Formoterol Fumarate/ Mometasone Furoate
- 1. Introduction to Formoterol Fumarate / Mometasone Furoate
- 2. Medical Uses and Approved Indications
- 3. Off-Label Uses of Formoterol Fumarate / Mometasone Furoate
- 4. Mechanism of Action and Pharmacological Profile
- 5. Dosage Forms and Recommended Administration
- 6. Composition and Excipients
- 7. Storage and Stability Guidelines
- 8. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- 9. Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- 10. Warnings and Important Safety Precautions
- 11. Special Population Considerations and Careful Administration
- 12. Overdose Management and Toxicity
- 13. Handling Precautions and Disposal Instructions
1. Introduction to Formoterol Fumarate / Mometasone Furoate
Formoterol Fumarate and Mometasone Furoate is a fixed-dose combination inhaler therapy prescribed for the long-term management of chronic airway disorders. This dual-action formulation synergizes a bronchodilator and an anti-inflammatory agent to improve pulmonary function and prevent respiratory symptoms.
The medication belongs to two pharmacologic classes:
- Formoterol Fumarate: a long-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA)
- Mometasone Furoate: an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)
Marketed under various brand names such as Dulera, Zenhale, and Elifor, it is available in both metered-dose and dry powder inhaler formats. The combination is indicated for the maintenance treatment of asthma and COPD, particularly in patients requiring both LABA and ICS therapy.
2. Medical Uses and Approved Indications
2.1 Treatment of Asthma
This combination is approved as a maintenance therapy for moderate to severe persistent asthma. It is beneficial in patients whose asthma remains uncontrolled on ICS alone, offering a step-up treatment approach to reduce daily symptoms and future exacerbations.
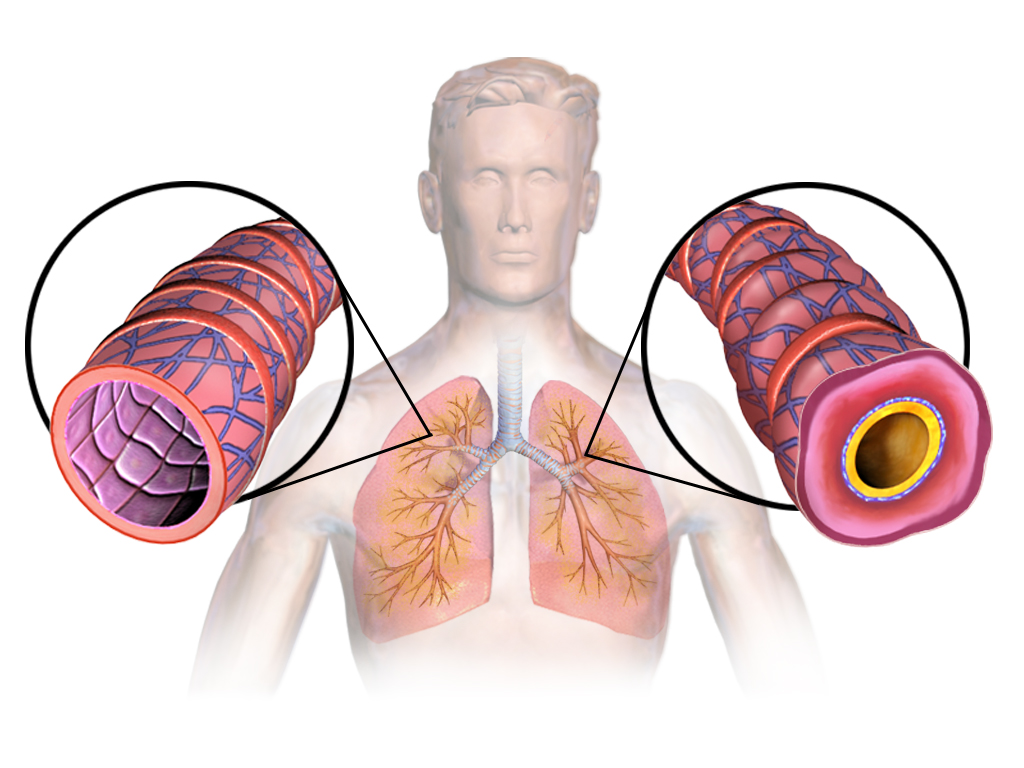
2.2 Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
In moderate to severe COPD, especially those with a history of exacerbations, this therapy helps reduce the frequency of flare-ups and improves airflow limitation. It is used in conjunction with long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) or alone when LAMAs are not tolerated.
