Tizanidine
- 1. Understanding Tizanidine
- 2. Tizanidine Uses
- Analyze the Science Behind Tizanidine
- 4. Determine Dosage and Administration for Tizanidine
- 5. Identify Side Effects of Tizanidine
- 6. Recognize Drug Interactions for Tizanidine
- 7. Consider Precautions and Contraindications for Tizanidine
- 8. Compare Alternatives to Tizanidine
- 9. Tizanidine FAQ
- What is the primary purpose of taking Tizanidine?
- How long does it take for Tizanidine to start working?
- Can I take Tizanidine with other medications?
- What are the potential side effects of Tizanidine?
- Is it safe to consume alcohol while taking Tizanidine?
- Can I take Tizanidine if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
- What Is a Substitute for Tizanidine?
- Understanding Tizanidine and Where to Purchase it

Here are the illustrations that conceptually represent Tizanidine in a medical context
1. Understanding Tizanidine
Tizanidine is a prescribed medicine used to alleviate muscle spasms and stiffness caused by different medical conditions, including multiple sclerosis (MS), spinal cord injuries, or chronic pain. In this section, we will explore the benefits of using Tizanidine and how it can contribute to improving patients' overall health and well-being.
What is Tizanidine?
Tizanidine is categorized as a type of medicine known as a skeletal muscle relaxant. Its mechanism involves inhibiting the transmission of nerve signals that trigger muscle contractions, thereby providing relief from muscle spasms and stiffness. You can find this medication in the form of tablets or capsules which are meant to be taken.
Common uses and benefits
- Muscle Spasms: If you're experiencing muscle contractions for various reasons, taking Tizanidine can be beneficial. It helps relieve the discomfort that comes with these spasms.(1)
- Multiple Sclerosis: MS is a disorder that affects the central nervous system (CNS). One common symptom among those with MS is muscle stiffness or spasticity. Tizanidine can help relax these muscles and improve mobility for individuals living with this condition.(2)
- Spinal Cord Injuries: After sustaining a cord injury, some patients may experience increased muscle tone or spasticity as their body tries to adapt to the damage in the CNS. Taking Tizanidine can provide relief from these symptoms. Promote overall recovery.(3)
- Pain Management: In cases where Tizanidine may be prescribed as part of a comprehensive pain management plan for patients dealing with chronic pain conditions. By relaxing the muscles and reducing tension, this medication can help alleviate discomfort associated with pain.
Apart from these uses, healthcare providers may prescribe Tizanidine for other off-label purposes based on individual patient needs. It's crucial to follow your physicians' instructions when taking this medication to achieve results and minimize the risks of adverse effects.
1. MayoClinic - Tizanidine
2. NCBI - Nightly sublingual tizanidine HCl in multiple sclerosis: clinical efficacy and safety
2. Tizanidine Uses
Tizanidine is an adaptable medication known for its ability to alleviate pain associated with muscle spasms and stiffness. In the following section, we will explore the ways in which Tizanidine can effectively minimize muscle spasms and stiffness, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for patients.
Muscle Spasms
Muscle spasms are when your muscles tighten up on their own, causing pain and discomfort. These spasms usually happen because you've been using your muscles much, not drinking enough water, or having imbalances in your body's electrolytes. Tizanidine helps by stopping the nerve signals that make your muscles contract, so it can give you relief from those spasms.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition that impacts the nervous system and causes difficulties with muscle control and coordination. As the disease progresses, individuals with MS often face challenges such as muscle stiffness and spasticity. Tizanidine can aid in relieving these symptoms by promoting relaxation in the muscles. It is a medication commonly used to address aspects of multiple sclerosis.
