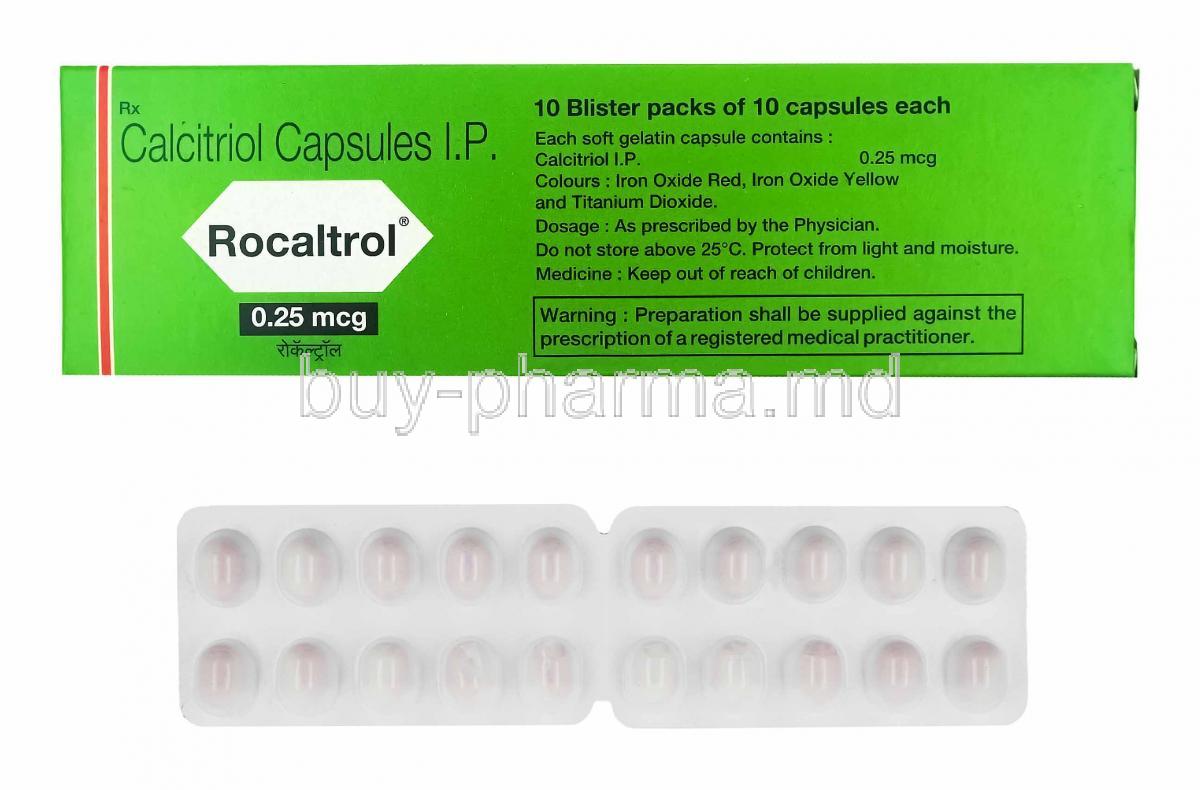
Introduction to Rocaltrol (Calcitriol)
Rocaltrol, known by its generic name calcitriol, is a synthetic form of vitamin D3 that serves as a critical therapeutic agent in calcium and phosphate regulation. As the hormonally active metabolite of vitamin D, it exerts profound effects on mineral metabolism, making it indispensable in specific clinical scenarios.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved calcitriol in the early 1970s, marking a milestone in endocrinology and nephrology. Since then, it has been integrated into standard treatment regimens for conditions marked by impaired calcium homeostasis. Its clinical relevance continues to expand, highlighting its enduring role in modern medicine.
By maintaining balance between calcium absorption, bone mineralization, and parathyroid hormone modulation, Rocaltrol remains a cornerstone therapy for patients requiring precise metabolic support.