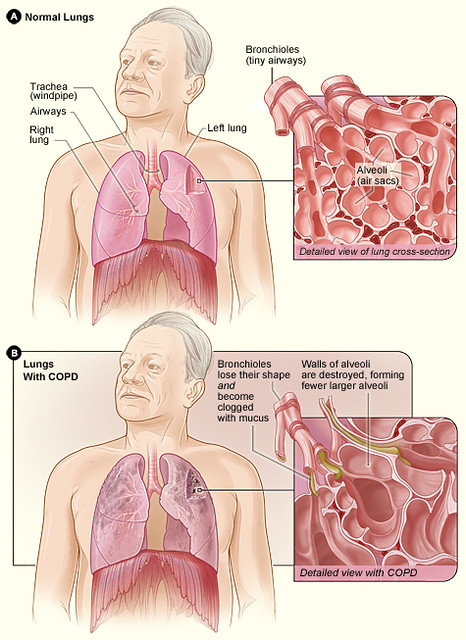
2.3 Prevention of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction (EIB)
3. Off-Label Uses of Formoterol Fumarate / Mometasone Furoate
- Treatment of eosinophilic bronchitis resistant to monotherapy
- Supportive therapy in allergic airway syndromes, including asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS)
- Adjunct in chronic cough linked to airway eosinophilia and inflammation

4. Mechanism of Action and Pharmacological Profile
4.1 Formoterol Fumarate: Beta2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonist
Formoterol binds selectively to beta2-receptors on bronchial smooth muscle, inducing muscle relaxation and bronchodilation. Its rapid onset (within minutes) and prolonged duration (up to 12 hours) make it suitable for both symptom relief and maintenance therapy.
4.2 Mometasone Furoate: Inhaled Corticosteroid
Mometasone suppresses airway inflammation by inhibiting cytokine production, reducing eosinophilic infiltration, and limiting hyperresponsiveness. It minimizes airway remodeling over long-term use, improving respiratory stability.
4.3 Synergistic Action of Combination Therapy
- Improves asthma control more effectively than ICS alone
- Reduces exacerbations and hospitalizations
- Allows for lower corticosteroid doses while maintaining efficacy
5. Dosage Forms and Recommended Administration
5.1 Available Formulations and Strengths
Available in metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) and dry powder inhalers (DPIs), common strengths include:
- Formoterol 5 mcg + Mometasone 100 mcg per inhalation
- Formoterol 5 mcg + Mometasone 200 mcg per inhalation
5.2 Standard Dosage Regimens
Dosage is individualized based on age, disease severity, and previous control:
- Adults: 2 inhalations twice daily
- Children (age-dependent): typically 1-2 inhalations twice daily
Adjustments are made based on clinical response and exacerbation history.