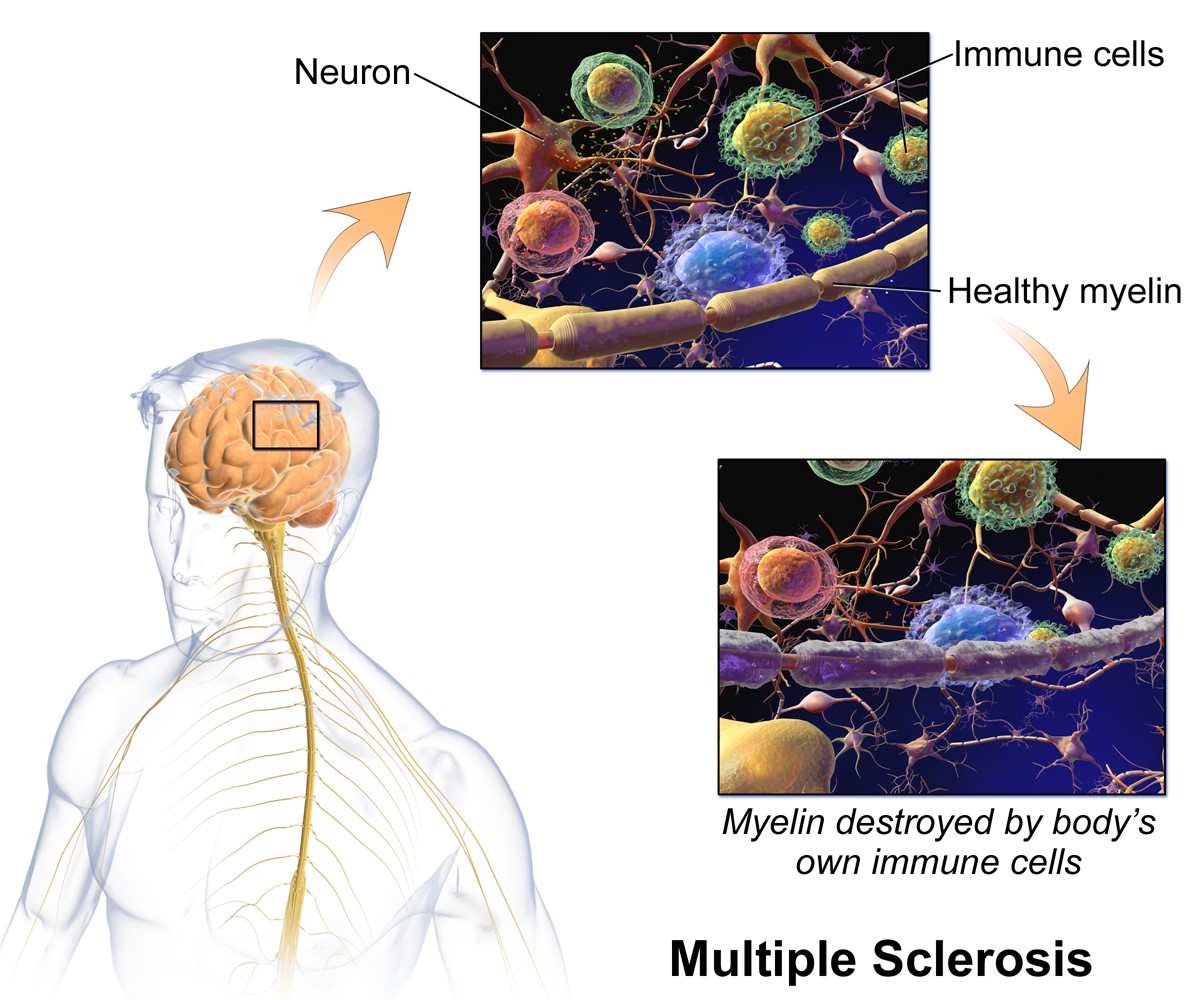
Multiple-Sclerosis
Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries can lead to a decrease in motor function, either partially or completely depending on the extent of nerve damage in the column. People who have experienced injuries often encounter a problem called increased muscle tone or spasticity in the affected limbs. Tizanidine assists in addressing this issue by promoting muscle relaxation.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain refers to lasting discomfort that persists for more than three months and can have a significant impact on one's daily life. Although Tizanidine is not specifically formulated for treating pain, its muscle-relaxing properties might offer some relief to individuals who experience painful muscle spasms or stiffness as a result of their condition.
