FCN, Fluconazole
- Introduction to Fluconazole (FCN)
- How Fluconazole Works
- Dosage and Administration of Fluconazole
- Uses of Fluconazole
- Off-Label Uses of Fluconazole
- Side Effects of Fluconazole
- Drug Interactions with Fluconazole
- Contraindications and Precautions
- Special Considerations in Administration
- Overdose and Management
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Conclusion: Integrating Fluconazole into Antifungal Therapy
Introduction to Fluconazole (FCN)
Fluconazole, often shortened to FCN plays a role in the fight against fungal infections. Its development represents a step forward in antifungal treatment providing a powerful yet safe option, for addressing mycoses. This article seeks to explore the facets of Fluconazole ranging from its historical origins to its current uses in medical practice.
Overview of Fluconazole
The historical development and FDA approval process of Fluconazole tell a story of extensive research and clinical trials. Back in the 20th century, Fluconazole emerged as a groundbreaking antifungal medication thanks to its improved effectiveness against specific fungi while being less toxic.
What sets Fluconazole apart is its chemical structure, which gives it strong antifungal properties. It comes in forms, like tablets, injections, and suspensions providing versatility in treating different types of fungal infections.
How Fluconazole Works
The effectiveness of Fluconazole in fighting infections is based on its complex pharmacodynamics. Its unique and effective way of working distinguishes it, from other antifungal medications.
Pharmacodynamics of Fluconazole
Fluconazole's pharmacodynamic properties involve its capability to specifically target and hinder the cytochrome P450 enzyme, a crucial element in the synthesis of fungal cell membranes.
This targeted inhibition demonstrates effectiveness against fungal cells while having minimal impact, on human cells ensuring a higher level of safety.
Mechanism of Action Against Fungal Infections
Fluconazole works by blocking an enzyme called lanosterol 14α demethylase which plays a crucial role in the production of ergosterol in fungi. By interrupting this process Fluconazole interferes with the structure of the cell membrane ultimately causing the cells to die. This targeted method has proven to be very successful, in eliminating a range of fungal pathogens.
Comparative Efficacy with Other Antifungals
When compared to antifungal medications Fluconazole shows better effectiveness, in treating certain fungal infections, especially those caused by Candida species. The way it is absorbed orally and distributed throughout the body tissues enhances its ability to effectively treat infections.
Candida Under the Microscope
Dosage and Administration of Fluconazole
The effectiveness of Fluconazole, as a treatment, relies on the proper dosage and administration. Customizing the dosage based on each patient's requirements improves both its effectiveness and safety.
Standard Dosage Guidelines
The recommended amount of Fluconazole to take depends on the type and seriousness of the infection. In complicated cases, a lower dose is sufficient but more severe infections may require higher doses. By following these guidelines you can achieve the possible results, in your treatment.
Adjustments for Specific Patient Populations
The dosage of Fluconazole needs to be adjusted in specific groups of patients like those, with kidney problems or who are either very young or very old.
This personalized approach helps minimize the chances of experiencing side effects while still ensuring the medicine is effective.
Administration Methods and Techniques
Fluconazole can be given either by mouth or through an IV depending on the situation. Often taking it orally is preferred due to its convenience and ease of use for patients. However, in cases where the infection is more severe or difficult to treat intravenous administration may be necessary.
Uses of Fluconazole
Fluconazole(1), a component in antifungal treatment is widely used to treat various fungal infections with great effectiveness. This medication is well known for its action and tolerability making it an important tool, in both the treatment and prevention of fungal diseases.
1. National Library of Medicine - Fluconazole
2. MedlinePlus - Fluconazole
Primary Indications: Candidiasis and Cryptococcal Meningitis
Fluconazole is highly effective in treating Candidiasis and Cryptococcal Meningitis. Candidiasis covers a range of infections from mucosal to systemic and Fluconazole is a reliable treatment option for it.
In the case of Cryptococcal Meningitis in patients with HIV/AIDS Fluconazole plays a crucial role in both initial treatment and ongoing therapy leading to a significant reduction, in morbidity.
2. ASM Journals - Fluconazole Monotherapy Is a Suboptimal Option for Initial Treatment of Cryptococcal Meningitis Because of Emergence of Resistance
Prophylactic Use in Immune-Compromised Patients
For individuals with weakened systems like those receiving chemotherapy or living with HIV/AIDS, the use of Fluconazole, as a preventive measure is evidence of its effectiveness.
This proactive approach significantly reduces the occurrence of fungal infections thus improving the well-being of these vulnerable patient populations.