5.3 Proper Inhalation Technique and Patient Counseling
- Demonstrate correct inhaler usage (MDI or DPI-specific)
- Rinse mouth after each use to reduce risk of oropharyngeal candidiasis
- Stress the importance of daily adherence for effective control
6. Composition and Excipients
- Active ingredients: Formoterol Fumarate and Mometasone Furoate per actuation
- Inactive components: Propellants (HFA), lactose monohydrate (in DPI), surfactants, stabilizers
- Lactose content: Important for patients with severe lactose intolerance or galactosemia
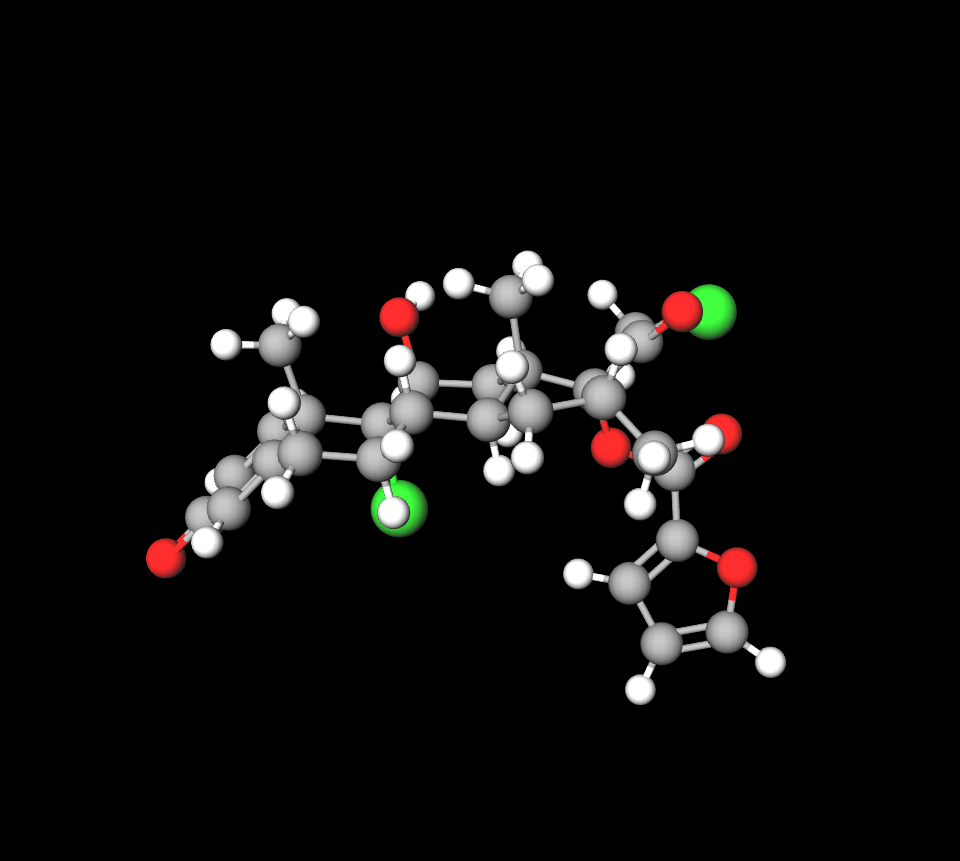
Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate
The combination of budesonide and formoterol is used to help manage and alleviate asthma symptoms, including breathing issues such as wheezing and shortness of breath, as well as coughs and chest tightness, in adults and children aged 6 years or older.
Glycopyrrolate and formoterol fumarate inhalation
Glycopyrrolate and formoterol fumarate inhalation is a combination drug used to manage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the long term, which includes conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is important to note that this medication is not intended for relief during breathing difficulties.
Formoterol fumarate vs albuterol
Albuterol works quickly but only lasts for 6 hours, whereas formoterol fumarate has a longer-lasting effect of 6 to 12 hours.
Mometasone furoate vs triamcinolone acetonide
In terms of Mometasone, it is seen as a potent topical corticosteroid. On the other hand, Triamcinolone's potency varies between medium and low based on its formulation and concentration.