Off-label Uses
Apart from the mentioned approved uses, healthcare professionals may prescribe Tizanidine for off-label purposes like fibromyalgia, migraine prevention, or restless leg syndrome. However, it is crucial to seek advice from your doctor before using Tizanidine for any off-label reasons.
Taking Tizanidine can be highly beneficial in managing health issues related to muscle spasms and stiffness. If you encounter any side effects or drug interactions make sure to consult your healthcare provider. Discuss with your healthcare provider if Tizanidine could potentially improve your health and quality of life.
Tizanidine has potential applications and can provide relief for individuals dealing with muscle spasms or other related conditions. Prior knowledge about this medication is necessary before usage. Here are some answers to frequently asked questions about Tizanidine.
Analyze the Science Behind Tizanidine
In this section, we'll explore the functionality of Tizanidine as a muscle relaxant and its effectiveness in treating conditions like muscle spasms, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and chronic pain. Understanding the principles behind Tizanidine can help you determine if it's a suitable solution for your needs.
How Tizanidine Works
Tizanidine falls into the category of medications known as alpha-2 adrenergic agonists. Its primary mechanism of action revolves around its effects on the nervous system (CNS), which helps in relaxing muscles. By stimulating alpha-2 receptors in the brainstem and spinal cord, it curbs nerve signals that trigger involuntary muscle contractions. Consequently, this leads to a decrease in muscle tension and spasticity.
Tizanidine as a Muscle Relaxant
As I mentioned before, Tizanidine is commonly used to treat muscle spasms. These spasms occur when muscles suddenly contract or tighten involuntarily. They can be caused by factors like injuries, overuse, or strain from physical activities such as exercise or sports. Tizanidine works by reducing muscle tension through its action on the receptors in the central nervous system that control the force of contraction in skeletal muscles. This helps alleviate pain associated with stiffness and improves mobility.
Role of Tizanidine in Multiple Sclerosis Management
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a term neurological condition that impacts the central nervous system, resulting in inflammation and damage to nerve fibers. This can cause symptoms, including muscle weakness, stiffness, and discomfort.
Tizanidine has shown effectiveness in managing muscle spasms associated with MS by reducing muscle contractions through its impact on receptors in the central nervous system. By affecting these receptors in the CNS, Tizanidine may potentially help improve movement and overall well-being for individuals experiencing MS-related muscle spasms by reducing muscle contractions.
Tizanidine's Role in Spinal Cord Injury Recovery
Spinal cord injuries frequently lead to a decline in motor function because the nerves responsible for controlling muscles below the site of injury become damaged. Tizanidine can be beneficial in managing spasticity associated with cord injuries by preventing involuntary muscle contractions caused by disrupted nerve signals.
By alleviating these symptoms, Tizanidine enables patients to actively engage in physical therapy sessions, thereby enhancing their functional capabilities.
Tizanidine as a Pain Relief Option for Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is a discomfort that lasts longer than the usual healing time or occurs without any clear reason. It can greatly impact our activities and overall well-being. In cases where chronic pain is caused by increased muscle tension or spasms, Tizanidine may be prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan along with other medications like pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Its ability to reduce muscle contractions makes it a practical choice for easing specific chronic pain conditions. Through studying the science behind Tizanidine we have gained insights into its potential benefits and risks. Now let's explore ways to determine the dosage and method of taking Tizanidine for maximum effectiveness
Tizanidine is a muscle relaxant primarily targeting the nervous system to alleviate muscle spasms and spasticity resulting from various conditions such as multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and chronic pain. Its capacity to hinder nerve signals that trigger contractions makes it an effective option, for managing these symptoms and enhancing overall mobility.
