Insulatard HM Penfill
- Introduction to Insulatard HM Penfill
- How Insulatard HM Penfill Works
- Approved and Off-Label Uses of Insulatard HM Penfill
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Insulatard HM Penfill
- Composition and Formulation of Insulatard HM Penfill
- Storage Requirements for Insulatard HM Penfill
- Common Side Effects of Insulatard HM Penfill
- Other Side Effects and Serious Adverse Reactions
- Drug Interactions Involving Insulatard HM Penfill
- Warnings and Precautions When Using Insulatard HM Penfill
- Contraindications for Insulatard HM Penfill Use
- Important Precautions and Monitoring
- Special Considerations for Administration to Elderly Patients
- Use of Insulatard HM Penfill During Pregnancy and Lactation
- Administration of Insulatard HM Penfill in Pediatric Populations
- Overdose and Emergency Management of Insulatard HM Penfill
- Handling Precautions for Insulatard HM Penfill
Introduction to Insulatard HM Penfill
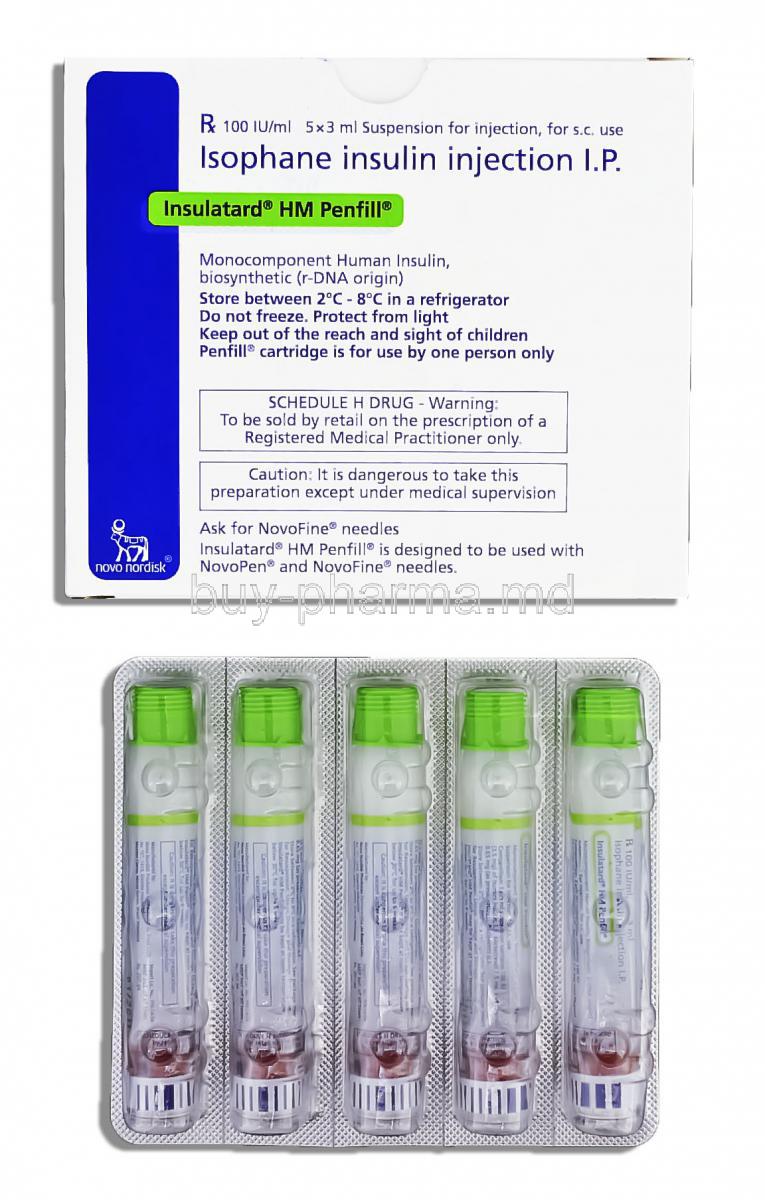
Overview of Insulatard HM Penfill
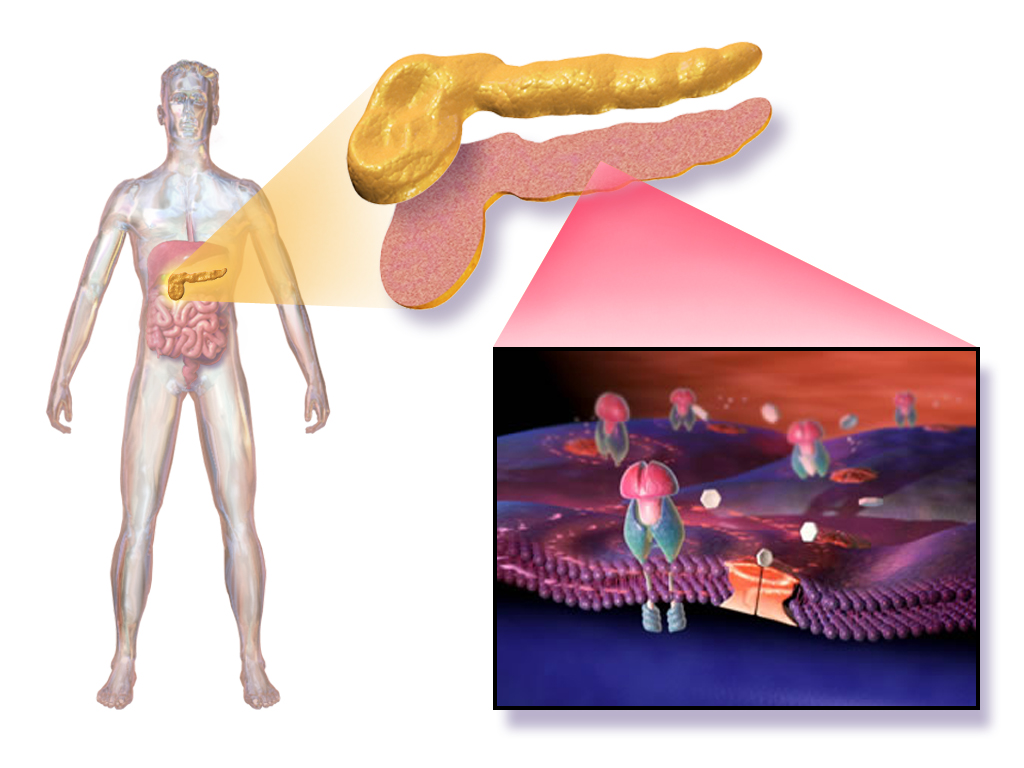
Insulatard HM Penfill is a prefilled cartridge containing intermediate-acting human insulin formulated to regulate blood glucose levels effectively. Designed for seamless use with compatible insulin delivery devices, it provides consistent basal insulin coverage for diabetic patients.
Classification as an Intermediate-Acting Human Insulin