7. Storage and Stability Guidelines
- Store below 25°C (77°F), away from direct sunlight and heat sources
- Keep inhalers dry and capped when not in use
- Discard after the labeled number of doses or expiration date
8. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
8.1 Common Side Effects
- Throat irritation, hoarseness
- Dry mouth, dysphonia
- Headache, nasal congestion, palpitations, and tremors
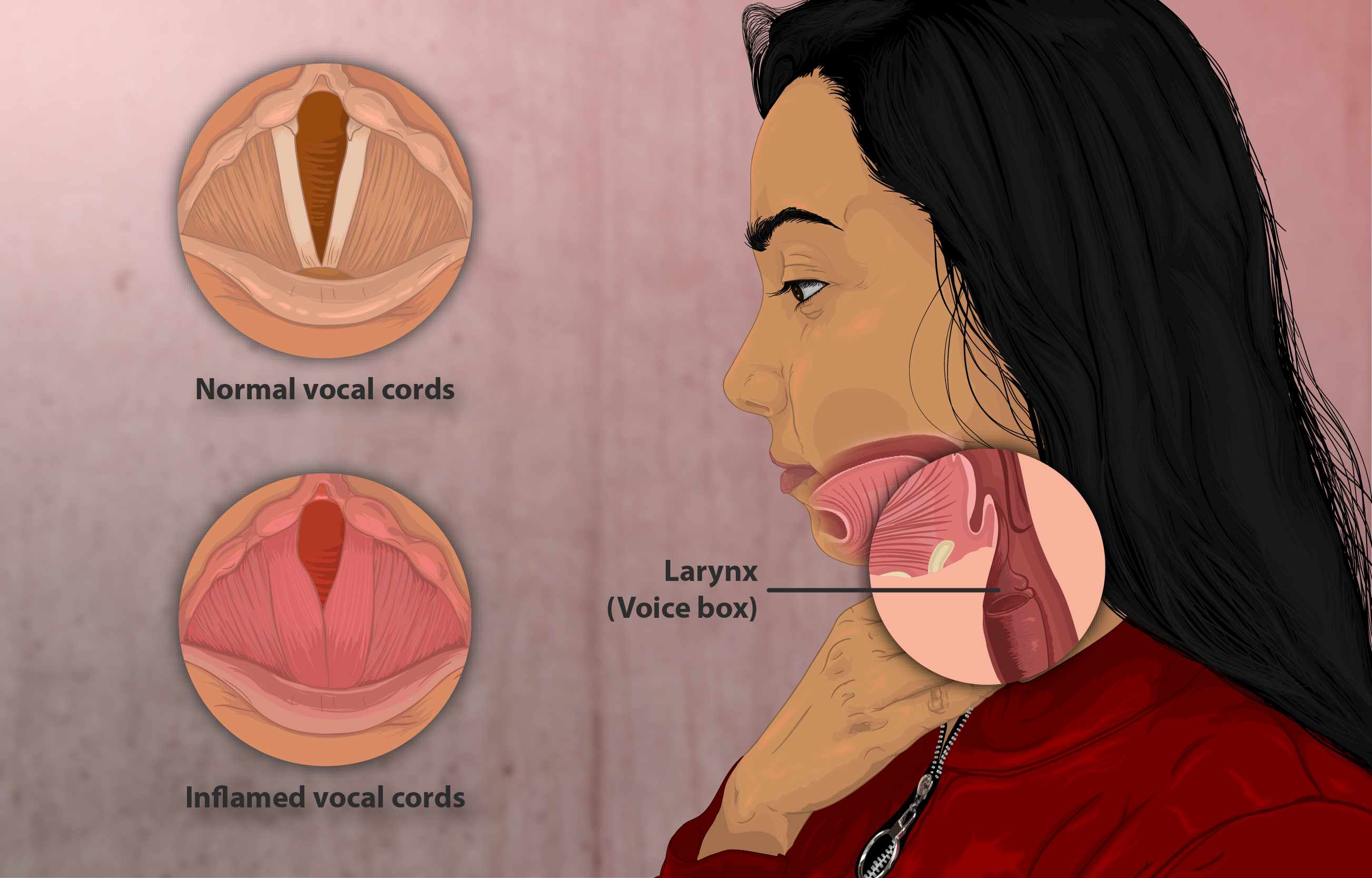
8.2 Less Common and Serious Adverse Effects
- Paradoxical bronchospasm requiring immediate discontinuation
- Systemic corticosteroid effects such as adrenal suppression or stunted growth (in children)
- Increased pneumonia risk, particularly in older COPD patients
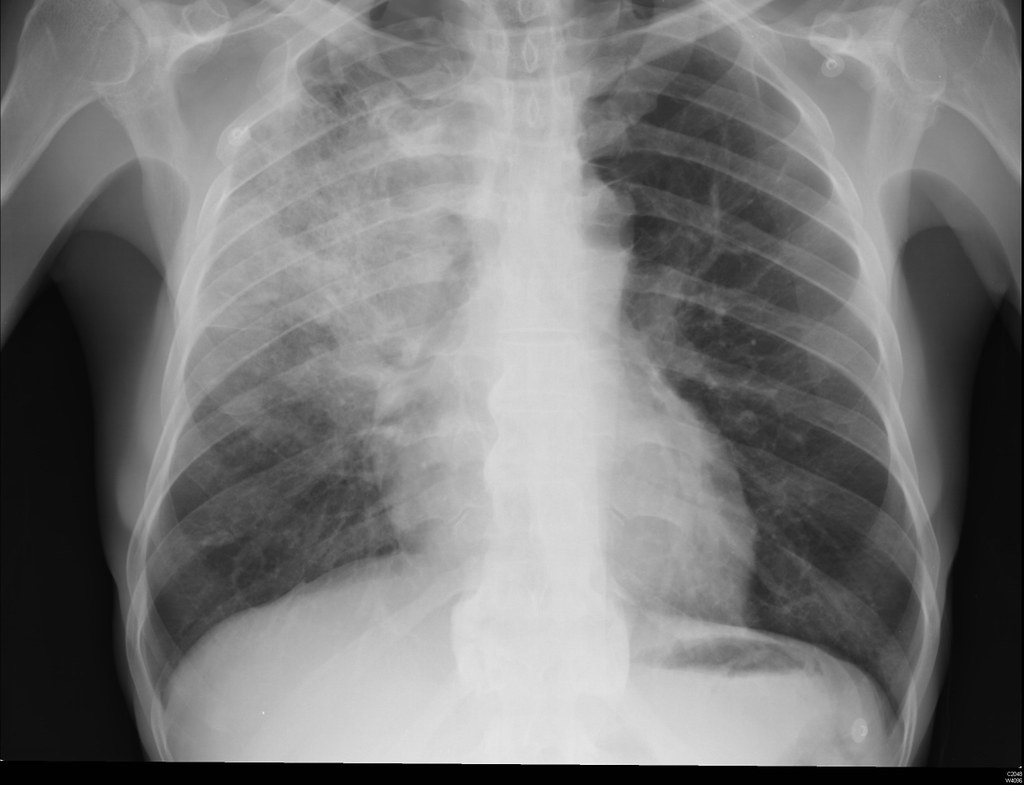
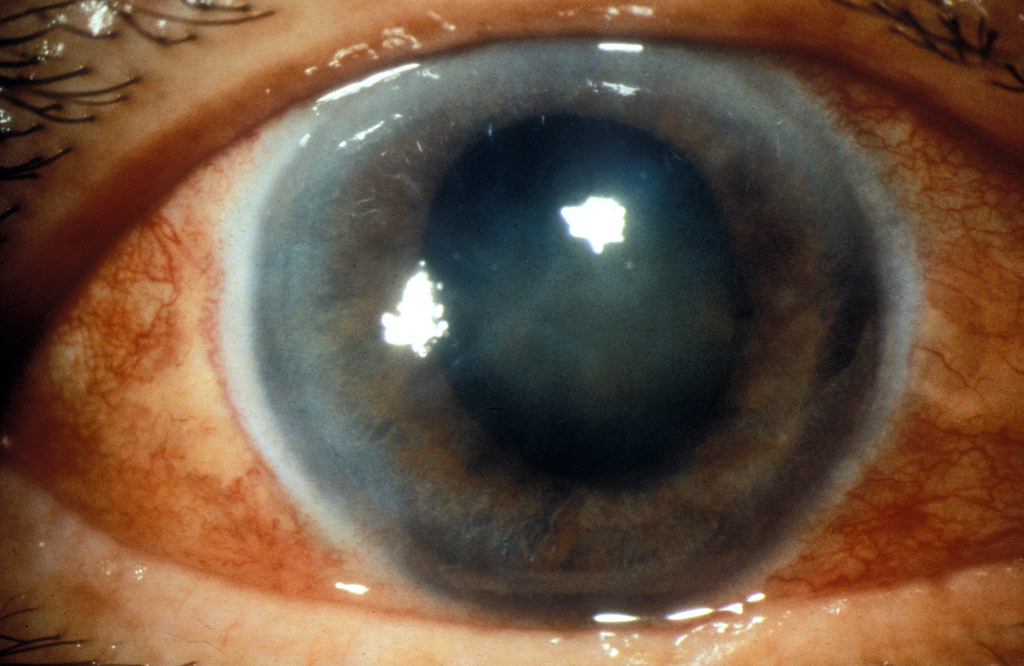
8.3 Long-Term Safety Considerations
- Potential reduction in bone mineral density with prolonged use
- Risk of ocular complications including glaucoma and cataracts
9. Drug Interactions and Contraindications
9.1 Potential Drug Interactions
- Beta-blockers may reduce the bronchodilatory effects of formoterol
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, ritonavir) can increase mometasone exposure
- Use with diuretics may potentiate risk of hypokalemia
9.2 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to formoterol, mometasone, or formulation components
- Acute episodes of asthma or COPD (not suitable for rescue use)
- Primary therapy for status asthmaticus or other acute airway compromise
10. Warnings and Important Safety Precautions