4. Determine Dosage and Administration for Tizanidine
Understanding the recommended dosage and usage instructions for Tizanidine is crucial when considering it as a treatment option to ensure effective use. In this section, we will discuss the dosing recommendations for Tizanidine guidelines, how to take it correctly, and factors that might affect your prescribed dosage.
Recommended Dosage
The usual initial dose of Tizanidine is 2 to be taken orally, up to three times daily. Your doctor may modify the dosage based on your response and any side effects you may encounter. It is generally recommended not to exceed a daily dose of 36 mg.
Remember that individual circumstances can differ, so always adhere to your healthcare provider's instructions concerning the dosage and frequency when using Tizanidine.
Tips for Taking Tizanidine
Here are some guidelines to follow when taking Tizanidine;
1. Take Tizanidine with a meal or a light snack to minimize the chances of experiencing side effects like nausea or stomach upset.
2. It is important to take Tizanidine with food or without food throughout your treatment. This helps maintain levels of the medication in your body, which can increase its effectiveness.
3. Avoid consuming alcohol while taking Tizanidine, as it can make you feel drowsy and intensify other side effects associated with the medication.
4. Swallow the Tizanidine tablets whole without crushing, chewing, or breaking them. This ensures that the medication is properly released and absorbed in your body.
5. Try to take your doses at around the times every day to maintain consistent levels of the medication in your body.
6. If you need to stop using Tizanidine, consult your healthcare provider for guidance on reducing your dose to avoid potential withdrawal symptoms.
7. Remember to discuss any concerns or questions about taking Tizanidine with your healthcare provider, as they can give advice based on your medical history and needs.
It is crucial to be aware of the dosage and administration of Tizanidine for its safe use. To ensure that Tizanidine is used safely, it's important to be aware of any negative reactions that may occur.
To use Tizanidine safely and effectively, follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines. Typically, the starting dose is 2 mg taken orally up to three times a day, with a daily dose of 36 mg in most cases.
Here are some tips for taking Tizanidine: take it with food, stick to a dosing schedule, avoid alcohol while on medication, swallow tablets whole without crushing or breaking them, and consult your healthcare provider before stopping treatment.
5. Identify Side Effects of Tizanidine
When using Tizanidine it's important to be aware that there can be side effects for different people. Understanding and effectively managing these reactions is crucial. In this section, we will explore the side effects of taking Tizanidine and offer useful advice, on how to deal with them.
Common Side Effects
- Drowsiness
- Feeling dizzy
- Lightheaded
- Weakness in the muscles
- Having a dry mouth
- Experiencing nausea
- Vomiting Dealing
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
These are some of the common side effects that have been reported by individuals taking Tizanidine. While not everyone experiences these symptoms, they may improve over time as your body adjusts to the medication.
Managing Side Effects: If you encounter any of the side effects while using Tizanidine, there are a few steps you can take to alleviate any discomfort;
- To address drowsiness or fatigue; Make sure you get enough rest each night and avoid engaging in activities that require alertness (such as driving) until you understand how this medication affects your energy levels.
- For dizziness or lightheadedness; Rise slowly when getting up from a lying position. If dizziness persists despite making adjustments, it is advisable to consult your doctor for further guidance.
- To cope with muscle weakness; Engage in gentle stretching and strengthening exercises to maintain muscle function. It may be helpful to seek recommendations from a physical therapist or healthcare professional.
- For Dry mouth, Drink water frequently, chew sugar-free gum, or consider using saliva substitutes to relieve dryness. It is also recommended to avoid caffeinated beverages that can exacerbate this condition.
- To alleviate nausea or vomiting; Consume meals more frequently throughout the day and avoid lying down immediately after eating. Ginger supplements or over-the-counter anti-nausea medications may also provide relief for these symptoms.
