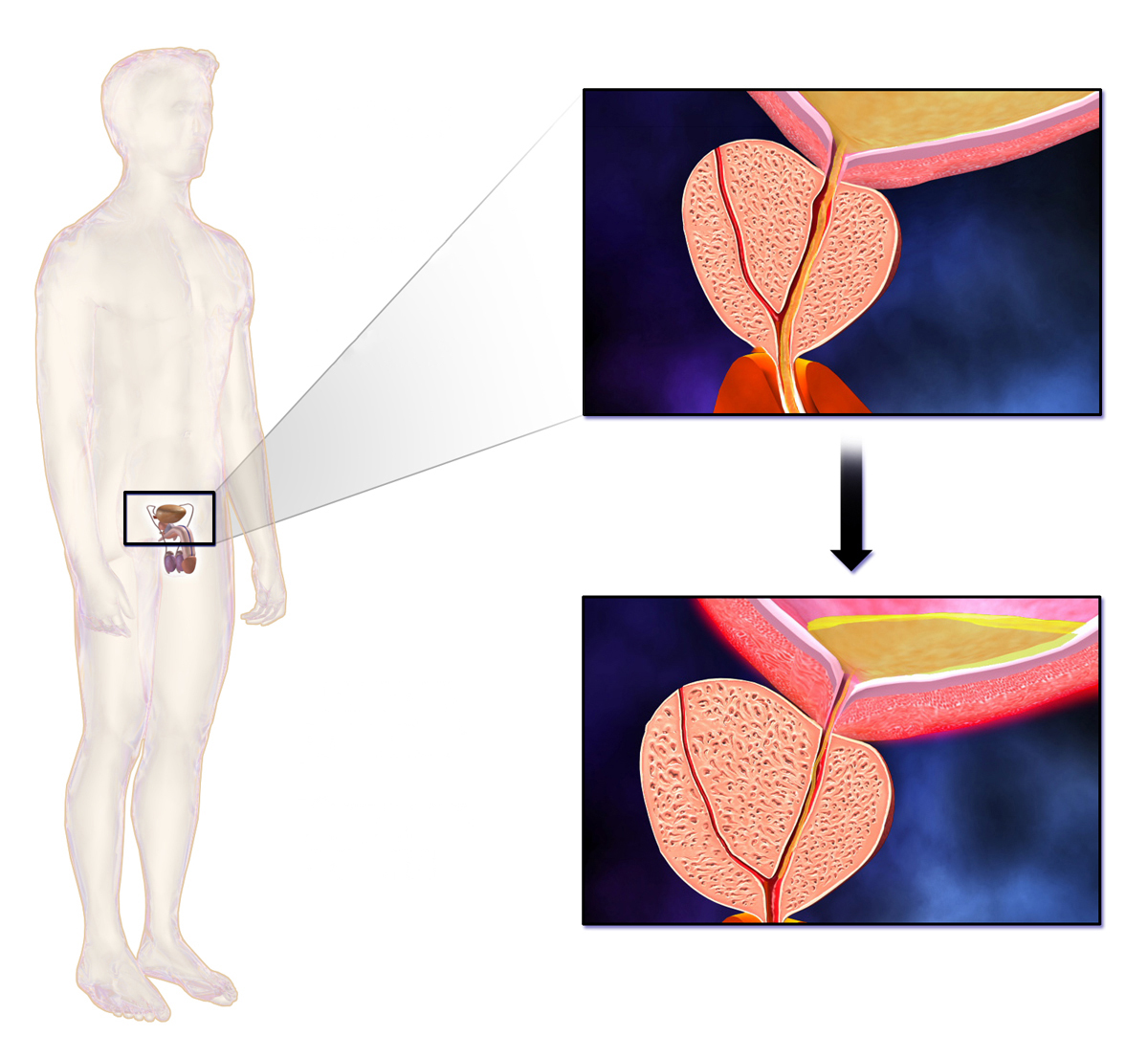
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Common Side Effects
- Feeling dizzy and lightheaded when you stand up could signal hypotension.

Dizziness
- Experiencing headaches of varying severity that can impact your tasks.
- Dealing with congestion or rhinitis as a result of vasodilation effects.
- Experiencing stomach issues, like nausea and diarrhea.

Nausea
Frequency and Management Strategies
The occurrence of side effects differs from person to person depending on factors, like age other health conditions, and the medications taken simultaneously. The main goal of managing these effects is to lessen them without affecting the effectiveness of the treatment. For instance, starting Tamsulosin at a dose and slowly raising it can reduce the chances of experiencing orthostatic hypotension. Likewise taking the medication before bedtime could help decrease feelings of dizziness and lightheadedness while awake.
Important Precautions
Identifying High-Risk Patients
Identifying patients who may be more susceptible to experiencing effects requires a comprehensive evaluation of their medical background considering any preexisting conditions and medications they are currently taking. Individuals with a past of blood pressure significant kidney problems or individuals using other medications that lower blood pressure might face heightened risks when using substances such, as Tamsulosin.
Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies
It is crucial to have methods in place to monitor and address any side effects that may arise during treatment to ensure the well-being of patients. Follow-up appointments are important for evaluating how well the medication is working and how well the patient can tolerate it giving healthcare providers a chance to make adjustments as needed.
Teaching patients about side effects and encouraging them to report any issues promptly can improve how these effects are managed making sure that the right actions are taken at the right time.
To sum up, despite the challenges that medications like Monolosin and Tamsulosin may bring in care being proactive in managing their side effects can greatly reduce their impact.
By being aware of adverse reactions following appropriate monitoring protocols and taking necessary precautions, for high-risk individuals healthcare professionals can improve treatment outcomes by ensuring both effectiveness and patient safety.