Formoterol Fumarate/Mometasone Furoate inhalers are effective in managing chronic airway diseases, but their use necessitates adherence to strict safety protocols due to potential systemic and respiratory risks.
- LABA-Related Asthma Mortality Warning: Long-acting beta2-agonists (LABAs), including formoterol, carry a boxed warning regarding the risk of asthma-related deaths. Monotherapy with a LABA is contraindicated in asthma. This risk is significantly reduced when combined with an inhaled corticosteroid, such as mometasone.
- Adrenal Suppression with High-Dose Corticosteroids: Prolonged use of high-dose inhaled corticosteroids may suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This suppression can result in signs of adrenal insufficiency, particularly during times of physiological stress such as surgery or infection.
- Immunosuppressive Effects of Long-Term ICS Use: Chronic exposure to inhaled corticosteroids may increase susceptibility to localized or systemic infections, including oral candidiasis, tuberculosis reactivation, or other opportunistic pathogens. Patients with weakened immune systems should be monitored closely.
11. Special Population Considerations and Careful Administration
11.1 Use in Elderly Patients
Elderly patients may exhibit heightened sensitivity to both pharmacologic agents due to age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and comorbidities.
- Initiate therapy at the lower end of the dosing spectrum.
- Monitor for cardiovascular complications such as arrhythmias, hypertension, or myocardial ischemia, especially in those with pre-existing conditions.