- To avoid constipation or diarrhea, it is important to have a balanced diet that includes plenty of fiber. Additionally, make sure to stay hydrated by drinking fluids. If needed, you can also consider using over-the-counter remedies for relief.
However, it's always an idea to consult with your doctor before starting any new treatment. When taking Tizanidine, it is crucial to communicate with your healthcare provider about any side effects you may experience. They can assess whether your dosage needs adjustment or if alternative treatments should be explored.
Serious Side Effects
In some instances, some patients may encounter significant adverse effects when using Tizanidine. These may include reactions like rashes or swelling, difficulty in breathing, chest discomfort, fainting episodes, hallucinations or confusion, intense dizziness, and unusual bleeding or bruising. If you experience any side effects, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Remember that your doctor has prescribed Tizanidine because they believe that its benefits outweigh the risks. However, it remains important to remain vigilant and promptly report any symptoms. Additionally, it's essential to be mindful of interactions with other medications while taking Tizanidine to ensure its safe and effective use.
When using Tizanidine, it is vital to be aware of side effects such as drowsiness, muscle weakness, and dry mouth. To manage these symptoms effectively, individuals can take measures such as getting rest, engaging in gentle exercises regularly, and staying hydrated by drinking water frequently. If you experience side effects like chest pain or unusual bleeding/bruising that occur unexpectedly during the course of treatment with Tizanidine, do not hesitate to seek immediate medical attention.
6. Recognize Drug Interactions for Tizanidine
In this section, we'll go over some information, about drug interactions and offer tips for using medications safely.
Potential Drug Interactions with Tizanidine
Certain medications can inhibit an enzyme called CYP1A2, which is responsible for metabolizing Tizanidine. When combined with these drugs, tizanidine levels in the blood can increase, leading to a risk of experiencing side effects. Examples of medications include fluvoxamine, ciprofloxacin, and certain antiarrhythmic drugs like amiodarone (source).
If you are already taking medication for blood pressure, it's important to be cautious when combining it with Tizanidine as it may cause excessive lowering of blood pressure (hypotension). Consult with your doctor if you are using medications such as ACE inhibitors or beta blockers to manage your blood pressure.
Combining Tizanidine with sedatives or other central nervous system depressants can intensify their drowsiness-inducing effects. This includes medications like diazepam or alprazolam from the benzodiazepine family; sleep aids such as zolpidem or eszopiclone, and opioids like morphine or oxycodone (source).
There have been studies suggesting that oral contraceptives might increase the levels of Tizanidine in the bloodstream, thereby potentially elevating the risk of side effects. If you are considering using birth control pills while taking Tizanidine, it is advisable to discuss this matter with your doctor (source).
Tips for Ensuring Safe Use of Tizanidine with Other Medications
It's crucial to inform your healthcare provider about any medications, supplements, or herbal products you plan on taking. To ensure effective treatment, keep an updated list of all the prescription and over-the-counter medications you're using.
Before starting or stopping any medication, consult with your doctor to avoid drug interactions and complications. Additionally, make sure to monitor your health condition while on multiple medications and promptly report any unusual symptoms or side effects to your healthcare provider.
Paying attention to drug interactions is vital when using Tizanidine for managing muscle spasms, chronic pain, or other prescribed conditions. By following these guidelines and discussing any concerns with your healthcare professional, you can minimize risks associated with taking Tizanidine and other drugs.
Recognizing drug interactions plays a role in safely managing your medications while considering precautions and potential adverse effects of Tizanidine in making informed decisions based on individual needs.
When using Tizanidine, it's important to be aware of drug interactions that may impact its effectiveness or lead to adverse effects. When taking Tizanidine, it's important to be cautious when using it alongside medications. This includes CYP1A2 inhibitors, blood pressure medications, sedatives, and CNS depressants. Combining these drugs can heighten the chances of experiencing side effects. To prioritize your safety, make sure to inform your healthcare provider about all the medicines you currently take or plan to take. Avoid self-medication well.
