Introduction to Ketoconazole Cream
What is Ketoconazole Cream?
Ketoconazole Cream is a topical antifungal agent designed to treat a variety of superficial fungal infections affecting the skin. It is particularly effective against dermatophytes and yeast species, making it a versatile treatment for both common and persistent fungal conditions.
Overview of Its Antifungal Classification (Imidazole Derivative)
Ketoconazole belongs to the imidazole class of antifungal agents. This classification denotes its chemical structure, characterized by a five-membered imidazole ring, and its mechanism of action—targeting the fungal cell membrane by inhibiting ergosterol synthesis.
Historical Background and FDA Approval
Originally developed in the late 1970s, ketoconazole was first introduced as an oral antifungal. The topical cream formulation soon followed, receiving FDA approval in the 1980s. Over the decades, it has become a cornerstone in dermatological antifungal therapy.
Formulation Types and Available Concentrations
Ketoconazole Cream is most commonly available in a 2% concentration. It may be formulated as a water-based or oil-based cream, and is often found in tubes ranging from 15g to 60g. Several branded and generic versions are available globally.
Medical Uses of Ketoconazole Cream
Treatment of Dermatophytosis (e.g., Athlete’s Foot, Jock Itch, Ringworm)
Ketoconazole is widely prescribed for tinea infections caused by dermatophytes. Conditions such as tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), tinea cruris (jock itch), and tinea corporis (ringworm) respond well to regular application of the cream.
Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff Control
Ketoconazole’s antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties make it effective in managing seborrheic dermatitis. It controls the overgrowth of *Malassezia* species, which play a pivotal role in the condition.
Tinea Versicolor and Candidal Skin Infections
This cream is effective against tinea versicolor, a superficial fungal infection causing discoloration of the skin. It also treats candidal infections, particularly in moist areas like the groin and underarms.
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (Topical Adjunct)
Though not a primary therapy, ketoconazole cream may be used as a supplementary topical agent for external symptoms of vulvovaginal candidiasis, such as itching and redness.
Cutaneous Candidiasis (Intertrigo, Diaper Rash)
Its use in intertriginous candidiasis and fungal diaper rash offers symptom relief and infection control, particularly when standard barrier creams are insufficient.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses
Off-Label Use for Fungal Acne (Malassezia Folliculitis)
Dermatologists frequently prescribe ketoconazole cream off-label to manage *Malassezia* folliculitis, a condition often misdiagnosed as acne but caused by fungal overgrowth in hair follicles.
Use in Hormonal Acne Due to Anti-Androgenic Effects
Ketoconazole exhibits mild anti-androgenic properties. It can inhibit local testosterone activity on the skin, making it a potential adjunct in managing hormonal acne.
Adjunct in Rosacea Management
Some clinicians employ ketoconazole cream alongside rosacea treatments to reduce *Demodex*-associated inflammation or secondary fungal colonization.
Role in Hyperpigmentation and Melasma (In Combination Regimens)
When combined with agents like hydroquinone or corticosteroids, ketoconazole has shown promise in managing melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, though further evidence is needed.
How Ketoconazole Cream Works: Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of Fungal Ergosterol Synthesis
Ketoconazole interferes with the synthesis of ergosterol, a vital component of fungal cell membranes. This disruption leads to increased cell permeability and subsequent fungal death.
Disruption of Fungal Cell Membrane Integrity
By altering the lipid composition of the cell membrane, ketoconazole compromises membrane structure, leading to leakage of intracellular contents and cell lysis.
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Androgenic Properties
Beyond its antifungal activity, ketoconazole possesses mild anti-inflammatory effects, reducing redness and irritation. Its anti-androgenic action further broadens its dermatologic utility.
Fungistatic vs Fungicidal Activity Depending on Concentration
At lower concentrations, ketoconazole exhibits fungistatic properties, halting fungal growth. At higher concentrations, it becomes fungicidal, eradicating existing fungal colonies.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Dosage for Common Fungal Infections
For most fungal skin infections, ketoconazole cream is applied once or twice daily, depending on the severity and location of the infection.
Frequency and Duration of Application
- Mild infections: once daily for 2–4 weeks - Moderate to severe infections: twice daily for up to 6 weeks - Maintenance therapy: twice weekly for chronic conditions like seborrheic dermatitis
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying the Cream
1. Clean and dry the affected area 2. Apply a thin layer of cream 3. Gently rub until absorbed 4. Wash hands after application unless treating the hands
What to Do If a Dose Is Missed
Apply the missed dose as soon as remembered. If it's close to the next scheduled dose, skip the missed one—do not double apply.