Classified as an intermediate-acting insulin, Insulatard HM bridges the gap between rapid-acting and long-acting insulins, offering a balanced profile suitable for maintaining basal glucose control throughout the day and night.
Key Therapeutic Indications and Relevance in Diabetes Management
- Essential therapy for individuals with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Often utilized for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus requiring insulin supplementation.
- Integral component of basal-bolus regimens when combined with short-acting insulin preparations.
How Insulatard HM Penfill Works
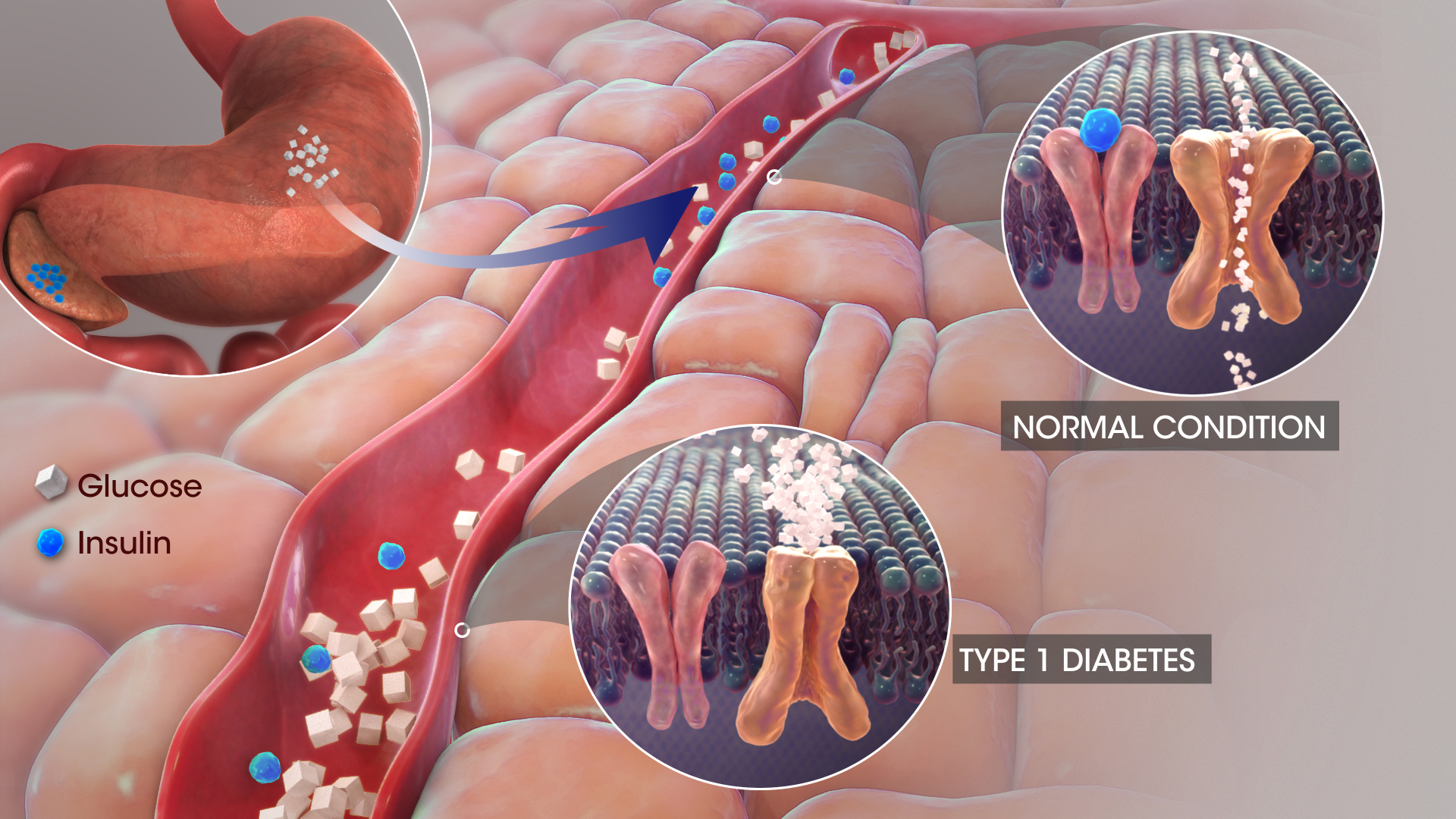
Mechanism of Action of Isophane Insulin (NPH Insulin)
Isophane insulin, also known as Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin, is designed to form microcrystals that dissolve slowly following subcutaneous injection, delivering a prolonged hypoglycemic effect by mimicking endogenous basal insulin secretion.
Onset, Peak, and Duration Profile of Insulatard
- Onset: Approximately 1.5 hours post-injection.
- Peak: 4 to 12 hours after administration.
- Duration: Up to 24 hours, with variability among individuals.
Impact on Glucose Uptake and Hepatic Glucose Production
Insulatard enhances peripheral glucose uptake, particularly in muscle and adipose tissue, while simultaneously suppressing hepatic glucose output, thereby ensuring holistic glycemic regulation.
Differences Between Insulatard and Rapid-Acting or Long-Acting Insulins
Unlike rapid-acting insulins that act within minutes and long-acting insulins that offer peakless control, Insulatard offers a distinct peak of action, requiring strategic timing to prevent hypoglycemia.
Approved and Off-Label Uses of Insulatard HM Penfill
Primary Use in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Insulatard is often used as a component in managing Type 1 Diabetes. It is commonly combined with mealtime insulin to establish a holistic approach to controlling blood sugar levels.
Primary Use in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Combination with Rapid-Acting Insulins for Intensified Therapy
To enhance control measures for diabetes management purposes, Insulatard is often paired with working insulins to better regulate both daily and mealtime blood sugar levels.
Off-Label Use in Gestational Diabetes Management
Use in Steroid-Induced Hyperglycemia
Insulatard may be employed off-label to counteract steroid-induced hyperglycemia, stabilizing glucose levels during corticosteroid therapy.
Use in Hospitalized Patients for Basal Insulin Coverage
Hospitalized individuals often benefit from Insulatard for maintaining basal insulin coverage, particularly during periods of reduced oral intake or acute illness.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Insulatard HM Penfill
Standard Dosage Recommendations for Adults with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Initial dosing typically starts at approximately 0.2 to 0.4 units/kg/day, adjusted based on individual blood glucose profiles and clinical judgment.