7. Consider Precautions and Contraindications for Tizanidine
Before using Tizanidine, it's important to be mindful of precautions and contraindications that may impact its suitability for your particular circumstances. In this section, we will delve into who should avoid taking Tizanidine and the precautions you should take when using this medication.
Who Should Not Take Tizanidine?
Tizanidine is generally considered safe. It's important to be cautious in certain cases due to potential risks. These include;
- Allergic Reactions: If you have a known allergy to Tizanidine or its components, it is advised not to take this medication.
- Liver Disease: Patients with liver disease may experience increased side effects from Tizanidine since their bodies have difficulty metabolizing the drug effectively. It is recommended to consult your doctor before starting treatment if you have any liver problems.
- Pregnancy & Breastfeeding: The safety of using Tizanidine during pregnancy has not been extensively studied. It's crucial to discuss with your healthcare provider whether the benefits outweigh the risks if you are pregnant or planning on becoming pregnant while taking this medication. Additionally, it is unclear whether Tizanidine passes into breast milk; therefore, breastfeeding mothers are advised to consult their doctors before using Tizanidine.
Precautions When Using Tizanidine
In addition to contraindications, patients should take precautions into account when using Tizanidine. If you have kidney problems, make sure to inform your healthcare provider, as they may need to adjust the medication or monitor you closely. It's also important to avoid or limit alcohol consumption while taking Tizanidine as it can increase the risk of side effects like drowsiness and dizziness.
Older adults should be particularly cautious about the side effects of Tizanidine such as dizziness and sedation so their healthcare providers might recommend a lower dosage. To ensure your safety and suitability for Tizanidine, discuss your history with your healthcare provider and carefully consider any potential risks. Always follow their recommended dosage adjustments and monitoring requirements based on your circumstances.
It's crucial to keep in mind all safety measures and warnings before taking Tizanidine as it has the potential for adverse effects. Now let's explore available medications that may be suitable for your condition.
8. Compare Alternatives to Tizanidine
When you're thinking about using Tizanidine as a muscle relaxant, it's important to look into options and carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of each choice. In this section, we'll talk about muscle relaxants, nonpharmacological alternatives, complementary therapies, the costs involved, and having a conversation with your doctor regarding Tizanidine.
Tizanidine vs. Other Muscle Relaxants
There are other muscle relaxants in the market that can be compared to Tizanidine. Some chosen options include Baclofen, Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), Methocarbamol (Robaxin), and Diazepam (Valium).
Therefore it is crucial to have a discussion with your healthcare provider about the advantages and disadvantages of any muscle relaxant medications you may be considering.
Non-Pharmacological Muscle Relaxant Options
Besides medication-based treatments such as Tizanidine or other muscle relaxants mentioned previously, there are also pharmacological methods to manage muscle spasms or pain;
1. Physical therapy: A skilled physical therapist can assist you in enhancing flexibility and strength through exercises tailored to your specific needs.
2. Massage therapy: This technique can help ease muscles and enhance blood circulation, providing relief from muscle spasms or discomfort.
3. Heat/cold therapy: Applying cold packs to the affected area can temporarily alleviate muscle discomfort.
4. Mind-body techniques: Practices like yoga, tai chi, and meditation can effectively manage stress levels that often contribute to muscle tension.
Complementary Therapies
Apart from the treatments for managing muscle-related issues, there are also complementary therapies available. Some popular choices include;
- Acupuncture; This is a Chinese medicine technique where thin needles are inserted into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote relaxation.
- Supplementation with magnesium; Magnesium is an essential mineral that helps with proper nerve function and muscle contraction. Taking magnesium supplements has been found to be helpful in reducing cramps and spasms.
- CBD oil; Derived from plants, CBD oil is a natural compound that has shown potential benefits in relieving chronic pain without causing any psychoactive effects associated with marijuana use.