Composition and Formulations
The therapeutic efficacy of Rocaltrol is anchored in its active pharmaceutical ingredient: calcitriol. As the most potent metabolite of vitamin D3, calcitriol is responsible for driving the physiological benefits attributed to the drug.
- Oral capsules: Available in varying strengths, commonly 0.25 mcg and 0.5 mcg, suitable for long-term outpatient therapy.
- Oral solution: Particularly advantageous for pediatric and geriatric patients with swallowing difficulties.
- Injection: Used in hospital and dialysis settings where rapid correction of calcium disturbances is needed.
Inactive excipients differ by formulation but often include oils, stabilizers, and preservatives to maintain bioavailability and stability.
How Rocaltrol (Calcitriol) Works
Calcitriol exerts its therapeutic effects by functioning as the hormonally active derivative of vitamin D. Its mechanisms are multifaceted and extend across several physiological systems:
- Intestinal absorption: Enhances uptake of calcium and phosphorus from the gut, directly influencing serum levels.
- Renal phosphate regulation: Promotes renal tubular reabsorption of phosphate, reducing urinary losses.
- Parathyroid hormone suppression: Modulates PTH secretion, preventing excessive bone resorption and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
- Bone remodeling: Facilitates mineralization, stabilizing skeletal integrity and promoting balanced bone turnover.
These processes collectively restore and maintain mineral equilibrium, crucial in both renal and metabolic disorders.
Approved Medical Uses of Rocaltrol
Rocaltrol has gained regulatory approval for several clinically significant indications:
- Hypocalcemia in chronic renal dialysis: Addresses calcium deficiency due to impaired renal conversion of vitamin D.
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism: Common in chronic kidney disease, calcitriol mitigates excessive parathyroid activity.
- Hypoparathyroidism: Used when the parathyroid glands fail to maintain adequate calcium levels.
- Rickets and osteomalacia: Corrects defective mineralization associated with vitamin D deficiency.
- Osteoporosis adjunct: Enhances bone mineral density when combined with other standard therapies.
Off-Label Uses of Calcitriol
Beyond its approved uses, calcitriol demonstrates potential benefits in diverse clinical areas:
- Psoriasis: Both systemic and topical calcitriol formulations may help regulate abnormal keratinocyte proliferation.
- Autoimmune disorders: Investigated for its immunomodulatory properties in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
- Cancer-related bone complications: May alleviate skeletal events in patients with malignancy-associated hypercalcemia.
- Neurological conditions: Studies suggest a role in multiple sclerosis and neuromuscular disorders, though evidence remains investigational.
- Endocrine disorders: Potential therapeutic adjunct in complex metabolic syndromes and endocrine dysregulation.
Dosage and Administration
Dosing of Rocaltrol is individualized and depends on indication, age, and renal function. Key considerations include:
- Adults: Typically initiated at 0.25 mcg daily, with gradual titration according to serum calcium and PTH levels.
- Children: Pediatric dosing requires weight-based calculations and vigilant biochemical monitoring.
- Renal impairment: Careful dose adjustment is crucial, as clearance is diminished in compromised kidneys.
Calcitriol may be administered orally or intravenously. Duration of therapy varies from short-term correction to lifelong maintenance. Regular monitoring of biochemical markers ensures safety and efficacy, with adjustments made to avoid hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia.
Side Effects of Rocaltrol
Common Side Effects
Adverse reactions are often linked to elevated calcium levels. Patients may experience:
- Nausea, vomiting, or general weakness due to hypercalcemia
- Headache and dizziness
- Altered taste perception including metallic sensation
- Dry mouth and gastrointestinal discomfort
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
Though less frequent, certain side effects warrant urgent clinical attention:
- Nephrocalcinosis: Deposition of calcium in kidney tissue, leading to long-term renal dysfunction.
- Severe hyperphosphatemia: May trigger vascular or soft tissue calcification.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Resulting from electrolyte imbalance, especially in patients on digitalis therapy.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Rash, swelling, or other allergic manifestations.
Routine laboratory monitoring minimizes risks and allows early identification of these complications.
