Introduction
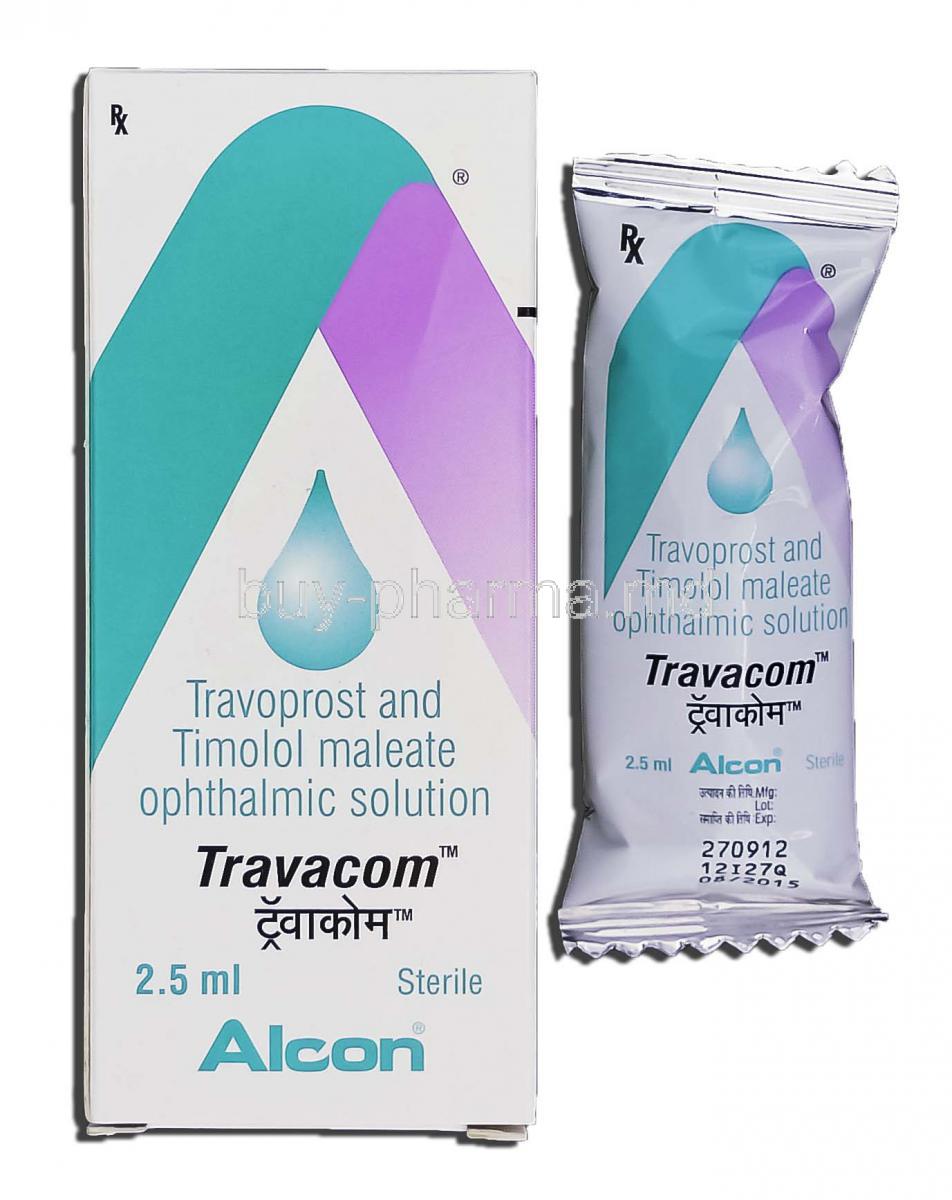
Overview of Travacom Eye Drop
Travacom Eye Drop is an advanced ophthalmic solution designed to reduce elevated intraocular pressure, a major risk factor for glaucomatous damage. This medication combines two potent agents to deliver superior therapeutic efficacy. By lowering pressure within the eye, it helps protect the optic nerve and preserve visual acuity over the long term.
Therapeutic Classification and Purpose
Classified as an antiglaucoma preparation, Travacom Eye Drop merges a prostaglandin analog with a beta-adrenergic blocker. Its dual action targets different pathways to achieve maximum pressure reduction, making it particularly suitable for patients requiring more than monotherapy to control their condition.