When considering treatment options, it's important to compare them to ensure you get the best medication for your specific needs.
When considering Tizanidine as a muscle relaxant, it's important to compare it with options such as Baclofen, Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), Methocarbamol (Robaxin), and Diazepam (Valium).
Additionally, pharmacological approaches like therapy, massage therapy, heat/cold therapy, and mind-body techniques can effectively manage muscle spasms or pain. Complementary therapies, like acupuncture, magnesium supplementation, and CBD oil, may also provide relief from pain.
9. Tizanidine FAQ
What is the primary purpose of taking Tizanidine?
Tizanidine is commonly used as a muscle relaxant for individuals who suffer from spasms caused by conditions such as sclerosis, spinal cord injury, or chronic pain. Relaxing the muscles and reducing spasticity can enhance mobility and overall well-being. Discover more about the applications of Tizanidine here.
How long does it take for Tizanidine to start working?
The effects of Tizanidine usually kick in around 1 to 2 hours after taking it. However, how quickly it works can vary from person to person based on factors such as metabolism and other medications you may be taking at the time. It's crucial to follow your doctor's recommended dosage instructions to achieve the possible results.
Can I take Tizanidine with other medications?
It's important to be cautious when taking medications with Tizanidine as they could potentially interact in a harmful way or reduce its effectiveness. Some known drugs that should not be combined with Tizanidine include fluvoxamine (Luvox), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), birth control pills containing ethinyl estradiol/norethindrone acetate/mestranol combination products, and others. You can find a list of drug interactions here. Remember to consult your healthcare provider before starting any new medication while using Tizanidine.
What are the potential side effects of Tizanidine?
Some common responses to tizanidine might involve feeling sleepy, dizzy having a mouth, or experiencing constipation. Although it is rare there could be serious side effects like liver damage or low blood pressure.
It is important to be vigilant for any symptoms and promptly reach out to your healthcare provider. If you encounter any symptoms while using Tizanidine make sure to get in touch with your healthcare provider right away. You can find information, about potential side effects here.
Is it safe to consume alcohol while taking Tizanidine?
No it is not advisable to drink alcohol while taking Tizanidine as it may heighten the chances of encountering effects such as drowsiness and impaired motor skills. It would be wise to refrain from consuming beverages while undergoing treatment with this medication.
Can I take Tizanidine if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
It is generally not recommended to take Tizanidine while pregnant unless it's absolutely necessary. This is because there is no data available on its safety for unborn babies. Additionally, it is unclear whether Tizanidine passes into breast milk. Therefore, if you are a nursing mother, it's important to consult your healthcare provider before using this medication. Please keep in mind that these FAQs are provided as guidance only. It's always best to consult with your doctor or pharmacist for advice on the use of Tizanidine based on your specific medical history and needs.
What Is a Substitute for Tizanidine?
If Tizanidine is not suitable for you, there are other muscle relaxants that you can consider. These include baclofen, cyclobenzaprine, and carisoprodol. However, it's important to consult your healthcare provider before making any changes, in medication. They will be able to determine the appropriate option based on your specific medical condition.
In summary, Tizanidine is a muscle relaxant used to treat muscle spasms caused by conditions. It usually takes effect within 1 or 2 hours. It should not be taken with certain medications or alcohol. Some common side effects include drowsiness and constipation. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, it is advisable to consult your healthcare provider before using this medication.
Understanding Tizanidine and Where to Purchase it
Before taking Tizanidine, it is crucial to have an understanding of its properties. Examining the aspects can help determine the appropriate dosage and administration as well as identify any potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
It's also important to take into account any precautions or contraindications associated with Tizanidine. If you're considering purchasing Tizanidine, make sure to compare options and fully comprehend its intended uses. For information, on Tizanidine or to make a purchase online, you can visit Buy Pharma.
Don't let pain hinder you any longer. Acquire Tizanidine today from Buy Pharma!