Drug Interactions
Rocaltrol (calcitriol) has clinically significant interactions with a variety of therapeutic agents. Understanding these interactions helps prevent severe complications such as hypercalcemia and cardiovascular instability.
- Thiazide diuretics: When combined, there is an increased risk of hypercalcemia due to reduced urinary calcium excretion.
- Digitalis glycosides: Elevated calcium levels may precipitate life-threatening arrhythmias in patients receiving digoxin or related drugs.
- Anticonvulsants: Agents such as phenytoin and phenobarbital may reduce vitamin D efficacy by accelerating metabolic degradation.
- Magnesium-containing antacids: Particularly in patients with renal impairment, this combination can lead to hypermagnesemia and toxicity.
- Corticosteroids: These drugs antagonize calcitriol activity by impairing calcium absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Cholestyramine: A bile acid sequestrant that reduces intestinal absorption of calcitriol, diminishing therapeutic benefit.
Warnings and Contraindications
Certain patient populations must avoid or carefully manage calcitriol therapy due to heightened risks.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to calcitriol or any excipient, pre-existing hypercalcemia, or vitamin D toxicity.
- Renal impairment: Patients with nephrolithiasis or chronic renal dysfunction require close supervision due to increased risk of calcium deposition.
- Laboratory monitoring: Frequent measurement of serum calcium and phosphate is essential to prevent metabolic imbalance.
- Long-term risks: Prolonged therapy may contribute to vascular or soft tissue calcification, with potential cardiovascular consequences.
Important Precautions and Careful Administration
Optimal outcomes require adherence to strict precautions in clinical practice.
- Dietary calcium intake should be regulated to prevent exaggerated increases in serum calcium.
- Laboratory values, including serum electrolytes and renal function markers, must be monitored regularly.
- Patients should avoid unsupervised supplementation with vitamin D or calcium to mitigate overdose risk.
- Dose escalation should be gradual, with careful titration guided by clinical and biochemical response.
Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Older adults may metabolize calcitriol differently, resulting in altered drug kinetics.
- Increased sensitivity to hypercalcemia has been documented in elderly patients.
- Lower initial doses and slow titration are recommended to minimize adverse reactions.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Calcitriol is categorized as Pregnancy Category C, reflecting uncertain safety.
- Maternal hypercalcemia may induce fetal skeletal malformations or suppress parathyroid development.
- Calcitriol is excreted into breast milk, necessitating neonatal monitoring for calcium disturbances.
Administration to Children
In pediatrics, calcitriol serves a pivotal role in managing hypocalcemia and rickets.
- Dosing requires meticulous calculation based on body weight to avoid overdose.
- Neonates and infants are especially vulnerable to toxicities, warranting frequent laboratory assessment.
Overdosage of Rocaltrol
Excessive intake of calcitriol can precipitate severe clinical syndromes.
- Symptoms: Persistent hypercalcemia, dehydration, fatigue, and dangerous arrhythmias.
- Treatment: Immediate discontinuation, aggressive hydration, and administration of loop diuretics to promote calcium excretion.
- Supportive care: Continuous monitoring of electrolytes and renal function is mandatory until stability is achieved.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper storage and handling maintain the stability and safety of Rocaltrol.
- Store at controlled room temperature, protected from light and moisture.
- Observe expiration dates carefully; expired medication should not be consumed.
- Healthcare professionals should handle injectable forms with caution to avoid contamination.
- Dispose of unused or expired medication according to medical waste protocols to prevent accidental ingestion.
Clinical Monitoring and Patient Education
Effective therapy requires both medical supervision and patient awareness.
- Routine monitoring of serum calcium, phosphate, and creatinine ensures early detection of imbalances.
- Patients should receive dietary guidance to align calcium intake with therapeutic goals.
- Clear counseling should emphasize adherence, avoidance of self-medication, and recognition of hypercalcemia symptoms.
- Compliance with the prescribed regimen is paramount for sustained therapeutic benefit and prevention of complications.