Titration and Individualized Dosing Based on Blood Glucose Monitoring
Adjustments to the dosage are determined based on monitoring one's blood glucose levels (through SMBGs) with the goal of maintaining fasting plasma glucose levels within therapeutic ranges.

Recommended Injection Techniques and Sites
- Preferred injection sites: abdomen, thigh, upper arm, buttocks.
- Site rotation is crucial to minimize the risk of lipodystrophy.
Timing of Administration Relative to Meals and Activities
Administering Insulatard once or twice daily, typically 30 minutes before a meal or at bedtime, is recommended to align its action with physiological needs.
Switching from Other Insulin Types to Insulatard
Adjusting to a new medication involves recalibrating dosages and closely monitoring blood sugar levels to avoid low or high glucose levels while adapting to the changes.
Composition and Formulation of Insulatard HM Penfill
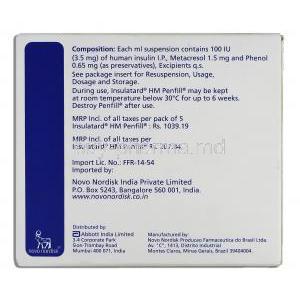
Active Ingredient: Human Insulin (Isophane Suspension)
In every milliliter of the solution, there are 100 IU of insulin in a form that guarantees dependable pharmacological effects.
List of Excipients and Their Roles
- Zinc chloride and protamine sulfate to stabilize insulin crystals.
- Phenol and m-cresol for antimicrobial preservation.
- Glycerol to adjust tonicity.
Description of Pharmaceutical Form and Penfill Cartridge Compatibility
You can find it in 3 mL cartridges as a liquid that works with Novorapid insulin pens for use and accurate dosages.
Storage Requirements for Insulatard HM Penfill
Proper Storage Before First Use (Temperature, Light Protection)
Make sure to store cartridges in the refrigerator at a temperature between 2°C and 7°C to keep them safe from light and freezing conditions.
In-Use Storage Conditions and Time Limits
After the use of Insulatard insulin medication, it can be stored at room temperature (below 30°C). It must be used within 6 weeks while making sure to shield it from heat and sunlight exposure.
Special Instructions for Transportation and Travel
Maintain cold chain logistics during transport; use insulated containers and avoid placing insulin directly against ice packs to prevent freezing.
Handling of Frozen or Improperly Stored Pens
Discard any cartridges that have been frozen, as freezing irreversibly damages insulin potency and reliability.
Common Side Effects of Insulatard HM Penfill
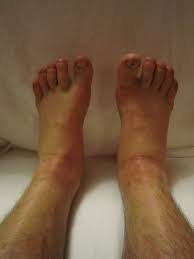
Local Injection Site Reactions (Redness, Swelling, Pain)
Symptoms seen after an injection include redness (erythema), swelling in a specific area, or mild pain that typically goes away quickly.
Hypoglycemia Symptoms and Warning Signs
- Shaking, sweating, rapid heartbeat.
- Confusion, irritability, visual disturbances.
Weight Gain as a Metabolic Effect
Edema and Sodium Retention Considerations
Other Side Effects and Serious Adverse Reactions
Severe Hypoglycemia and Insulin Shock
Severe episodes may result in unconsciousness, seizures, and necessitate emergency glucagon or intravenous glucose therapy.
Allergic Reactions (Generalized and Localized)
Rare systemic allergic reactions can present as rash, pruritus, or anaphylaxis requiring immediate medical intervention.
Lipodystrophy at Injection Sites (Lipoatrophy and Lipohypertrophy)
Repeated injections at the same site can cause localized adipose tissue loss or hypertrophy, underscoring the importance of site rotation.
Rare but Serious Insulin Resistance or Antibody Formation
Drug Interactions Involving Insulatard HM Penfill
Interactions with Oral Antidiabetic Agents
Concurrent use with sulfonylureas or meglitinides may potentiate hypoglycemia, requiring dose adjustments of one or both agents.
Effects of Beta-Blockers, Corticosteroids, Diuretics, and Thyroid Hormones
- Beta-blockers may mask adrenergic symptoms of hypoglycemia.
- Corticosteroids and thyroid hormones may necessitate insulin dose increases.
- Diuretics can exacerbate hyperglycemia by promoting potassium loss.