Duration of Treatment Based on Condition
The duration may vary: - Tinea infections: 2–4 weeks - Seborrheic dermatitis: 2–6 weeks - Candidiasis: 1–2 weeks
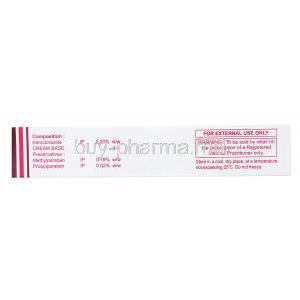
Composition and Ingredients of Ketoconazole Cream
Active Ingredient: Ketoconazole Concentration (e.g., 2%)
The active pharmaceutical ingredient is ketoconazole, typically in a 2% concentration. It directly targets fungal cells for localized treatment.
Inactive Ingredients and Their Functions
Common excipients include: - Propylene glycol: enhances skin penetration - Cetyl alcohol: moisturizes and stabilizes the cream - Sodium sulfite: acts as a preservative - Purified water: vehicle for the formulation
Product Variations by Brand and Generic Formulations
Several branded and generic versions exist, including Nizoral, Ketoderm, and Extina. While formulations may vary slightly, the therapeutic outcome remains consistent.
Potential Side Effects of Ketoconazole Cream
Common Side Effects: Localized Irritation, Stinging, Itching
Patients may experience mild, transient irritation at the application site. These symptoms usually subside without intervention.
Rare Side Effects: Allergic Reactions, Contact Dermatitis
In hypersensitive individuals, allergic dermatitis or rash may develop. Discontinuation is advised if symptoms persist or worsen.
Skin Discoloration or Dryness with Prolonged Use
Chronic use may lead to temporary hypopigmentation or dryness, especially in sensitive skin areas.
Risk of Systemic Absorption and Related Effects (Rare)
Although systemic absorption is minimal, large-area application under occlusion or on broken skin may increase systemic exposure, posing theoretical risks.
Drug Interactions and Absorption Considerations
Potential Interaction with Topical Corticosteroids
Concurrent use may potentiate skin thinning and other corticosteroid-related side effects. Alternating application or physician monitoring is advised.
Systemic Drug Interaction Risk in Damaged Skin or Occlusion
Damaged or inflamed skin increases percutaneous absorption. Caution is necessary when treating large areas or using occlusive dressings.
Use with Other Antifungals or Dermatological Agents
Ketoconazole can be used in combination regimens but should be spaced appropriately to avoid compound irritation or antagonistic effects.
Interaction with Hormonal Medications in Off-Label Use
Given its anti-androgenic properties, ketoconazole may theoretically influence systemic hormone levels if absorbed, especially with extended use.
Important Warnings and Precautions
Risk of Hypersensitivity Reactions
Individuals with known sensitivity to imidazole derivatives should avoid use. Anaphylactic reactions, though rare, require immediate medical attention.
Avoidance on Broken or Inflamed Skin Unless Directed
Application to compromised skin barriers increases systemic absorption and irritation. Use only under professional supervision in such cases.
Use Around Eyes, Mucous Membranes, and Open Wounds
Avoid contact with the eyes, nostrils, mouth, and mucosal tissues. Rinse thoroughly with water in case of accidental exposure.
Risk of Long-Term Use Without Medical Supervision
Prolonged use may lead to skin barrier disruption, microbial resistance, or local adverse effects. Treatment beyond 6 weeks should be reevaluated by a healthcare provider.
Contraindications to Use
Known Hypersensitivity to Ketoconazole or Excipients
Ketoconazole cream is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to ketoconazole itself or any of its formulation components. Even minimal exposure in such cases can trigger localized or systemic allergic reactions, including rash, swelling, or anaphylaxis.
Severe Skin Reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson Syndrome)
While rare, ketoconazole has been associated with serious dermatologic reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Patients with a history of severe cutaneous adverse reactions should avoid this medication entirely.
History of Contact Allergy to Imidazole Antifungals
Individuals with prior allergic contact dermatitis to other imidazole-class antifungals—such as clotrimazole or miconazole—may experience cross-reactivity with ketoconazole. Patch testing may be warranted in uncertain cases.
Careful Administration Considerations
Monitoring for Irritation in Prolonged Use
Prolonged application, especially on sensitive or occluded skin, may lead to irritation, erythema, or desquamation. Regular monitoring is essential during extended treatment courses.
Caution in Immunocompromised or Diabetic Patients
- Immunocompromised individuals (e.g., those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy) may exhibit altered skin response and healing. - Diabetic patients, particularly those with peripheral neuropathy, should use ketoconazole cream with caution due to delayed wound healing and higher infection risks.
Concurrent Use with Corticosteroids or Occlusive Dressings
Combining ketoconazole with topical corticosteroids or applying under occlusive dressings increases the risk of skin thinning, systemic absorption, and adverse effects. Use should be closely supervised.