Other FDA-Approved Uses
Fluconazole apart from its uses has also been approved by the FDA for a wide range of other fungal infections. These include, but Are not limited to;
- Treating candidiasis in the mouth and esophagus when local treatment is not enough
- Managing urinary tract infections and peritonitis caused by Candida species
- Addressing coccidioidomycosis when more invasive treatment options are not feasible.
The fact that Fluconazole can be used in ways highlights its versatility, as an antifungal medication.
Off-Label Uses of Fluconazole
Fluconazole although well known for its approved uses by the FDA also attracts interest due to its effectiveness in off-label applications. These additional uses, across medical disciplines, showcase the versatile pharmacological characteristics of Fluconazole.
Application in Dermatological Conditions
Fluconazole off-label use has proven to be highly beneficial in the field of dermatology. It has been effectively used to treat conditions such as;
- Tinea Corporis and Tinea Cruris which are superficial fungal infections that often do not respond well to topical treatments but show positive results with the Fluconazoles systemic approach.
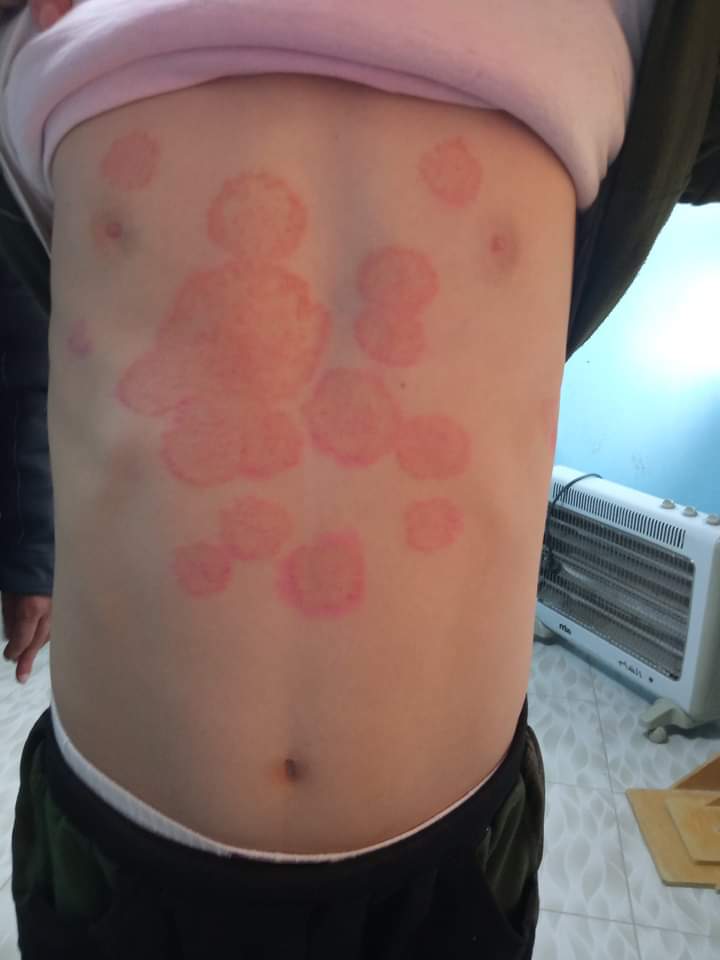
Tinea Corporis
- Additionally, Fluconazole is a treatment option for Onychomycosis, a challenging nail infection due to its ability to stay in keratinous tissues for an extended period of time.