Interaction
In the field of pharmacotherapy, it's important to consider how medications interact with each other and with a person's lifestyle. These interactions can greatly affect how effective and safe a medication is, which means that providing patients with counseling and guidance on medication use is crucial. This section delves into the complexities of drug interactions and how factors, like food and lifestyle choices, can influence the effectiveness of medications offering strategies to minimize any effects.
Drug-Drug Interactions and Management
Using Monolosin and Tamsulosin with other medications can lead to various interactions that affect how the drugs work in the body. For example, taking Tamsulosin along with alpha blockers can increase the chance of low blood pressure so it's important to be careful. Likewise combining Monolosin with inhibitors of CYP3A4, an enzyme that helps break down the medication in the body can raise its levels in the blood and raise the risk of side effects. To manage these interactions;
- Review the patient's medications thoroughly before prescribing new ones.
- Adjusting doses orUsing different medications that are less likely to interact.
- Keep an eye out for any signs of interactions. Making changes, to treatment as needed.
Food and Lifestyle Interactions
Some foods and habits can impact how medications such as Monolosin and Tamsulosin work in the body. For instance, drinking grapefruit juice may disrupt the breakdown of drugs possibly causing higher drug levels and side effects. Patients should remember to;
- Steer clear of grapefruit juice and other foods that can interact with medications.
- Stick to a routine in terms of lifestyle and diet to prevent changes, in drug effectiveness.
- Talk about any lifestyle adjustments that could influence medication usage with their healthcare provider.
Warnings
Critical Adverse Reactions and Preventative Measures
Although Monolosin and Tamsulosin are usually well tolerated they can still lead to adverse reactions. Major worries involve low blood pressure, sudden urinary retention and in rare instances priapism. To prevent these issues; Recognize symptoms of reactions early on. Adjust treatment promptly upon noticing severe side effects. Inform patients, about the signs of serious reactions and stress the importance of reporting them promptly.
Contraindications
Absolute and Relative Contraindications for Use
It's important to note that Monolosin and Tamsulosin should not be used in patient groups and circumstances. People with known allergies to the ingredients or any other components should avoid these medications. In cases of liver or kidney issues, it might be necessary to adjust the dosage or explore alternative treatments for safety reasons. Being aware of these contraindications is crucial, in preventing negative consequences.
Careful Administration
Special Populations and Conditions
Special groups, such as individuals, expectant mothers, breastfeeding women, and those with multiple health conditions need special attention when using Monolosin and Tamsulosin. It's crucial to customize treatment according to each patient's needs and health status to reduce risks and ensure effectiveness.
Key strategies involve assessing the patient's health and medication history thoroughly adjusting doses or considering alternative treatments based on individual factors and regularly monitoring for both positive effects and potential side effects while making necessary adjustments.
To sum up, managing drug interactions by following warnings and contraindications and administering medications carefully to specific populations are essential, for improving patient outcomes in pharmacotherapy.
By approaching medication use and staying well informed healthcare providers can effectively manage the complexities of drug therapy to guarantee safety and efficacy for their patients.
Storage
The effectiveness and safety of medications depend greatly on how they are stored. It is crucial to follow guidelines for storing drugs like Monolosin and Tamsulosin to ensure they maintain their intended effects over time. By storing medications we can prevent the breakdown of key ingredients ensuring that the drugs remain potent and beneficial, for patient health.
Optimal Storage Conditions
Monolosin and Tamsulosin should be kept in a dry spot shielded from direct sunlight and moisture to maintain their effectiveness. It's best to store them at temperatures ranging from 15°C to 30°C (59°F, to 86°F). These measures help prevent chemical breakdown ensuring the medications retain their intended potency levels.
Stability and Shelf Life
The effectiveness and longevity of medicines depend on following the storage guidelines. Monolosin and Tamsulosin usually remain viable for 2 to 3 years after being made provided they are stored correctly. It's crucial, for patients and healthcare professionals to inspect expiration dates as the potency of medications may decrease after this timeframe.
Handling Precautions
Safe Handling Practices for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to follow safety protocols when working with medications to avoid unintended exposure or pollution. This involves wearing gloves while administering drugs refraining from direct contact, with the substances, and maintaining a tidy and well-ventilated work environment.
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
It's really important to get rid of medications to keep people and the environment safe. You shouldn't throw away expired medicines like Monolosin and Tamsulosin in the regular trash or down the drain. Instead take them back to a pharmacy for disposal following the rules, in your area to avoid harming the environment.
Overdose
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosing
Taking much medication, like Monolosin and Tamsulosin can cause serious negative reactions. Warning signs could be low blood pressure feeling lightheaded throwing up or in rare situations sudden kidney failure. It's crucial to notice these signs to take action promptly.
Immediate Actions and Antidote Information
In case of an overdose, it is crucial to seek medical help. The treatment primarily involves providing care, such as monitoring vital signs and administering intravenous fluids if needed to address low blood pressure. It's important to note that there isn't an antidote, for overdosing on Monolosin or Tamsulosin underscoring the significance of preventing overdose by ensuring correct dosage and administration.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
This conversation has shed light on the significance of storing Monolosin and Tamsulosin in the conditions to uphold their effectiveness and safety. It has also emphasized the importance of healthcare providers practicing handling and proper disposal methods along, with stressing the crucial role of dealing with overdose scenarios. Following these recommendations guarantees that these medications can fulfill their functions successfully.
Future Directions in Therapy and Research
The field of pharmacotherapy is constantly changing, with studies on how drugs like Monolosin and Tamsulosin work in the body their safety, and how they are used for treatment. Advances, in how drugs are made delivered, and disposed of aim to improve how well they work, their safety, and how they impact the environment. These advancements are expected to lead to patient care and treatment results.