Discontinuation Criteria in Case of Adverse Effects
Therapy should be promptly discontinued if: - Severe irritation or contact dermatitis occurs - Signs of hypersensitivity (e.g., hives, swelling, breathing difficulty) develop - No clinical improvement is seen after 2–4 weeks of appropriate use
Precautions for Special Populations
Administration in Elderly Patients
Skin Sensitivity and Absorption Differences
Aging skin tends to be thinner and more fragile, potentially altering drug absorption and increasing susceptibility to irritation or dryness.
Monitoring for Delayed Healing or Increased Irritation
Healing capacity may be diminished in older adults. Careful monitoring for delayed resolution or worsening of skin integrity is recommended during treatment.
Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
FDA Pregnancy Category and Evidence from Studies
Ketoconazole topical is generally considered a category C medication. Although systemic absorption is minimal, caution is advised due to the lack of well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
Risk Assessment of Systemic Absorption
Systemic absorption is unlikely when used on intact skin in recommended dosages. However, caution should be exercised when applied to large areas or under occlusion.
Breastfeeding Precautions and Nipple Application Avoidance
Lactating women should avoid applying ketoconazole cream directly to the nipple area to prevent infant ingestion. If used near the breast, ensure thorough cleansing before nursing.
Administration in Pediatric Patients
Age-Appropriate Formulations and Safety
Ketoconazole cream may be used in children under medical supervision, especially in cases of candidal infections. However, safety data in infants under 6 months is limited.
Use in Diaper Rash and Candidal Infections in Infants
It can be beneficial in treating fungal diaper rash caused by *Candida albicans*. Application should be done sparingly, avoiding prolonged use.
Monitoring for Hypersensitivity and Side Effects
Pediatric skin is more permeable, and monitoring for signs of irritation, rash, or allergic response is crucial during use.
Ketoconazole Cream Overdose and Misuse
Possibility and Symptoms of Topical Overdose
Topical overdose is rare but may present as: - Severe skin irritation - Erythema or blistering - Secondary bacterial infection due to disrupted skin barrier
Consequences of Ingestion or Misuse
Accidental oral ingestion—especially by children—can result in gastrointestinal upset, dizziness, or, in rare cases, hepatotoxicity. Immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
Emergency Measures and Medical Attention
If overdose or ingestion is suspected: - Rinse skin or mouth thoroughly with water - Seek emergency care - Provide the product label or ingredient list to the attending physician
Proper Storage and Handling Instructions
Recommended Storage Temperature and Light Protection
Store ketoconazole cream at controlled room temperature, typically between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect the container from direct sunlight and excessive heat.
Shelf-Life and Expiration Date Management
Always check the expiration date before use. Do not use the product beyond its indicated shelf life, as potency and safety cannot be guaranteed.
Tips for Safe Storage Around Children and Pets
- Keep out of reach of children and animals - Store in a secure cabinet - Avoid leaving the tube open or within easy access
Handling and Application Precautions
Hand Hygiene Before and After Use
- Wash hands thoroughly before application to prevent contamination - Clean hands afterward unless treating a hand infection
Preventing Contamination of the Cream
Avoid direct contact between the applicator tip and skin or surfaces. Recap tightly after each use to maintain product integrity.
Disposal of Expired or Contaminated Product
Do not flush unused cream down the drain. Dispose of it through a local pharmacy take-back program or according to regional hazardous waste guidelines.
Use of Gloves or Applicators When Needed
Gloves or sterile applicators may be used to avoid direct hand contact, especially when treating infected or highly sensitive areas.
Conclusion and Treatment Outcome Expectations
Timeline for Symptom Improvement
- Relief of itching and irritation often begins within 2–4 days - Full resolution of infection typically occurs within 2–6 weeks depending on the condition and severity
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Seek medical advice if: - Symptoms worsen or persist after 4 weeks - Adverse reactions develop - The infection recurs frequently
Prevention of Recurrence and Reinfection Strategies
- Maintain skin hygiene and dryness - Avoid sharing personal items (e.g., towels, footwear) - Treat underlying conditions like excessive sweating or immune suppression
Importance of Adherence and Follow-Up
Consistent application as directed is essential for therapeutic success. Skipping doses or discontinuing early may lead to relapse or resistance. Follow-up with a healthcare provider ensures complete resolution and minimizes complications.
Ketoconazole Cream FAQ
- What is ketoconazole cream used for?
- Where not to put ketoconazole cream?
- How long can I use ketoconazole cream?
- What is the best use of ketoconazole?
- What happens if I use too much ketoconazole cream?
- What happens if I use ketoconazole daily?
- Does ketoconazole stop itching?
- How fast does ketoconazole cream work?
- Is ketoconazole cream effective?
- What is the danger of ketoconazole?
- Can normal people use ketoconazole?
- How many days should I take ketoconazole?
- What is a substitute for ketoconazole?
- Is ketoconazole an antibiotic?
- Should I use ketoconazole cream in the morning or night?