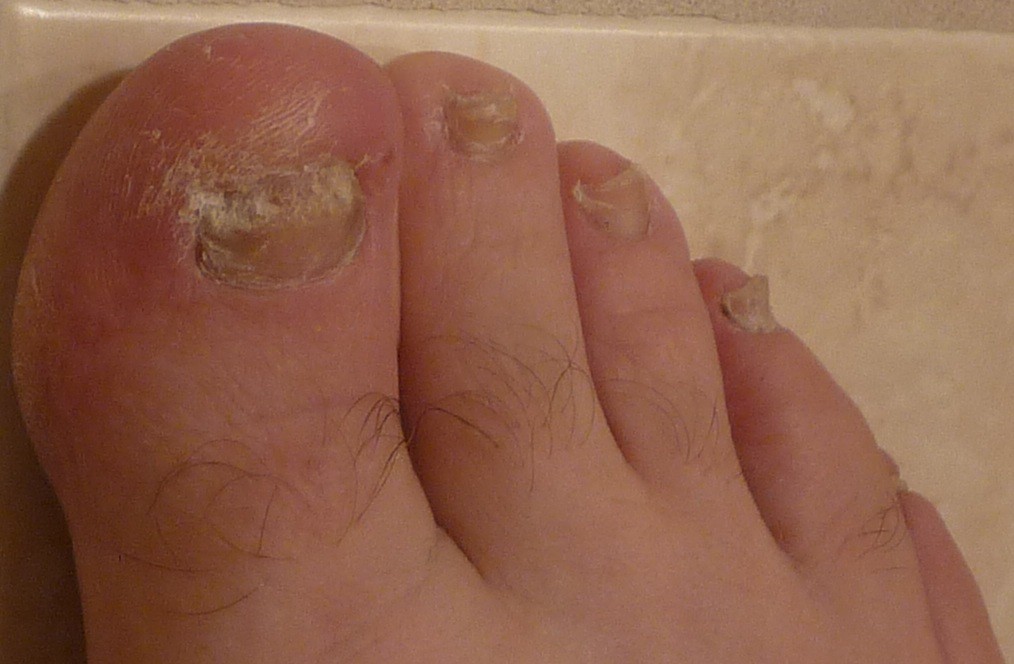
Onychomycosis
These applications highlight the usefulness of Fluconazole, in managing dermatological fungal infections.
Use in Rare Fungal Infections
Fluconazole is a medication that can be used to treat rare and unusual fungal infections. Its effectiveness in these common types of infections which often have limited treatment options makes it a valuable alternative for patients. Some examples of these infections include ;
- Blastomycosis is a fungal infection where Fluconazole can be an effective treatment option especially in mild to moderate cases.
- Another example is Chromoblastomycosis, a skin infection where Fluconazole can serve as a powerful ally when surgical options are limited or not recommended.
This expanded range of applications highlights the adaptability of Fluconazole, in addressing fungal challenges.
Emerging Research and Potential New Indications
Ongoing research is constantly expanding the horizons of Fluconazole applications.
- Recent studies are indicating that there could be potential uses for this medication, including its role, in neurological disorders where fungal elements are involved.
- Additionally, there is a possibility of employing combination therapies to manage resistant infections.
This exciting field of research is opening up possibilities for the use of Fluconazole, which could potentially revolutionize antifungal therapy.
Side Effects of Fluconazole
Although Fluconazole is an effective antifungal medication it is not without its potential side effects. These can vary from common reactions to more severe adverse events, which require careful monitoring and appropriate management.
Common Side Effects: Frequency and Severity
The typical side effects of Fluconazole are usually mild and temporary.
- These may include symptoms, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Headaches and dizziness are also possible. They often go away without needing any treatment
- . In some cases of reactions skin rashes may occur, requiring discontinuation of the medication.
The frequency and intensity of these side effects usually depend on the dosage.
Serious Adverse Reactions: Risk Factors and Management
Some patients might have side effects from taking Fluconazole. These can include liver problems, heart issues for those with existing conditions, and serious skin reactions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
It's important to identify risk factors and have strategies, in place to manage these reactions effectively. Regular liver function tests should be done to detect any liver damage early on. If any of these reactions occur immediate medical attention is necessary.
Long-Term Side Effects and Monitoring
Extended use of Fluconazole can lead to severe adverse effects, such, as adrenal insufficiency and hormonal imbalances. Ongoing gastrointestinal disturbances may also persist. It is recommended to monitor and assess these effects to minimize their impact.
Drug Interactions with Fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication that has the potential to interact with different drugs affecting how well they work and their safety.
Common Drug-Drug Interactions
There are some things to consider when taking Fluconazole alongside other medications.
- It can increase the levels of hypoglycemics, warfarin, and phenytoin in the blood.
- There is also a risk of myopathy when taking statins at the same time.
- Additionally, it may reduce the effectiveness of contraceptives.
It's crucial to be aware of these interactions and monitor them carefully to ensure medication management.
Impact on Efficacy of Concurrent Medications
Fluconazole has the ability to either enhance or reduce the effectiveness of medications. It works by inhibiting P450 enzymes, which can impact how certain drugs are metabolized when taken together. This could potentially result in levels of the medication, in the body and increase the risk of experiencing harmful effects.
Guidelines for Avoiding Adverse Interactions
To prevent any effects healthcare professionals should take the following steps when prescribing Fluconazole;
1. Before prescribing Fluconazole healthcare providers should conduct a review of the patient's medications.
2. If necessary they should adjust the dosages of any medications that might be affected or explore alternative treatment options.
