Introduction to Enrofloxacin Chewable Tablets
Overview of Enrofloxacin as a Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic for Veterinary Use
Enrofloxacin is a potent, synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic developed specifically for veterinary application. Known for its bactericidal properties, it effectively combats a broad array of Gram-negative and some Gram-positive pathogens. This makes it particularly valuable in treating infections resistant to other antimicrobial agents.
Availability in Chewable Tablet Form for Dogs and Cats
Designed with compliance in mind, Enrofloxacin is widely available in chewable tablet form. These palatable tablets cater to both dogs and cats, easing administration and reducing stress for pet owners. Their formulation ensures adequate absorption and precise dosing.
Regulatory Status and Common Brand Names
Enrofloxacin is FDA-approved for veterinary use and is commonly found under brand names such as Baytril® and other generics. It adheres to stringent veterinary pharmaceutical standards, ensuring safety and efficacy across various clinical scenarios.
Key Therapeutic Benefits and Convenience of Administration
- Broad-spectrum antimicrobial coverage - Rapid onset of action - High tissue penetration - Easy-to-administer chewable format These attributes make it a trusted choice for both acute and chronic infections in small animal medicine.
Medical Uses and Indications of Enrofloxacin Chewable Tablets
Approved Uses in Veterinary Medicine
- Dermatitis and Pyoderma: Enrofloxacin is highly effective against common skin pathogens such as Staphylococcus pseudintermedius.
- Urinary Tract Infections: It is commonly prescribed for bacterial cystitis and other UTIs in dogs and cats.
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Used in managing conditions like kennel cough, bronchitis, and pneumonia caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Wound Infections: Promotes recovery in traumatic or post-surgical infections.
- Otitis Externa: Frequently combined with topical agents to treat bacterial ear infections.
Off-Label and Less Common Uses
- Prostatitis and Deep Tissue Infections: Enrofloxacin's tissue penetration makes it effective for hard-to-reach infections.
- Use in Exotic Species: Off-label use in birds, reptiles, and small mammals is guided by veterinary discretion.
- Gastrointestinal Infections: Occasionally used in bacterial enteritis where culture indicates sensitivity.
Mechanism of Action: How Enrofloxacin Works
Inhibition of Bacterial DNA Gyrase and Topoisomerase IV
Enrofloxacin inhibits enzymes essential for bacterial DNA replication—DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV—leading to bacterial death.
Bactericidal Activity and Broad-Spectrum Effectiveness
Unlike bacteriostatic agents, Enrofloxacin rapidly kills susceptible organisms. Its broad-spectrum activity covers E. coli, Salmonella, Pseudomonas, and more.
Rapid Absorption and Systemic Distribution in Tissues
After oral administration, Enrofloxacin demonstrates excellent bioavailability, achieving therapeutic concentrations in skin, lungs, liver, kidneys, and urinary tract.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosing Recommendations
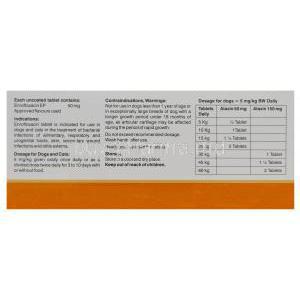
- Dogs: 5–20 mg/kg once daily
- Cats: 5 mg/kg once daily
- Treatment duration: Typically 5–10 days depending on infection
Always complete the full course to prevent antimicrobial resistance.
Administration Instructions
Enrofloxacin chewable tablets can be given with or without food. Most pets accept them willingly due to enhanced flavoring. If a dose is missed, administer it as soon as remembered unless the next dose is imminent—do not double dose.