Conditions it is Commonly Prescribed For
- Open-angle glaucoma
- Ocular hypertension
- Cases where monotherapy fails to achieve sufficient pressure control
Composition and Formulation
Active Ingredients: Travoprost and Timolol Maleate
The solution contains Travoprost, a prostaglandin analog, and Timolol Maleate, a non-selective beta-blocker. Both act in synergy to improve aqueous humor outflow and reduce its production simultaneously.
Mechanism of Combining Prostaglandin Analog with Beta-Blocker
Travoprost enhances uveoscleral outflow, while Timolol curtails aqueous humor secretion. By addressing both ends of intraocular pressure regulation, the formulation achieves a comprehensive therapeutic effect.
Available Concentrations and Dosage Forms
Travacom Eye Drop is supplied as a sterile ophthalmic solution in multi-dose dropper bottles, typically in fixed concentrations of the active agents to ensure consistency of administration.
Mechanism of Action (How Travacom Eye Drop Works)
Role of Travoprost in Reducing Intraocular Pressure
Travoprost, a prostaglandin F2α analog, binds to FP receptors within the eye, remodeling extracellular tissue to facilitate enhanced uveoscleral outflow.
Function of Timolol Maleate as a Beta-Blocker
Timolol suppresses aqueous humor secretion by inhibiting beta-adrenergic receptor activity in the ciliary body, thereby lowering the rate of fluid production.
Synergistic Effect of Combination Therapy
When used together, the two agents deliver superior pressure reduction compared to either drug alone, making the combination especially useful in patients with difficult-to-control glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
Medical Uses
Primary Use in Open-Angle Glaucoma
Travacom Eye Drop is primarily indicated for open-angle glaucoma, the most prevalent form of the disease. It slows progression and mitigates optic nerve damage.
Use in Ocular Hypertension to Reduce Intraocular Pressure
In patients without glaucoma but with elevated intraocular pressure, the drops reduce ocular strain and help delay disease onset.
Prevention of Optic Nerve Damage and Vision Loss
By maintaining intraocular pressure within target ranges, the medication helps safeguard the optic nerve from irreversible injury and long-term vision deterioration.
Off-Label Uses
Potential Role in Secondary Glaucoma
Travacom may be considered in forms of secondary glaucoma such as pseudoexfoliation glaucoma when standard regimens prove inadequate.
Management of Steroid-Induced Ocular Hypertension
It is sometimes used to counteract elevated eye pressure caused by long-term corticosteroid therapy.
Adjunct Therapy in Patients Unresponsive to Monotherapy
For individuals whose intraocular pressure remains uncontrolled with a single agent, Travacom offers a fixed-dose alternative that simplifies treatment adherence.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines for Adults
Typically instilled once daily into the affected eye(s), unless otherwise directed by a physician. Frequency should not exceed recommended limits to avoid reduced efficacy.
Method of Instillation and Patient Instructions
- Wash hands before use.
- Tilt head back and pull down lower eyelid.
- Instill one drop into the conjunctival sac.
- Avoid touching the dropper tip to any surface, including the eye.
Importance of Adherence to Dosing Schedule
Consistency is critical. Skipping doses or irregular use diminishes pressure control and increases risk of optic nerve damage.
What to Do if a Dose is Missed
If a dose is missed, administer it as soon as remembered unless it is nearly time for the next dose. Double dosing is discouraged.
Special Administration Considerations
Administration in Elderly Patients
Older patients may require closer monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory status, though no routine dosage adjustment is mandated.
Administration in Pregnant Women
Due to potential fetal risks, Travacom is generally avoided unless the benefits outweigh the risks. Physicians weigh therapeutic necessity against safety concerns.
Administration in Nursing Mothers
As timolol may be excreted in breast milk, caution is advised. Alternative treatments are considered when nursing is ongoing.
Administration in Children
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been firmly established. Use in children is limited and requires specialist oversight.