Potential Interaction with Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption can unpredictably augment or diminish insulin's hypoglycemic effect, making moderation and caution critical.
Adjustment Needs When Co-Administering with Other Medications
Assessing medications is crucial to adapt insulin doses when starting or changing other treatments or stopping them altogether.
Warnings and Precautions When Using Insulatard HM Penfill
Risk of Masking Hypoglycemia Symptoms with Beta-Blockers
Beta-adrenergic blockers can obscure critical warning signs of hypoglycemia, such as tremors and palpitations, potentially delaying timely intervention. Patients co-administered beta-blockers should maintain heightened vigilance and frequent glucose monitoring.

Caution in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Renal and hepatic dysfunction impair insulin metabolism and clearance, elevating the risk of prolonged hypoglycemia. Dose reductions and intensified glucose monitoring are prudent strategies in this vulnerable cohort.
Precautions During Infections, Surgery, or Stressful Events
Acute physiological stress from infection, surgery, or trauma may precipitate unpredictable insulin requirements. Temporary insulin dose adjustments and closer clinical surveillance are essential during such periods.
Risks Associated with Inappropriate Injection Techniques
Improper injection practices, such as failure to rotate sites or incorrect needle insertion depth, can result in erratic insulin absorption, lipodystrophy, and suboptimal glycemic control. Proper technique training is imperative.
Contraindications for Insulatard HM Penfill Use
Known Hypersensitivity to Human Insulin or Any Excipient
Use of Insulatard is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity reactions to human insulin or formulation constituents, as severe allergic responses may ensue.
Hypoglycemia Episodes at the Time of Intended Insulin Administration
Administration of Insulatard during existing hypoglycemia is contraindicated and may exacerbate neuroglycopenic symptoms, risking loss of consciousness or seizures.
Situations Requiring Suspension or Reassessment of Insulin Therapy
It is important to review the use of insulin in situations where there is a decline in kidney function over time, or liver function worsens, or if changes in eating habits require adjustments to the treatment plan.
Important Precautions and Monitoring
Importance of Regular Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG)
Regular self monitor of blood glucose (SMBG) plays a role in adjusting doses promptly spotting low or high blood sugar levels while striving to meet each patients specific blood sugar goals; it's essential for patients to be skilled, at using glucometers accurately.
Adjustments During Changes in Diet, Exercise, or Illness
- Increased carbohydrate intake may necessitate higher insulin doses.
- Heightened physical activity may lower insulin requirements and necessitate pre-exercise adjustments.
- During illness, frequent monitoring and possible dose modifications are warranted to prevent decompensation.
Special Considerations for Administration to Elderly Patients
Age-Related Changes in Insulin Sensitivity
As people grow older, their kidneys may not clear out substances effectively, and their body's response to glucose changes too; this means that adjusting insulin doses should be personalized for each person.
Increased Risk of Hypoglycemia and Falls
Hypoglycemia in elderly patients can precipitate falls, fractures, and cognitive impairment. Conservative titration and comprehensive fall risk assessments are recommended.
Recommendations for Dosing Adjustments and Monitoring Frequency
Lower starting doses, gradual titration, and more frequent SMBG are advised in elderly populations to minimize adverse outcomes.
Use of Insulatard HM Penfill During Pregnancy and Lactation
Safety Profile of Human Insulin in Pregnancy
Human insulin is the gold standard for glycemic management during pregnancy, posing no teratogenic risk when appropriately administered and monitored.
Adjustments Needed Across Different Pregnancy Stages
- First trimester: Reduced insulin requirements due to enhanced insulin sensitivity.
- Second and third trimesters: Progressive dose escalation in response to placental hormone-mediated insulin resistance.
Insulin Management During Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding mothers can safely continue Insulatard, although insulin needs may decrease postpartum, necessitating careful dose recalibration to avert hypoglycemia.
Risks Versus Benefits Discussion for Expectant Mothers
Maintaining stringent glycemic control mitigates risks of fetal macrosomia, congenital anomalies, and maternal complications, underscoring the favorable benefit-risk profile of Insulatard during pregnancy.
Administration of Insulatard HM Penfill in Pediatric Populations
Use in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Insulatard is widely utilized in pediatric diabetes care, providing predictable basal insulin coverage essential for optimal metabolic control in children and adolescents.
Dosage Individualization and Growth Considerations
Dosing must be dynamically adjusted to accommodate changing insulin sensitivities associated with growth spurts, puberty, and varying levels of physical activity.
