Seroflo, Salmeterol/ Fluticasone Propionate Inhaler
- Introduction
- Seroflo Composition and Formulation
- Mechanism of Action
- Seroflo Inhaler Uses
- Off-Label Uses
- Seroflo Inhaler Dosage and Administration
- Special Administration Considerations
- Fluticasone/Salmeterol Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Important Precautions
- Careful Administration
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Overdosage
- Patient Education and Safety Measures
Introduction
Overview of Seroflo Inhaler
Importance in Respiratory Medicine
Global Usage and Clinical Relevance
Seroflo Composition and Formulation
Active Ingredients: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate
Available Strengths and Inhaler Types
Role of Each Component in Combination Therapy
Fluticasone umeclidinium vilanterol
Foracort vs seroflo
Asthalin vs seroflo
Budecort vs seroflo
Seroflo vs symbicort
Azelastine vs fluticasone
Mechanism of Action
Salmeterol Mechanism of Action: Long-Acting Beta-2 Agonist and Bronchodilation
Fluticasone Propionate Mechanism of Action: Corticosteroid Anti-Inflammatory Effect
Synergistic Effect in Controlling Asthma and COPD
Seroflo Inhaler Uses
Treatment of Persistent Asthma
Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Prevention of Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm
Reduction of Exacerbations in Chronic Respiratory Disorders
Off-Label Uses
Use in Severe Allergic Rhinitis Resistant to Standard Therapy
Adjunctive Therapy in Bronchiectasis
Off-Label Pediatric Applications in Selected Cases
Investigational Roles in Chronic Cough Syndromes
Seroflo Inhaler Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage for Adults with Asthma
Recommended Regimen for COPD Patients
Pediatric Dosing and Age-Specific Adjustments
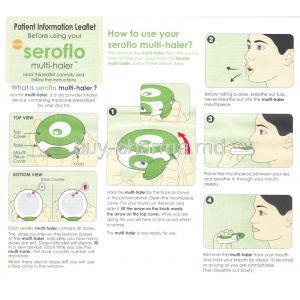
How to Use Seroflo and Patient Counseling for Effective Use
Missed Dose and Dose Adjustment Guidelines
Special Administration Considerations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Administration to Pregnant Women
Use During Lactation
Administration to Children
Fluticasone/Salmeterol Side Effects
Salmeterol Side Effects
Serious Adverse Effects
Drug Interactions
Interaction with CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Concomitant Use with Beta-Blockers
Effects of Diuretics and Risk of Hypokalemia
Interaction with Other Corticosteroids or Immunosuppressants
Alcohol and Lifestyle Factors Influencing Safety
Contraindications
Salmeterol contraindications
Warnings and Important Precautions
Risk of Asthma-Related Death with LABA Monotherapy
Need for Regular Monitoring of Pulmonary Function
Importance of Not Discontinuing Corticosteroid Therapy Abruptly
Long-Term Risk of Osteoporosis and Cataracts
Risk of Adrenal Suppression with Chronic Use
Fluticasone Salmeterol Alternatives
Careful Administration
Patients with Cardiovascular Disease or Arrhythmias
Individuals with Hepatic or Renal Impairment
Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Monitoring Blood Glucose
Patients with Ocular Conditions Such as Glaucoma or Cataracts
Fluticasone salmeterol nursing considerations
Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Temperature and Humidity Conditions
Protecting Inhaler from Direct Sunlight and Moisture
Instructions for Priming and Cleaning the Inhaler Device
Handling Precautions to Prevent Cross-Contamination
Overdosage
Clinical Presentation of Salmeterol Overdose
Manifestations of Fluticasone Overdose
Emergency Management and Supportive Therapy
Patient Education and Safety Measures
Importance of Adherence to Prescribed Regimen
Guidance on Rinsing Mouth After Inhalation to Prevent Candidiasis
Monitoring for Early Signs of Adverse Reactions
Role of Regular Follow-Ups with Healthcare Providers
Seroflo, Salmeterol/ Fluticasone Propionate Inhaler FAQ
- Is Seroflo inhaler a steroid?
- What is the medication Seroflo used for?
- What are the ingredients in sereflo?
- What are the disadvantages of Seroflo inhaler?
- Can we use Seroflo daily?
- Does Seroflo cause weight gain?
- How many puffs of Seroflo inhaler?
- Is Seroflo good for cough?
- Can I stop using Seroflo 500 suddenly?
- Is Seroflo an antibiotic?
- Is Seroflo a preventer?
- What are the side effects of Seroflo?
- Can I stop Seroflo?
- Is Seroflo 250 addictive?
- What type of inhaler is Sereflo?
- When to take Seroflo?
- What are the disadvantages of Seroflo inhaler?
- How quickly does Seroflo work?
- Is Seroflo habit forming?
Is Seroflo inhaler a steroid?
No
What is the medication Seroflo used for?
Seroflo 250 Inhaler is a blend of two medications that relax the airways and facilitate easier breathing. It is utilized in the management of asthma
What are the ingredients in sereflo?
Each metered dose delivers 25 micrograms of salmeterol (as salmeterol xinafoate) and either 125 or 250 micrograms of fluticasone propionate.
What are the disadvantages of Seroflo inhaler?
Some typical side effects are coughing, infections of the upper respiratory tract, throat and nasal passage inflammation, sinus swelling, stomach upset, throat fungal infections, voice changes, headaches, aggressive behavior, and dry mouth.
Can we use Seroflo daily?
Yes
Does Seroflo cause weight gain?
Yes
How many puffs of Seroflo inhaler?
2
Is Seroflo good for cough?
Yes
Can I stop using Seroflo 500 suddenly?
No
Is Seroflo an antibiotic?
No
Is Seroflo a preventer?
Yes
What are the side effects of Seroflo?
- Nausea
- Increased heart rate
- pain
- Vomiting
- Respiratory infection
Can I stop Seroflo?
No
Is Seroflo 250 addictive?
No
What type of inhaler is Sereflo?
salmeterol/fluticasone pressurised metered dose inhaler (pMDI)
When to take Seroflo?
every day, twice a day
What are the disadvantages of Seroflo inhaler?
Some frequent side effects consist of coughing, upper respiratory infections, throat and nasal passage inflammation, sinusitis, stomach discomfort, fungal infections in the throat, voice changes, headaches, aggressive behavior, and dry mouth.
How quickly does Seroflo work?
5 minutes
Is Seroflo habit forming?
No