Side Effects of Travacom Eye Drop
Common Side Effects
- Eye redness and irritation
- Blurred vision shortly after instillation
- Sensation of a foreign body
- Eyelash growth and darkening of iris or eyelid skin
Serious Side Effects
- Bradycardia, arrhythmias, or hypotension
- Respiratory issues, particularly in patients with asthma
- Severe allergic responses including swelling and rash
- Corneal complications or ocular infections
Warnings and Precautions
Travacom requires judicious use under medical supervision. Risks include:
- Systemic absorption of timolol, leading to cardiovascular or respiratory complications
- Prolonged use of prostaglandin analogs may alter ocular tissues
- Regular intraocular pressure monitoring is essential
- Potential cosmetic effects such as iris pigmentation and eyelash thickening
- Contamination of the dropper tip can introduce ocular infection
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to Travoprost, Timolol, or any excipients
- Patients with bronchial asthma or severe COPD
- Individuals with severe bradycardia, advanced heart block, or overt cardiac failure
- Pregnancy and lactation where risk outweighs benefit
Drug Interactions
Interaction with Systemic Beta-Blockers
When Travacom Eye Drop is administered alongside systemic beta-blockers, the pharmacological effects may intensify. This can result in additive suppression of cardiac function, reduced heart rate, and heightened risk of hypotension. Patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions require vigilant monitoring when concurrent therapy is unavoidable.
Interaction with Calcium Channel Blockers and Antiarrhythmic Agents
Timolol within the formulation may potentiate the effects of calcium channel blockers and antiarrhythmic agents. This interaction can compromise myocardial contractility, slow atrioventricular conduction, and precipitate bradyarrhythmias. Close observation is recommended for patients on such regimens, particularly those with underlying conduction abnormalities.
Concomitant Use with CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit the CYP2D6 enzyme, such as quinidine or certain antidepressants, can elevate plasma concentrations of timolol. This may amplify systemic beta-blockade and increase the risk of adverse effects, including fatigue, dizziness, or significant cardiac complications. Physicians often consider alternative therapies or dose modifications in such scenarios.
Interaction with Other Intraocular Pressure-Lowering Medications
Co-administration with additional ocular hypotensives, such as prostaglandin analogs or carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, may yield unpredictable intraocular pressure responses. While sometimes beneficial, excessive pressure reduction or local irritation may occur. Combination therapy should be carefully justified and regularly reviewed.
Careful Administration and Monitoring
Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Timolol can obscure symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as tachycardia and tremors. Diabetic patients must monitor blood glucose levels diligently and remain alert to atypical signs of low blood sugar.
Patients with Thyroid Disorders
Beta-blockers may mask clinical manifestations of hyperthyroidism, including tachycardia. This concealment can delay diagnosis or precipitate thyroid storm if abrupt withdrawal occurs. Medical supervision is mandatory for individuals with thyroid dysfunction.
Individuals with History of Severe Allergies or Anaphylaxis
Patients predisposed to severe allergic reactions may not respond adequately to standard doses of epinephrine while using timolol-containing eye drops. Such individuals should exercise extreme caution and consult healthcare professionals prior to initiation.
Patients Undergoing Surgery
Beta-blockade may interfere with anesthetic agents during surgical procedures, potentially exaggerating cardiovascular depression. Surgeons and anesthesiologists must be informed of ongoing timolol therapy to ensure perioperative safety.
Overdosage and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose
- Severe bradycardia
- Marked hypotension
- Bronchospasm and respiratory distress
- Acute cardiac failure in susceptible patients
Immediate Supportive Measures
At the first sign of overdose, symptomatic support is paramount. This includes airway stabilization, oxygen supplementation, and intravenous fluids to counteract hypotension.
Emergency Treatment Protocols
Depending on the clinical presentation, interventions may include intravenous atropine for bradycardia, vasopressors for persistent hypotension, and bronchodilators for bronchospasm. In extreme cases, cardiac pacing or advanced life support measures may be required.
Handling and Storage Precautions
Recommended Storage Temperature and Conditions
The solution should be stored at controlled room temperature, away from excessive heat, direct sunlight, and moisture. Extreme temperatures may compromise stability and efficacy.
Shelf-Life After Opening the Bottle
Once opened, the product is generally safe for use up to 4 weeks, after which sterility and potency cannot be guaranteed. Patients are advised to mark the date of opening on the bottle for reference.
Avoiding Contamination During Use
The dropper tip must not come into contact with the eye, fingers, or any surface to prevent microbial contamination. Infections introduced this way can cause severe ocular complications.
Safe Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Unused or expired drops should not be discarded in household waste. They must be disposed of following local pharmaceutical waste guidelines or returned to pharmacies offering medication take-back services.