Monitoring Requirements in School-Aged Children
Enhanced vigilance is required for blood glucose fluctuations during school hours, with clear action plans communicated to teachers and caregivers.
Importance of Caregiver Education and Supervision
Parents, school personnel, and caregivers must be thoroughly educated on insulin administration, hypoglycemia management, and emergency procedures to ensure pediatric safety.
Overdose and Emergency Management of Insulatard HM Penfill
Clinical Presentation of Insulin Overdose (Hypoglycemia)
Symptoms can vary from signs, like increased heart rate and sweating, to serious neurological issues, such as confusion or seizures that may lead to a coma.
Immediate Actions and Use of Glucagon or Intravenous Glucose
Prompt administration of oral carbohydrates, intramuscular glucagon, or intravenous dextrose is essential, depending on the severity of hypoglycemia and patient consciousness.
Post-Recovery Monitoring and Adjustment Strategies
After taking medication for an overdose incident so as not to experience a sudden drop or increase in blood sugar levels afterward is crucial to maintain control and stability.
Prevention Strategies to Minimize Overdose Risk
- Double-checking doses before administration.
- Clear patient education regarding correct pen usage.
- Use of reminder tools or digital insulin dosing apps where appropriate.
Handling Precautions for Insulatard HM Penfill
Proper Handling of Penfill Cartridges to Maintain Sterility
Cartridges should be visually inspected for clumps or discoloration and gently rolled between the palms to ensure homogeneous suspension before each use. Needle hygiene practices must be meticulously observed.
Safe Disposal of Used Needles and Cartridges
Dispose of used needles in FDA-cleared sharps disposal containers. Empty cartridges should be discarded per local regulations governing biohazardous waste.
Environmental Considerations for Disposal
Adhere to environmentally responsible disposal protocols to prevent needle-stick injuries and minimize pharmaceutical contamination of ecosystems.
Patient Education on Correct Storage and Transport Practices
Patients must be instructed on maintaining optimal storage temperatures during daily use and travel, emphasizing the avoidance of freezing and direct heat exposure to preserve insulin potency.
Insulatard HM Penfill FAQ
- What is insulatard penfill used for?
- What type of insulin is insulatard hm?
- When is the best time to take insulatard?
- How do you use penfill insulin?
- What are the side effects of insulatard insulin?
- Where do you inject insulatard?
- How long does Insulatard last?
- What is the alternative to insulatard penfill?
- How do you change penfill insulin?
- What type of insulin is Insulatard?
- Can insulatard be given at bedtime?
- Should insulatard be given before or after meals?
- What is insulatard hm used for?
- What is the peak time of insulatard insulin?
- What temperature should insulatard be kept at?
- How long does it take for insulatard to work?
What is insulatard penfill used for?
To lower the blood sugar levels in individuals diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (diabetes).
What type of insulin is insulatard hm?
It is a form of man-made insulin created to imitate the insulin produced by the body.
When is the best time to take insulatard?
Insulatard is a type of lasting insulin that your doctor might suggest taking twice daily, alongside or independent of a rapid insulin injection, during meals.
How do you use penfill insulin?
Carefully lift your skin at the injection site and, with a swift motion, insert the needle entirely into your skin. Slide your thumb to the top of the insulin pen. Ensure it is secure before pressing down on the injection button. Once you've counted to 10, pull out the needle from your skin.
What are the side effects of insulatard insulin?
- sweating
- trembling or shaking
- anxiety
- confusion or difficulty concentrating
- fast heartbeat (palpitations)
- tingling lips
- changes to your vision
Where do you inject insulatard?
Thigh
How long does Insulatard last?
24 hours
What is the alternative to insulatard penfill?
Humulin I KwikPen
How do you change penfill insulin?
Please remove the needle and the empty cartridge from the pen device to prepare for replacement with a cartridge and a fresh needle according to the provided instructions on how to insert them and prime the pen for immediate use.
What type of insulin is Insulatard?
There are two types of action insulin available, namely Humulin I and Insulatard.
Can insulatard be given at bedtime?
Yes
Should insulatard be given before or after meals?
Before breakfast, evening meal or bedtime
What is insulatard hm used for?
Insulatard is prescribed to lower blood sugar levels in individuals diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (diabetes).
What is the peak time of insulatard insulin?
4-12 hours
What temperature should insulatard be kept at?
Below 30°C
How long does it take for insulatard to work?
1½ hours