- How do you apply ketoconazole cream?
- Can I apply ketoconazole daily?
- How many times can you use ketoconazole cream?
- Can you buy ketoconazole cream over the counter?
- What skin fungus is treated with ketoconazole?
- What is ketoconazole cream used for?
- Where not to put ketoconazole cream?
- What happens if I use ketoconazole daily?
- Does ketoconazole stop itching?
- What is the danger of ketoconazole?
- Can normal people use ketoconazole?
- How do you apply ketoconazole cream?
- Can I apply ketoconazole daily?
- What skin fungus is treated with ketoconazole?
What is ketoconazole cream used for?
Ketoconazole cream is used to treat: Athlete's foot (tinea pedis; ringworm of the foot), Ringworm of the body (tinea corporis), Ringworm of the groin (tinea cruris; jock itch);
Where not to put ketoconazole cream?
Make sure you avoid getting the cream in your eyes or mouth. If it does happen, wash them with water promptly.
How long can I use ketoconazole cream?
2-6 weeks
What is the best use of ketoconazole?
Utilized for addressing yeast infections, like candida (thrush), blastomycosis (Gilchrist's condition), coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever), histoplasmosis (Darling's infection), chromoblastomycosis (chromo ailment), or paracoccidioidomycosis.
What happens if I use too much ketoconazole cream?
You might experience itchiness or a burning sensation on your skin. It's possible that redness may not be as noticeable on skin tones.
What happens if I use ketoconazole daily?
Skin irritation is a side effect that may manifest as bumps resembling pimples on the skin in areas where the product has been applied. Moreover, Ketoconazole shampoo could lead to the scalp or hair becoming oily or dry alterations, and changes in hair texture or color are also consequences.
Does ketoconazole stop itching?
It can also be employed in addressing dermatitis-state leading to parching of the skin, with flakiness and itchiness.
How fast does ketoconazole cream work?
2 to 4 weeks
Is ketoconazole cream effective?
Yes
What is the danger of ketoconazole?
Taking ketoconazole can lead to liver harm that may be severe to the point of needing a liver transplant or even resulting in death.
Can normal people use ketoconazole?
Yes
How many days should I take ketoconazole?
Maximum of four weeks
What is a substitute for ketoconazole?
- Terbinafine
- Lamisil
- Ciclopirox topical
- Penlac Nail Lacquer
- Itraconazole
- Sporanox
Is ketoconazole an antibiotic?
No
Should I use ketoconazole cream in the morning or night?
Evening
How do you apply ketoconazole cream?
Apply an amount of ketoconazole gel to the skin and its surrounding areas by gently rubbing it with your fingertips; after the application of this medication, refrain from washing the treated area for a minimum of 3 hours.
Can I apply ketoconazole daily?
Yes
How many times can you use ketoconazole cream?
Once or twice a day
Can you buy ketoconazole cream over the counter?
Yes
What skin fungus is treated with ketoconazole?
The cream containing ketoconazole is applied to address tinea corporis, tinea cruris, and tinea pedis, which are skin infections causing red scaly rashes, on various body areas, such as jock itch in the groin or buttocks, and athletes' foot between the toes.
What is ketoconazole cream used for?
Treatment with Ketoconazole cream is commonly recommended for infections such as Athletes' foot (known as tinea pedis or ringworm of the foot), Ringworm of the body (referred to as tinea corporis), and Ringworm of the groin (also known as tinea cruris or jock itch).
Where not to put ketoconazole cream?
Be cautious to avoid contact with your eyes or mouth; in case of contact, with either area occurs, wash thoroughly with water immediately.
What happens if I use ketoconazole daily?
Skin irritation is a side effect that may manifest as bumps resembling pimples on the areas of your skin where the product has been applied. Using Ketoconazole shampoo could potentially lead to oiliness or dryness in your hair or scalp, along with alterations in hair texture and possible discoloration.
Does ketoconazole stop itching?
It can also be utilized to address seborrhoeic dermatitis. A condition that leads to dryness and flakiness with a sensation on the skin.
What is the danger of ketoconazole?
Taking ketoconazole could potentially lead to harm to the liver. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary, resulting in fatality.
Can normal people use ketoconazole?
Yes
How do you apply ketoconazole cream?
Apply an amount of ketoconazole gel to the surrounding skin areas and gently massage it with your fingertips until absorbed. Avoid washing the treated area for 3 hours after application.
Can I apply ketoconazole daily?
Yes
What skin fungus is treated with ketoconazole?
Ketoconazole cream is commonly applied to address tinea corporis, which is also known as ringworm, a skin infection that leads to a scaly rash, on various areas of the body. It is also used for tinea cruris or jock itch an infection affecting the skin in the groin or buttocks well as tinea pedis more commonly recognized as athletes foot, a fungal infection of the skin on the feet and, between the toes.