- Assess for signs of glucose intolerance or electrolyte disturbances.
11.2 Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety profile in pregnancy and lactation is not fully established, requiring careful evaluation of maternal benefits versus fetal or neonatal risks.
- Classified as FDA Pregnancy Category C, use only if the expected benefit justifies potential risk.
- Animal studies suggest possible fetal harm at high systemic exposures; human data are limited.
- Mometasone and formoterol may be excreted in breast milk. Consider potential effects on the nursing infant, such as adrenal suppression or growth retardation.
11.3 Use in Pediatric Population
Pediatric administration should be guided by age-appropriate formulations and close clinical supervision.
- Approved use typically starts from age 5 or 12 years, depending on the specific product.
- ICS therapy, particularly at higher doses or prolonged use, may lead to growth velocity suppression. Routine growth monitoring is advised.
12. Overdose Management and Toxicity
Overuse or accidental overdose of this combination inhaler can lead to systemic complications requiring immediate medical attention.
- LABA Overdose: Symptoms may include tachycardia, tremors, nervousness, chest pain, arrhythmia, or significant hypokalemia. Beta-agonist toxicity may also result in elevated blood glucose and lactic acidosis.
- Corticosteroid Overdose: High systemic exposure may induce Cushingoid features, weight gain, moon face, and HPA axis suppression. In extreme cases, adrenal crisis may occur, particularly in patients on long-term therapy.