3. It is important to monitor for any signs of toxicity or changes, in the effectiveness of other medications being taken concurrently.
By following these measures healthcare providers can minimize the risk of interactions and ensure patient safety.
Contraindications and Precautions
When prescribing Fluconazole it is important to consider any contraindications and take necessary precautions to prioritize the safety of the patient.
Absolute Contraindications for Fluconazole Use
Fluconazole should not be used in patients who have a known allergy to Fluconazole or similar azole antifungals. It is also important to avoid using Fluconazole with terfenadine or cisapride as it can pose a risk of serious cardiac events. These contraindications are crucial to follow in order to prevent life-threatening reactions.
Precautions in Special Populations
It is important to exercise caution when prescribing Fluconazole for the following cases;
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women as there may be potential risks for the fetus or infant.
- Patients with renal impairment may require adjustments in the dosage.
- Elderly patients might be more prone, to experiencing adverse effects.
Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
Allergic responses, to Fluconazole while uncommon have the potential to be serious. Symptoms can vary from skin rashes to a severe reaction known as anaphylaxis. It is essential to seek medical attention in cases of severe hypersensitivity reactions.
Special Considerations in Administration
When administering Fluconazole it is crucial to pay attention to specific groups of patients. It's important to customize the approach in order to achieve effectiveness while minimizing any potential risks.
Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly patients need to be extra careful when taking Fluconazole because of their underlying health conditions and the likelihood of taking multiple medications at the same time. It might be necessary to adjust the dosage considering that kidney function is often reduced in this age group.
Fluconazole in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Using Fluconazole during pregnancy and breastfeeding can be a situation. It's important to analyze the risks and benefits before deciding whether to use this medication. In the trimester of pregnancy, it may be worth considering other antifungal treatments as well.
Pediatric Use: Safety and Efficacy
The use of Fluconazole, in children has been proven to be safe and effective. It is crucial to follow the appropriate dosage based on their age. It is recommended to monitor for any potential adverse effects especially in newborns and infants as the drug may take longer to be eliminated from their system.
Overdose and Management
Although Fluconazole is generally well tolerated it is important to seek medical assistance in case of an overdose. It is crucial to be aware of the symptoms and know how to manage the situation.
Recognizing Symptoms of Fluconazole Overdose
Signs of taking much Fluconazole may manifest as hallucinations displaying paranoid behavior and experiencing severe liver toxicity. Identifying these symptoms on is crucial, for effective handling.
Immediate Actions and Antidote Availability
Immediate medical attention is crucial in situations where an overdose is suspected. There is no antidote available, for Fluconazole overdose so treatment focuses on providing support and addressing symptoms. In cases of overdose hemodialysis may be considered as a potentially effective treatment option.
Long-Term Management and Monitoring
The management of an overdose of Fluconazole, in the term, requires monitoring the functioning of the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system (CNS). It is essential to follow up and provide supportive care to minimize any potential long term effects.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Properly storing and handling Fluconazole is crucial to maintain its effectiveness and ensure safety, in healthcare environments.
Optimal Storage Conditions for Fluconazole
Store fluconazole at room temperature ensuring it is kept away, from light and moisture. This will help maintain its stability and effectiveness as extreme temperatures and direct sunlight can cause the medication to degrade.
Safe Handling Practices in Healthcare Settings
In healthcare environments, it is essential to handle Fluconazole to avoid any potential contamination. Healthcare professionals must adhere to safety measures, which include wearing gloves while dealing with the medication.
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
To ensure the disposal of Fluconazole it is important to follow environmental safety guidelines. It is necessary to dispose of any expired medication correctly in order to protect the environment and minimize the chance of accidental ingestion.
Conclusion: Integrating Fluconazole into Antifungal Therapy
Fluconazole is a breakthrough in the field of antifungal treatment providing effective and safe options, for dealing with different types of fungal infections.
Summary of Key Points
The article emphasized the significance of taking into account patient characteristics when administering Fluconazole dealing with cases of overdose and ensuring proper storage and handling. Paying attention to these factors guarantees the medication's effective and safe usage.
Final Recommendations for Healthcare Practitioners and Patients
Healthcare professionals need to stay alert and attentive when it comes to the interactions and potential side effects of the drug well as the specific requirements of various patient groups. Patients should make sure to follow their prescribed dosages and promptly report any reactions or concerns they may have. By practicing these measures Fluconazole can effectively contribute to therapy as a valuable component.