Composition and Formulation Details
Active Ingredient: Enrofloxacin Concentration per Tablet
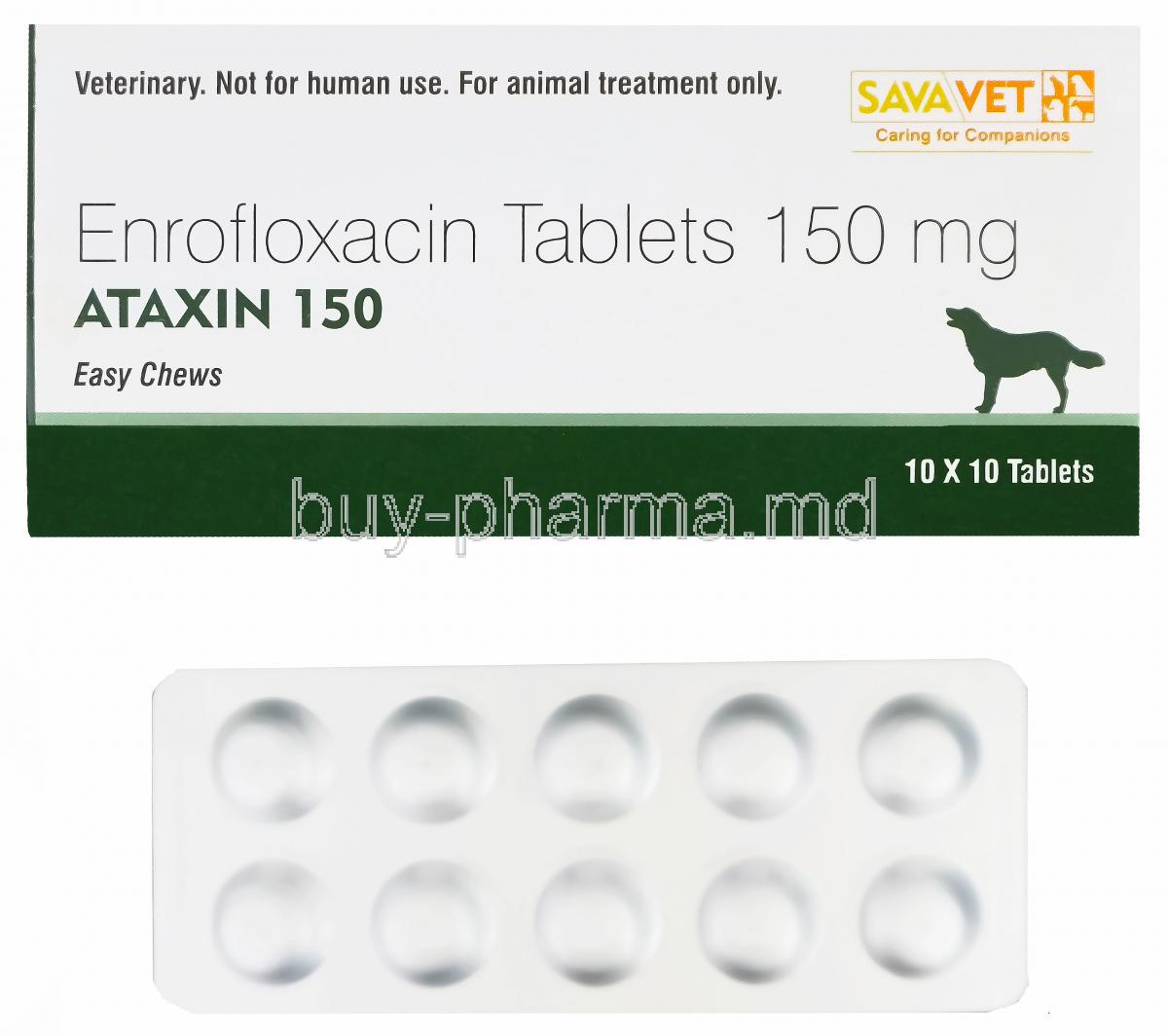
Each tablet contains a precise dose of Enrofloxacin, typically available in 15 mg, 50 mg, and 150 mg strengths.
Inactive Ingredients and Flavoring Agents
- Lactose monohydrate - Beef or poultry flavorings - Magnesium stearate - Microcrystalline cellulose
Available Tablet Strengths and Packaging
Tablets are scored for flexible dosing and available in blister packs or bottles of 30, 100, or more, tailored for clinical and home use.
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Common Side Effects
- Mild vomiting or nausea - Diarrhea - Lethargy or reduced appetite These typically resolve without intervention.
Rare but Serious Adverse Effects
- Articular cartilage damage: Especially in young, growing dogs - Neurological symptoms: Seizures, tremors, or disorientation - Hypersensitivity: Facial swelling, hives, or respiratory distress Veterinary attention is required if serious effects emerge.
Drug Interactions and Compatibility
Interaction with Theophylline, Antacids, and Sucralfate
Concurrent use with antacids or sucralfate may impair absorption. Theophylline levels may increase due to reduced hepatic clearance.
Risk of QT Prolongation with Concurrent Medications
Caution is advised when used with drugs known to prolong QT interval, including certain antifungals and antiarrhythmics.
Veterinary Advice on Combining with NSAIDs or Corticosteroids
While often co-prescribed, combining with NSAIDs or steroids increases the risk of seizures and gastrointestinal side effects. Veterinary supervision is critical.
Warnings and Safety Information
Caution in Animals with Known Seizure Disorders
Enrofloxacin lowers the seizure threshold. It should be used with extreme caution or avoided in epileptic pets.
Avoid Use in Dogs During Rapid Growth Phase
Particularly in large breeds under 8 months, the risk of cartilage damage necessitates careful consideration.
Potential for Development of Bacterial Resistance
Misuse or incomplete dosing may result in resistant bacterial strains, reducing future therapeutic options.
Contraindications for Use
- Hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones
- Neonatal puppies and kittens unless life-saving
- Severe hepatic or renal dysfunction where metabolism or excretion is impaired
Careful Administration and Risk Management
Monitoring Liver and Kidney Function During Prolonged Use
Long-term therapy necessitates periodic blood tests to monitor organ function and prevent toxicity.