- Treatment Protocols: Discontinue the medication, provide supportive care, correct electrolyte imbalances, and monitor cardiovascular and metabolic status. In severe cases, hospital admission and endocrinology consultation may be necessary.
13. Handling Precautions and Disposal Instructions
Safe handling and disposal of inhalers are crucial for patient safety and environmental sustainability.
- Do not spray near eyes, open flames, or sources of ignition. Contents are pressurized and may be flammable.
- Store the inhaler with the cap on, and avoid puncturing or incinerating even when empty.
- Dispose of used inhalers per local regulations. Some regions offer pharmaceutical take-back programs to safely handle devices containing propellants or residual medication.
Formoterol Fumarate/ Mometasone Furoate FAQ
- What are the side effects of mometasone furoate on the heart?
- Is formoterol good for cough?
- What are the side effects of formoterol?
- What is a mometasone furoate inhaler used for?
- What is the most common side effect of mometasone?
- How many times a day can you use formoterol?
- What is the medical condition treated by mometasone formoterol?
- Is mometasone safe to use daily?
- What are the benefits of mometasone furoate?
- What is the best time to take mometasone?
- What is the warning for mometasone furoate?
- Who should not use mometasone furoate?
- Does mometasone weaken the immune system?
- How safe is formoterol?
- What are the advantages of formoterol?
- Why is formoterol preferred in asthma?
- How long does formoterol fumarate stay in your system?
- Is formoterol a reliever?
- What are the side effects of mometasone furoate on the heart?
- Is formoterol the same as salbutamol?
- What is the warning for formoterol?
- Is mometasone an antihistamine?
- Is formoterol a reliever or preventer?
- What is the duration of action of formoterol inhaler?
- How long does it take for formoterol to work?
- What are the systemic effects of formoterol?
What are the side effects of mometasone furoate on the heart?
Heart rate fluctuations, such as an irregular heartbeat, dizziness, faintness or lightheadedness, chest discomfort, and difficulty breathing.
Is formoterol good for cough?
The application of the budesonide/formoterol inhaler showed a reduction in cough.
What are the side effects of formoterol?
- Nervousness
- Headache
- Shaking
- Dry mouth
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea
- Vomiting
What is a mometasone furoate inhaler used for?
Mometasone is typically prescribed to manage asthma symptoms and enhance lung function.
What is the most common side effect of mometasone?
Headaches, sneezing, dizziness
How many times a day can you use formoterol?
Two times a day
What is the medical condition treated by mometasone formoterol?
Asthma
Is mometasone safe to use daily?
Yes
What are the benefits of mometasone furoate?
Treatment of asthma and eczema
What is the best time to take mometasone?
Morning and evening
What is the warning for mometasone furoate?
Adrenal gland problems, high blood sugar, eyesight problems
Who should not use mometasone furoate?
- Allergic reaction
- Chickenpox
- Acne or rosacea
Does mometasone weaken the immune system?
No
How safe is formoterol?
Safe at normal dosage
What are the advantages of formoterol?
Formoterol acts specifically within the lungs to widen the air passages by relaxing the muscles as a bronchodilator.
Why is formoterol preferred in asthma?
Formoterol acts as a bronchodilator providing relief of symptoms with a lasting effect.
How long does formoterol fumarate stay in your system?
12 hours
Is formoterol a reliever?
Yes
What are the side effects of mometasone furoate on the heart?
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
Is formoterol the same as salbutamol?
Formoterol starts working as fast as salbutamol but lasts longer in its effects.
What is the warning for formoterol?
Swelling of face, difficulty swallowing, hives
Is mometasone an antihistamine?
It consists of an antihistamine and a nasal steroid.
Is formoterol a reliever or preventer?
Both
What is the duration of action of formoterol inhaler?
12 hours
How long does it take for formoterol to work?
1-3 minutes
What are the systemic effects of formoterol?
Heart rate changes, diastolic blood pressure and plasma and glucose concentrations