Use with Caution in Dehydrated or Debilitated Animals
Such patients may exhibit altered pharmacokinetics and heightened sensitivity to adverse effects.
Recommendations for Animals with Cardiovascular Conditions
Enrofloxacin may exacerbate arrhythmias in susceptible animals, requiring ECG monitoring in high-risk cases.
Important Precautions During Treatment
Avoid Excessive Sunlight or UV Exposure During Therapy
Photosensitivity reactions have been documented; minimize direct sun exposure during the course.
Monitor for Changes in Behavior, Coordination, or Eating Habits
Sudden behavioral shifts could indicate neurological side effects requiring immediate veterinary evaluation.
Importance of Veterinary Follow-Up During Treatment Course
Reevaluation ensures therapeutic success and helps prevent complications or relapse.
Special Populations: Use in Specific Groups
Use in Elderly Pets
Geriatric animals exhibit physiological changes that may influence the pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin. With age, hepatic and renal clearance mechanisms can diminish, leading to altered drug metabolism and excretion.
- Organ Function Decline: Diminished kidney filtration and hepatic enzyme activity necessitate dosage reconsideration.
- Risk of Accumulation: Chronic administration may result in elevated plasma levels and heightened toxicity.
Routine blood work, including liver enzymes and serum creatinine, is recommended to evaluate organ reserve and adjust treatment parameters accordingly.
Use in Pregnant and Lactating Animals
The administration of enrofloxacin to pregnant or nursing animals remains a subject of caution due to insufficient data.
- Safety Data Deficiency: Reproductive studies in companion animals are limited. As such, it is generally contraindicated unless the therapeutic benefit outweighs the potential risk.
- Teratogenic Potential: Enrofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, may interfere with cartilage development in the fetus, particularly during critical stages of gestation.
When administration is deemed necessary, the lowest effective dose should be used under strict veterinary supervision.
Use in Puppies, Kittens, and Juvenile Animals
Young, rapidly growing animals are particularly susceptible to adverse orthopedic effects from fluoroquinolones.
- Growth Plate Vulnerability: In large-breed puppies under 8 months, the drug may cause irreversible damage to developing cartilage, leading to lameness or joint deformities.
- Veterinary Oversight: If enrofloxacin is essential in pediatric patients, a tailored dose regimen is imperative, with close observation for musculoskeletal symptoms.
In kittens, the risk is comparatively lower, but caution remains necessary, especially during early developmental stages.
Overdose and Toxicity Management
Symptoms of Enrofloxacin Overdose
An overdose can precipitate acute and sometimes life-threatening symptoms:
- Severe gastrointestinal distress: persistent vomiting and diarrhea
- Neurological disturbances: tremors, disorientation, seizures
- Cardiotoxic effects: arrhythmias or rapid heartbeat (in rare cases)
These manifestations often appear within hours of excessive ingestion.
Immediate Actions and Emergency Intervention
Swift intervention is critical. If an overdose is suspected:
- Contact a veterinary emergency service immediately
- Induce emesis only under veterinary instruction
- Provide supportive measures such as IV fluids or anticonvulsants if advised
Do not delay treatment. Early decontamination significantly improves prognosis.
Decontamination and Supportive Care
- Activated charcoal may be administered to reduce systemic absorption - Intravenous fluid therapy helps flush the kidneys and stabilize circulation - Antiepileptic medications are used in case of seizures Veterinary hospitalization may be required for severe cases.
Proper Handling and Administration Precautions
Safe Handling for Pet Owners
Although designed for animal use, enrofloxacin should be handled with care:
- Wash hands thoroughly after administering tablets
- Avoid contact with eyes or mucous membranes
If accidental contact occurs, rinse immediately with water.
Preventing Accidental Ingestion
Keep chewable tablets out of reach of children and other household pets.
- Store in a secure, closed container
- Do not leave tablets in open areas or mixed with pet food unattended
Enrofloxacin is not intended for human consumption and may cause harm if ingested.
Veterinary-Only Use
This medication is intended for prescription use by licensed veterinarians. Human or unprescribed animal use is strictly prohibited.
Storage and Stability Information
Ideal Storage Conditions
To maintain potency, enrofloxacin chewable tablets should be stored:
- At controlled room temperature, typically between 15–30°C (59–86°F)
- In a dry place, protected from direct sunlight and moisture
Avoid storing in humid environments such as bathrooms or kitchens.
Shelf Life and Expiration
Each product has a clearly marked expiration date. Expired tablets may lose efficacy or become unstable.
- Do not administer past the expiration date
- Inspect for any discoloration or crumbling before use
Safe Disposal of Medication
Do not flush unused tablets down the toilet. Follow these steps:
- Return to a veterinary clinic for proper disposal
- Use local pharmaceutical take-back programs when available
Environmental safety and pet welfare require conscientious medication disposal practices.